Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Anatomy Reviewer
Enviado por
pluiedecielDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Anatomy Reviewer
Enviado por
pluiedecielDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ANATOMY
Spleen mesoderm-derived from dorsal mesentery Supplied by splenic artery, from the foregut Obturator nerve is the only nerve that exits the pelvis through obturator foramen. Psoas innervated by lumbar plexus Thigh extension gluteus maximus, supplied by inferior gluteal nerve. Adjustable gastric banding encircle upper stomach, must pass through lesser omentum Lesser omentum double layer of peritoneum from liver to lesser curvature to D1 Hepatogastric ligament Hepatoduodenal ligament Falciform ligament attaches liver to anterior body wall Greater omentum reflects on itself, with gastrocolic ligament from curvature to transverse colon Gastrocolic ligament anterior wall of the lesser sac, provides access to anterior pancreas and posterior wall of the stomach Vitelline duct persistnce at umbilicus, between intestine and body; discharge of meconium Horseshoe kidney inferior mesenteric artery traps Optic tract projections LGN Superior colliculus reflex gaze Pretectal ara light reflex Suprachiasmatic nucleus circadian rhythms From LGN to visual cortex geniculocalcarine tract or optic radiation Lower fibers from lower retina = upper contralateral visual field = circuitious route = temporal lobe (Meyers loop) lingual gyrus Upper fibers parietal lobe cuneus gyrus Brocas area: inferior frontal gyrus of dominant hemisphere (Brodmann areas 44 and 45) Wernickes: Brodmann 22, sensory receptive aphasia, superior temporal gyrus
Frontal eye field: middle frontal gyrus. Brodmann 6 and 8; DAMAGE: eyes deviate to ipsilateral side Lung apices extend above clavicle and first rib. Ansa cervicalis: sternothyroid, sternothyroid, omohyoid; INJURED superior to cricoid cartilage Rectus abdominis: most important muscle in Valsalva manuever Heart, posterior surface: LA, adjacent to esophagus; only its auricle is visible anteriorly Heart, anterior surface; RV, seen on lateral Xray TEE: anterior: see LA, posterior: see descending aorta Arm abduction: supraspinatus (main), 10-15 degrees, then deltoid if >30 Empty can test is sensitive for supraspinatus pathology; tendon is most injured due to impingement between acromion and head of the humerus Wernickes encephalopathy: mamillary body Paralysis of stapedius muscle, innervated by CN7 wider oscillation of stapes hyperacusis Tensor tympani: CN V3 Spinal cord ends at conus medullaris: L2 Nerves exit cauda equina Conus medullaris syndrom: lesions at L2, flaccid paralysis of bladder and rectum, impotence, saddle anesthesia CAUSED BY disk herniation, tumors, spinal fractures Cauda equina: from massive rupture of IV disk SYMPTOMS: low back pain, saddle anesthesia, loss of anocutaneous reflex (S4) Cremasteric fascia: internal oblique Internal spermatic fascia: transversalis fascia Testicular hydrocoele: serous fluid accumulates in tunica vaginalis Tunical albuginea: fibrous tissue CABG: LAD only, graft from L internal mammary artery (aka left internal thoracic) Multiple coronary arteries: great saphenous vein
Saphenous vein: A to medial malleolus Joins femoral vein at proximal though 3-4 cm IL to pubic tubercle: ACCESSED HERE Popliteal artery + vein + tibial nerve Small saphenous vein: lateral foot, course posteriorly to drain into popliteal vein
Thumb ADDuction: ulnar n., deep branch Thumb opposition: median n. Long thoracic n. = serratus anterior = winging of the scapula; unable to abduct arm from horizontal; injured during LN dissection Duodenal ulcers: anterior: perforation Posterior: hemorrhage (gastroduodenal artery) Recurrent laryngeal nerve: all muscles of larynx except cricothyroid Loops below aortic arch on L, subclavian a. on R Superior: inferior thyroid artery Motor innervation: Hypoglossus (CN 12): all muscles of tongue EXCEPT PALATOGLOSSUS, CN(10) General innervation: Ant 2/3: CN V3 (lingual nerve), 9, 10 Gustatory: chorda tmypani of CN7, 9, 10
Caudate nucleus: Huntington Putamen: Wilsons Posterior limb, internal capsule: carries corticospinal motor, somatic sensory, auditory and visual fibers Genu: corticobulbar Anterior: some thalamocortical
Retroperitoneal hematoma, A to psoas muscle compresses femoral n. Quads affected (vastus), difficulty of stairs, knee buckling loss of patellar reflex Superior gluteal n.: gluteus minimus, tensior fascia lata thigh abduction PROBLEM with waddling gait, Trendelenburg Inferior gluteal n. exits through greater sciatic foramen: gluteus maximus thigh extension PROBLEM: arising from seat, climbing stairs Syringomyelia: C8-T1: CHRONIC loss of upper extremity PAIN AND TEMP sensation, UE hyporeflexia, LE hyperreflexia, kyphoscoliosis ALS: upper, lower motor neurons NPH: gait apraxia, urinary incontinence
Binocular vision: central 120 degrees, monocular, 40 deg bilateral Common peroneal nerve injury: Footdrop At neck of fibula Superficial branch: lateral, sensory foot dorsum Deep: anterior, sensory between toe 1 and 2 Sciatic common peroneal, tibial n.
Direct inguinal hernia: Hesselbachs (weak spot on transversalis fascia), inferior epigastric vessels LATERAL, LESS incarceration, no scrotum descent, PULP, only pass through SUPERFICIAL inguinal ring, covered only by external spermatic fascia Indirect inguinal hernia: process vaginalis, covered with 3 layers Posterior descending artery: 90% from RCA, 10% from LCX; supplies inferior wall of LV (diaphragmatic surface) CSF flow: Lateral ventricles interventricular rd foramen of Monroe 3 ventricle cerebral th aqueduct of Sylvius 4 ventricle lateral Luschka or medial Magendie subarachnoid space Pseudotumor cerebri: overweight young females, decreased CSF outflow at arachnoid villi Ventromedial hypothalamus: for satiety Lateral: for hunger Anterior: for cooling Posterior: for heat Ulnar nerve injury: P to medial epicondyle Between the hook of the hamate and pisiform bone within Guyons canal Median nerve: INJURED supracondylar humerus, brachial artery Axillary nerve: surgical neck of humerus, with anterior circumflex humeral artery Radial nerve: midshaft of humerus, crutch misfit, along with deep brachial artery Upper trunk of brachial plexus: musculocutaneous n., head and shoulder violently stretched apart Lower trunk: sudden upward jerking of shoulder Mesenteric artery syndrome: SMA Transverse portion of duodenum is entrapped between SMA and aorta (45deg) partial SBO Causes: correction of scoliosis, diminished fat BBB: tight junctions (aka zona occludens) Desmosomes: stratum spinosum, cell anchors Hemidesmosomes: to BM Repeated kneeling Prepatellar bursa (+) fluctuant edema over lower pole of patella Anserine bursitis: medial knee
Superficial inguinal LN: drains all cutaneous LN from umbilicus to feet, including external genitalia and anal canal UP TO DENTATE, EXCLUDING posterior calf (popliteal) Light reflex pathway: CN 2 pretectal nucleus (superior colliculus) Edinger-Westphal efferent CN 3 ciliary ganglion Kidney transplant: donor in R iliac fossa, anastomose donor renal artery with ext. iliac a. Upper donor ureter is preserved, supplied by branches of the renal artery Broad ligament of the uterus Ovarian ligament Round ligament links horns of uterus to ext.genitalia, contains artery of Sampson Suspensory ligament NAVL of ovary, ligated in ovarian mass surgery Transverse cervical ligament (aka cardinal) from cervix, vagina lateral fornix, contains UTERINE ARTERY, ligated in radical hysterectomy Dopaminergic systems Mesolimbic-mesocortical: schizophrenia Nigrostriatal: Parkinsonism Tuberoinfundibular: hyperprolactinemia MIDDLE CRANIAL FOSSA Optic canal: CN 2, ophthalmic artery, central retinal vein Superior orbital fissure: 3, 4, v1, 6, ophthalmic vein Foramen rotundum: V2 Foramen ovale: V3, lesser petrosal n, accessory meningeal artery Foramen spinosum: MMA and vein **Foramen lacerum: occluded by cartilage POSTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA Internal acoustic meatus: 7, 8 Jugular foramen (Vernet): 9, 10, 11, jugular vein, inferior petrosal and sigmoid sinuses, posterior meningeal artery Hypoglossal canal: 12 Foramen magnun: spinal roots of 11, brainstem, vertebral arteries Acoustic reflex: stapedius and tensor tympani contract to lessen responsiveness of ossicles to sound. Stapes to oval window IN, round window goes OUT, allows cochlear fluid to move.
Ciliary muscle: accomodation Contracts, zonules relax, lens spherical, focus on near object Thalamic nuclei VPL: spinothalamic tract (pain and temp) and medical lemniscus (position and proprioceptuon) Brodmann 3, 1, 2 VPL: trigeminal, gustatory MGN: auditory, Brodmann 41, 42 temporal lobe Olfactory tract is the only sensory pathway where input is not processed by the thalamus. Sciatica (L5, S1) shooting pain down posterior thigh and leg, decreased ankle reflex Artery of Percheron: rare normal variant of PCA, bilateral thalamic or dorsal midbrain strokes
Obturator artery supplies the femoral head in children
Trochanteric anastomosis Superior, inferior gluteal a. Medial (posterior), lateral femoral circumflex a. Splenic v. + superior mesenteric v. = portal v. Esophageal varices: L gastric v. esophageal v. Hemorrhoids: Superior rectal v. middle, inferior rectal v. Caput medusae: Paraumbilical v. superior , inferior epigastric v. Neurofibromas from Scwann cells, neural crest Pink nodules with a rubbery texture that show BUTTONHOLING with gentle pressure Endoderm: thyroid, bulk of liver, pancreas, lungs, as these structures form from outpouchings of the primitive gut tube Vertebrae is from paraxial mesoderm Notochord nucleus pulposus Varicocoele, L, from pampiniform plexus R testicular vein IVC L testicular vein L renal vein (between aorta and SMA) IVC R kidney R renal v. R suprarenal gland IVC L suprarenal gland L renal v. IVC Humerus abduction: supraspinatus Adduction: lattisimus dorsi (thoracodorsal n.) Medial rotation: subscapularis Flexion: deltoid
Anterior choroidal a. last branch of ICA, supplies posterior limb and genu of internal capsule, optic tract, LGN, choroid plexus, hippocampus, amygdala Pterion: FPTS, MMA, epidural hematoma ECA Maxillary a. MMA Kiesselbachs plexus: ophthalmic, facial, maxillary artery branches (sphenopalatine) Thalamic syndrome: complete contralateral sensory loss, with some proprioceptive defects Lacunar infarcts lipohyalinosis and microarethomas Oligodendrocyte apoptosis MS, pink patches in white matter tracts Glenohumeral joint anterior dislocation Flattening of the deltoid prominence, protrusion of the acromion Axillary n. injured
Anterior urethra: bulbous and penile segment Posterior urethra: prostatic, membranous Membranous segment weakest point of posterior urethra Bulbous segment straddle injury Posterior drawer test apply pressure on anterior tibia Posterior cruciate ligament Posterior, runs Anteriorly, inserts into INternal condyle (PAIN), prevents ANTERIOR DISPLACEMENT of FEMUR RELATIVE TO TIBIA when knee is FLEXED Medial articular surface of the knee bears more weight.
Femoral hernias R, women, prone to incarceration strangulation Midbrain:2, 3, 4 Pons: 5, 6, 7, 8 Medulla: 9,10, 11, 12 Trochlear nerve is the only CN to decussate before innervating its target. Coronary sinus: endpoint of venous drainage in heart, visible with RA dilation (pulmonary hypertension)
Intestinal gas at biliary tree gallstone ileus, cholecysenteric fistula Stone stuck at ILEOCECAL VALVE Area postrema absent BBB, dorsal medulla th near 4 ventricle Cricothyrotomy superficial cervical fascia (fat, platysma), pretracheal fascia, cricothyroid membrance Intraventricular hemorrhage of the newborn: germinal matrix at the subventricular zone Subdural: cortical bridging veins, shaken baby Epidural: MMA SAH: Berry aneurysms Iliopsoas most important of hip flexors Vagus n. some cutaneous sensation to posterior external auditory canal vagal stimulation; rest is V3 (auriculotemporal branch) Inner surface of the tympanic membrane: CN9 Aortic rupture: at arch or isthmus in trauma Aneurysm secondary to HPN, syphilis: ascending aorta, where R brachiocephalic branches off R brachiocephalic v. = R subclavian + R IJV R subclavian drains R EJV R brachiocephalic (aka inominate vein) drains R lymphatic duct
Double vision when walking down the stairs or reading newspaper = vertical diplopia, CN 4 MLF lesion = internuclear ophthalmoplegia Impaired horizonal eye movement Weak adduction of affected eye Simultaneous abduction nystagmus of other eye Lunate dislocate, scaphoid fracture (avascular necrosis) Dupuytrens contracture progessive fibroproliferative disease of the palmar fascia Patellar ligament is the continuation of the quadriceps femoris tendon Swallow a bite, goes down the right R main bronchus has a larger diameter, is shorter, more vertical Ureter: under gonadal A/V, uterine artery (uterosacral ligament) Over common/external iliac Lateral to internal iliac, medial to gonadal in the true pelvis T1 to L2: with lateral horns intermediolateral nucleus, sympathetic preganglionic neurons
Supermedial: superior gluteal n. Inferomedial: sciatic n. Superolateral: RIGHT SPOT for injection Inferolateral: tendons
CN3 lesion: between posterior cerebral and superior cerebellar arteries GSE (ischemia), GVE fibers (compression) Kerley B lines short horizontal lines perpendicular to pleural surface, representing edema of interlobular septa Pacemaker leads R atrium, ventricle pass through L SCV L ventricle coronary sinus, atrioventricular groove posteriorly Muscles that close the jaw: masseter, medial pterygoid, temporalis muscle Open the jaw: lateral pterygoid Parasympathetic mixed: 10, 9, 7, 3 Motor mixed: 10, 9, 7, 5 Pure sensory: 1, 2, 8
Distal LC of stomach: R gastric a. Proximal LC: L gastric a. Distal GC: R gastroepiploic a. D1: Not retroperitoneal D2: head of pancreas, ampulla of Vater D3: uncinate process of pancreas, SMA, SMV D4: upwards, Ligament of Treitz jejunum Piriform recess: internal laryngeal nerve, afferent limb of cough reflex Posterior inferior cerebellar artery: lateral medullary (Wallenberg syndrome) Contralateral loss of pain, temperature Ipsilateral CN 5, 8, 9, 10, 11 deficits Horners syndrome
Median nerve: between FDS and FDP, ape-hand Ulnar nerve: between FCU and FDP, claw hand Ureters and bladder and retroperitoneal. Filter for pulmo embolism at IVC. Radial head subluxation Nursemaids elbow Annular ligament torn
EMBRYOLOGY
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Universal Genetic CodeDocumento1 páginaUniversal Genetic CodepluiedecielAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Harrisons Reviewer 2Documento59 páginasHarrisons Reviewer 2pluiedecielAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Ortho 251 NotesDocumento13 páginasOrtho 251 NotesJoan Marie S. FlorAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Antenatal CareDocumento26 páginasAntenatal CarepluiedecielAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Stretching and FlexibilityDocumento47 páginasStretching and Flexibilitymartin.wilfred7257Ainda não há avaliações
- 6 Factors of HypertrophyDocumento54 páginas6 Factors of HypertrophyEdgar MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Mobility Training For The Young AthleteDocumento8 páginasMobility Training For The Young AthletePedro GouveiaAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Catalogo Ancla GiiDocumento2 páginasCatalogo Ancla GiiLUCIA SOLISAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 21Documento37 páginasChapter 21Ivan Olo SarumpaetAinda não há avaliações
- Kne20 25302 v1 Biosure Opt Tg-FinalDocumento16 páginasKne20 25302 v1 Biosure Opt Tg-FinalJuan Martinez Del AngelAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Nexgen Legacy Lps Flex Knee BrochureDocumento8 páginasNexgen Legacy Lps Flex Knee BrochureKamelBelkhirAinda não há avaliações
- Hcai Pick ListDocumento18 páginasHcai Pick ListKelly DanielssonAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Quads Knee Strengthening ExercisesDocumento7 páginasQuads Knee Strengthening ExercisesAtu KaushalAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
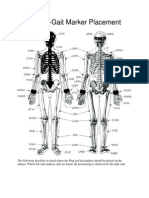
- Plug-In Gait Reference GuideDocumento107 páginasPlug-In Gait Reference GuideQv D3Ainda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- OsteologyDocumento96 páginasOsteologyBenita Putri MD100% (2)
- Evaluation of The Hip: History, Physical Examination, and ImagingDocumento11 páginasEvaluation of The Hip: History, Physical Examination, and ImagingmilelytaAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Current Concepts: Biomechanics of Knee LigamentsDocumento11 páginasCurrent Concepts: Biomechanics of Knee LigamentsBarbaraAndradeQuirozAinda não há avaliações
- Update A1 OsceDocumento120 páginasUpdate A1 OsceIndra SetyaAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Lateral Tibia Tray Overhang After TKRDocumento4 páginasLateral Tibia Tray Overhang After TKRAnandAinda não há avaliações
- Warmup VolleyballDocumento2 páginasWarmup Volleyballapi-345720435Ainda não há avaliações
- Physical Education and Health 11Documento50 páginasPhysical Education and Health 11Janel Gel RamosAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Orthopedics PDFDocumento14 páginasOrthopedics PDFSam christenAinda não há avaliações
- ACL InjuryDocumento5 páginasACL InjuryGlen LazarusAinda não há avaliações
- How To Build Strong Legs and Healthy KneesDocumento3 páginasHow To Build Strong Legs and Healthy KneesJeff Armstrong100% (1)
- Steroid Injections in Adult Patients With Joint and Soft Tissue Conditions JCG0055v3 PDFDocumento18 páginasSteroid Injections in Adult Patients With Joint and Soft Tissue Conditions JCG0055v3 PDFSarath KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Abu Hureyra Abu HureyraDocumento4 páginasAbu Hureyra Abu Hureyrabozana0405100% (1)
- 5-Flexibility TestsDocumento62 páginas5-Flexibility TestsMr. MixerAinda não há avaliações
- Solomomow 2006 Ligamento y Control MotorDocumento19 páginasSolomomow 2006 Ligamento y Control MotorBeto RebolledoAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Chapter 6 Test ControlDocumento7 páginasChapter 6 Test ControlSheikhAinda não há avaliações
- Signs in MedicineDocumento25 páginasSigns in MedicinepavanAinda não há avaliações
- Latihan Soal Xii 2024 - Siswa-1Documento17 páginasLatihan Soal Xii 2024 - Siswa-1aqilahpramesti65Ainda não há avaliações
- Cerebral Palsy Special Tests and Corrective ProceduresDocumento11 páginasCerebral Palsy Special Tests and Corrective ProceduresOj AlimbuyuguenAinda não há avaliações
- TC3HP - Técnica QuirúrgicaDocumento84 páginasTC3HP - Técnica QuirúrgicaRafael RecioAinda não há avaliações
- Plug in Gait Marker PlacementDocumento4 páginasPlug in Gait Marker PlacementPaolaFernandaNovoaHerreraAinda não há avaliações