Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Actual NCP
Enviado por
Mabz BoholDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Actual NCP
Enviado por
Mabz BoholDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
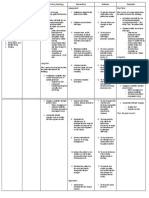
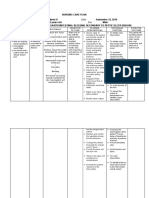
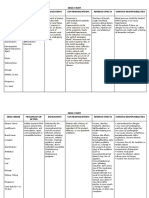
Medical Diagnosis: Renal Failure Problem: Fluid Volume Excess RT Decreased Glomerular Filtration Rate and Sodium Retention
Assessment Subjective: (none) Objective: Patient manifested:
Nursing Diagnosis Fluid Volume Excess R/T decrease Glomerular filtration Rate and sodium retention
congestion (SOB, DOB)
vein status Patient may manifest:
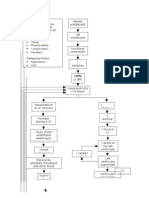
Scientific Explanation Renal disorder impairs glomerular filtration that resulted to fluid overload. With fluid volume excess, hydrostatic pressure is higher than the usual pushing excess fluids into the interstitial spaces. Since fluids are not reabsorbed at the venous end, fluid volume overloads the lymph system and stays in the interstitial spaces leading the patient to have edema, weight gain, pulmonary congestion and HPN at the same time due to decrease GFR, nephron hyperthrophized leading to decrease ability of the kidney to concentrate urine
Planning Short Term: After 4-8 hours of nursing interventions, patient will demonstrate behaviors to monitor fluid status and reduce recurrence of fluid excess Long Term: After 3 days of nursing intervention the patient will manifest stabilize fluid volume AEB balance I & O, normal VS, stable weight, and free from signs of edema.
Interventions 1. Establish rapport 2. Monitor and record vital signs 3. Assess possible risk factors 4. Monitor and record vital signs. 5. Assess patients appetite 6. Note amount/rate of fluid intake from all sources 7. Compare current weight gain with admission or previous stated weight
Rationale 1. To assess precipitating and causative factors. 2. To obtain baseline data 3. To obtain baseline data 4. To note for presence of nausea and vomiting 5. To prevent fluid overload and monitor intake and output 6. To monitor fluid retention and evaluate degree of excess 7. For presence of crackles or congestion
Evaluation Short Term: The patient shall have demonstrated behaviors to monitor fluid status and reduce recurrence of fluid excess Long Term: The patient shall have manifested stabilized fluid volume AEB balance I & O, normal VS, stable weight, and free from signs of edema.
and impaired excretion of fluid thus leading to oliguria/anuria.
8. To evaluate degree of excess 8. Auscultate 8. To evaluate breath sounds degree of excess 9. To determine fluid retention 9. Record 9. To determine occurrence of fluid retention 10. May indicate dyspnea increase in fluid 10. May indicate retention 10. Note presence increase in fluid of edema. retention 11. May indicate cerebral edema. 11. Measure 11. May indicate abdominal girth for cerebral edema. 12. To evaluate changes. degree of fluid 12. To evaluate excess. 12. Evaluate degree of fluid mentation for excess. 13. To prevent confusion and pressure ulcers. personality 13. To prevent changes. pressure ulcers. 14. To monitor fluid andTo electrolyte 13. Observe skin 14. monitor fluid imbalances mucous membrane. and electrolyte imbalances 14. Change position 15. To lessen fluid retention andfluid of client timely. 15. To lessen overload. retention and 15. Review lab data overload. 16. To monitor like BUN, kidney function Creatinine, Serum 16. To monitor electrolyte. kidney function and fluid retention. 16. Restrict sodium 17. Weight gain and fluid intake if indicates fluid retention or edema. indicated 18. Weight gain may indicate fluid 17. Record I&O retention and accurately and edema. calculate fluid
volume balance 18. Weigh client 19. Encourage quiet, restful atmosphere. 20. Promote overall health measure.
19. To conserve energy and lower tissue oxygen demand. 20. To promote
Você também pode gostar
- IVF Basic Principles SourceDocumento3 páginasIVF Basic Principles SourcereadtometooAinda não há avaliações
- Scalp PsoriasisDocumento11 páginasScalp Psoriasisvasu7900Ainda não há avaliações
- Infection of The Skin, Soft Tissue, Etc.Documento84 páginasInfection of The Skin, Soft Tissue, Etc.fmds100% (1)
- Pankaj Das - Aarogyam 1.2 + FBSDocumento10 páginasPankaj Das - Aarogyam 1.2 + FBSplasmadragAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatAinda não há avaliações
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPDocumento3 páginasBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPsimonjosanAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocumento3 páginasNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Hypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFDocumento6 páginasHypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFBella TogasAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Decreased Cardiac Output 1Documento2 páginasNCP Decreased Cardiac Output 1Arnel MacabalitaoAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocumento15 páginasAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRanusha AnushaAinda não há avaliações
- IntroductionDocumento10 páginasIntroductionNareman Alaa50% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus: Anatomy, Physiology, Types, Diagnosis and ManagementDocumento66 páginasDiabetes Mellitus: Anatomy, Physiology, Types, Diagnosis and ManagementyuliAinda não há avaliações
- Haad ReviewerDocumento11 páginasHaad ReviewerGhielyn Roque Baligod0% (1)
- NCPDocumento15 páginasNCPCamille PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisAinda não há avaliações
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Documento4 páginasNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Failure NCPDocumento3 páginasRenal Failure NCPjsksAinda não há avaliações
- Managing Electrolyte Imbalances: A Case of Self-Induced HyperkalemiaDocumento3 páginasManaging Electrolyte Imbalances: A Case of Self-Induced HyperkalemiaPaul JacksonAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocumento8 páginasNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiAinda não há avaliações
- Imbalanced NutritionDocumento2 páginasImbalanced NutritionRizza 이 동해 Ocampo100% (1)
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocumento4 páginasHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento3 páginasNCP Fluid Volume DeficitNecheal BaayAinda não há avaliações
- Administering Blood TransfusionDocumento10 páginasAdministering Blood Transfusionkatz_hotchickAinda não há avaliações
- NCP LeprosyDocumento3 páginasNCP LeprosyJane MinAinda não há avaliações
- Drug-Study NCPDocumento5 páginasDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.Ainda não há avaliações
- Which It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToDocumento8 páginasWhich It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToAriane-Gay Cristobal DuranAinda não há avaliações
- NCP FVDDocumento1 páginaNCP FVDsisjing88510Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan for Pre-operative AnxietyDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan for Pre-operative AnxietyVoid LessAinda não há avaliações
- HypopituitarismDocumento2 páginasHypopituitarismAnne de VeraAinda não há avaliações
- Case CHFDocumento10 páginasCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- Case Study Ugib Lower MBDocumento65 páginasCase Study Ugib Lower MBQuolette Constante100% (1)
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareDocumento6 páginasIncomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareTherese MargaretAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsDocumento1 páginaAcute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsAi RouAinda não há avaliações
- NCP2 - DengueDocumento4 páginasNCP2 - DengueSummer SuarezAinda não há avaliações
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDocumento5 páginasANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDavid CalaloAinda não há avaliações
- Liver Cirrhosis Care PlanDocumento3 páginasLiver Cirrhosis Care PlanWendy EscalanteAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumonia Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasPneumonia Drug Studyatienza02Ainda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesAinda não há avaliações
- NCP PainDocumento2 páginasNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Risk For ConstipationDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Risk For Constipationkenneth_bambaAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocumento6 páginasChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyAinda não há avaliações
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocumento8 páginasNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocumento18 páginasNursing Care Plan Renal FailureKundan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Client Assessment BasicsDocumento56 páginasClient Assessment Basicsdanny_ng080% (1)
- Case Study RespiDocumento3 páginasCase Study RespiMark Jheran AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalAinda não há avaliações
- CASE STUDY PheumoniaDocumento5 páginasCASE STUDY PheumoniaEdelweiss Marie CayetanoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerJefferson Baluyot PalmaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP CvaDocumento4 páginasNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeAinda não há avaliações
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDocumento5 páginasHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseAna Katrina OcanaAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition diagnosis: Imbalanced nutrition less than requirementsDocumento3 páginasNutrition diagnosis: Imbalanced nutrition less than requirementsIlisa ParilAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPDocumento2 páginasRisk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPPaula AbadAinda não há avaliações
- Health-Perception-Health-Management PatternDocumento3 páginasHealth-Perception-Health-Management PatternBela MillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocumento5 páginasAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocumento3 páginasImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliAinda não há avaliações
- Code Green Introduction Reviewer - RedDocumento4 páginasCode Green Introduction Reviewer - RedJamieAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento1 páginaAcute Renal FailureSonia Letran Singson100% (1)
- Urgent Care Clinic Improves Patient Flow by 30 MinutesDocumento2 páginasUrgent Care Clinic Improves Patient Flow by 30 MinuteselonaAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Donation ProgramDocumento1 páginaBlood Donation ProgramMhOt AmAdAinda não há avaliações
- Thoracentesis Reflective EssayDocumento2 páginasThoracentesis Reflective EssayAnjae GariandoAinda não há avaliações
- SLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Documento20 páginasSLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Mayzelle RizAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid VolumeDocumento2 páginasFluid Volumecoldfire28Ainda não há avaliações
- Deficient Knowledge Related To Urinary Tract Infection: "Di Ako Aware About Sa UTI"as Verbalized by The ClientDocumento2 páginasDeficient Knowledge Related To Urinary Tract Infection: "Di Ako Aware About Sa UTI"as Verbalized by The ClientSeanmarie CabralesAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.Documento2 páginasRisk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.eleinsamAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Acute PancreatitisDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Acute PancreatitisJamaica SaranquinAinda não há avaliações
- Post-op-Case-Conference-DM FootDocumento44 páginasPost-op-Case-Conference-DM FootShereen DS Lucman100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocumento3 páginasFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoAinda não há avaliações
- Gynzone TrainingDocumento62 páginasGynzone TrainingMariana PinheiroAinda não há avaliações
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDocumento5 páginasSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoAinda não há avaliações
- TETRASODIUM EDTA - National Library of Medicine HSDB DatabaseDocumento21 páginasTETRASODIUM EDTA - National Library of Medicine HSDB DatabaseElena TrofinAinda não há avaliações
- Basic and Clinical Pharmacology 12th Edition-Bertram Katzung Susan Masters Anthony Trevor-290-296 PDFDocumento7 páginasBasic and Clinical Pharmacology 12th Edition-Bertram Katzung Susan Masters Anthony Trevor-290-296 PDFalinamatei1000000Ainda não há avaliações
- Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences Score Sheet For CASE Write-UpDocumento30 páginasFaculty of Medicine and Health Sciences Score Sheet For CASE Write-UpJared Khoo Er HauAinda não há avaliações
- TSEBTDocumento17 páginasTSEBTcornejo1Ainda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento16 páginasUntitledAstriUtamaAinda não há avaliações
- Case Sheet for Maternity ServicesDocumento22 páginasCase Sheet for Maternity ServicesGulfeshan ArshiAinda não há avaliações
- IV Drug ReactionsDocumento19 páginasIV Drug Reactionsphp_czarina04421Ainda não há avaliações
- Rds NRP 2021Documento33 páginasRds NRP 2021Aiwi Goddard MurilloAinda não há avaliações
- Entamoeba HistolyticaDocumento38 páginasEntamoeba HistolyticaAbdul Ghafar OrakzaiiiAinda não há avaliações
- Herpes Simplex I and IIDocumento50 páginasHerpes Simplex I and IItummalapalli venkateswara raoAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal KurapDocumento3 páginasJurnal Kurapbunga farnadaAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Insulin For Diabetes TreatmentDocumento2 páginasTypes of Insulin For Diabetes TreatmentKrystale Mae ValdezAinda não há avaliações
- Volume 11 Jan Dec 2005Documento69 páginasVolume 11 Jan Dec 2005Elizabeth GomezAinda não há avaliações
- Stem Cell Therapy and EthicsDocumento2 páginasStem Cell Therapy and EthicsRaniya Khan [Student]Ainda não há avaliações
- Fucidin®: Product MonographDocumento21 páginasFucidin®: Product MonographLeonita SabrinaAinda não há avaliações
- Blood ReportDocumento15 páginasBlood ReportSaadAinda não há avaliações
- Cells in The PBSDocumento31 páginasCells in The PBSDelzell Dame CasaneAinda não há avaliações
- Andrew Eastman Resume 3Documento2 páginasAndrew Eastman Resume 3api-281509868Ainda não há avaliações
- Commercial Chicken Vaccination Part 3 Injectable AdministrationDocumento6 páginasCommercial Chicken Vaccination Part 3 Injectable AdministrationAnjum IslamAinda não há avaliações
- To Extract Ornot To Extract PDFDocumento2 páginasTo Extract Ornot To Extract PDFmehdi chahrourAinda não há avaliações
- Beyond Bowels: Understanding Co-existing Symptoms in IBSDocumento8 páginasBeyond Bowels: Understanding Co-existing Symptoms in IBSparthibanemails5779Ainda não há avaliações