Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
1.1 Subchapter Notes
Enviado por
Me, Myself and I0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
32 visualizações2 páginasDistributive property requires that a number attached to parentheses multiply with every quantity contained in the parentheses. Identity is a value that operates without creating any change. Inverse is the number that can operate with a given number to produce the identity.
Descrição original:
Título original
Copy of 1.1 Subchapter Notes
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDistributive property requires that a number attached to parentheses multiply with every quantity contained in the parentheses. Identity is a value that operates without creating any change. Inverse is the number that can operate with a given number to produce the identity.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
32 visualizações2 páginas1.1 Subchapter Notes
Enviado por
Me, Myself and IDistributive property requires that a number attached to parentheses multiply with every quantity contained in the parentheses. Identity is a value that operates without creating any change. Inverse is the number that can operate with a given number to produce the identity.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
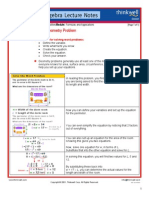
Properties, Identities, & Inverses
• Distributive property: a (b + c) = ab + ac.
• Identities: values that operate without causing any change.
• Inverses: values that operate to produce the identity.
• Commutative property: a + b = b + a; ab = ba.
• Associative property: a + b + c = (a + b) + c = a + (b + c); abc = (ab)c = a(bc).
• Multiplying by 0: The answer always is 0.
The distributive property requires that a number attached
to parentheses multiply with every quantity contained in the
parentheses.
It may be possible to combine within the parentheses and
then multiply. More often, the multiplication must be done
first.
An identity is a value that operates without creating any
change. There are two identities:
0 is the additive identity. It can be added without changing
any number to which it is added.
1 is the multiplicative identity. It can be multiplied without
changing any number with which it multiplies.
An inverse is the number that can operate with a given
number to produce the identity.
The additive inverse for any number is that number with the
opposite sign. When the number and its inverse are added,
the result is 0.
The multiplicative inverse for any number is the reciprocal
of that number. When the number and its inverse are
multiplied, the result is 1.
Remember: the reciprocal of any number is the number
flipped on its head.
The commutative property indicates that numbers can be
added or multiplied in any order to get the same answer.
In this example, two numbers are added together. Regardless
of which comes first, the addition produces the same result.
In this example, two numbers are multiplied together.
Regardless of which come first, the multiplication produces
the same result.
This property does not hold for subtraction or division.
www.thinkwell.com © Thinkwell Corp. 1
The associative property indicates that numbers can be
grouped in any combination for addition and multiplication
and the operation will produce the same result.
In this addition example, the numbers are grouped in two
ways to show that the final result is the same regardless of
the grouping.
In this multiplication problem the same point is made, again
showing the numbers grouped differently but producing the
same answer.
The number 0 presents special issues for the operations of
multiplication and division.
Multiplication with 0 always produces 0 as the answer. The
underlying cause of that result is that if there are 0 quantities
of any set of objects, there are 0 objects.
Dividing by 0 is never done.
As shown in this example, division depends on knowing that
the dividing number multiplied with the answer produces the
original number.
There is no number that multiplies with 0 to produce any
original number. Therefore, division by 0 cannot be done.
2 © Thinkwell Corp. www.thinkwell.com
Você também pode gostar
- 1.1 Sub Chapter NotesDocumento2 páginas1.1 Sub Chapter NotesMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Using The Cartesian System S.P 3.1.1Documento4 páginasUsing The Cartesian System S.P 3.1.1Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Solving A System by Substitution: (Sample Problems)Documento4 páginasSolving A System by Substitution: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Sigh More 7.6.3 Inverse ProportionDocumento2 páginasSigh More 7.6.3 Inverse ProportionMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Solving Inconsistent Systems: (Sample Problems)Documento4 páginasSolving Inconsistent Systems: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Questions On Mixture and Investment ProblemsDocumento8 páginasQuestions On Mixture and Investment ProblemsMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Solving Equations With Rational Exponents: (Sample Problems)Documento4 páginasSolving Equations With Rational Exponents: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Solving Systems With Two Equations: (Sample Problems)Documento4 páginasSolving Systems With Two Equations: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Solving Systems With Three Variables: (Sample Problems)Documento4 páginasSolving Systems With Three Variables: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Solving Dependent Systems: (Sample Problems)Documento3 páginasSolving Dependent Systems: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Solving A System by Elimination: (Sample Problems)Documento4 páginasSolving A System by Elimination: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Solving A System by Graphing S.P 5.1.2Documento7 páginasSolving A System by Graphing S.P 5.1.2Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Question X y InterceptsDocumento1 páginaQuestion X y InterceptsMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Scatterplots and Predictions: (Sample Problems)Documento3 páginasScatterplots and Predictions: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Cost and Revenue: (Sample Problems)Documento4 páginasLinear Cost and Revenue: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Math Glossary Honors Algebra Cty Online CourseDocumento6 páginasMath Glossary Honors Algebra Cty Online CourseMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Investments: (Sample Problems)Documento4 páginasInvestments: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Order of Operation (If Parentheses, Square Brackets, or Fraction Bars Are Present:)Documento4 páginasOrder of Operation (If Parentheses, Square Brackets, or Fraction Bars Are Present:)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Interpreting Line Graphs: (Sample Problems)Documento3 páginasInterpreting Line Graphs: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Graphing The Solution Set of A System of Inequalities S.P 5.4.3Documento4 páginasGraphing The Solution Set of A System of Inequalities S.P 5.4.3Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Final Review With SolutionsDocumento13 páginasFinal Review With SolutionsMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Graphing Linear and Nonlinear Inequalities: (Sample Problems)Documento4 páginasGraphing Linear and Nonlinear Inequalities: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 TestDocumento6 páginasChapter 10 TestMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Graph PaperDocumento1 páginaGraph PaperMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Decoding Circle FormulasDocumento1 páginaDecoding Circle FormulasMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Solving A Quadratic Geometry Problem: Unit: Quadratic Equations and Inequalitiesmodule: Formulas and ApplicationsDocumento5 páginasSolving A Quadratic Geometry Problem: Unit: Quadratic Equations and Inequalitiesmodule: Formulas and ApplicationsMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Final Review Without SolutionsDocumento11 páginasFinal Review Without SolutionsMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Constructing A Linear Model From A Set of Data S.P 4.3.1Documento4 páginasConstructing A Linear Model From A Set of Data S.P 4.3.1Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 Sample ProblemsDocumento101 páginasChapter 10 Sample ProblemsMe, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 09 Test - Relations and Functions: y y X X 3Documento3 páginasChapter 09 Test - Relations and Functions: y y X X 3Me, Myself and IAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)