Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Lucky Cement Analysis
Enviado por
Khadija JawedDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lucky Cement Analysis
Enviado por
Khadija JawedDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lucky Cement Limited (LCL) is Pakistans largest producer and leading exporter of quality cement Sponsored by well known
Yunus Brothers Group one of the largest export houses of Pakistan. Lucky cement belongs to the construction and material (cement) sector at KSE . It started in 1994 by Tabba memons and got listed at the Karachi stock exchange in 1995 . The total outstanding shares at JUNE 30,2013 were 323,375,000 and the number of shares available for public trading (free float) were 115,184,380.
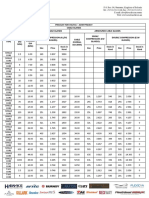
Analysis : Profitability ratios are a class of financial metrics that are used to assess a business's ability to generate earnings as compared to its expenses and other relevant costs incurred during a specific period of time. Gross profit margin measures the companys manufacturing and distribution efficiency during the production process. The ratios show that for lucky cement there has been an overall increase of 6.96 percent i from 2009 till 2013 which implies that the company is making a reasonable profit by controlling its production costs ( using alternate energy sources and reducing power cost ) where as the margin has decreased in between in 2010 .Hence, shows production costs (mainly transportation and energy costs as stated in directors report) rose during that period. Lucky cement is leading the market as compared to the industry (19.82 %) and competitor (20.23 %). The fall in the gross profit margin in 2010 has significantly impacted the net profit margin which is 4.66 % but overall the company has performed well from 2009 till 2013 with an overall increase of 8.23 %. Its net profit margin is much higher than its competitor which shows the company is profitable. This would mean that the company is controlling its operating and selling expenses efficiently along with its production expenses. Return on Assets shows the earning power of the assets regardless of how the assets are financed. The trend has overall increased by 5.17% except in 10 . This is a good sign because the company is earning more money on its assets. The ratio is significantly lower as compared to the industry (65%) indicating inefficient use of companys assets and the ratio is almost the same for the competitor. Reason: Both, the operating profit as well the average assets have increased but the increase in operating profit is more. Return on common equity shows the profit generated with the money invested by common stock owners. The trend is the same as other profitability ratios with an overall increase of 4.21 % except 2010. The competitors ROCE is less than the company which is a good signal because itll attract more stock investors because per dollar earning are high. Reason: The average common equity has remained the same but the net profit has increased to 9713948 in the final year, hence the ROCE has overall increased. Liquidity ratios measure the ability of the firm to meet its short-term financial obligations. The current ratio has shown an overall sharp increase in 2012 and 2013 except in 2010 which indicates a safe liquidity but also implies that the company is facing problems getting paid on its receivables .Too many assets compared to current liabilities hence the company is not efficiently using its current assets specifically its accounts receivables. Reason: The current assets have increased (significant increase in cash and loans given) overall while the current liabilities have decreased (significant fall in trade payables).The current ratio is better than the competitor as the competitors have a higher current ratio which could be a reason for its low profitability as compared to lucky .However, our current ratio is lesser as compared to the industry. The quick ratio shows the firms ability to re-pay its current liabilities after what is usually the least liquid asset of the current asset is subtracted. The quick ratio has been falling till 2011 but then there has been a sharp rise in 2012 and 2013. In the last two years, the quick ratio has increased by 1.49 which means the company can meet its financial obligations with the available quick funds on hand. This can be proved as the cash balances have risen sharply in 2012 and 2013 (unutilized cash could have been invested somewhere profitable).The inventory levels have decreased in the 2012 and 2013 from 2011 which is another reason for the rise in the quick ratio . The quick ratio has been lesser than the industry average and competitor. Asset management ratios: Asset Management Ratios assess how effectively the firm is using assets to generate sales . Inventory turnover ratio shows how many times, on average, the inventory is sold and replaced during the fiscal year? Inventory turnover ratio has decreased in the initial
years but then increased in 2012 and 2013. This is because average inventory has fallen and cost of goods sold have risen in the initial years. However , the fall in the inventory turnover can be explained by a rise in cost of goods sold along with a rise in average inventory but the rise in average inventory has been greater than the rise in cost of goods sold (significant increase in purchases). This implies higher sales and shows the company keeps adequate amount of inventory required to produce (less overstocking, and obsolescence).The company is performing better than the industry average and competitor(14.23 and 15.04 respectively). Receivable turnover shows how many times receivables are collected, on average, during the fiscal year? The company has a fluctuating trend with a slight increase of 1.31 . The average receivables and credit sales, both have increased but credit sales have increased more as compared to average receivables . Fluctuations in the ratio can be explained by instability in average receivables and credit sales. The company has a lower ratio as compared to industry and competitor both which implies that the company should re-assess its credit policies in order to ensure the timely collection of credit sales that is not earning interest for the firm. The company should offer discounts in order to encourage prompt payment from the receivables so that the cash received could be invested somewhere else. DSI: A financial measure of a company's performance that gives investors an idea of how long it takes a company to turn its inventory (including goods that are work in progress, if applicable) into sales. The companys DSI have overall increased by 2.38 but they fell in the years 2010 and 2011. This means that it takes a longer time to convert inventory to sales which is because of a higher inventory turnover ratio in the later years such as 2012 and 2013. This possible could be because of inefficient use of inventory. The DSI ratios of lucky cement are low as compared to the industry average and competitors which is a good sign stating that it as compared to others it manages its inventory efficiently. DSO: A measure of the average number of days that a company takes to collect revenue after a sale has been made. The companys DSO ratios have remained almost same over the period 2009 to 2013, but with fluctuations in between. This is because of the receivable turnover ratio which has also been almost the same over the period with just a slight increase. This steadiness of the ratio could be a good sign as the company has maintained and not increased the number of days it takes to collect money from the receivables, however it has a higher DSO ratio as compared to the industry average and other competitor which implies that it should consider changing its credit policies in order to reduce the number of days. Operating cycle is the time between the purchase of the raw inventory and the cash collection from the sale of final goods made from that raw materials. The companys operating cycle have increased by 1.72 with a decline only in 2010. This is because of an increase in the DSI ratio specifically as the DSO has remained almost the same so this would mean that the operating cycle has become a bit longer because it takes longer to convert the inventory into sales. This isnt a good sign because as the operating cycle extends, it necessitates borrowing and thereby, reduces profitability . The companys ratios are lower than that of company but higher than the competitor so therefore the company needs to manage its inventory and receivables efficiently. Payable turnover measures how many times the company pays its suppliers bills, on average, during the fiscal year? The companys payable turnover ratio has increased overall except in 2011. This would mean that the company now takes a shorter time to pay its payables which would also improve the liquidity position of the company as the payables would be less and also is a signal of good relation with the suppliers. However, the cash which is used to pay the payables could be used to invest somewhere else which could have even further improved the profitability position of the company. The reduced ratio in 2011 shows the company was taking more time to pay its suppliers. The reason is clear from the financial statements which show that the cash balance in
that year reduced significantly The company has a lower payable turnover ratio as compared to competitors which isnt a good sign because it would mean comparatively its paying later to its payable which signals a cash problem which the company might be facing and if not resolved it could harm the companys relations with suppliers. DPO measures the number of days it takes for the company to pay its suppliers, on average, during a fiscal year. DPO has been falling till 13 except in 11 which means the company is trying to reduce the payback time to its suppliers. Itll have the same implications as for payable turnover with good relations for suppliers but if the company would pay its suppliers late, it could invest the cash somewhere profitable. 2011 year wasnt a good year in terms of liquidity with the company facing cash problems and hence, took more days to repay. But the company then worked in 12 and 13 on this problem and recovered with significant increase in cash to 2,805,840 in 13 along with profitable investments. Cash conversion cycle is the time between the payment for the purchase of raw inventory and collection of cash from the sale of the final goods made from those raw materials. The CCC is negative for the company which a desirable A negative cash cycle is one in which you dont pay for your inventory or materials until after youve sold the final product associated with them. It means youre using your working capital as efficiently as possible and have available cash for other things that could be profitable. But the trend is showing a fall which is because of the increase in DSO and a decrease in DPO. It means extra cash is available for less days. The cycle is much better than the competitor ( 17.55 ) which shows that our companys cashflow is managed properly and there are no liquidity problems. Asset turnover ratio shows how effective is the firm in using its overall assets to generate sales. There ratio has increased over the years except 10. From 08 to 13 there has been an increase of 10.8% because both the sales as well as average total assets have risen but the increase in sales is more. Sales revenue have increased as the annual reports suggest because of the rise in domestic sales quantity ( market share of export sales have also increased as directors report states) However the fall in 10 can be explained by a decrease in sales revenue in that year, significantly impacting the ratio. The increasing trend implies greater efficiency of the assets, generating more sales per unit of average asset, showing a good performance in asset management. Whats more? This ratio is also higher than the industry showing the great performance of the market leader. Debt Management: Debt Management Ratios attempt to measure the firm's use of Financial Leverage and ability to avoid financial distress in the long run. DEBT RATIO: is a measure of a company's total debt to its total assets. A debt ratio is a measure of how risky it would be for a bank to extend a loan to a company. The debt ratio of lucky cement limited has overall decreased by 21.19%. This trend is due to increasing total assets both current and non-current of the company and decreasing total debt, current and non-current liabilities, over the years which has led to an overall decrease in the debt ratio. Low risk is associated with low debt ratio and also indicates high borrowing capacity of the firm. Moreover, low debt ratio means that the firm has high financial flexibility. The debt ratio of lucky cement is low compared to industry ratios but higher than the competitor. D/E Ratio: The debt-to-equity ratio is a financial ratio indicating the relative proportion of entity's equity and debt used to finance an entity's assets. Debt-to-equity ratio is the key financial ratio and is used as a standard for judging a company's financial standing. The D/E ratio of lucky cement has had an overall sharp decline of 42.79% from 2008 to 2012. It has been declining every year and this trend is due to decreasing total debt, both current and non-current liabilities, and increasing total equity over the years which has led to a sharp decline in the ratio. Low D/E ratio indicates good financial position because it means that the firm is not aggressively financing its growth with
debt. It indicates stability and low chances of bankruptcy (mainly based on equity )The debt ratio of lucky cement is low compared to industry ratios which is a good indicator. Times Interest Earned Ratio (TIE): TIE ratio is how many times the company can cover its finance cost from its earnings on a pre-tax basis. It is used to measure a company's ability to meet its debt obligations. TIE ratio of lucky cement has had a drastic increase of 130.38% from 08-09 to 12-13. It increased steadily till 2012 and then it had a sharp rise in 2013. This trend is due to increasing operating profits of the firm with a sharp rise in 2013 and decreasing interest expense over the years which has led to an overall increase in the TIE ratio. This sharp rise of times interest earned ratio is favorable for our company because it indicates greater ability of the business to repay its interest and debt. The TIE ratio of lucky cement is high compared to industry ratios but lower than the competitor. This implies that our competitor has greater ability to cover its interest expense and repay tis debts as compared to lucky cement. Market Value ratios evaluate the economic status of your company in the wider marketplace. These ratios give management an idea of what the firm's investors think of the firm's performance and future prospects. Book Value/Share: The purpose of calculating book value per share is to relate shareholder's equity to the number of shares of common stock outstanding. It gives a more "real" value to the common shares outstanding. The Book Value/Share of lucky cement has had an overall increase of 54.99 from 08-09 till 12-13. This increasing trend is due to a steady rise in the total common equity of lucky cement over the years. The increasing ratio is a favorable sign for the investors of the company because it determines the level of safety associated with each individual share after all debts are paid accordingly. It indicates a higher amount of money that a holder of a common share would get if a company were to liquidate. The book value/share of company is higher than the industry and competitor both. Market Value/Book Value: It is the calculation of how much are investors willing to pay per dollar of book value. The market value/book value of lucky cement has had an overall increase of 0.84 from 08-09 to 12-13. This increasing trend is due to the steady increase in the book value of the company as well as the market prices which has led to an overall increase in the market value/book value over the years. This implies that investor expectations about future profits are positive and market believes that lucky cement will proper. The market value/book value of lucky cement is much higher than its competitor which indicates that investors have higher expectations from lucky cement as compared to the competitor. Earnings per Share (EPS): It is the portion of a company's profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock.The EPS of lucky cement has had an overall increase of 15.82 from 08-09 to 12-13. Except for 2010 the EPS has increased continuously every year. This increasing trend is due to the continuous rise in profit after taxation of lucky cement. This is a favorable trend for our company because growth in EPS is an important measure of management performance because it shows how much money the company is making for its shareholders due to changes in profit. EPS ratio is better than both competitor and industry. Price to Earnings Ratio: It is the calculations of how much are investors willing to pay per dollar of earnings of the firm. The P/E ratio of lucky cement has had an overall increase of 2.87 from 08-09 to 12-13. The P/E ratio has been increasing over the years but has had fluctuations in between. This increasing trend is due to the continuous rise in the market price and the earnings per share of the company which has caused an overall increase in the P/E ratio. This indicates that the company is in its growth phase of its business cycle and their stock price may be high since investors are trading on the potential of the firm. The P/E ratio of lucky cement is much higher than the competitor which indicates that our company has higher market price.
SOURCES: Secondary sources were used to collect the data and analyse it . The sources used were : 1- LUCKY CEMENT WEBSITE for all financial statements- http://www.luckycement.com 2- KSC WEBSITE for market prices- http://www.kse.com.pk 3- Industry ratios- http://www.sbp.org.pk/departments/stats/bsa.pdf
Você também pode gostar
- Offtake SampleDocumento20 páginasOfftake SampleKwadwo Asase100% (4)
- GM Vs Ford Financial AnalysisDocumento33 páginasGM Vs Ford Financial Analysissagar100% (2)
- Singapore Airline Dividend CaseDocumento2 páginasSingapore Airline Dividend CaseAamir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Integrative Case 3 - Encore InternationalDocumento2 páginasIntegrative Case 3 - Encore InternationalEufracio Mabingnay Sr.Ainda não há avaliações
- Ratio Analysis of Fauji Cement and Lucky CementDocumento46 páginasRatio Analysis of Fauji Cement and Lucky Cementsidra_ali82% (22)
- Finance Case StudyDocumento18 páginasFinance Case StudyMuntasir Ahmmed100% (1)
- List of Case Questions: Case #1 Oracle Systems Corporation Questions For Case PreparationDocumento2 páginasList of Case Questions: Case #1 Oracle Systems Corporation Questions For Case PreparationArnold TampubolonAinda não há avaliações
- Report - Sainsbury Financial AnalysisDocumento12 páginasReport - Sainsbury Financial AnalysistastingohAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Analysis of DG Khan Cement Factory, Ratio AnalysisDocumento57 páginasFinancial Analysis of DG Khan Cement Factory, Ratio AnalysisM Fahim Arshed50% (8)
- Pak. St. Notes. 1857-1947Documento87 páginasPak. St. Notes. 1857-1947Khadija Jawed83% (6)
- Continuous Casting Investments at USX Corporation: Group 9Documento5 páginasContinuous Casting Investments at USX Corporation: Group 9Kartik NarayanaAinda não há avaliações
- Britannia Industries Ltd. (India) Ratio AnalysisDocumento35 páginasBritannia Industries Ltd. (India) Ratio AnalysisMansiShahAinda não há avaliações
- SWOT Analysis: Singapore Airlines Use of Competitive Advantage For Growth (2018)Documento3 páginasSWOT Analysis: Singapore Airlines Use of Competitive Advantage For Growth (2018)ashAinda não há avaliações
- On Comparative Analysis of Financial Statement of Pepsi Co & Coca Cola.Documento7 páginasOn Comparative Analysis of Financial Statement of Pepsi Co & Coca Cola.Saikat BhattacharjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Reporting and AnalysisDocumento34 páginasFinancial Reporting and AnalysisNatasha AzzariennaAinda não há avaliações
- Schizophrenia Eval EssayDocumento4 páginasSchizophrenia Eval EssayKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- 914 1Documento40 páginas914 1Lovena RaichandAinda não há avaliações
- ANALYSIS of Walt Disney CaseDocumento11 páginasANALYSIS of Walt Disney CaseStacy D'Souza100% (3)
- Financial AnalysisDocumento8 páginasFinancial AnalysisNor Azliza Abd RazakAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Pakistan Cement SectorDocumento43 páginasAnalysis of Pakistan Cement SectorLeena SaleemAinda não há avaliações
- Company Analysis Accounting For Managers: (An Investment Firm)Documento35 páginasCompany Analysis Accounting For Managers: (An Investment Firm)Arya Mishra100% (1)
- Financial Reporting Analysis ProjectDocumento39 páginasFinancial Reporting Analysis ProjectSunny Sharma100% (1)
- Ratio Analysis - Tata and M Amp MDocumento38 páginasRatio Analysis - Tata and M Amp MNani BhupalamAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Analysis Shell PakistanDocumento17 páginasFinancial Analysis Shell PakistanYasir Bhatti100% (1)
- Goldstar Example of Ratio AnalysisDocumento13 páginasGoldstar Example of Ratio AnalysisRoshan SomaruAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio Analysis DG Khan Cement CompanyDocumento6 páginasRatio Analysis DG Khan Cement CompanysaleihasharifAinda não há avaliações
- International Business - Case StudyDocumento18 páginasInternational Business - Case StudyLinh LinhAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Analysis of Lucky Cement LTD For The Year 2013Documento11 páginasFinancial Analysis of Lucky Cement LTD For The Year 2013Fightclub ErAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Statements: Analysis of Attock Refinery LimitedDocumento1 páginaFinancial Statements: Analysis of Attock Refinery LimitedHasnain KharAinda não há avaliações
- Nestle Report AnalysisDocumento3 páginasNestle Report AnalysisAkshatAgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment On Financial Statement Ratio Analysis PDFDocumento27 páginasAssignment On Financial Statement Ratio Analysis PDFJosine JonesAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Statement Analysis of Square PharmaceuticalsDocumento15 páginasFinancial Statement Analysis of Square PharmaceuticalsAushru HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Comparative Ratio Analysis of Two Companies: Bata & Apex 2011-14Documento21 páginasComparative Ratio Analysis of Two Companies: Bata & Apex 2011-14Arnab Upal100% (2)
- Financial Statement Analysis of Lucky CementDocumento27 páginasFinancial Statement Analysis of Lucky CementRaja UmairAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 3 MFRS8 Q PDFDocumento3 páginasTutorial 3 MFRS8 Q PDFKelvin LeongAinda não há avaliações
- FSA Atlas Honda AnalysisDocumento20 páginasFSA Atlas Honda AnalysisTaimoorAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Costs of Al Shaheer Corporation Going PublicDocumento3 páginasAnswer Costs of Al Shaheer Corporation Going PublicSyed Saqlain Raza JafriAinda não há avaliações
- Market Value Ratios: Trend Analysis Earnings Per ShareDocumento4 páginasMarket Value Ratios: Trend Analysis Earnings Per ShareRabab KazmiAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Report Analysis: Analisis Pelaporan KewanganDocumento12 páginasFinancial Report Analysis: Analisis Pelaporan KewangantanaAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio Analysis of Lucky Cement (2006-2007)Documento32 páginasRatio Analysis of Lucky Cement (2006-2007)nuplin.zain100% (4)
- Assignment On Ratio Analysis of Singer BangladeshDocumento17 páginasAssignment On Ratio Analysis of Singer BangladeshSISohelJnu100% (2)
- Atlas Honda - Financial AnalysisDocumento26 páginasAtlas Honda - Financial AnalysisSaiyd Ihtixam AehsunAinda não há avaliações
- Air Asia - FMDocumento5 páginasAir Asia - FMahfauzi100% (1)
- Chapter 6. Financial Forecasting and BudgetingDocumento2 páginasChapter 6. Financial Forecasting and BudgetingJhazz DoAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio Analysis of Lucky Cement Limited 2019Documento15 páginasRatio Analysis of Lucky Cement Limited 2019Umer Ali SangiAinda não há avaliações
- Capital Structure Analysis of Lafarge SuDocumento21 páginasCapital Structure Analysis of Lafarge SuRakibul IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Analysis For Eastman KodakDocumento4 páginasFinancial Analysis For Eastman KodakJacquelyn AlegriaAinda não há avaliações
- Coca Cola and PepsicoDocumento35 páginasCoca Cola and PepsicoSaikat BhattacharjeeAinda não há avaliações
- ABSTRACT Ratio AnalysisDocumento13 páginasABSTRACT Ratio AnalysisDiwakar SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio Analysis TheoryDocumento22 páginasRatio Analysis TheoryTarun Sukhija100% (1)
- M&A Case StudyDocumento2 páginasM&A Case StudyNoahAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio AnalysisDocumento56 páginasRatio Analysisvishi takhar80% (10)
- Analysis of Annual Report - UnileverDocumento7 páginasAnalysis of Annual Report - UnileverUmair KhizarAinda não há avaliações
- Ford Moto Company Ratio AnalysisDocumento7 páginasFord Moto Company Ratio AnalysisEmon hassanAinda não há avaliações
- Itc LTD PDFDocumento18 páginasItc LTD PDFKriti BansalAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocumento53 páginasFinancial Ratio AnalysisLaurentia Nurak100% (4)
- SDMT - Final Assignment Case Study PDFDocumento3 páginasSDMT - Final Assignment Case Study PDFCR7 الظاهرةAinda não há avaliações
- Capital Structure Analysis of IndiaDocumento14 páginasCapital Structure Analysis of IndiaMahbubul Islam KoushickAinda não há avaliações
- Air Asia Financial AnalysisDocumento16 páginasAir Asia Financial AnalysisMohamed ShaminAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocumento61 páginasFinancial Statement AnalysisChaitanya DachepallyAinda não há avaliações
- Final Accounts Illustration ProblemsDocumento11 páginasFinal Accounts Illustration ProblemsSarath kumar CAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocumento6 páginasFinancial Statement AnalysisEmmanuel PenullarAinda não há avaliações
- ASEAN Corporate Governance Scorecard Country Reports and Assessments 2019No EverandASEAN Corporate Governance Scorecard Country Reports and Assessments 2019Ainda não há avaliações
- Profitability RatiosDocumento5 páginasProfitability RatiosWaqqar Un NisaAinda não há avaliações
- BUS 104, Introduction To Finance Group AssignmentDocumento12 páginasBUS 104, Introduction To Finance Group AssignmentJannatul FerdausAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio Analysis of Fauji FertilizerDocumento6 páginasRatio Analysis of Fauji FertilizersharonulyssesAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of Reasoned ActionDocumento2 páginasTheory of Reasoned ActionKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of PhobiasDocumento18 páginasEvaluation of PhobiasKhadija Jawed100% (1)
- CAReer Job Advertisements (Public)Documento3 páginasCAReer Job Advertisements (Public)Khadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of Reasoned ActionDocumento2 páginasTheory of Reasoned ActionKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of PhobiasDocumento18 páginasEvaluation of PhobiasKhadija Jawed100% (1)
- Research Methodology Ayesha 2013Documento9 páginasResearch Methodology Ayesha 2013Khadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Adherence 2013Documento9 páginasEvaluation of Adherence 2013Khadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Health and SafetyDocumento5 páginasEvaluation of Health and SafetyKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Risk Analysis Risk Management Aviation Engineering Healthcare Swiss Cheese Reason 1990 Aviation SafetyDocumento1 páginaRisk Analysis Risk Management Aviation Engineering Healthcare Swiss Cheese Reason 1990 Aviation SafetyKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of Reasoned ActionDocumento2 páginasTheory of Reasoned ActionKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Adherence 2013Documento9 páginasEvaluation of Adherence 2013Khadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Abnormality Definitions and ModelsDocumento8 páginasEvaluation of Abnormality Definitions and ModelsKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- 1930, AddressDocumento19 páginas1930, AddressKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- 1930, AddressDocumento19 páginas1930, AddressKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- 1930, AddressDocumento19 páginas1930, AddressKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Lucky Cement AnalysisDocumento6 páginasLucky Cement AnalysisKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Garwood, Julie - Shadow MusicDocumento134 páginasGarwood, Julie - Shadow MusicKhadija Jawed67% (3)
- The Myth of AllahbadDocumento6 páginasThe Myth of AllahbadKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Salient Features of Objectives ResolutionDocumento1 páginaSalient Features of Objectives ResolutionKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Abnormality Definitions and ModelsDocumento8 páginasEvaluation of Abnormality Definitions and ModelsKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Primary SourcesDocumento25 páginasPrimary SourcesKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- GobbetsDocumento10 páginasGobbetsKhadija JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Lopez Dee Vs SECDocumento14 páginasLopez Dee Vs SECMark Ebenezer BernardoAinda não há avaliações
- M.a.part - I - Macro Economics (Eng)Documento341 páginasM.a.part - I - Macro Economics (Eng)Divyesh DixitAinda não há avaliações
- Palm Beach County GOP Newsletter - May 2012Documento13 páginasPalm Beach County GOP Newsletter - May 2012chess_boxerAinda não há avaliações
- Managerial Finance: Article InformationDocumento22 páginasManagerial Finance: Article Informationlia s.Ainda não há avaliações
- ACKSDocumento4 páginasACKSPinky Bhattacharyya50% (2)
- Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise ApplicationsDocumento2 páginasAchieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise Applicationsranvirsingh76Ainda não há avaliações
- Walt Disney: 2. Leadership Style-I. Have VisionDocumento3 páginasWalt Disney: 2. Leadership Style-I. Have Visiondhron choudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Repco Micro Finance Limited: Corporate Office, Chennai-35Documento4 páginasRepco Micro Finance Limited: Corporate Office, Chennai-35Abaraj IthanAinda não há avaliações
- The Warehouse Receipts Law Reviewer (Credit and Transactions)Documento11 páginasThe Warehouse Receipts Law Reviewer (Credit and Transactions)Anonymous oTRzcSSGun0% (1)
- MTPDocumento5 páginasMTPNavyanth KalerAinda não há avaliações
- Economics - Final Exam Review Questions-Fall 2016Documento4 páginasEconomics - Final Exam Review Questions-Fall 2016arvageddonAinda não há avaliações
- Diongzon V Mirano (Ethics)Documento1 páginaDiongzon V Mirano (Ethics)MMACAinda não há avaliações
- "Customer Relationship Management in ICICI Bank": A Study OnDocumento6 páginas"Customer Relationship Management in ICICI Bank": A Study OnMubeenAinda não há avaliações
- Voltas Pricelist - Ashr 2019Documento7 páginasVoltas Pricelist - Ashr 2019P S Raju KucherlapatiAinda não há avaliações
- SoW 9. 10, 11 Economics Normal Track (3 YEARS)Documento36 páginasSoW 9. 10, 11 Economics Normal Track (3 YEARS)Yenny TigaAinda não há avaliações
- Final Exam Review-VrettaDocumento4 páginasFinal Exam Review-VrettaAna Cláudia de Souza0% (2)
- Report On The Karmayog CSR Ratings and Study 2008Documento21 páginasReport On The Karmayog CSR Ratings and Study 2008Ankit SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- MBA 507 ReportDocumento19 páginasMBA 507 ReportSifatShoaebAinda não há avaliações
- SCM SummaryDocumento47 páginasSCM SummaryEmanuelle BakuluAinda não há avaliações
- Leadership:: You're Doing It WrongDocumento9 páginasLeadership:: You're Doing It WrongOaNa MironAinda não há avaliações
- W5 - Culturing Corporate EntrepreneurshipDocumento33 páginasW5 - Culturing Corporate EntrepreneurshipIlya Faqihah Binti Baderul Sham C20A1529Ainda não há avaliações
- QUIZ Group 1 Answer KeyDocumento3 páginasQUIZ Group 1 Answer KeyJames MercadoAinda não há avaliações
- 2009 - Banca Mondiala - Analize Si Recomandari StrategiceDocumento92 páginas2009 - Banca Mondiala - Analize Si Recomandari StrategiceBalaniscu BogdanAinda não há avaliações
- Agri Report On User Needs and Requirements v1.0 PDFDocumento56 páginasAgri Report On User Needs and Requirements v1.0 PDFJavierJMAinda não há avaliações
- Nail Making Business Project ReportDocumento4 páginasNail Making Business Project ReportBrian KiruiAinda não há avaliações
- Shrey MehtaDocumento1 páginaShrey MehtaMatt RobertsAinda não há avaliações