Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Anatomy
Enviado por
Ronel Sayaboc AsuncionDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Anatomy
Enviado por
Ronel Sayaboc AsuncionDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
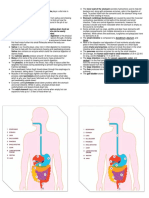
GALL BLADDER
The gall bladder functions to concentrate and store bile. It is a hollow, pear shaped organ with walls composed of three layers: a mucosa , muscularis externa , and adventitia (serosa). Notice the very tall, simple columnar epithelium of the mucosa which is thrown into numerous villus-like folds . The lamina propria of the mucosa is highly vascular with no lymphatics. Note the arrangement of the smooth muscle in the muscularis externa with longitudinal fibers closer to the lamina propria and circular fibers more peripheral (no muscularis mucosa or submucosa exists).
If fertilization and implantation occurs, the follicle will develop into the corpus luteum, "yellow body". The name is based historically upon its histological appearance, the yellow colour due to the high level of steoidogenesis
occuring to support the pregnancy and prevent menses. The main steroidal hormone produced by the corpus luteum is progesterone.
VEINS The capillaries formed by the arterioles continue as carriers of deoxygenated blood as they carry the waste products that have diffused in from the cells. These capillaries join together to form venules. The venules join together and form bigger vessels called the veins. The veins and venules are also lined by smooth muscles. However, the walls of the veins are not as thick as those of arteries. All the veins of the upper body except the pulmonary vein join together to form the superior vena cava and the veins of the lower body join together to form the inferior vena cava. These two veins pour their blood into the right auricle through separate openings. The pulmonary vein brings the blood from the lungs to the heart. Thus, the blood vessels that bring the blood to the heart are called the veins. The veins carry deoxygenated blood except for the pulmonary vein that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs. The blood drawn from the veins is dark red in colour. The blood moves in the veins towards the heart by the action of the muscles in its walls and skeletal muscles around them. The skeletal muscles are more active during exercise. The veins all along their length have valves that prevent the backflow of blood. This is because the veins have fewer muscles to propel the blood more forcefully. NEURO VASCULAR BUNDLES The long axons of neurons along with the associated structures are called the nerve fibres. The fibres may be enclosed within sheaths called as myelin sheath. However, the action potential is not generated in the areas where there is a sheath over the fibre. Along the fibres there are regions where the myelin sheath is absent. These regions are called the nodes of Ranvier. The action potential jumps from one node to the other.
Many nerve fibres are bunched together to form a nerve. The bundles of fibres are enclosed within connective tissue called the epineurium THYMUS The thymus gland is situated in the upper chest near the front side of the heart. It is pinkishgrey in colour and consists of two lobes. At birth the gland is quite small, weighting about 10 grams, and increases in size in the adult. It is composed of tiny lobules held together by connective tissue. It is also called as "the throne of immunity" or traning school of T-lymphocyte. Thymus secretes a hormone named thymosin. It accelerates cell division, thus influencing the rate of growth during early life. It stimulates the proliferation and maturation of T-lymphocytes, increasing resistance to infection. It also hastens attainment of sexual maturity. Its production decreases with advancing age and entirely cases by about 50 years. OVARIES Human ovaries are a pair of almond shaped structures about 3cm long, 1.5cm wide lying one on either side of the vertebral column in the abdominal cavity. Each ovary is attached to the dorsal abdominal wall by a mesentery called mesovarium. Each ovary is covered by a layer of germinal epithelium. During embryonic life, the cells of the germinal epithelium proliferate thousands of primordial follicles. The stroma is composed of fibrous connective tissue which is differentiated into outer cortex and inner medulla. The cortex contains thousands of tiny undeveloped ovarian follicles. Medulla contains only blood vessels and nerve fibres.
A fully mature ovarian follicle is called a Graafian follicle. It has an outer multilayered membrana granulosa formed of 2 - 3 layers of follicle cells. The oocyte is surrounded by a vitelline membrane, zona radiata and corona radiata. The oocyte is attached to the membrana granulosa by a group of cells called discus proligerus. The graafian follicle has a follicular cavity or antrum filled with a colourless follicular fluid. The fluid is termed as liquor folicelli. In human female, on an average every 28 days one graafian follicle matures and ruptures releasing an ovum. After this the follicle turns into the corpus luteum made up of large conical yellowish cells. Corpus luteum serves as a temporary endocrine gland, by releasing female sex hormones namely progesterone and estrogen. Ovary Histology In a normal adult female, there are nearly four lakh follicles present in the two ovaries. Of them only one ovum matures and is liberated in each menstrual cycle by alternate ovaries. Others undergo regression and disappear due to death, during the reproductive years of the females. This phenomenon is referred to as follicular atresia. The maturation of the graafian follicle is under the control of the FSH and LH (Follicle Secreting Hormone and Luetinising Hormone). The interstitial cells of the ovary secrete the hormone estrogen. The progesterone is secreted by the corpus luteum. Cerebrum It is the largest part of the brain and is made up of two hemispheres called the cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined together by a thick band of fibres called the corpus callosum. The cerebrum is made up of four distinct lobes - frontal, parietal, temporal and occipetal.
The outer portion of the cerebrum is called the cortex and the inner part is called the medulla. The cortex consists of the cells of the neurons and appears grey in colour. It is also called the grey matter. The medulla consists of the fibres of the neurons and is white. The cortex is highly convoluted which increase the surface area. It is believed that higher the number of convolutions, higher is the intelligence. The cerebrum has sensory areas, association areas and motor areas. The sensory areas receive the messages, the association areas associate this information with the previous and other sensory informations and the motor areas are responsible of the action of the voluntary muscles. Cerebrum is responsible for the intelligence, thinking, memory, consciousness and will power. Lacrymal glands They are also called the tear glands as they produce secretion called tears. The lacrymal glands are present one on the outer upper border of each eye. The lacrymal secretion is watery, alkaline and carries out the following functions i) ii) iii) iv) cleans the eyes ii) keeps the eyes moist iii) keeps the eyes free of bateria as it contains bacteriolytic lysozyme iv) provides nutrition to the cornea.
GALL BLADDER It is a small sac-like elongated organ near the liver. The excess bile juice is stored in the gall bladder. It is connected to the liver by a duct called the cystic duct. If there is no food in the intestine, the bile juice flows into the gall bladder and is stored there. It is pumped out by the
muscular contraction of the gall bladder wall when the food comes into the small intestine. The cystic duct opens into the common bile duct which opens into the small intestine LIVER Liver is the largest gland and is found in the upper part of the abdomen on the right side of the body just below the diaphragm. Its secretion is called bile juice. It is alkaline and rich in organic salts called the bile salts. The alkaline nature serves to neutralize the acidic pH of the gastric juice and creates the right environment for the intestinal enzymes to function. The bile salts act on the fats and emulsify them (breaking them into small globules) which increases their surface area. The bile juice is greenish yellow in colour due to the pigments called the bilirubin and biliverdin. These pigments are formed from the worn out and dead red blood cells. Thus, bile juice has an excretory function as it serves to remove the wastes from the blood stream. The bile juice is secreted out of the liver through hepatic ducts which then continue as common bile duct. It goes into the duodenum of the small intestine. But if there is no food in the small intestine, it is passed along the cystic duct into the gall bladder. The latter is the storage organ for excess bile. About 1litre of bile is produced by the liver daily. Functions of Liver The liver is an important organ in the body, in addition to being a digestive gland. Its importance can be understood by listing its functions which are as follows: It produces bile which helps in digestion of fats and lipids It converts glucose to glycogen and helps to control the level of sugar in blood
It carries out deamination of excess amino acids. The resultant ammonia is converted to harmless urea and transported to the kidneys. The carboxylic acids remaining from the amino acids are converted to glucose. It acts as a storehouse for fats, glucose, vitamins A,D,E and K, iron and copper It stores water and thus regulates the fluid balance in the blood It produces red blood cells in the embryos. In adults, it destroys old red blood cells. The new ones are synthesised in the bone marrow. It produces the clotting factor fibrinogen It produces an anti-coagulant called heparin It metabolises the toxic chemicals and renders them harmless after which they are excreted It is a site of many metabolic reactions that generates heat to maintain the body temperature
PROSTATE GLAND The prostate gland is of the size of a golf ball and is spongy in texture. These are compound tubular glands situated just below the urinary bladder. It secretes a thin alkaline substance that contributes to the largest part of the semen. It increases sperm motility and provides nutrition to the sperms.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- STO. NIÑO BIAAN ELEMENTARY SCHOOL-Form3-March2021Documento1 páginaSTO. NIÑO BIAAN ELEMENTARY SCHOOL-Form3-March2021Ronel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- STO. NIÑO BIAAN ELEMENTARY SCHOOL-Form3-March2021Documento1 páginaSTO. NIÑO BIAAN ELEMENTARY SCHOOL-Form3-March2021Ronel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Year - Round: B. Core Behavioral Competencies (Dep-Ed)Documento1 páginaYear - Round: B. Core Behavioral Competencies (Dep-Ed)Ronel Sayaboc Asuncion100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- Sto. Nino Biaan ES - SPPDDocumento7 páginasSto. Nino Biaan ES - SPPDRonel Sayaboc Asuncion100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Ratee Rater Approving Authority: Mary Grace N. Bartolome Gina A. Torres Juliet B. BatallonesDocumento1 páginaRatee Rater Approving Authority: Mary Grace N. Bartolome Gina A. Torres Juliet B. BatallonesRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Sto Nino Biaan ES Faculty and StaffDocumento6 páginasSto Nino Biaan ES Faculty and StaffRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- IPCRF Development Plans and Action ItemsDocumento1 páginaIPCRF Development Plans and Action ItemsRonel Sayaboc Asuncion100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Developing Teaching Skills and InnovationDocumento1 páginaDeveloping Teaching Skills and InnovationRonel Sayaboc Asuncion100% (6)
- Developing teaching skills and competenciesDocumento1 páginaDeveloping teaching skills and competenciesRonel Sayaboc Asuncion100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- Year - Round: B. Core Behavioral Competencies (Dep-Ed)Documento1 páginaYear - Round: B. Core Behavioral Competencies (Dep-Ed)Ronel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- B. Core Behavioral Competencies (Dep-Ed) : Year - RoundDocumento1 páginaB. Core Behavioral Competencies (Dep-Ed) : Year - RoundRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Consolidated Ippd NewDocumento7 páginasConsolidated Ippd NewRonel Sayaboc Asuncion100% (3)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Weekly home learning planDocumento10 páginasWeekly home learning planRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- ICT Room Seat PlanDocumento1 páginaICT Room Seat PlanRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Narrative DSPC 2019Documento3 páginasNarrative DSPC 2019Ronel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Digestive System FactsDocumento2 páginasDigestive System FactsRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- ID MakingDocumento2 páginasID MakingRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Weekly Home Learning PlanDocumento7 páginasWeekly Home Learning PlanRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Template For Ort 2020Documento1 páginaTemplate For Ort 2020Ronel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- SPPD SchoolDocumento3 páginasSPPD SchoolRonel Sayaboc Asuncion94% (35)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- DOLCH WORD LIST COMBINED LIST BY FREQUENCYDocumento1 páginaDOLCH WORD LIST COMBINED LIST BY FREQUENCYRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- BSP Registration FormDocumento1 páginaBSP Registration FormRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture On Circulatory SystemDocumento3 páginasLecture On Circulatory SystemRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System FactsDocumento2 páginasDigestive System FactsRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Second Summative Test in ScienceDocumento2 páginasSecond Summative Test in ScienceRonel Sayaboc Asuncion100% (4)
- Ia LMDocumento13 páginasIa LMRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Healthy ClassroomDocumento1 páginaHealthy ClassroomRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Documento7 páginasDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Ronel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- MUSIC VI 3rd QuarterDocumento5 páginasMUSIC VI 3rd QuarterRonel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Sto. Niño Biaan ES Template 1Documento15 páginasSto. Niño Biaan ES Template 1Ronel Sayaboc AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Rreinforcement Pad Leak Test ProcedureDocumento5 páginasRreinforcement Pad Leak Test ProcedureAmin Thabet100% (2)
- g21 Gluta MsdsDocumento3 páginasg21 Gluta Msdsiza100% (1)
- 2.assessment of Dental Crowding in Mandibular Anterior Region by Three Different MethodsDocumento3 páginas2.assessment of Dental Crowding in Mandibular Anterior Region by Three Different MethodsJennifer Abella Brown0% (1)
- RTG E-One - Manual de Manutenção 41300-41303 (EN)Documento328 páginasRTG E-One - Manual de Manutenção 41300-41303 (EN)Conrado Soares100% (1)
- Auramo Oy spare parts listsDocumento12 páginasAuramo Oy spare parts listsYavuz ErcanliAinda não há avaliações
- Operating Instructions: Katflow 100Documento52 páginasOperating Instructions: Katflow 100Nithin KannanAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of Nanomaterials, The Four Main Types of Intentionally Produced NanomaterialsDocumento5 páginasClassification of Nanomaterials, The Four Main Types of Intentionally Produced NanomaterialssivaenotesAinda não há avaliações
- Antenna LecDocumento31 páginasAntenna Lecjosesag518Ainda não há avaliações
- How To Become A Coffee Aficionado: Tips & Tricks: Kate Macdonnell Brewing Updated: Feb 06 2023Documento17 páginasHow To Become A Coffee Aficionado: Tips & Tricks: Kate Macdonnell Brewing Updated: Feb 06 2023sadenaikeAinda não há avaliações
- GSIS vs. de LeonDocumento9 páginasGSIS vs. de Leonalwayskeepthefaith8Ainda não há avaliações
- 50-Orthodontic Objectives in Orthognathic Surgery-State of The PDFDocumento15 páginas50-Orthodontic Objectives in Orthognathic Surgery-State of The PDFDeena A. AlshwairikhAinda não há avaliações
- DR - Hawary Revision TableDocumento3 páginasDR - Hawary Revision TableAseel ALshareefAinda não há avaliações
- Solcon Catalog WebDocumento12 páginasSolcon Catalog Webquocviet612Ainda não há avaliações
- EEDMATH1 - Teaching Mathematics in The Primary Grades Beed 2E Learning Activity PlanDocumento3 páginasEEDMATH1 - Teaching Mathematics in The Primary Grades Beed 2E Learning Activity PlanBELJUNE MARK GALANANAinda não há avaliações
- Switzerland: Food and CultureDocumento18 páginasSwitzerland: Food and CultureAaron CoutinhoAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System Packet BDocumento5 páginasCirculatory System Packet BLouise SalvadorAinda não há avaliações
- A. Kumar Aswamy Job Offer LetterDocumento1 páginaA. Kumar Aswamy Job Offer LetterHimanshu PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Perforamance Based AssessmentDocumento2 páginasPerforamance Based AssessmentJocelyn Acog Bisas MestizoAinda não há avaliações
- Gate Installation ReportDocumento3 páginasGate Installation ReportKumar AbhishekAinda não há avaliações
- Case Studies On Industrial Accidents - 2Documento84 páginasCase Studies On Industrial Accidents - 2Parth N Bhatt100% (2)
- Venus in MulaDocumento2 páginasVenus in MulaGovind BallabhAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics Sessional: Dhaka University of Engineering & Technology, GazipurDocumento17 páginasFluid Mechanics Sessional: Dhaka University of Engineering & Technology, GazipurMd saydul islamAinda não há avaliações
- Ethamem-G1: Turn-Key Distillery Plant Enhancement With High Efficiency and Low Opex Ethamem TechonologyDocumento25 páginasEthamem-G1: Turn-Key Distillery Plant Enhancement With High Efficiency and Low Opex Ethamem TechonologyNikhilAinda não há avaliações
- Mabuhay Wedding Package2006Documento3 páginasMabuhay Wedding Package2006Darwin Dionisio ClementeAinda não há avaliações
- Copia de Tissue Response To Dental CariesDocumento7 páginasCopia de Tissue Response To Dental Cariesjorefe12Ainda não há avaliações
- Malaysia's Trade Potential in Colourful AfricaDocumento18 páginasMalaysia's Trade Potential in Colourful AfricaThe MaverickAinda não há avaliações
- 559 Fault CodeDocumento4 páginas559 Fault Codeabdelbagi ibrahim100% (1)
- Test Report OD63mm PN12.5 PE100Documento6 páginasTest Report OD63mm PN12.5 PE100Im ChinithAinda não há avaliações
- Quality Nutrition and Dietetics PracticeDocumento3 páginasQuality Nutrition and Dietetics PracticeNurlienda HasanahAinda não há avaliações
- English Financial Assistance ApplicationDocumento4 páginasEnglish Financial Assistance ApplicationAlyssa JenningsAinda não há avaliações