Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Course Handout FD
Enviado por
Sabik NainarDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Course Handout FD
Enviado por
Sabik NainarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Srinivasan Engineering College, Perambalur
Odd Semester 2012 2013 Course Handout
Date: 20.06.2013 Course No. Course Title Course Instructor Instructor-in-charge : : : : AE 2301 3003 FLIGHT DYNAMICS G.Muralidharan G.Muralidharan
Scope and Objective of the Course:
This course will introduce the basic forces acting on the aircraft and their relevance to statics and dynamics of aircraft. The initial part of the course will deal with the static force and moment balance on the aircraft that leads to static stability concepts, the location of centre of gravity and the necessity for control surfaces for the aircraft. The second part of the course will deal with the dynamics of the aircraft under the influence of aerodynamic forces and moments. The mathematical modeling of the aircraft, its transfer functions and aerodynamic stability derivatives are discussed. Stability augmentation and autopilots along with Handling Qualities of the aircraft as specifications for control design will be discussed. The effects of gust and practical implementation of control systems in aircraft will also be introduced.
Text book(s) [TB]
1. Perkins, C.D., and Hage, R.E., Airplane Performance stability and Control, John Wiley & Son:,
Inc, New York.
References [RB]
1. Etkin, B., Dynamics of Flight Stability and Control, Edn. 2, John Wiley, New York, 1982. 2. Nelson, R.C. Flight Stability and Automatic Control, McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1998.. 3. Dommasch, D.O., Shelby, S.S., and Connolly, T.F., Aero plane Aero dynamics, Third Edition, Issac Pitman, London, 1981
Course Plan / Schedule:
S.No
1 2 3
Introduction International Standard Atmosphere Forces and moments acting on a flight vehicle Equation of motion of a rigid flight vehicle Different types of drag - Drag polar of vehicles from low speed to high speeds Variation of thrust, power and SFC with velocity and altitudes for air breathing engines and rockets Power available and power required curves.
Learning objectives
Ref. to Text Book
No. of lectures
To learn about the properties of air with respect to altitude variations. To learn about Forces and moments
R1 R1 R1
1 1 2
acting on a flight vehicle
To learn about equation of motion for calculating aircraft performance from the steady level flight. To learn about various types of drag affecting aircraft and drag reduction methods.
R1
8 9
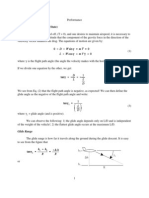
To learn about power available and power required curves for piston engine and jet engine aircrafts. To learn about range and endurance for Range and endurance piston engine aircrafts and jet engine aircrafts. Climbing and gliding flight To learn about climbing and gliding
R1
T1 T1
2 2
Format No: FM2 / Issue: 01 / Revision: 00
10
11
(Maximum rate of climb and steepest angle of climb, minimum rate of sink and shallowest angle of glide) Turning performance (Turning rate turn radius). Bank angle and load factor Limitations of pull up and push over V-n diagram and load factor. Performance of airplane in level flight - Maximum speed in level flight Conditions for minimum drag and power required Degree of freedom of rigid bodies in space - Static and dynamic stability Purpose of controls in airplanes Inherently stable and marginal stable airplanes Static, Longitudinal stability - Stick fixed stability Basic equilibrium equation Stability criterion Effects of fuselage and nacelle - Influence of CG location Power effects - Stick fixed neutral point Stick free stability-Hinge moment coefficient - Stick free neutral points Symmetric maneuvers - Stick force gradients - Stick _ force per 'g' Aerodynamic balancing. Determination of neutral points and maneuver points from flight test Basic equilibrium equation Stability criterion Effects of fuselage and nacelle - Influence of CG location Power effects - Stick fixed neutral point Dihedral effect - Lateral control Coupling between rolling and yawing moments Adverse yaw effects - Aileron reversal
performance of the aircraft from the equation of motion.
To learn about turning performance of aircraft. To learn about load factor considerations and maneuvering limitations. To learn about velocity and load factor diagram with respect to maneuvering conditions. To learn about minimum drag and minimum power required conditions.
T1 T1
2 2
T1 2 T1 2
12
13
T1 To study about the various degrees of freedom with respect to flight control and learn about the difference between stability and control.
14
15 16 17
To learn about the basic stability equation. To learn about stability equation with wing contribution and with tail contribution. To learn about neural point and power effects of aircraft.
T1 T1 T1 T1
1 2 2
18
To learn about stick fixed and stick free forces conditions for aircraft.
19
20 21 22 23 24 25
To learn about determination of neutral points and maneuver points from flight test. To learn basic equilibrium equation for Stability criterion. To study the effects of fuselage and nacelle with respect to CG location. To study about the power effects for the stability criteria. To study about lateral dihedral effect. To learn about how rolling effect is possible w.r.t yawing and yaw due to roll. To study about aileron reversal w.r.t high velocity conditions.
T1 2 R1 R1 R1 R1 R2 R2 1 2 1 2 1 1
Format No: FM2 / Issue: 01 / Revision: 00
26
27 28
Static directional stability Weather cocking effect Rudder requirements One engine inoperative condition - Rudder lock
To learn about weather cocking effect and basic rudder requirements for the flight stability. To learn about rudder lock operation and one engine inoperative condition for the aircraft. Dynamic longitudinal stability: To derive the equations of motion for longitudinal stability condition. Equations of motion
R2 1 R2 1 R2 R2 1 R2 R2 R2 R2 1 1 1 1 1
29
30 31 32 33
Stability derivatives Characteristic equation of stick fixed case Modes and stability criterion Effect of freeing-the stick Brief description of lateral and directional. Dynamic stability - Spiral, divergence, Dutch roll, Auto rotation and spin.
To learn the stability derivatives from the equation of motion. To learn about Modes and stability
criterion.
To study about lateral and directional stability. To study unstable conditions of aircraft. To study unstable conditions of aircraft
Total number of classes planned: 45Hrs Evaluation scheme Internal Assessment
EC No. Evaluation Components Duration Weight Date & Time Venue
40% 10% 20%
Will be announced by the exam cell
13
Continuous
SLIP TEST QUESTIONS: Slip test-1 Slip test-2 Slip test-3 Slip test-4 Slip test-5 Slip test-6 Slip test-7 Slip test-8 Slip test-9 Slip test-10
Explain the types of drag and its reduction methods. Explain Equations of motion, Minimum drag and Minimum power condition. Explain Gliding flight, V-n diagram. Explain Range and Endurance equations. Explain wing-body with tail configuration. Explain stick fixed and stick free stability. Explain Stability derivatives, Rouths discrimenent. Explain One engine inoperative condition, Rudder lock. Explain Spin, Auto rotation. Explain Dutch roll, Weather cocking effect.
Format No: FM2 / Issue: 01 / Revision: 00
To be announced later
1 2 3 4 5 12
Unit Test 1 Unit Test 2 Unit Test 4 Model Exam1 Model Exam2 Assignment Attendance Percentage
1.30hr 1.30hr 1.30hr 3hr 3hr 15 days
30%
I. II.
Assignment topic: Part-A Question with answer will be issued by the instructor on completion of each unit.
Timings for chamber consultation: Students should contact the Course Instructor in his chamber during lunch break.
Notices: All notices will be displayed on the Department Notice Board.
HOD
Instructor-In-Charge
Instructor
Format No: FM2 / Issue: 01 / Revision: 00
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Unit VDocumento26 páginasUnit VSabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-1 EOADocumento30 páginasUnit-1 EOASabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Aircraft Control SystemsDocumento29 páginasBasic Aircraft Control SystemsRyu WatanabeAinda não há avaliações
- EKTDocumento54 páginasEKTAkash AdhvaryuAinda não há avaliações
- Aircraft Communication and NavigationDocumento14 páginasAircraft Communication and NavigationShakil Mahmud60% (5)
- Gliding FlightDocumento7 páginasGliding FlightSabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- MFDDocumento4 páginasMFDSabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamics of Flight Stability and ControlDocumento395 páginasDynamics of Flight Stability and Controllakicar2100% (32)
- Lateral-Directional Flying Qualities Theory and TestingDocumento236 páginasLateral-Directional Flying Qualities Theory and TestingPedro SquariziAinda não há avaliações
- AE 51 TWO MARK QP-Flight DynamicsDocumento16 páginasAE 51 TWO MARK QP-Flight DynamicsSaravanan AtthiappanAinda não há avaliações
- AE 51 TWO MARK QP-Flight DynamicsDocumento16 páginasAE 51 TWO MARK QP-Flight DynamicsSaravanan AtthiappanAinda não há avaliações
- Noorul Islam College of Engineering, KumaracoilDocumento37 páginasNoorul Islam College of Engineering, KumaracoilJames PraveenAinda não há avaliações
- Flight Dynamics Important 16 Marks QuestionsDocumento1 páginaFlight Dynamics Important 16 Marks QuestionsSabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- Aerodynamicforces & DRAG POLARDocumento4 páginasAerodynamicforces & DRAG POLARmgskumarAinda não há avaliações
- Untethered Hovering Flapping Flight of A 3D-Printed Mechanical InsectDocumento14 páginasUntethered Hovering Flapping Flight of A 3D-Printed Mechanical InsectSabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- OrnithopterDocumento8 páginasOrnithopterSabik Nainar0% (1)
- Noorul Islam College of Engineering, KumaracoilDocumento37 páginasNoorul Islam College of Engineering, KumaracoilJames PraveenAinda não há avaliações
- Big BirdDocumento74 páginasBig BirdSabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- Ornithopter 2Documento9 páginasOrnithopter 2Sabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- Aucr 2008Documento57 páginasAucr 2008Sabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- Experimental Stress Analysis - UnitwiseDocumento4 páginasExperimental Stress Analysis - UnitwiseSabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- Esa QB FinalDocumento6 páginasEsa QB FinalSabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- Ae2201 Mechanics of MachineDocumento37 páginasAe2201 Mechanics of MachineSabik NainarAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- CH 2Documento92 páginasCH 2AnaPaulaLopesAinda não há avaliações
- Relative Velocity AnswersDocumento11 páginasRelative Velocity AnswersCanjiAinda não há avaliações
- A Level Physics CIE: 17. OscillationsDocumento28 páginasA Level Physics CIE: 17. OscillationsA2-A23030 Trivedi Parshva JigneshAinda não há avaliações
- Uoh Fluidmechanics Lesson01 Presentation.Documento22 páginasUoh Fluidmechanics Lesson01 Presentation.Usman Ali Usman AliAinda não há avaliações
- Physics ReviewerDocumento24 páginasPhysics ReviewerHazir HaslefttheroomAinda não há avaliações
- Projectiles SolutionsDocumento9 páginasProjectiles SolutionsNickolas RogersAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamics of Machines-Unit 2 - NotesDocumento30 páginasDynamics of Machines-Unit 2 - NotesSYLVIA ANITAAinda não há avaliações
- Moir 2017Documento21 páginasMoir 2017Chris Sake100% (1)
- FM HM Syllabus JnukDocumento2 páginasFM HM Syllabus JnukVenkata NarayanaAinda não há avaliações
- JEE (Main) 2022 Physics Revision BulletinDocumento4 páginasJEE (Main) 2022 Physics Revision BulletinFroFee FAinda não há avaliações
- Kinematics - Problems With Vectors 1Documento24 páginasKinematics - Problems With Vectors 1Alexandre CabrelAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 14 Lights and OpticsDocumento13 páginasChapter 14 Lights and OpticsshengAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment in Physical ScienceDocumento2 páginasAssignment in Physical ScienceEda Angela OabAinda não há avaliações
- Motion in Two Dimension - Practice ProblemsDocumento15 páginasMotion in Two Dimension - Practice ProblemsAvik PatraAinda não há avaliações
- Bevel Gear01Documento21 páginasBevel Gear01Viksit KumarAinda não há avaliações
- CN PHY Vector (L) PDFDocumento39 páginasCN PHY Vector (L) PDFPaathshala Education ITAinda não há avaliações
- Superposition of Perpendicular Harmonic OscillationsDocumento11 páginasSuperposition of Perpendicular Harmonic OscillationsNandana HarikrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Turbulent FlowsDocumento8 páginasIntroduction To Turbulent FlowsDoddy CarvalloAinda não há avaliações
- (Iii) CoupleDocumento45 páginas(Iii) Coupleashok KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Notes PDFDocumento82 páginasPhysics Notes PDFnatsdorf100% (4)
- Problem StatementDocumento5 páginasProblem StatementShubhendra Nath SahaAinda não há avaliações
- Optimal Design of A Damped Dynamic Vibration AbsorberDocumento21 páginasOptimal Design of A Damped Dynamic Vibration AbsorberShrikant DholeAinda não há avaliações
- Unit: Waves Name: - Lesson 5: Doppler Effect DateDocumento6 páginasUnit: Waves Name: - Lesson 5: Doppler Effect DateBetty WangAinda não há avaliações
- Triangle Velocity For Centrifugal PumpDocumento27 páginasTriangle Velocity For Centrifugal PumpWinter NaiAinda não há avaliações
- WAVE PROPERTIES OF LIGHT Chapter - 19Documento26 páginasWAVE PROPERTIES OF LIGHT Chapter - 19JonAinda não há avaliações
- 5.E Newton's Laws of Motion (Exercises) - Physics LibreTextsDocumento1 página5.E Newton's Laws of Motion (Exercises) - Physics LibreTextsMuhamad AfdalAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Lab 1Documento7 páginasDSP Lab 1anji.guvvalaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 06 HWDocumento40 páginasCH 06 HWAliciaTorres76% (33)
- Torsional Vibration 4.1 What Is Torsional Vibration?: M I K QDocumento7 páginasTorsional Vibration 4.1 What Is Torsional Vibration?: M I K QMohammad Muhtasim Mashfy, 170011054Ainda não há avaliações
- Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow PDFDocumento7 páginasGradually Varied Unsteady Flow PDFDeepankumar Athiyannan0% (1)