Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Assignment04 (2:11:14)
Enviado por
Gabriel SmithDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Assignment04 (2:11:14)
Enviado por
Gabriel SmithDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ASSIGNMENT 4
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS: ENGR 2070 SPRING 2014 DUE: Monday 10 February
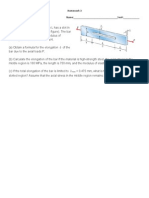
1. A wire is used to hang a lantern over a pool. Neglect the weight of the wire, and assume it is straight, but strainfree, before the lantern is hung. When the lantern is hung, it causes a 9 inch sag in the wire. Determine the normal strain in the wire with the lantern hanging as shown.
9 in.
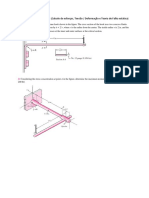
2. The rotation of the "rigid" beam AF is resisted by the stretching of rod AB until the beam comes into contact with the top column DE. Assume that the angle through which beam AF rotates is small enough that only vertical motion of the beam is significant. a) A load P is applied at end F that is just sufficient to close the 4 mm gap between the beam and the top of the column at D. What is the normal strain in rod AB for this value of load P? b) If load P is increased further until the strain in AB reaches 0.005 mm/mm, what is the corresponding strain in column DE? 4 mm
3. Two identical symmetrically placed rubber pads transmit load from a rectangular bar to a C-shaped bracket, as shown. a) Determine the average shear stress in the rubber pads on planes parallel to the top and bottom surfaces of the pads if P = 300 N and the dimensions of the rubber pads are: b = 30 mm, w = 80 mm, and h = 25 mm. b) If the relative displacement between the rectangular bar and the C-shaped bracket, = 2 mm due to the 300 N load, what is the average shear strain in the rubber pad?
Page 1 of 2
4. The data in the table was obtained in a tensile test of a flat-bar steel specimen having the dimensions shown. a) Using Excel, plot engineering stress versus engineering strain. b) Determine the stress and strain at the proportional limit, the modulus of elasticity of this material, the ultimate stress, and the fracture stress for the material. c) Use the 0.2% offset method to determine the yield stress of the material.
Tension Test Data for Flat Steel Bar P (kips) 1.2 2.4 3.6 4.8 5.7 5.95 6.25 6.50 6.65 6.85 6.90 L (in.) 0.0008 0.0016 0.0024 0.0032 0.0040 0.0050 0.0060 0.0075 0.0100 0.0125 0.0150 Thickness t = 0.30 in.
5. A tensile test is performed on an aluminum specimen that is 0.45 inch in diameter using a gage length of 2 inch, as shown in the figure. a) When the load is increased by an amount P = 2 kips, the distance between gage marks increases by an amount L = 0.002 inch. a) Calculate the modulus of elasticity for this specimen. b) If the proportional limit stress for this specimen is 60 ksi, what is the distance between gage marks at this value of stress? 0.45 in.
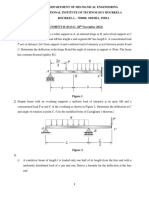
6. Two wires are connected to a rigid bar, as shown. The wire on the left is made of A36 steel, having a cross-sectional area of 0.15 in2. The 6061-T6 aluminum-alloy wire on the right has a cross-sectional area of 0.20 in2. a) If a weight W = 1900 lb is applied as shown, how much vertical deflection will it experience due to the stretch in the wires (calculate the deflection at the bar/weight center, 10 inch from the left end)? b) Where should the weight be located so that the bar would remain horizontal?
Page 2 of 2
Você também pode gostar
- Assignment For IPEDocumento4 páginasAssignment For IPEAbirHasanAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Materials 1 PDFDocumento2 páginasMechanics of Materials 1 PDFEj ApeloAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDocumento7 páginasMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Solid Problems On Stress and StrainDocumento4 páginasMechanics of Solid Problems On Stress and StrainYogeswaranAinda não há avaliações
- HW#3Documento9 páginasHW#3felipe GAinda não há avaliações
- Es 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)Documento3 páginasEs 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)akosikapitansinoAinda não há avaliações
- IINEEA1 Tutorial 1Documento6 páginasIINEEA1 Tutorial 1michaeljxmesAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of MaterialsDocumento11 páginasStrength of Materialsjerold_arandiaAinda não há avaliações
- Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringDocumento2 páginasFaculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringpranithAinda não há avaliações
- Simple StressDocumento2 páginasSimple StressMariz Ellaine BaltazarAinda não há avaliações
- Aat 1Documento4 páginasAat 1HARNITH EVILLAinda não há avaliações
- FINAL ExamDocumento3 páginasFINAL ExamNahzgie GabzLac FloresAinda não há avaliações
- B.Tech Assgn-1Documento6 páginasB.Tech Assgn-1K Pushpendu PrashantAinda não há avaliações
- Lista Exercicios PDFDocumento8 páginasLista Exercicios PDFLeonardo NecoAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento4 páginasAssignment 1TanmayAinda não há avaliações
- First Project ExamplesDocumento49 páginasFirst Project ExamplesMeleti Meleti MeletiouAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz1 QuestionDocumento2 páginasQuiz1 QuestionIsabella Womsiwor0% (1)
- 9A01302 Strength of Materials - IDocumento8 páginas9A01302 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- 2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsDocumento6 páginas2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsMartin MugoniAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Set2 Es 13 1st13-14Documento2 páginasProblem Set2 Es 13 1st13-14Gino JardinicoAinda não há avaliações
- S. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseDocumento3 páginasS. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseTejas AdakAinda não há avaliações
- Es 13 Thy Prob Set 1 I. Stresses: Max MaxDocumento5 páginasEs 13 Thy Prob Set 1 I. Stresses: Max MaxMichael Sean DeangAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials-I: Inst Ruct Ions To Candidat EsDocumento2 páginasStrength of Materials-I: Inst Ruct Ions To Candidat EsJaskaran SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDocumento11 páginasAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- Steel QuestionnaireDocumento3 páginasSteel QuestionnaireenggAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocumento20 páginasTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- Simple Stresses 1Documento21 páginasSimple Stresses 1Midas Troy VictorAinda não há avaliações
- 4 - Simple StrainDocumento24 páginas4 - Simple StrainLorene Ropeta.Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture On Strength of Materials August 2014Documento87 páginasLecture On Strength of Materials August 2014Cha Castillo100% (1)
- MOS Assignment II Autumn 2022-23Documento6 páginasMOS Assignment II Autumn 2022-23PankajAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Documento4 páginasStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Jesus RodeloAinda não há avaliações
- ExamsDocumento8 páginasExamsJoy CeeAinda não há avaliações
- CEMDEF40 - Practice Problems 1 PDFDocumento2 páginasCEMDEF40 - Practice Problems 1 PDFEldridge EastAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of MaterialDocumento3 páginasMechanics of MaterialChhaya Sharma100% (1)
- Handouts PDFDocumento3 páginasHandouts PDFMayoune GalvezAinda não há avaliações
- 7 - MOS-I Assignment QuestionsDocumento5 páginas7 - MOS-I Assignment QuestionsSrikant Potluri100% (1)
- HandoutsDocumento3 páginasHandoutssheena Marjorie Cabidog100% (1)
- MOM Assignment IDocumento3 páginasMOM Assignment IAll_regAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocumento2 páginasStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Documento51 páginasMechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Joshua DariaAinda não há avaliações
- 121 - Pdfsam - 1mechanics of Materials (3 Ed) (Team Nanban) TMRGDocumento20 páginas121 - Pdfsam - 1mechanics of Materials (3 Ed) (Team Nanban) TMRGEugenio DerbesAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment # 2FDocumento9 páginasAssignment # 2FCrisnico PeligrinoAinda não há avaliações
- Score 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerDocumento5 páginasScore 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerChristian M. MortelAinda não há avaliações
- Prac Prob PSADDocumento10 páginasPrac Prob PSADjeannechoiashAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas 1 (Allowable Stress)Documento5 páginasTugas 1 (Allowable Stress)WAHYU DWI LESTARIAinda não há avaliações
- Strength 1 WorksheetDocumento4 páginasStrength 1 WorksheetHabib NuredinAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Set 2 PDFDocumento5 páginasProblem Set 2 PDFLynx101Ainda não há avaliações
- StrengthDocumento101 páginasStrengthSigue Ramel Hinayas0% (1)
- Practical Problems (Chap 1 Chap 4)Documento2 páginasPractical Problems (Chap 1 Chap 4)tevin sessa100% (1)
- Assignment 1D: by Er.A.P.S.ChadhaDocumento14 páginasAssignment 1D: by Er.A.P.S.ChadhaMANISH SHUKLAAinda não há avaliações
- Strema 102Documento4 páginasStrema 102Hazel VidallonAinda não há avaliações
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDocumento4 páginas9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Beam - Stresses - P and SDocumento27 páginasBeam - Stresses - P and SDianne Rose M. MadlangbayanAinda não há avaliações
- Concepts of Stress1 PDFDocumento18 páginasConcepts of Stress1 PDFCarl Malone Lotivio LorillaAinda não há avaliações
- Dme Home Assignment 2019-20Documento4 páginasDme Home Assignment 2019-20VenkateshAinda não há avaliações
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Muhammad Firdaus - A Review of Personal Data Protection Law in IndonesiaDocumento7 páginasMuhammad Firdaus - A Review of Personal Data Protection Law in IndonesiaJordan Amadeus SoetowidjojoAinda não há avaliações
- Harish Raval Rajkot.: Civil ConstructionDocumento4 páginasHarish Raval Rajkot.: Civil ConstructionNilay GandhiAinda não há avaliações
- Sample TRM All Series 2020v1 - ShortseDocumento40 páginasSample TRM All Series 2020v1 - ShortseSuhail AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Integra Facade BrochureDocumento2 páginasIntegra Facade BrochureHarshit PatadiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Miata Wiring NA8 DiagramDocumento65 páginasMiata Wiring NA8 DiagramseanAinda não há avaliações
- The Ins and Outs Indirect OrvinuDocumento8 páginasThe Ins and Outs Indirect OrvinusatishAinda não há avaliações
- Re BuyerDocumento20 páginasRe BuyerElias OjuokAinda não há avaliações
- Ems Speed Sensor Com MotorDocumento24 páginasEms Speed Sensor Com MotorKarina RickenAinda não há avaliações
- Asian Paints Final v1Documento20 páginasAsian Paints Final v1Mukul MundleAinda não há avaliações
- Pre K Kindergarten Alphabet Letter TracingDocumento28 páginasPre K Kindergarten Alphabet Letter TracingNeha RawatAinda não há avaliações
- Clevite Bearing Book EB-40-07Documento104 páginasClevite Bearing Book EB-40-07lowelowelAinda não há avaliações
- SQL TestDocumento10 páginasSQL TestGautam KatlaAinda não há avaliações
- Bus105 Pcoq 2 100%Documento9 páginasBus105 Pcoq 2 100%Gish KK.GAinda não há avaliações
- Projected Costs of Generating Electricity (EGC) 2005Documento233 páginasProjected Costs of Generating Electricity (EGC) 2005susantojdAinda não há avaliações
- Master Thesis On Smart GridDocumento6 páginasMaster Thesis On Smart Gridsandraandersondesmoines100% (2)
- Perbandingan Implementasi Smart City Di Indonesia: Studi Kasus: Perbandingan Smart People Di Kota Surabaya Dan Kota MalangDocumento11 páginasPerbandingan Implementasi Smart City Di Indonesia: Studi Kasus: Perbandingan Smart People Di Kota Surabaya Dan Kota Malanglely ersilyaAinda não há avaliações
- OMN-TRA-SSR-OETC-Course Workbook 2daysDocumento55 páginasOMN-TRA-SSR-OETC-Course Workbook 2daysMANIKANDAN NARAYANASAMYAinda não há avaliações
- BS en 50216-6 2002Documento18 páginasBS en 50216-6 2002Jeff Anderson Collins100% (3)
- d10 Sandra Darby FinalDocumento3 páginasd10 Sandra Darby FinalFirstCitizen1773Ainda não há avaliações
- Denial of LOI & LOP For Ayurveda Colleges Under 13A For AY-2021-22 As On 18.02.2022Documento1 páginaDenial of LOI & LOP For Ayurveda Colleges Under 13A For AY-2021-22 As On 18.02.2022Gbp GbpAinda não há avaliações
- BypassGoldManual PDFDocumento6 páginasBypassGoldManual PDFBrad FrancAinda não há avaliações
- Smart Cockpit System Questions - FlattenedDocumento85 páginasSmart Cockpit System Questions - FlattenedBarut Brkk100% (4)
- WKS 8 & 9 - Industrial Dryer 2T 2020-2021Documento26 páginasWKS 8 & 9 - Industrial Dryer 2T 2020-2021Mei Lamfao100% (1)
- Résumé Emily Martin FullDocumento3 páginasRésumé Emily Martin FullEmily MartinAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1 - Vertical Alignment - SolutionsDocumento6 páginasAssignment 1 - Vertical Alignment - SolutionsArmando Ramirez100% (1)
- Chapter 2.2 Quantitative Analysis NewDocumento44 páginasChapter 2.2 Quantitative Analysis NewMinase TilayeAinda não há avaliações
- Neural Computing and ApplicationsDocumento49 páginasNeural Computing and ApplicationsLine PhamAinda não há avaliações
- 27 Points of Difference Between Personnel Management & HRDDocumento2 páginas27 Points of Difference Between Personnel Management & HRDMurtaza Ejaz33% (3)
- Top249 1 PDFDocumento52 páginasTop249 1 PDFCarlos Henrique Dos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- PST SubjectDocumento2 páginasPST SubjectCarol ElizagaAinda não há avaliações