Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Machine Design
Enviado por
Bhupender Singh ChughDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Machine Design
Enviado por
Bhupender Singh ChughDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CHAPTER 5
MACHINE DESIGN
YEAR 2012 MCQ 5.1
TWO MARKS
A fillet welded joint is subjected to transverse loading F as shown in the figure. Both legs of the fillets are of 10 mm size and the weld length is 30 mm. If the allowable shear stress of the weld is 94 MPa, considering the minimum throat area of the weld, the maximum allowable transverse load in kN is
(A) 14.44 (C) 19.93
MCQ 5.2
(B) 17.92 (D) 22.16
A force of 400 N is applied to the brake drum of 0.5 m diameter in a bandbrake system as shown in the figure, where the wrapping angle is 180c. If the coefficient of friction between the drum and the band is 0.25, the braking torque applied, in Nm is
(A) 100.6 (C) 22.1
MCQ 5.3
(B) 54.4 (D) 15.7
A solid circular shaft needs to be designed to transmit a torque of 50 Nm. If the allowable shear stress of the material is 140 MPa, assuming a factor of safety of 2, the minimum allowable design diameter is mm is (A) 8 (B) 16 GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 214
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
(C) 24
(D) 32
YEAR 2011 MCQ 5.4
TWO MARKS
Two identical ball bearings P and Q are operating at loads 30 kN and 45 kN respectively. The ratio of the life of bearing P to the life of bearing Q is (B) 27 (A) 81 16 8 (C) 9 4
YEAR 2010
(D) 3 2
TWO MARKS
MCQ 5.5
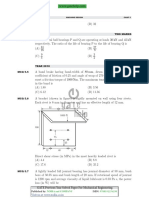
A band brake having band-width of 80 mm, drum diameter of 250 mm, coefficient of friction of 0.25 and angle of wrap of 270 degrees is required to exert a friction torque of 1000 Nm. The maximum tension (in kN) developed in the band is (A) 1.88 (B) 3.56 (C) 6.12 (D) 11.56
MCQ 5.6
A bracket (shown in figure) is rigidly mounted on wall using four rivets. Each rivet is 6 mm in diameter and has an effective length of 12 mm.
Direct shear stress (in MPa) in the most heavily loaded rivet is (A) 4.4 (B) 8.8 (C) 17.6
MCQ 5.7
(D) 35.2
A lightly loaded full journal bearing has journal diameter of 50 mm, bush bore of 50.05 mm and bush length of 20 mm. If rotational speed of journal is 1200 rpm and average viscosity of liquid lubricant is 0.03 Pa s, the power loss (in W) will be GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 215
(A) 37 (C) 118
(B) 74 (D) 237
YEAR 2009 MCQ 5.8
TWO MARKS
A forged steel link with uniform diameter of 30 mm at the centre is subjected to an axial force that varies from 40 kN in compression to 160 kN in tension. The tensile (Su), yield (Sy) and corrected endurance (Se) strengths of the steel material are 600 MPa, 420 MPa and 240 MPa respectively. The factor of safety against fatigue endurance as per Soderbergs criterion is (A) 1.26 (B) 1.37 (C) 1.45 (D) 2.00
Common Data For Q.9 and Q.10
A 20c full depth involute spur pinion of 4 mm module and 21 teeth is to transmit 15 kW at 960 rpm. Its face width is 25 mm.
MCQ 5.9
The tangential force transmitted (in N) is (A) 3552 (B) 2611 (C) 1776 (D) 1305
MCQ 5.10
Given that the tooth geometry factor is 0.32 and the combined effect of dynamic load and allied factors intensifying the stress is 1.5; the minimum allowable stress (in MPa) for the gear material is (A) 242.0 (B) 166.5 (C) 121.0 (D) 74.0
YEAR 2008 MCQ 5.11
TWO MARKS
A journal bearing has a shaft diameter of 40 mm and a length of 40 mm. The shaft is rotating at 20 rad/s and the viscosity of the lubricant is 20 mPas . The clearance is 0.020 mm. The loss of torque due to the viscosity of the lubricant is approximately. (A) 0.040 Nm (B) 0.252 Nm (C) 0.400 Nm (D) 0.652 Nm
MCQ 5.12
A clutch has outer and inner diameters 100 mm and 40 mm respectively. Assuming a uniform pressure of 2 MPa and coefficient of friction of liner material is 0.4, the torque carrying capacity of the clutch is (A) 148 Nm (B) 196 Nm GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 216
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
(C) 372 Nm
MCQ 5.13
(D) 490 Nm
A spur gear has a module of 3 mm, number of teeth 16, a face width of 36 mm and a pressure angle of 20c. It is transmitting a power of 3 kW at 20 rev/s. Taking a velocity factor of 1.5 and a form factor of 0.3, the stress in the gear tooth is about. (A) 32 MPa (B) 46 MPa (C) 58 MPa (D) 70 MPa
MCQ 5.14
One tooth of a gear having 4 module and 32 teeth is shown in the figure. Assume that the gear tooth and the corresponding tooth space make equal intercepts on the pitch circumference. The dimensions a and b , respectively, are closest to
(A) 6.08 mm, 4 mm (C) 6.28 mm, 4.3 mm
MCQ 5.15
(B) 6.48 mm, 4.2 mm (D) 6.28 mm, 4.1 mm
Match the type of gears with their most appropriate description. Type of gear P. Helical Q. Spiral Bevel C. Hypoid S. Rack and pinion Description 1. Axes non parallel and non intersecting 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Axes parallel and teeth are inclined to the axis Axes parallel and teeth are parallel to the axis Axes are perpendicular and intersecting, and teeth are inclined to the axis. Axes are perpendicular and used for large speed reduction Axes parallel and one of the gears has infinite radius (B) P-1, Q-4, R-5, S-6 (D) P-6, Q-3, R-1, S-5
(A) P-2, Q-4, R-1, S-6 (C) P-2, Q-6, R-4, S-2
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 217
Common Data For Q.16 and Q.17
A steel bar of 10 # 50 mm is cantilevered with two M 12 bolts (P and Q) to support a static load of 4 kN as shown in the figure.
MCQ 5.16
The primary and secondary shear loads on bolt P, respectively, are (A) 2 kN, 20 kN (B) 20 kN, 2 kN (C) 20 kN, 0 kN (D) 0 kN, 20 kN
MCQ 5.17
The resultant shear stress on bolt P is closest to (A) 132 MPa (B) 159 MPa (C) 178 MPa (D) 195 MPa
YEAR 2007 MCQ 5.18
ONE MARK
A ball bearing operating at a load F has 8000 hours of life. The life of the bearing, in hours, when the load is doubled to 2F is (A) 8000 (B) 6000 (C) 4000 (D) 1000
YEAR 2007 MCQ 5.19
TWO MARKS
A thin spherical pressure vessel of 200 mm diameter and 1 mm thickness is subjected to an internal pressure varying form 4 to 8 MPa. Assume that the yield, ultimate and endurance strength of material are 600, 800 and 400 MPa respectively. The factor of safety as per Goodmans relation is (A) 2.0 (B) 1.6 (C) 1.4 (D) 1.2
MCQ 5.20
A natural feed journal bearing of diameter 50 mm and length 50 mm operating at 20 revolution/ second carries a load of 2 kN. The lubricant used has a viscosity of 20 mPas. The radial clearance is50 m . The Sommerfeld number for the bearing is (A) 0.062 (B) 0.125 GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 218
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
(C) 0.250
MCQ 5.21
(D) 0.785
A bolted joint is shown below. The maximum shear stress, in MPa in the bolts at A and B , respectively are
(A) 242.6, 42.5 (C) 42.5, 42.5
MCQ 5.22
(B) 42.5, 242.6 (D) 18.75, 343.64
A block-brake shown below has a face width of 300 mm and a mean coefficient of friction of 0.25. For an activating force of 400 N, the braking torque in Nm is
(A) 30 (C) 45
MCQ 5.23
(B) 40 (D) 60
The piston rod of diameter 20 mm and length 700 mm in a hydraulic cylinder is subjected to a compressive force of 10 kN due to the internal pressure. The end conditions for the rod may be assumed as guided at the piston end and hinged at the other end. The Youngs modulus is 200 GPa. The factor GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 219
of safety for the piston rod is (A) 0.68 (C) 5.62
(B) 2.75 (D) 11.0
Common Data For Q.24 and Q.26
A gear set has a pinion with 20 teeth and a gear with 40 teeth. The pinion runs at 30 rev/s and transmits a power of 20 kW. The teeth are on the 20c full-depth system and have a module of 5 mm. The length of the line of action is 19 mm.
MCQ 5.24
The center distance for the above gear set in mm is (A) 140 (B) 150 (C) 160 (D) 170
MCQ 5.25
The contact ratio of the contacting tooth is (A) 1.21 (B) 1.25 (C) 1.29 (D) 1.33
MCQ 5.26
The resultant force on the contacting gear tooth in N is (A) 77.23 (B) 212.20 (C) 2258.1 (D) 289.43
YEAR 2006 MCQ 5.27
TWO MARKS
A disc clutch is required to transmit 5 kW at 2000 rpm. The disk has a friction lining with coefficient of friction equal to 0.25. Bore radius of friction lining is equal to 25 mm. Assume uniform contact pressure of 1 MPa. The value of outside radius of the friction lining is (A) 39.4 mm (B) 49.5 mm (C) 97.9 mm (D) 142.9 mm
MCQ 5.28
Twenty degree full depth involute profiled 19 tooth pinion and 37 tooth gear are in mesh. If the module is 5 mm, the centre distance between the gear pair will be (A) 140 mm (B) 150 mm (C) 280 mm (D) 300 mm
MCQ 5.29
A cylindrical shaft is subjected to an alternating stress of 100 MPa. Fatigue strength to sustain 1000 cycles is 490 MPa. If the corrected endurance strength is 70 MPa, estimated shaft life will be (A) 1071 cycles (B) 15000 cycles GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 220
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
(C) 281914 cycles
MCQ 5.30
(D) 928643 cycles
A 60 mm long and 6 mm thick fillet weld carries a steady load of 15 kN along the weld. The shear strength of the weld material is equal to 200 MPa . The factor of safety is (A) 2.4 (B) 3.4 (C) 4.8
YEAR 2005
(D) 6.8
ONE MARK
MCQ 5.31
Which one of the following is criterion in the design of hydrodynamic journal bearings ? (A) Sommerfeld number (B) Rating life (C) Specific dynamic capacity
YEAR 2005
(D) Rotation factor
TWO MARKS
Common Data For Q.32 and Q.33
A band brake consists of a lever attached to one end of the band. The other end of the band is fixed to the ground. The wheel has a radius of 200 mm and the wrap angle of the band is 270c. The braking force applied to the lever is limited to 100 N and the coefficient of friction between the band and the wheel is 0.5. No other information is given.
MCQ 5.32
The maximum tension that can be generated in the band during braking is (A) 1200 N (B) 2110 N (C) 3224 N (D) 4420 N
MCQ 5.33
The maximum wheel torque that can be completely braked is (A) 200 Nm (B) 382 Nm (C) 604 Nm (D) 844 Nm
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 221
YEAR 2004 MCQ 5.34
ONE MARK
Two mating spur gears have 40 and 120 teeth respectively. The pinion rotates at 1200 rpm and transmits a torque of 20 Nm. The torque transmitted by the gear is (A) 6.6 Nm (B) 20 Nm (C) 40 Nm (D) 60 Nm
MCQ 5.35
In terms of theoretical stress concentration factor (Kt) and fatigue stress concentration factor (K f ), the notch sensitivity q is expressed as (K f 1) (Kt 1) (Kt 1) (C) (K f 1) (A) (K f 1) (Kt + 1) (K f + 1) (D) (Kt + 1) (B)
MCQ 5.36
The S-N curve for steel becomes asymptotic nearly at (A) 103 cycles (B) 10 4 cycles (C) 106 cycles (D) 109 cycles
YEAR 2004 MCQ 5.37
TWO MARKS
In a bolted joint two members are connected with an axial tightening force of 2200 N. If the bolt used has metric threads of 4 mm pitch, the torque required for achieving the tightening force is
(A) 0.7 Nm (C) 1.4 Nm
MCQ 5.38
(B) 1.0 Nm (D) 2.8 Nm
Match the following Type of gears P. Q. R. S. (A) (B) (C) Bevel gears Worm gears Herringbone gears Hypoid gears P-4 P-2 P-3 Q-2 Q-3 Q-2 R-1 R-4 R-1 S-3 S-1 S-4 1. 2. 3. 4. Arrangement of shafts Non-parallel off-set shafts Non-parallel intersecting shafts Non-parallel, non-intersecting shafts Parallel shafts
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 222
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
(D)
P-1
Q-3
R-4
S-2
ONE MARK
YEAR 2003 MCQ 5.39
A wire rope is designated as 6 # 19 standard hoisting. The numbers 6 # 19 represent (A) diameter in millimeter # length in meter (B) diameter in centimeter # length in meter (C) number of strands # numbers of wires in each strand (D) number of wires in each strand # number of strands
YEAR 2003 MCQ 5.40
TWO MARKS
MCQ 5.41
Square key of side d/4 each and length l is used to transmit torque T from the shaft of diameter d to the hub of a pulley. Assuming the length of the key to be equal to the thickness of pulley, the average shear stress developed in the key is given by (B) 16T (A) 4T ld ld 2 (C) 8T (D) 16T ld 2 d 3 In a band brake the ratio of tight side band tension to the tension on the slack side is 3. If the angle of overlap of band on the drum is 180c, the coefficient of friction required between drum and the band is (A) 0.20 (B) 0.25 (C) 0.30 (D) 0.35
Common Data For Q.42 and Q.43
The overall gear ratio in a 2 stage speed reduction gear box (with all spur gears) is 12. The input and output shafts of the gear box are collinear. The counter shaft which is parallel to the input and output shafts has a gear ( Z2 teeth) and pinion (Z 3 = 15 teeth) to mesh with pinion (Z1 = 16 teeth) on the input shaft and gear (Z 4 teeth) on the output shaft respectively. It was decided to use a gear ratio of 4 with 3 module in the first stage and 4 module in the second stage.
MCQ 5.42
Z2 and Z 4 are (A) 64 and 45 (C) 48 and 60
(B) 45 and 64 (D) 60 and 48
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 223
MCQ 5.43
The centre distance in the second stage is (A) 90 mm (B) 120 mm (C) 160 mm (D) 240 mm
YEAR 2002 MCQ 5.44
ONE MARK
The minimum number of teeth on the pinion to operate without interference in standard full height involute teeth gear mechanism with 20c pressure angle is (A) 14 (B) 12 (C) 18 (D) 32
YEAR 2002 MCQ 5.45
TWO MARKS
The coupling used to connect two shafts with large angular misalignment is (A) a flange coupling (B) an Oldhams coupling (C) a flexible bush coupling (D) a Hookes joint
MCQ 5.46
A static load is mounted at the centre of a shaft rotating at uniform angular velocity. This shaft will be designed for (A) the maximum compressive stress (static) (B) the maximum tensile (static) (C) the maximum bending moment (static) (D) fatigue loading
MCQ 5.47
Large speed reductions (greater than 20) in one stage of a gear train are possible through (A) spur gearing (B) worm gearing (C) bevel gearing (D) helical gearing
MCQ 5.48
If the wire diameter of a closed coil helical spring subjected to compressive load is increased from 1 cm to 2 cm, other parameters remaining same, the deflection will decrease by a factor of (A) 16 (B) 8 GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 224
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
(C) 4
(D) 2
YEAR 2001 MCQ 5.49
ONE MARK
Bars AB and BC , each of negligible mass, support load P as shown in the figure. In this arrangement,
(A) bar AB is subjected to bending but bar BC is not subjected to bending. (B) bar AB is not subjected to bending but bar BC is subjected to bending. (C) neither bar AB nor bar BC is subjected to bending. (D) both bars AB and BC are subjected to bending.
YEAR 2001 MCQ 5.50
TWO MARKS
Two helical tensile springs of the same material and also having identical mean coil diameter and weight, have wire diameters d and d/2. The ratio of their stiffness is (A) 1 (B) 4 (C) 64 (D) 128 *********
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 225
SOLUTION
SOL 5.1
Option (C) is correct. Given : Width of fillets s = 10 mm , l = 30 mm , = 94 MPa
The shear strength of the joint for single parallel fillet weld is, P = Throat Area # Allowable stress = t#l# t = s sin 45c = 0.707 s P = 0.707 # s # l # = 0.707 # (0.01) # (0.03) # (94 # 106) = 19937 N or 19.93 kN
SOL 5.2
From figure
Option (B) is correct. T1 = 400 N, = 0.25, = 180c = 180c # = rad. 180c D = 0.5 m, r = D = 0.25 m 2 For the band brake, the limiting ratio of the tension is given by the relation, T1 = e T2 400 = e0.25 # = 2.19 T2 T2 = 400 = 182.68 N 2.19 For Band-drum brake, Braking Torque is Given : TB = (T1 T2) # r = (400 182.68) # 0.25 = 54.33 Nm , 54.4 Nm
SOL 5.3
Option (B) is correct. F.O.S = Allowable shear stress Design shear stress Design shear stress for solid circular shaft GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 226
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
Therefore or,
# 10 = 16T = 16 # 50 3 d 3 d 3 F.O.S = 140 # d 3 16 # 50 # 10 3 2 = 140 # d 3 16 # 50 # 10 3 d 3 = 2 # 16 # 50 # 10 140 # d = 15.38 mm , 16 mm
From T = r J
SOL 5.4
Option (B) is correct. Given : WP = 30 kN , WQ = 45 kN k Life of bearing, L = b C l # 106 revolutions W C = Basic dynamic load rating = Constant For ball bearing, k = 3 L = b C l # 106 revolutions W These are the identical bearings. So for the Life of P and Q. LP = WQ 3 = 45 3 = 3 3 = 27 b 30 l b2l c LQ m cWP m 8 So,
3
SOL 5.5
Option (D) is correct. Given : b = 80 mm , d = 250 mm , = 0.25 , = 270c, TB = 1000 Nm Let, T1 " Tension in the tight side of the band (Maximum Tension) T2 " Tension in the slack side of the band (Minimum Tension) Braking torque on the drum, TB = (T1 T2) r T1 T2 = TB = 1000 = 8000 N r 0.125 We know that limiting ratio of the tension is given by, T1 = e = ea0.25 # 180 # 270k = 3.246 T2 T2 = T1 3.246 Substitute T2 in equation (i), we get & 3.246T1 T1 = 25968 T1 T1 = 8000 3.246 2.246T1 = 25968 & T1 = 25968 = 11.56 kN 2.246 GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
...(i)
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 227
SOL 5.6
Option (B) is correct. Given : d = 6 mm , l = 12 mm , P = 1000 N Each rivets have same diameter, So equal Load is carried by each rivet. Primary or direct force on each rivet, F = P = 1000 = 250 N 4 4 Shear area of each rivet is, A = ^6 # 103h2 = 28.26 # 106 mm2 4 Direct shear stress on each rivet, 250 =F = = 8.84 # 106 - 8.8 MPa A 28.26 # 106 Option (A) is correct. Given : d = 50 mm , D = 50.05 mm , l = 20 mm , N = 1200 rpm , = 0.03 Pa s Tangential velocity of shaft, 3 u = dN = 3.14 # 50 # 10 # 1200 = 3.14 m/ sec 60 60 And Radial clearance, y = D d = 50.05 50 = 0.025 mm 2 2 Shear stress from the Newtons law of viscosity, 3.14 = # u = 0.03 # = 3768 N/m2 y 0.025 # 103 Shear force on the shaft, F = # A = 3768 # ( # d # l) = 3768 # 3.14 # 50 # 103 # 20 # 103 = 11.83 N T = F # d = 11.83 # 50 # 103 = 0.2957 Nm 2 2 We know that power loss, P = 2NT = 2 # 3.14 # 1200 # 0.2957 60 60 Torque, = 37.13 W - 37 W
SOL 5.7
SOL 5.8
Option (A) is correct. Given : Su or u = 600 MPa , Sy or y = 420 MPa , Se or e = 240 MPa , d = 30 mm Fmax = 160 kN (Tension), Fmin = 40 kN (Compression) 3 Maximum stress, max = Fmax = 160 # 10 = 226.47 MPa (30) 2 A 4 3 Minimum stress, min = Fmin = 40 # 10 = 56.62 MPa A (30) 2 4# GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 228
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
Mean stress, Variable stress,
m = max + min = 226.47 56.62 = 84.925 MPa 2 2 226.47 ( 56.62) v = max min = 2 2 = 141.545 MPa
From the Soderbergs criterion, 1 = m + v y e F .S. 1 = 84.925 + 141.545 = 0.202 + 0.589 = 0.791 420 240 F .S. So, F.S. = 1 = 1.26 0.791
SOL 5.9
Option (A) is correct. Given : m = 4 mm , Z = 21, P = 15 kW = 15 # 103 W N = 960 rpm b = 25 mm , = 20c Pitch circle diameter, D = mZ = 4 # 21 = 84 mm Tangential Force is given by, FT = T r Power transmitted, & T = 60P P = 2NT 60 2N Then FT = 60P # 1 r = Pitch circle radius r 2N
3 1 = 60 # 15 # 10 # 2 # 3.14 # 960 42 # 103
...(i)
= 3554.36 N - 3552 N
SOL 5.10
Option (B) is correct. From Lewis equation F p FT b = T d = by b#y#m 3552 = 25 # 103 # 0.32 # 4 # 103 b = 111 MPa Minimum allowable (working stress)
pd = = = 1 pc m m
W = b # Cv = 111 # 1.5 = 166.5 MPa
SOL 5.11
Option (A) is correct. Given : d = 40 mm , l = 40 mm , = 20 rad/ sec Z () = 20 mPa s = 20 # 103 Pa s , c (y) = 0.020 mm GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 229
Shear stress,
= u y
From the Newtons law of viscosity...(i)
u = r = 0.020 # 20 = 0.4 m/ sec 3 0.4 = 400 N/m2 = 20 # 10 # 0.020 # 10 3 Shear force is generated due to this shear stress, F = A = # dl A = dl = Area of shaft = 400 # 3.14 # 0.040 # 0.040 = 2.0096 N T = F # r = 2.0096 # 0.020 = 0.040192 Nm - 0.040 Nm
Loss of torque,
SOL 5.12
Option (B) is correct. Given : d1 = 100 mm & r1 = 50 mm , d2 = 40 mm & r1 = 20 mm p = 2 MPa = 2 # 106 Pa , n = 0.4 When the pressure is uniformly distributed over the entire area of the friction faces, then total frictional torque acting on the friction surface or on the clutch is given by, (r ) 3 (r2) 3 T = 2p ; 1 E 3 = 2 # 3.14 # 0.4 # 2 # 106 6(50) 3 (20) 3@ # 109 3 = 195.39 Nm - 196 Nm
SOL 5.13
Option (B) is correct. Given : m = 3 mm , Z = 16 , b = 36 mm , = 20c, P = 3 kW N = 20 rev/ sec = 20 # 60 rpm = 1200 rpm , Cv = 1.5 , y = 0.3 Module, m =D Z D = m # Z = 3 # 16 = 48 mm P = 2NT 60
3 T = 60P = 60 # 3 # 10 2 # 3.14 # 1200 2N
Power,
= 23.88 Nm = 23.88 # 103 Nmm 3 Tangential load, WT = T = 2T = 2 # 23.88 # 10 = 995 N 48 R D From the lewis equation Bending stress (Beam strength of Gear teeth) 1 b = WT Pd = WT :Pd = PC = m = m D by bym 995 = 36 # 103 # 0.3 # 3 # 103 GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 230
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
995 = 30.70 # 106 Pa = 30.70 MPa 3.24 # 105 Permissible working stress b = W = b # Cv = 30.70 # 1.5 = 46.06 MPa , 46 MPa
SOL 5.14
Option (D) is correct.
Given : m = 4 , Z = 32 , Tooth space = Tooth thickness = a We know that, m =D Z Pitch circle diameter, D = mZ = 4 # 32 = 128 mm And for circular pitch, Pc = m = 3.14 # 4 = 12.56 mm We also know that circular pitch, Pc = Tooth space + Tooth thickness = a + a = 2a a = Pc = 12.56 = 6.28 mm 2 2 From the figure, or b = addendum + PR PQ a/2 3.14 = = sin = 64 64 OQ
= sin1 (0.049) = 2.81c OP = 64 cos 2.81c = 63.9 mm PR = OR OP = 64 63.9 = 0.1 mm OR = Pitch circle radius And b = m + PR = 4 + 0.1 = 4.1 mm Therefore, a = 6.28 mm and b = 4.1 mm
SOL 5.15
Option (A) is correct. Types of Gear P. Helical Q. Spiral Bevel Description 2. Axes parallel and teeth are inclined to the axis 4. Axes are perpendicular and intersecting, and teeth are inclined to the axis
ISBN: 9788192276250
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 231
R. Hypoid S.
1. Axes non parallel and non-intersecting
Rack and pinion 6. Axes are parallel and one of the gear has infinite radius
So, correct pairs are P-2, Q-4, R-1, S-6
SOL 5.16
Option (A) is correct.
In this figure WS represent the primary shear load whereas WS1 and WS2 represent the secondary shear loads. Given : A = 10 # 50 mm2 , n = 2 , W = 4 kN = 4 # 103 N We know that primary shear load on each bolt acting vertically downwards, Ws = W = 4 kN = 2 kN 2 n Since both the bolts are at equal distances from the centre of gravity G of the two bolts, therefore the secondary shear load on each bolt is same. For secondary shear load, taking the moment about point G , Ws1 # r1 + Ws2 # r2 r1 2r1 Ws1 2 # 0.2 # Ws1 = W#e = r2 and Ws1 = Ws2
So,
= 4 # 103 # (1.7 + 0.2 + 0.1) = 4 # 103 # 2 3 Ws1 = 8 # 10 = 20 # 103 = 20 kN 2 # 0.2
SOL 5.17
Option (B) is correct. From the figure, resultant Force on bolt P is F = Ws2 Ws = 20 2 = 18 kN Shear stress on bolt P is, 18 # 103 = F = = 159.23 MPa - 159 MPa 3 2 Area ( 12 10 ) # 4# GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 232
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
SOL 5.18
Option (D) is correct. Given : W1 = F , W2 = 2F , L1 = 8000 hr We know that, life of bearing is given by k L = b C l # 106 revolution W For ball bearing, k = 3 , L = b C l # 106 revolution W For initial condition life is, 3 L1 = bC l # 106 F 8000 hr = bC l # 106 F For final load,
3 3
...(i)
3 3 L2 = b C l # 106 = 1 # bC l # 106 8 2F F From equation (i) = 1 (8000 hr) = 1000 hr 8
SOL 5.19
Option (B) is correct. Given : d = 200 mm , t = 1 mm , u = 800 MPa , e = 400 MPa Circumferential stress induced in spherical pressure vessel is, p r p 100 = # = # = 50p MPa 2t 2#1 Given that, pressure vessel is subject to an internal pressure varying from 4 to 8 MPa. So, min = 50 # 4 = 200 MPa max = 50 # 8 = 400 MPa Mean stress, m = min + max = 200 + 400 = 300 MPa 2 2 Variable stress, v = max min = 400 200 = 100 MPa 2 2 From the Goodman method, 1 = m + v = 300 + 100 = 3 + 1 = 5 & F.S. = 8 = 1.6 5 u e 800 400 8 4 8 F .S. Option (B) is correct. Given : d = 50 mm , l = 50 mm , N = 20 rps , Z = 20 mPa sec = 20 # 103 Pa sec Radial clearance = 50 m = 50 # 103 mm , Load = 2 kN We know that, p = Bearing Pressure on the projected bearing area = Load on the journal l#d
ISBN: 9788192276250
SOL 5.20
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 233
3 = 2 # 10 = 0.8 N/mm2 = 0.8 # 106 N/m2 50 # 50 2 c = diameteral clearance Sommerfeld Number = ZN b d l p c = 2 # radial clearance 3 2 20 50 S.N. = 20 # 10 # #b 6 3 l 0.8 # 10 100 # 10 3 20 1 2 6 = 20 # 10 # # b 2 l # 10 = 0.125 6 0.8 # 10
SOL 5.21
Option (A) is correct.
Given : Diameter of bolt d = 10 mm , F = 10 kN , No. of bolts n = 3 Direct or Primary shear load of each rivet 3 FP = F = 10 # 10 N n 3 FP = 3333.33 N The centre of gravity of the bolt group lies at O (due to symmetry of figure). e = 150 mm (eccentricity given) Turning moment produced by the load F due to eccentricity = F # e = 10 # 103 # 150 = 1500 # 103 Nmm Secondary shear load on bolts from fig. rA = rC = 40 mm and rB = 0 We know that F # e = FA [(rA) 2 + (rB) 2 + (rC ) 2] rA (rA = rC and rB = 0 ) = FA # [2 (rA) 2] rA 1500 # 103 = FA # [2 (40) 2] = 80FA 40 FA = 1500 # 10 = 18750 N 80 GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
3
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 234
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
FB = 0 FC = FA # rC = 18750 # 40 rA 40 = 18750 N From fig we find that angle between FA and FP = A = 90c FB and FP = B = 90c FC and FP = C = 90c Resultant load on bolt A , RA = (FP ) 2 + (FA) 2 + 2FP # FA cos A
(rB = 0)
= (3333.33) 2 + (18750) 2 + 2 # 3333.33 # 18750 # cos 90c RA = 19044 N Maximum shear stress at A A = RA = 19044 = 242.6 MPa (d) 2 (10) 2 4 4 Resultant load on Bolt B , RB = FP = 3333.33 N Maximum shear stress at B , B = RB = 3333.33 = 42.5 MPa (d) 2 (10) 2 4 4#
SOL 5.22
(FB = 0)
Option (C) is correct.
Given : P = 400 N , r = 300 mm = 150 mm , l = 600 mm 2 x = 200 mm , = 0.25 and 2 = 45c Let, RN " Normal force pressing the brake block on the wheel Ft "Tangential braking force or the frictional force acting at the contact surface of the block & the wheel. GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 235
Here the line of action of tangential braking force Ft passes through the fulcrum O of the lever and brake wheel rotates clockwise. Then for equilibrium, Taking the moment about the fulcrum O , RN # x = P # l RN = P # l = 400 # 0.6 = 1200 N x 0.2 Tangential braking force on the wheel, Braking Torque, Ft = RN TB = Ft # r = RN # r = 0.25 # 1200 # 0.15 = 45 Nm
SOL 5.23
Option (C) is correct. Given : d = 20 mm , l = 700 mm , E = 200 GPa = 200 # 109 N/m2 = 200 # 103 N/mm2 Compressive or working Load = 10 kN According to Eulers theory, the crippling or buckling load (Wcr ) under various end conditions is given by the general equation, 2 EI ...(i) Wcr = c 2 l Given that one end is guided at the piston end and hinged at the other end. So, c =2 From equation (i), 2 EI = 22 E 4 Wcr = 2 2 I = d4 # 64 d 64 l l2
3 # 10 # 3.14 # (20) 4 = 2 # 9.81 # 200 64 (700) 2 = 62864.08 N = 62.864 kN We know that, factor of safety (FOS) Crippling Load FOS = = 62.864 = 6.28 10 Working Load
The most appropriate option is (C).
SOL 5.24
Option (B) is correct. Given : ZP = 20 , ZG = 40 , NP = 30 rev/ sec , P = 20 kW = 20 # 103 W , m = 5 mm Module, m = D = DP = DG Z ZP ZG DP = m # ZP = 5 # 20 = 100 mm or, DG = m # ZG = 5 # 40 = 200 mm Centre distance for the gear set, GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 236
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
L = DP + DG = 100 + 200 = 150 mm 2 2
SOL 5.25
Option (C) is correct. Given : Length of line of action, L = 19 mm Pressure angle, = 20c Length of path of contact (L) Length of arc of contact = cos = 19 = 20.21 mm cos 20c Contact ratio or number of pairs of teeth in contact, Length of arc of contact = circular pitch = 20.21 = 20.21 = 1.29 m 3.14 # 5 Option (C) is correct.
SOL 5.26
Let, T " Torque transmitted in N m We know that power transmitted is, P = T = T # 2N 60
3 T = 60P = 60 # 20 # 10 = 106.157 Nm 2 # 3.14 # 1800 2N Tangential load on the pinion FT = T RP = 106.157 = 2123.14 N 0.05 From the geometry, total load due to power transmitted, F = FT = 2123.14 - 2258.1 N cos cos 20c
SOL 5.27
Option (A) is correct. GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 237
Given : P = 5 kW , N = 2000 rpm , = 0.25 , r 2 = 25 mm = 0.025 m , p = 1 MPa Power transmitted, P = 2NT 60
3 T = 60P = 60 # 5 # 10 = 23.885 Nm 2 # 3.14 # 2000 2N When pressure is uniformly distributed over the entire area of the friction faces, then total frictional torque acting on the friction surface or on the clutch, (r ) 3 (r2) 3 T = 2p ; 1 E 3
Torque,
23.885 # 3 = 2 # 3.14 # 0.25 # 1 # 106 # [r 13 (0.025) 3] 23.885 # 3 r 13 (0.025) 3 = 2 # 3.14 # 0.25 # 106 r 13 1.56 # 105 = 45.64 # 106 = 4.564 # 105 r 13 = (4.564 + 1.56) # 105 = 6.124 # 105 r1 = (6.124 # 105) 1/3 = 3.94 # 102 m = 39.4 mm
SOL 5.28
Option (A) is correct. Given : ZP = 19 , ZG = 37 , m = 5 mm Also, m =D Z For pinion, pitch circle diameter is, DP = m # ZP = 5 # 19 = 95 mm And pitch circle diameter of the gear, DG = m # ZG = 5 # 37 = 185 mm Now, centre distance between the gear pair (shafts), L = DP + DG = 95 + 185 = 140 mm 2 2 2
SOL 5.29
Option (C) is correct.
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 238
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
We know that in S-N curve the failure occurs at 106 cycles (at endurance strength) We have to make the S-N curve from the given data, on the scale of log 10 . Now equation of line whose end point co-ordinates are 6 ^log 10 1000, log 10 490h and ^log 10 10 , log 10 70h or ^3, log 10 490h and ^6, log 10 70h, y log 10 490 log 10 70 log 10 490 = x3 63 y 2.69 = 1.845 2.69 3 x3 y y1 y 2 y1 b x x1 = x 2 x1 l
y 2.69 = 0.281 (x 3) Given, the shaft is subject to an alternating stress of 100 MPa So, y = log 10 100 = 2 Substitute this value in equation (i), we get 2 2.69 = 0.281 (x 3) 0.69 = 0.281x + 0.843 x = 0.843 0.69 = 5.455 0.281 log 10 N = 5.455 N = 105.455 = 285101 The nearest shaft life is 281914 cycles. And
SOL 5.30
...(i)
Option (B) is correct.
Given : l = 60 mm = 0.06 m , s = 6 mm = 0.006 m , P = 15 kN = 15 # 103 N Shear strength = 200 MPa We know that, if is the allowable shear stress for the weld metal, then the shear strength of the joint for single parallel fillet weld, P = Throat Area # Allowable shear stress = t#l# GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 239
P = 0.707s # l # t = s sin 45c = 0.707s P 15 # 103 = = 58.93 MPa = 0.707 # 0.006 # 0.06 0.707 # s # l Factor of Safety, FOS =
SOL 5.31
Shear strength = 200 MPa = 3.39 - 3.4 58.93 MPa Allowable shear stress
Option (A) is correct. The coefficient of friction for a full lubricated journal bearing is a function of three variables, i.e. = b ZN , d , l l p c d ZN Here, =Bearing characteristic Number, d =Diameter of the bearing p l =Length of the bearing, c =Diameteral clearance 2 Sommerfeld Number = ZN b d l p c It is a dimensionless parameter used extensively in the design of journal bearing. i.e. sommerfeld number is also function of b ZN , d l. Therefore p c option (A) is correct.
SOL 5.32
Option (B) is correct.
Given : r = 200 mm = 0.2 m , = 270c = 270 # = 3 radian , = 0.5 180 2 At the time of braking, maximum tension is generated at the fixed end of band near the wheel. Let, T2 " Tension in the slack side of band T1 "Tension in the tight side of band at the fixed end Taking the moment about the point O , & T2 = 200 N T2 # 1 = 100 # 2 For the band brake, the limiting ratio of the tension is given by the relation T1 = e & T1 = T2 # e T2 GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 240
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
T1 = 200 # e0.5 # 2 = 200 # 10.54 = 2108 N - 2110 N So, maximum tension that can be generated in the band during braking is equal to 2110 N
SOL 5.33
Option (B) is correct. Maximum wheel torque or braking torque is given by, TW = (T1 T2) r = (2110 200) # 0.2 = 382 Nm
SOL 5.34
Option (D) is correct.
Given : ZP = 40 teeth , ZG = 120 teeth , NP = 1200 rpm , TP = 20 Nm ZP = NG ZG NP NG = ZP # NP = 40 # 1200 = 400 rpm 120 ZG Power transmitted is same for both pinion & Gear. P = 2NP TP = 2NG TG 60 60 Velocity Ratio, NP TP = NG TG TG = NP TP = 1200 # 20 = 60 Nm 400 NG So, the torque transmitted by the Gear is 60 Nm
SOL 5.35
Option (A) is correct. When the notch sensitivity factor q is used in cyclic loading, then fatigue stress concentration factor may be obtained from the following relation. K f = 1 + q (Kt 1) K f 1 = q (Kt 1) K 1 q = f Kt 1
SOL 5.36
Option (C) is correct. The S-N curve for the steel is shown below : GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 241
We can easily see from the S-N curve that, steel becomes asymptotic nearly at 106 cycles .
SOL 5.37
Option (C) is correct. Given : Ft = 2200 N , p = 4 mm = 0.004 m Torque required for achieving the tightening force is, T = Ft # r = Ft # Pitch = 2200 # 0.004 = 1.4 Nm 2 2 # 3.14 Option (B) is correct. Type of Gears P. Q. R. S. Bevel gears Worm gears Herringbone gears Hypoid gears 2. 3. 4. 1. Arrangement of shafts Non-parallel intersecting shafts Non-parallel, non-intersecting shafts Parallel shafts Non-parallel off-set shafts
SOL 5.38
So, correct pairs are P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-1.
SOL 5.39
Option (C) is correct. The wire ropes are designated by the number of strands multiplied by the number of wires in each strand. Therefore, 6 # 19 = Number of strands # Number of wires in each strand. Option (C) is correct. Given : Diameter of shaft = d Torque transmitted = T Length of the key = l We know that, width and thickness of a square key are equal. GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
SOL 5.40
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 242
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
w =t=d 4 Force acting on circumference of shaft F = T = 2T r d i.e. A = width # length = d # l = dl 4 4 2T/d Force Average shear stress, = = = 8T shearing Area dl/4 ld 2 Shearing Area,
SOL 5.41
(r = d/2)
Option (D) is correct. Let, T1 " Tension in the tight side of the band, T2 " Tension in the slack side of the band "Angle of lap of the band on the drum Given : T1 = 3 , = 180c = # 180 = radian 180 T2 For band brake, the limiting ratio of the tension is given by the relation, T1 = e or 2.3 log T1 = bT2 l T2 2.3 # log (3) = # 2.3 # 0.4771 = # 3.14 = 1.09733 = 0.349 - 0.35 3.14
SOL 5.42
Option (A) is correct.
Let N1 , N2 , N 3 and N 4 are the speeds of pinion 1, gear 2, pinion 3 and gear 4 respectively. GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 243
Given : Z1 = 16 teeth , Z 3 = 15 teeth and Z 4 = ? , Z2 = ? N1 = Z2 /Z1 Velocity ratio N \ 1/Z N4 Z 3 /Z 4 ...(i) = Z2 # Z 4 = 12 Z1 Z3 N1 = Z 2 = 4 But for stage 1, ...(ii) N2 Z1 from eq. (i) So, 4 # Z 4 = 12 Z3 Z4 = 3, & Z 4 = 3 # 15 = 45 teeth Z3 From equation (ii),
SOL 5.43
Z2 = 4 # Z1 = 4 # 16 = 64 teeth
Option (B) is correct. Let centre distance in the second stage is D . D = R4 + R3 = D4 + D3 2 D4 = D3 = 4 But, Z4 Z3 Or, So, D 4 = 4 # Z 4 = 4 # 45 = 180 D 3 = 4 # Z 3 = 4 # 15 = 60 D = 180 + 60 = 120 mm 2
m = D/Z module
SOL 5.44
Option (C) is correct. In standard full height involute teeth gear mechanism the arc of approach is not be less than the circular pitch, therefore Maximum length of arc of approach = Circular pitch ...(i) where Maximum length of the arc of approach Max. length of the path of approach = cos r sin = = r tan cos Circular pitch, PC = m = 2r m = 2r Z Z Hence, from equation (i), we get r tan = 2r Z Z = 2 = 2 = 17.25 - 18 teeth tan tan 20c GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 244
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
SOL 5.45
Option (D) is correct. (A) Flange coupling :- It is used to connect two shaft having perfect coaxial alignment and no misalignment is allowed between them. (B) Oldhams coupling :- It is used to join two shafts which have lateral misalignment. (C) Flexible bush coupling :- It is used to join the abutting ends of shafts when they are not in exact alignment. (D) Hooks joint :- It is used to connect two shafts with large angular misalignment.
SOL 5.46
Option (D) is correct. When the shaft rotates, the bending stress at the upper fibre varies from maximum compressive to maximum tensile while the bending stress at the lower fibres varies from maximum tensile to maximum compressive. The specimen subjected to a completely reversed stress cycle. This is shown in the figure.
When shaft is subjected to repeated stress, then it will be designed for fatigue loading.
SOL 5.47
Option (B) is correct. For a worm gear the velocity ratio ranges between 10 : 1 to 100 : 1. So, Large speed reductions (greater than 20) in one stage of a gear train are possible through worm gearing. Option (A) is correct. For Helical spring, deflection is given by, 3 n = 8PD3 n = 64PR 4 Gd Gd 4 where, P = Compressive load d = Wire diameter R = Coil diameter GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
SOL 5.48
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
CHAP 5
MACHINE DESIGN
PAGE 245
G = Modulus of rigidity From the given conditions \ 14 d Given d1 = 1 cm and d2 = 2 cm 2 = d1 4 1 b d2 l 2 = 1 4 = 1 16 1 b 2 l 2 = 1 16 So, deflection will decrease by a factor of 16.
SOL 5.49
Option (C) is correct. Bars AB and BC have negligible mass. The support load P acting at the free end of bars AB and BC . Due to this load P , In bar AB compressive stress and in bar BC tensile stress are induced. However, none of these bars will be subjected to bending because there is no couple acting on the bars. Option (C) is correct. Let L1 & L2 are lengths of the springs and n1 & n2 are the number of coils in both the springs. Given : W1 = W2 m1 g 1 g A 1 # L 1 # g d 2 D n 1 1 4 1# = m2 g = 2 g = A 2 # L 2 # g 2 = d2 D 2 n 2 4 # m = L = Dn D1 = D 2
SOL 5.50
Given :
2 2 d1 # n1 = d 2 # n 2 d1 = d & d 2 = d 2 2
d 2 # n1 = d # n 2 4 or, n1 = n 2 4 The deflection of helical spring is given by, 3 = 8PD4 n Gd 4 Spring stiffness, k = P = Gd 8D3 n GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 246
MACHINE DESIGN
CHAP 5
From the given conditions, we get 4 k\d n So, k 1 = d1 4 n2 k 2 b d 2 l # a n1 k k1 = d 4 n2 k2 c d/2 m # n2 /4 k1 = 16 4 = 64 # k2 *******
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
Você também pode gostar
- Design and Analysis of Centrifugal CompressorsNo EverandDesign and Analysis of Centrifugal CompressorsAinda não há avaliações
- Machine DesignDocumento38 páginasMachine DesignBanwari Lal PrajapatAinda não há avaliações
- SDocumento16 páginasSKumar KoteAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Design: 10 MM 30 MM 94 MpaDocumento38 páginasMachine Design: 10 MM 30 MM 94 MpaSreevathsaAinda não há avaliações
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationNo EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationAinda não há avaliações
- GATE - IES QuestionsDocumento4 páginasGATE - IES QuestionsMahesh Chandrabhan ShindeAinda não há avaliações
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsAinda não há avaliações
- Machine DataDocumento38 páginasMachine DataEr Mahavir MiyatraAinda não há avaliações
- ManengDocumento88 páginasManengArvind MeenaAinda não há avaliações
- MD Class Test 1Documento5 páginasMD Class Test 1Sambit Das0% (1)
- Common Data For Q. - 24 and Q.26: 20 KW 5 MM 19 MMDocumento1 páginaCommon Data For Q. - 24 and Q.26: 20 KW 5 MM 19 MMSameerChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- 30 MM 40 KN 160 KN 600 Mpa 420 Mpa 240 Mpa: Common Data For Q. - 9 and Q.10Documento1 página30 MM 40 KN 160 KN 600 Mpa 420 Mpa 240 Mpa: Common Data For Q. - 9 and Q.10SameerChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Design-1Documento1 páginaMachine Design-1SameerChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Design-2Documento1 páginaMachine Design-2SameerChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Dme Question BankDocumento4 páginasDme Question BankRavi Patil100% (1)
- Theory of Machines & Machine DesignDocumento3 páginasTheory of Machines & Machine DesignAvilash JainAinda não há avaliações
- MDDocumento5 páginasMDYogesh DanekarAinda não há avaliações
- Final Exam MCT3214 Nov09Documento6 páginasFinal Exam MCT3214 Nov09Deerah Aziz100% (1)
- B.Tech Degree S8 (S, FE) / S6 (PT) (S, FE) Examination June 2023 (2015 Scheme)Documento3 páginasB.Tech Degree S8 (S, FE) / S6 (PT) (S, FE) Examination June 2023 (2015 Scheme)Venkitaraj K PAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of MachinesDocumento27 páginasTheory of MachinesbalameckAinda não há avaliações
- Machine DesignDocumento6 páginasMachine DesignRishi SinghAinda não há avaliações
- QB Unit-3,4,5Documento7 páginasQB Unit-3,4,5Agranshu BhardwajAinda não há avaliações
- DME Question Bank Unit (3-4-5)Documento7 páginasDME Question Bank Unit (3-4-5)PrathamAinda não há avaliações
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDocumento6 páginas4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Design &estimation (Dme-306) Question BankDocumento4 páginasDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Design &estimation (Dme-306) Question BankDharmendra SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Problems s8Documento4 páginasProblems s8zangue billy jamesAinda não há avaliações
- Integrated Mechanical Design Jan - 10Documento4 páginasIntegrated Mechanical Design Jan - 10SasiKumar PetchiappanAinda não há avaliações
- Forming QuestionsDocumento3 páginasForming QuestionsSarath Philip Mathew VenkadathAinda não há avaliações
- Instruction: Solve The Following ProblemsDocumento1 páginaInstruction: Solve The Following ProblemsAdriel JohnAinda não há avaliações
- 114 PDFDocumento73 páginas114 PDFMonu SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- 07a6ec05 Designofmachinemembers IIDocumento11 páginas07a6ec05 Designofmachinemembers IIzahid_polyAinda não há avaliações
- Previous Exam QuestionsDocumento8 páginasPrevious Exam QuestionssallyreffatAinda não há avaliações
- DME Chapter Three: or (Summer 15)Documento7 páginasDME Chapter Three: or (Summer 15)honeyfunnyAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Me 5dcdm2Documento3 páginas12 Me 5dcdm2Abhyudaya SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Dme Model Key 2019Documento25 páginasDme Model Key 2019Siva RamanAinda não há avaliações
- Common Subject Code: Shivaji University, KolhapurDocumento10 páginasCommon Subject Code: Shivaji University, Kolhapursatyamchgl2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Question Bank - DMEDocumento6 páginasQuestion Bank - DMEBdhdhshAinda não há avaliações
- DTS ND06-QPDocumento3 páginasDTS ND06-QPsrajapratyAinda não há avaliações
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocumento1 páginaVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Design Questions PDFDocumento5 páginasMachine Design Questions PDFrajibAinda não há avaliações
- 103 Manufacturing Engineering PDFDocumento73 páginas103 Manufacturing Engineering PDFSushil Kumar Singh100% (1)
- 0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsDocumento3 páginas0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsSaravanan MathiAinda não há avaliações
- 60 MM 6 MM 15 KN 200 Mpa: Common Data For Q. - 32 and Q.33Documento1 página60 MM 6 MM 15 KN 200 Mpa: Common Data For Q. - 32 and Q.33SameerChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- 15A03602 Design of Machine Members - IIDocumento2 páginas15A03602 Design of Machine Members - IIJagannath CherkuAinda não há avaliações
- Manufacturing Engineering-9 PDFDocumento1 páginaManufacturing Engineering-9 PDFSameerChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Me 2303 - Design of Machine Elements December 2010Documento3 páginasMe 2303 - Design of Machine Elements December 2010Ilaya Perumal K0% (1)
- Dme Model 2Documento6 páginasDme Model 2YashwanthI-StyleKuttiAinda não há avaliações
- Dme 2 QP CombinedDocumento9 páginasDme 2 QP CombinedPrasinAinda não há avaliações
- MTP 5Documento4 páginasMTP 5tinku singhAinda não há avaliações
- DME Question Bank Unit (1 2)Documento5 páginasDME Question Bank Unit (1 2)PrathamAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Machine Elements - IIDocumento8 páginasDesign of Machine Elements - IIprasaad26Ainda não há avaliações
- No of Pages: 4 Course Code: 12M502: Fig.1 Fig 2Documento4 páginasNo of Pages: 4 Course Code: 12M502: Fig.1 Fig 2CRAZY PIANO PLAYERAinda não há avaliações
- QUIZ Without AnswersDocumento24 páginasQUIZ Without AnswersSanjay TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- PMD ModelDocumento8 páginasPMD ModelDamodara SatyaDeva MadhukarAinda não há avaliações
- DTE Unit 1 MCQs (Keys Shafts and Couplings)Documento6 páginasDTE Unit 1 MCQs (Keys Shafts and Couplings)Mannam Sarath Sarath100% (2)
- QB Unit-1,2Documento5 páginasQB Unit-1,2Agranshu BhardwajAinda não há avaliações
- 12me52 MQP-1Documento3 páginas12me52 MQP-1SumitKumarAinda não há avaliações
- Question Paper - Design of Machine Elements 2 Oct-19-October - 2019Documento2 páginasQuestion Paper - Design of Machine Elements 2 Oct-19-October - 2019ChanduAinda não há avaliações
- $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffNo Everand$100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (18)
- Summary: Greenlights: by Matthew McConaughey: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Greenlights: by Matthew McConaughey: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- House Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetNo EverandHouse Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetAinda não há avaliações
- Bare Bones: I'm Not Lonely If You're Reading This BookNo EverandBare Bones: I'm Not Lonely If You're Reading This BookNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (11)
- Altamont: The Rolling Stones, the Hells Angels, and the Inside Story of Rock's Darkest DayNo EverandAltamont: The Rolling Stones, the Hells Angels, and the Inside Story of Rock's Darkest DayNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (25)
- The Storyteller: Expanded: ...Because There's More to the StoryNo EverandThe Storyteller: Expanded: ...Because There's More to the StoryNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (13)
- Ikigai: The Japanese Life Philosophy to Finding Happiness and PeacefulnessNo EverandIkigai: The Japanese Life Philosophy to Finding Happiness and PeacefulnessNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (91)
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsNo EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsAinda não há avaliações
- To Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryNo EverandTo Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (26)
- Twelve Caesars: Images of Power from the Ancient World to the ModernNo EverandTwelve Caesars: Images of Power from the Ancient World to the ModernNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (9)
- No Lifeguard on Duty: The Accidental Life of the World's First SupermodelNo EverandNo Lifeguard on Duty: The Accidental Life of the World's First SupermodelNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (42)
- Storyworthy: Engage, Teach, Persuade, and Change Your Life through the Power of StorytellingNo EverandStoryworthy: Engage, Teach, Persuade, and Change Your Life through the Power of StorytellingNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (152)
- The Hotel on Place Vendôme: Life, Death, and Betrayal at the Hotel Ritz in ParisNo EverandThe Hotel on Place Vendôme: Life, Death, and Betrayal at the Hotel Ritz in ParisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (49)
- I Didn't Come Here to Make Friends: Confessions of a Reality Show VillainNo EverandI Didn't Come Here to Make Friends: Confessions of a Reality Show VillainNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (47)