Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Research Approaches and Designs
Enviado por
Annapurna DangetiDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Research Approaches and Designs
Enviado por
Annapurna DangetiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
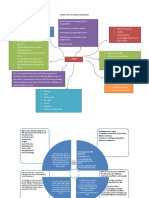
RESEARCH APPROACHES AND DESIGNS Introduction Research design is a broad plan to conduct a study, and research approach is an important
element of the research design, which governs it. A research design is a framework or guide used for the planning, implementation, and analysis of a study. It is a systematic plan of what is to be done, how it will be done, & how the data will be analysed. Research design basically provides an outline of how the research will be carried out & the methods that will be used. It includes the descriptions of the research approaches, dependent & independent variables, sampling design, and a planned format for data collection, analysis and presentation. Definition Research design can be defined as a blue print to conduct a research study, which involves the description of research approach, study setting, sampling size, sampling technique, tools and method of data collection and analysis to answer a specific research questions or for testing research hypothesis. Elements Research design is also known as a blueprint that researchers select to carry out their research study; sometimes research design is used interchangeably with the term methodology.
Qualitative
+ The approach
Quantitative Or both
With/without a conceptual framework
Method of data analysis
Elements of Research Design
Population, sample and sampling technique
Tools & Method(s) of data collection
Time and place of data collection
ELEMENTS OF RESEARCH DESIGN The approach It involves the description of the plan to investigate the phenomenon under study in a structured (quantitative), unstructured (qualitative) or a combination of the two methods. The approach helps to decide about the presence or absence as well as manipulation and control over variables. It also helps to identify the presence or absence of and comparision between groups. Population, sample, and sampling technique Research design also provides the researcher with directions about population, sample, and sampling technique, which will be used for the research study. The time, place, and sources of data collection Time (specifying days, months, and years of study), location (study setting) and the sources of the requisite data are the other important constituents essential to ensure effective planning to conduct a research study. Tools and methods of data collection This element of research design involves the description of different tools and methods of data collection. For eg: questionnaires, interviews, direct observation or any other methods that suit the particular approach of the research as well as nature of the phenomenon under study. Methods of data analysis A research design must also include the description of the methods of data analysis-either quantitative or qualitative data analysis techniques-that helps the researcher to collect the relevant data, which later can be analysed as per the research design plan.
SELECTION OF RESEARCH DESIGN Research designs are plans and the procedures for research that span the decisions from broad assumptions to detailed methods of data collection and analysis. The selection of a research design largely depends on the nature of the research problem, the resources available (cost, time, expertise of the researcher), accessibility of subjects, & research ethics. Factors affecting selection of research design Nature of the research problem: It helps the researcher to decide about the selection of a research design. Based on the nature of research problem or phenomenon, researchers decide whether it should be investigated through an experimental, quasiexperimental, or non experimental approach Purpose of the study: Study may be conducted for the purpose of prediction, description, exploration, or correlation of the research variables. The purpose of the research study helps the researcher to choose a suitable research design Researchers knowledge and experience: Researchers avoid using those designs wherein they lack confidence, relevant knowledge, or experience. The awareness of and expertise in existing research designs are important factors pertaining to the researchers. Researchers interest and motivation: Motivated researchers always analyse most aspects of research design before selecting one or a combination, while casual and callous researchers may choose research designs that may lead to failure Research ethics and principles: The incorporation and application of ethical and legal principles in the research design are essential. This includes moral obligations such as respect for participants and their rights, informed consent, and protection from harm, iincluding any adverse effects to educational progress, health and well being. TYPES OF RESARCH DESIGN Research designs are classified into two broad categories Quantitative research designs Qualitative research designs Types of quantitative research designs Broad Types of research designs categories I. Experimental 1. True experimental design research designs Post-test-only control design Pre-test-posttest control group design Solomon four-group design Factorial design Randomized block design Crossover design 2. Quasi-experimental design Nonrandomized control group design Time-series design 3. Pre-experimental designs One-shot case design One-group pretest-post-test design II.Nonexperimental 1. Descriptive design research designs Univariant descriptive design Exploratory descriptive design Comparative descriptive design Main features Manipulation of independent variable, in the presence of control group, randomization
Manipulation of independent variable, but absence of either randomization or control group Manipulation of independent variables, but limited control over extraneous variables, no randomization and control group Accurate description of characteristics of individual, situation, or group, & the frequency with which a certain phenomenon occurs in natural setting without imposing any control or manipulation Univariant descriptive: Studies undertaken to describe the frequency of occurrence of a phenomenon rather than to study relationship Exploratory: Investigating the phenomenon & its related factors about which very little is known Comparative: Comparing occurrences of a phenomenon in 2 or more groups Examining the relationship between two or more variables in a
2. Correlational/Ex post facto design
Prospective design Retrospective design 3. Developmental research design Cross sectional design Longitudinal design 4. Epidemiological designs Case-control studies Cohort studies 5. Survey research design III. Other additional research designs 1. methodological studies 2. Meta-analysis 3.Secondary data analysis 4. Outcome research 5. Evaluation studies 6. Operational research
natural setting without manipulation or control (cause & effect relationship) Prospective: Examining relationship from cause to effect Retrospective: Examining relationship from effect to cause Examining the phenomenon in respect to the time Cross-sectional: Examining the phenomenon only at one point in time Longitudinal: Examining the phenomenon at more than one point in time The investigation of the distribution & causes of diseases in a population is known as epidemiology Survey studies are investigation in which self-reported data are collected from sample with the purpose of describing population on some variables of interest Research conducted to develop, test, & evaluate the research instruments & methods Quantitatively combing & integrating the findings of the multiple research studies on a particular topic A research design in which the data collected in one research is reanalyzed by another researcher, usually to test new hypothesis Outcome research involves the evaluation of care practices & systems in place. It is used in nursing to develop evidence-based practice and improve nursing actions It is research design which involves the judgement about success of a programmes, practices, procedures, or policies Operational research involves the study of complex human organizations & services to develop new knowledge about institutions, programmes, use of facilities, & personnel in order to improve working efficiency of an organization
Types of qualitative designs Types of research designs Phenomenological research Ethnographic research Grounded theory Case studies Historical research Action research
Main features Phenomenological research examines human experiences through the descriptions provided by people involved Ethnographic research involves the information collected from certain cultural groups, by living with people of those groups and from their key informants, who are believed to be most knowledgeable about the selected culture Theory is developed inductively from a corpus of data acquired by a participant-observer Research on a phenomenon by studying in depth a single case example. The case can be an individual person, an event, a group, or an institution Systematic collection & objective evaluation of data related to past occurrences in order to test hypotheses concerning causes, effects, or trends of these events that may help to explain present events & anticipate future events Action research seeks action to improve practices & study the effect of the action that was taken
Você também pode gostar
- Research Approach and DesignDocumento43 páginasResearch Approach and Designsweta100% (1)
- Chapter3 Research Design and Methodology MARILYN JOSEDocumento57 páginasChapter3 Research Design and Methodology MARILYN JOSEJorie FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Data Collection MethodsDocumento59 páginasData Collection Methodsmadhu.k.kumar4214100% (1)
- Sampling ErrorsDocumento8 páginasSampling ErrorsAjaya DhakalAinda não há avaliações
- Steps in Research ProcessDocumento37 páginasSteps in Research ProcessVipeen Thackarey100% (1)
- Methods and Techniques of Data Collection in ResearchDocumento35 páginasMethods and Techniques of Data Collection in ResearchRKValand100% (2)
- Qualitative & Quantitative ResearchDocumento4 páginasQualitative & Quantitative Researchsajid bhattiAinda não há avaliações
- Types and Methods of Data Collection Advantagds and DisadvantagesDocumento13 páginasTypes and Methods of Data Collection Advantagds and Disadvantagesanu prasad100% (1)
- Data Collection Procedures in Research Methodology PDFDocumento30 páginasData Collection Procedures in Research Methodology PDFjepeeae100% (1)
- Seminar ON Sampling TechniquesDocumento21 páginasSeminar ON Sampling TechniquesGayathri RAinda não há avaliações
- Types Sampling MethodsDocumento40 páginasTypes Sampling MethodsRAJESH67% (6)
- Research Tools & Data Collection MethodsDocumento37 páginasResearch Tools & Data Collection MethodsSaravana KadirvelAinda não há avaliações
- Sampling Design: Advanced Research Methods (ARM)Documento54 páginasSampling Design: Advanced Research Methods (ARM)musadiq_naik100% (2)
- Research ProcessDocumento31 páginasResearch Processmahantesh93% (15)
- Chapter 1. What Is Action Research?Documento9 páginasChapter 1. What Is Action Research?Lea Alyana CapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Research ObjectiveDocumento16 páginasResearch ObjectiveMuhammad AbdurrahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding the Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchDocumento2 páginasUnderstanding the Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchSabhari Nath50% (2)
- Methods of Data CollectionDocumento42 páginasMethods of Data CollectionamitjhaimeAinda não há avaliações
- Probability Sampling Methods ExplainedDocumento9 páginasProbability Sampling Methods ExplainedEng Mohammed100% (1)
- Collection of DataDocumento17 páginasCollection of DatabharathisankarrAinda não há avaliações
- Step-by-Step Guide to Qualitative Data AnalysisDocumento28 páginasStep-by-Step Guide to Qualitative Data AnalysisCinda Si IndarellaAinda não há avaliações
- Methods of Data CollectionDocumento20 páginasMethods of Data CollectionS291991Ainda não há avaliações
- Review of LiteratureDocumento17 páginasReview of LiteratureAnusha Verghese100% (7)
- Non Probability SamplingDocumento9 páginasNon Probability SamplingMary Grace Broqueza100% (1)
- Review of LiteratureDocumento23 páginasReview of LiteratureHana Ashraf100% (1)
- Types of Sampling in ResearchDocumento7 páginasTypes of Sampling in ResearchZulfinaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 - Introduction To ResearchDocumento72 páginas1 - Introduction To Researchmeghrie Artinian100% (3)
- Methods of Data Collection Lecture Notes Unit I Research MethodologyDocumento2 páginasMethods of Data Collection Lecture Notes Unit I Research MethodologyAmit Kumar100% (4)
- Data Collection MethodsDocumento17 páginasData Collection Methodsmanojpatel5167% (9)
- Data Collection Procedure ContentDocumento19 páginasData Collection Procedure ContentAmy Lalringhluani Chhakchhuak100% (2)
- Chapter 10: Nature of Research Design and MethodsDocumento10 páginasChapter 10: Nature of Research Design and MethodsVero SteelAinda não há avaliações
- Final Assessment For Introduction To Research Methods (RMCR3101)Documento4 páginasFinal Assessment For Introduction To Research Methods (RMCR3101)Maddah HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson No 5 - Elements of Research DesignDocumento26 páginasLesson No 5 - Elements of Research Designargan_hfd74% (27)
- Pre-Experimental and Quasi Experimental DesignsDocumento29 páginasPre-Experimental and Quasi Experimental DesignsGerome Rosario100% (1)
- Classification of Research DesignDocumento15 páginasClassification of Research DesignArihantAskiGoswami100% (4)
- 2.2.1 Lecture-Cum-Discussion MethodDocumento5 páginas2.2.1 Lecture-Cum-Discussion MethodAnnie Rose GonzagaAinda não há avaliações
- Sampling MethodsDocumento6 páginasSampling Methods'Sari' Siti Khadijah HapsariAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT III - Research DesignDocumento28 páginasUNIT III - Research DesignBishnu Pandey100% (1)
- Case Study MethodDocumento18 páginasCase Study MethodsubhashreeAinda não há avaliações
- Methods of Data Collection: Primary, Secondary, Observation, Interview & QuestionnaireDocumento19 páginasMethods of Data Collection: Primary, Secondary, Observation, Interview & QuestionnairePraveen Nair100% (2)
- Methods of Data Collection in Qualitative ResearchDocumento3 páginasMethods of Data Collection in Qualitative ResearchAkhwand SaulatAinda não há avaliações
- SamplingDocumento39 páginasSamplingWaqas Mahmood100% (1)
- SamplingDocumento28 páginasSamplingapi-383092350% (2)
- What Is Sampling?Documento45 páginasWhat Is Sampling?Abhishek DhawanAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Research Design ExplainedDocumento22 páginasQualitative Research Design ExplainedAbu Bashar33% (3)
- Research ProblemDocumento17 páginasResearch ProblemAjmal Mohammed86% (7)
- Probability Vs Non Probability SamplingDocumento39 páginasProbability Vs Non Probability SamplingKunal Kapoor100% (1)
- Conceptual FrameworkDocumento12 páginasConceptual FrameworkElenear De OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Research Methodology IntroductionDocumento7 páginasResearch Methodology IntroductionDurga Prasad DashAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Sampling and Data CollectionDocumento47 páginasChapter 2 Sampling and Data CollectionJonnifer QuirosAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation of Data Analysis and InterpretationDocumento31 páginasPresentation of Data Analysis and InterpretationLou Cabanting100% (3)
- Method and Technique of Data Collection: Primary and Secondary DataDocumento44 páginasMethod and Technique of Data Collection: Primary and Secondary DataSuruchi Kaprwan100% (2)
- Types of ResearchDocumento16 páginasTypes of ResearchPriya Sharma100% (1)
- Sampling and Sampling MethodsDocumento26 páginasSampling and Sampling MethodsChirag Patil50% (2)
- Introduction to Research DesignDocumento75 páginasIntroduction to Research DesignNicole SiahAinda não há avaliações
- Criminological Research 2 Prelim NotesDocumento15 páginasCriminological Research 2 Prelim NotesLexce MendezAinda não há avaliações
- Research & Methodology (Unit1,2,3,4)Documento10 páginasResearch & Methodology (Unit1,2,3,4)Amit Vikram OjhaAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect DataDocumento39 páginasUnderstanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect DataTammyQuiwaHermosaAinda não há avaliações
- Research DesignDocumento61 páginasResearch DesignAnsu Maliyakal100% (1)
- Breastfeeding PositionsDocumento2 páginasBreastfeeding PositionsAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocumento25 páginasBleeding in Early PregnancyAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- New Text DocumentDocumento1 páginaNew Text DocumentAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Today Is The Big DayDocumento9 páginasToday Is The Big DayAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Pediatrics MnemonicsDocumento11 páginasPediatrics MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Get Some Now": in Ascending Resistor Value OrderDocumento5 páginasGet Some Now": in Ascending Resistor Value OrderAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- NEUROLOGY MNEMONICSDocumento26 páginasNEUROLOGY MNEMONICSAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- ObstetricsDocumento5 páginasObstetricsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Microbiology Mnemonics: NHS, Diphtheria Toxin, and MoreDocumento17 páginasMicrobiology Mnemonics: NHS, Diphtheria Toxin, and MoreAnnapurna Dangeti100% (2)
- Heart Auscultation MnemonicsDocumento11 páginasHeart Auscultation MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Nephrology MnemonicsDocumento5 páginasNephrology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Nephrology MnemonicsDocumento5 páginasNephrology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Medicine Mnemonics Memory AidsDocumento23 páginasInternal Medicine Mnemonics Memory AidsAnnapurna Dangeti0% (1)
- Embryology MnemonicsDocumento5 páginasEmbryology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroenterology MnemonicsDocumento10 páginasGastroenterology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Emergency Medicine MnemonicsDocumento18 páginasEmergency Medicine MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- First AidDocumento5 páginasFirst AidAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Genetics MnemonicsDocumento7 páginasGenetics MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Mental Status Examination: A Structured Approach to Observing a Patient's Mental StateDocumento52 páginasMental Status Examination: A Structured Approach to Observing a Patient's Mental StateAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry MnemonicsDocumento20 páginasBiochemistry MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Cardiology MnemonicsDocumento18 páginasCardiology MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Immunoglobulin GDocumento1 páginaImmunoglobulin GAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Hand WashingDocumento39 páginasHand WashingAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocumento63 páginasAnatomy MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Psychiatric EmergenciesDocumento25 páginasPsychiatric EmergenciesAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- SIGNS IN OBGYN: Key Ultrasound and Clinical IndicatorsDocumento2 páginasSIGNS IN OBGYN: Key Ultrasound and Clinical IndicatorsAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1Documento11 páginasUnit 1Annapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Slide 1Documento20 páginasSlide 1Annapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs To Treat Endocrine System DisordersDocumento2 páginasDrugs To Treat Endocrine System DisordersAnnapurna DangetiAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Flora of The Human BodyDocumento7 páginasNormal Flora of The Human Bodyshahbaz88% (16)
- Ramdump Modem 2023-05-13 21-52-06 PropsDocumento21 páginasRamdump Modem 2023-05-13 21-52-06 PropsNanda TampanAinda não há avaliações
- Cloudsoc For Amazon Web Services Solution Overview enDocumento6 páginasCloudsoc For Amazon Web Services Solution Overview enmanishAinda não há avaliações
- FLSPfister IB05000 I GBTRWSD0216 MailDocumento26 páginasFLSPfister IB05000 I GBTRWSD0216 MailLuis Angel BusturiaAinda não há avaliações
- Ib Items: PotionsDocumento8 páginasIb Items: PotionsZeNoWTFAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamin D DeficinyDocumento11 páginasVitamin D DeficinyسالمAinda não há avaliações
- Waste Management: Spoilage of LandscapeDocumento7 páginasWaste Management: Spoilage of Landscapeshauryasahu2004Ainda não há avaliações
- Ascha_ASJ19_Nonsurgical Management of Facial Masculinization and FeminizationDocumento15 páginasAscha_ASJ19_Nonsurgical Management of Facial Masculinization and Feminizationallen.515Ainda não há avaliações
- Time ManagementDocumento30 páginasTime ManagementVaibhav Vithoba NaikAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On: Perfetti Van MelleDocumento20 páginasPresentation On: Perfetti Van MelleAkash RaiAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Engineering Paper 1 SummaryDocumento20 páginasMechanical Engineering Paper 1 SummaryK.v.SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Eye, E.N.T. & Dental AnaesthesiaDocumento22 páginasEye, E.N.T. & Dental AnaesthesiawellawalalasithAinda não há avaliações
- Optimize soil preparation with a versatile mini tillerDocumento2 páginasOptimize soil preparation with a versatile mini tillerRickson Viahul Rayan C100% (1)
- Mind Map Burn & BleedingDocumento2 páginasMind Map Burn & BleedingUlfia KhoirinnissaAinda não há avaliações
- Makalah Silverius Simatupang A24050072Documento5 páginasMakalah Silverius Simatupang A24050072Maul MaulanaAinda não há avaliações
- Uia Teaching Hospital BriefDocumento631 páginasUia Teaching Hospital Briefmelikeorgbraces100% (1)
- FAO Shrimp Culture - Pond Design, Operation and ManagementDocumento53 páginasFAO Shrimp Culture - Pond Design, Operation and Managementfanuskhan80% (5)
- Science 9 Worksheet Week 5Documento4 páginasScience 9 Worksheet Week 5Jaybie TejadaAinda não há avaliações
- Boge Screw UsaDocumento40 páginasBoge Screw UsaAir Repair, LLC100% (1)
- F6003 5W40 Synthetic Oil Technical Data SheetDocumento1 páginaF6003 5W40 Synthetic Oil Technical Data SheetValeriy ValkovetsAinda não há avaliações
- Report Information From Proquest: February 24 2014 06:18Documento19 páginasReport Information From Proquest: February 24 2014 06:18Emma Elena StroeAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Bank Accounts Registration FormDocumento2 páginasMultiple Bank Accounts Registration FormAjith JainAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrogen DryerDocumento2 páginasHydrogen Dryersanju_cgh5518Ainda não há avaliações
- Carbon Steel Alloys Steel, Pipe Dimension With Weight Test Pressures According To ANSI B36, 10 For ASTM A53/A 106/API 5L/A335/ SpecificationDocumento6 páginasCarbon Steel Alloys Steel, Pipe Dimension With Weight Test Pressures According To ANSI B36, 10 For ASTM A53/A 106/API 5L/A335/ SpecificationsanjibkrjanaAinda não há avaliações
- FAT Form Winch UnitDocumento7 páginasFAT Form Winch UnitYadi KusmayadiAinda não há avaliações
- One Stop English - Cornish Village - Pre-IntermediateDocumento5 páginasOne Stop English - Cornish Village - Pre-Intermediatec_a_tabetAinda não há avaliações
- FAQ For Company Law 2013Documento24 páginasFAQ For Company Law 2013Archanat07100% (1)
- Annotated Bibliography For Elder AbuseDocumento6 páginasAnnotated Bibliography For Elder Abuseapi-302577490Ainda não há avaliações
- Pile Foundation As Per IRC 112Documento59 páginasPile Foundation As Per IRC 112ARVIND SINGH RAWAT0% (1)
- Courses at NeevDocumento10 páginasCourses at NeevDr Mohan SavadeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 EconomicsDocumento5 páginasChapter 1 Economicsjordan cedeñoAinda não há avaliações