Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Basic Principles Bio Mech
Enviado por
obelix_papa34Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Basic Principles Bio Mech
Enviado por
obelix_papa34Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Basic Principles of Biomechanics Outline Definition Planes of motion Axes of motion Newtons Laws of motion Joint mechanics Example:
Application to standing posture eferences !ichaud: "oot orthoses and other forms of conser#ati#e foot care Pages $%& Pages $'%($ Definition of Biomechanics )the application of mechanical laws to li#ing structures* specificall+ to the locomotor s+stem of the human ,od+ Planes of motion -human ,od+. /agittal % flex0extension "rontal -coronal. % a,0adduction 1rans#erse % rotation Planes of motion -foot. /agittal % flexion 2 extension
"rontal % in#ersion 2 e#ersion
1rans#erse % a,duction 2 adduction
"igure $34
Axes of motion
5maginar+ line 0 rod passing through the centre of an o,6ect* around which rotation occurs Perpendicular to plane of motion otation occurs perpendicular to the axis Axes of motion -foot.
Joints of the lower lim,
Joints of the lower lim, uniaxial hinge* pi#ot 5nterphalangeal 6oint -hinge. ,iaxial cond+loid* ellipsoid* saddle !PJs "lex0ext*add0a,duction triaxial 0 pol+axial hip 6oint -,all and soc7et. plane 0 gliding intercuneiform 6oints Definitions re forces "orce % a push -or pull. that alters* or tends to alter* the state of motion of a ,od+ -cause a change in #elocit+ of an o,6ect. 5f the ,od+ is at rest* a force exerted ,+ another ,od+ will set it in motion -or at least tend to do so. 5f a ,od+ is mo#ing in a straight line* a force exerted ,+ another ,od+ will change* or tend to change the #elocit+ at which it is mo#ing A #ector 8uantit+ % direction and magnitude 9nit of measurement % Newton -N. Newtons Laws of motion Newtons "irst Law -law of inertia0principle of conser#ation of momentum. )E#er+,od+ at rest* or mo#ing with constant #elocit+ in a straight line* will continue in that state unless compelled to change ,+ an external force exerted upon it Newtons /econd Law -law of acceleration. )1he acceleration of a ,od+ is proportional to the force causing it and ta7es place in the direction in which the force acts " : ma O a:"0m -" : force exerted* m : the mass* a : acceleration. Newtons 1hird Law )"or e#er+ action* there is an e8ual and opposite reaction
)"or e#er+ force that is exerted ,+ one ,od+ on another* there is an e8ual and opposite force exerted ,+ the second ,od+ on the first NB* action is the force exerted on one ,od+ and the reaction is the contrar+ force exerted on the other ,od+ ;ommon sources of force acting on the human ,od+ 5nternal muscular External % <ra#itational 0weight -" : ma=33:mass -7g.> gra#it+-$? m0s(. "rictional 5mpact0<round reaction Joint mechanics Joint axis location depends on shapes of articular surfaces !otion around an axis is dependent on the force applied -com,ination of muscular* gra#itational* inertial* frictional* and ground%reacti#e forces. force will most effecti#el+ produce motion when: line of application is perpendicular to 6oint axis large perpendicular distance ,etween line of action and axis -le#er arm. door hinge analog+ Joint mechanics
moment : force @ le#er arm
Assuming "$:"(:"A:"' !oment "$ B !oment "( B !oment "A B !oment "' otational 2 non%rotational components of force Chen a force is applied perpendicular to an axis* the force ma+ ,e resol#ed into rotational and non%rotational components otational force produces motion Non%rotational component will either compress or distract 6oint
Joint compression % sta,ilit+ ,ut excessi#e ma+ cause fracture Chen a force applied is NO1 perpendicular to an axis* the force ma+ ,e resol#ed into perpendicular and parallel components -to 6oint axis. Perpendicular component produces 6oint rotation and compression0distraction Parallel component produces 6oint shear and is una,le to produce motion without 6oint su,luxation Joint shear force
Joint mechanics summar+: rotational and nonrotational components of force !ost forces in ,od+ are not perpendicular to 6oint axes otational component % 6oint rotation Nonnonrotational components Perpendicular component % 6oint compression%distraction force Parallel component % shear force /ummar+ definition planes and axes of motion t+pes of 6oints "orce Newtons Laws Joint mechanics rotational and non%rotational components
Você também pode gostar
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- AUDI OptimizationDocumento37 páginasAUDI OptimizationKiran DamaAinda não há avaliações
- Motion in Two Dimensions: Important TermsDocumento10 páginasMotion in Two Dimensions: Important TermsanonymousAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid Flow Rate For FlowmetersDocumento4 páginasLiquid Flow Rate For Flowmetersابوالحروف العربي ابوالحروفAinda não há avaliações
- 9203 2 INS InternationalPhysics G 16nov20!07!00 GMTDocumento4 páginas9203 2 INS InternationalPhysics G 16nov20!07!00 GMT王涛Ainda não há avaliações
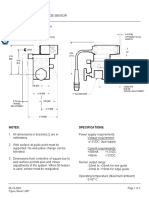
- Installation of the SE-26A Line Guide SensorDocumento2 páginasInstallation of the SE-26A Line Guide SensorDeniMestiWidiantoAinda não há avaliações
- Dhio Corporate Brochure 2023 FordistributionDocumento12 páginasDhio Corporate Brochure 2023 FordistributionsrashmiiiscAinda não há avaliações
- Asmeptc19 3 04Documento142 páginasAsmeptc19 3 04Angel LunaAinda não há avaliações
- Final Paper 01 - Structured Essay English MediumDocumento7 páginasFinal Paper 01 - Structured Essay English Mediumsigiriya.photographyAinda não há avaliações
- Some Applications On The Fields of Laser, PCF and PCF-Sensor by Comsol SoftwareDocumento32 páginasSome Applications On The Fields of Laser, PCF and PCF-Sensor by Comsol SoftwareNadia F Mohammad Al-RoshdeeAinda não há avaliações
- A Laboratory Report: Protein ExtractionDocumento9 páginasA Laboratory Report: Protein ExtractionNadine RebolledoAinda não há avaliações
- C StructDesign Bendapudi Feb10 (1) Part 1Documento0 páginaC StructDesign Bendapudi Feb10 (1) Part 1Rubén MenaAinda não há avaliações
- Dmu BooksDocumento25 páginasDmu BooksEsuendalew DebebeAinda não há avaliações
- Seismic Story Shear Calculation StaadDocumento23 páginasSeismic Story Shear Calculation StaadRajendra KambleAinda não há avaliações
- Fulltext01 1Documento123 páginasFulltext01 1shimic32000Ainda não há avaliações
- Water and Its Forms: Name: - DateDocumento2 páginasWater and Its Forms: Name: - DateNutrionist Preet PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Zeolite Is Alive, Do Not Use For DetoxDocumento9 páginasZeolite Is Alive, Do Not Use For DetoxSY LodhiAinda não há avaliações
- New Aqua Calibration CertificateDocumento20 páginasNew Aqua Calibration Certificateahmed mohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Stress Analysis Using Actual Coke DrumDocumento11 páginasStress Analysis Using Actual Coke Drumash1968Ainda não há avaliações
- Gomes, GabrielDocumento12 páginasGomes, GabrielVálter LúcioAinda não há avaliações
- En 10164-1993Documento8 páginasEn 10164-1993Marija IvanovskaAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Gas Tanker TrainingDocumento136 páginasAdvanced Gas Tanker TrainingPrassanna Venkatesh100% (2)
- Laws of Motion: Comparing Aristotle and Galileo's ViewsDocumento13 páginasLaws of Motion: Comparing Aristotle and Galileo's Viewsjal bayani0% (1)
- Centrifugal Vs Reciprocating Compressor - Turbomachinery Magazine PDFDocumento2 páginasCentrifugal Vs Reciprocating Compressor - Turbomachinery Magazine PDFReyes SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture - Week 2 - Introduction To SteelDocumento49 páginasLecture - Week 2 - Introduction To SteelAhmed MaherAinda não há avaliações
- Catalog - o Ring Handbook - Ode5705 GB PDFDocumento164 páginasCatalog - o Ring Handbook - Ode5705 GB PDFJeffrie Nagara NasutionAinda não há avaliações
- Phase DiagramDocumento13 páginasPhase DiagramJayzl Lastrella CastanedaAinda não há avaliações
- 2.va1 Gedi 00HTF M M5 PHL 0001 - 1Documento23 páginas2.va1 Gedi 00HTF M M5 PHL 0001 - 1hoangduythanhqbAinda não há avaliações
- Air Crew Radiation Exposure - An OverviewDocumento8 páginasAir Crew Radiation Exposure - An OverviewStarxteelAinda não há avaliações
- ThreeBond 1530b Moisture Curing Elasomeric AdhesiveDocumento2 páginasThreeBond 1530b Moisture Curing Elasomeric AdhesiveAnderson MartinsAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Transformations QuizDocumento3 páginasEnergy Transformations QuizAngeli MercedAinda não há avaliações