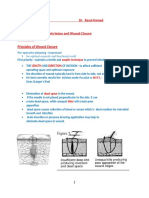
Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Abigail B
Enviado por
bjhilarioDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Abigail B
Enviado por
bjhilarioDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Abigail B.
Habiling BSN IV- 3; Group 3 SUTURES
ABSORBABLE SUTURES- it breaks down over time in the body. The amount of time it takes a suture to break down in the body depends on a few factors such as suture type, size and the location it is placed. 1. Surgical Gut- used in suturing oral mucosa, small vessels 2. Chromic Sutures- large vessel ties, muscle, fascia 3. Synthetic Absorbable a. Vicryl- use in general soft tissue approximation and/or ligation, including use in ophthalmic procedures, but not for use in cardiovascular and neurological tissues. b. Dexon- use in general soft tissue approximation and/or ligation, including use in ophthalmic procedures, but not for use in cardiovascular and neurological tissues. Note Suture absorption rates can increase in patients with fever, infection or protein deficiency. Also, the strength to a suture will decrease significantly prior to its complete breakdown time. Therefore a suture with higher tissue tension will have a greater chance of failure prior to the amount of time listed above Non-Absorbable Suture
Nylon (Ethilon), Gortex, Silk, Fiberwire, Ethibond, Prolene and Steel are all example of non absorbable suture. When used on the skin, these sutures will be removed however when used in the body they will be retained inside the tissue. Common uses for non absorbable suture: Interrupted skin suturing when sutures will be removed later, 4-0 Nylon Securing drains to skin, 2-0 Silk Repair stitches for blood vessels, 6-0 Prolene
Vessel graft stitches for AAA, Fem-Pop or Carotid Artery grafts 5-0, 6-0 prolene or gortex Bowel repair stitch, 3-0 silk Achilles Tendon Repair, #5 Ethibond or Fiberwire Color Coding: Plain Gut: Yellow Chromic: Brown Silk- Light Blue Nylon: Green Prolene- Royal Blue Vicryl- Violet Cotton- Pink NEEDLES
Classification of Needles 1.According to the Eye a. Regular eyed threaded like ordinary sewing needle b. Eyeless or swayed atraumatic, also known as dulex, atroloo c. French or Spring Eye there is slit from the end of the needle to the eye, through which is the sutureis drawn to thread it. 2.According to Shape, of shaft, cutting or non-cutting a.Non-cutting these are rounded bodied and are use on tissue that offers a small amount of resistance to the needle as it passes thru. - used to suture the viscera, peritoneum, muscle b.Cutting these make a slight tear in tissue, and the suture tends to cut it a little more. -used for tough tissues that a round needle cannot well go through such as tendon, peritoneum,fascia, subcutaneous and skin. 3.According to Shaft or Body a. Straight used primarily for skin closures b. Curved used inside for quickly recovery of the point of needle.
BLADES
Você também pode gostar
- Plastic & Hand Surgery in Clinical Practice: Classifications and DefinitionsNo EverandPlastic & Hand Surgery in Clinical Practice: Classifications and DefinitionsAinda não há avaliações
- Net Making Made Simple - A Guide to Making Nets for Sport and HomeNo EverandNet Making Made Simple - A Guide to Making Nets for Sport and HomeAinda não há avaliações
- Science IV - Self TestDocumento5 páginasScience IV - Self TestAries MuraoAinda não há avaliações
- Abdominal OrgansDocumento28 páginasAbdominal OrgansRS BuenavistaAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology LectureDocumento45 páginasPharmacology LecturebjhilarioAinda não há avaliações
- Sutures and NeedlesDocumento4 páginasSutures and Needlesjgcriste100% (4)
- Urinary Incontinence ModuleDocumento103 páginasUrinary Incontinence Modulesny007Ainda não há avaliações
- SutureDocumento4 páginasSutureDanica DeeAinda não há avaliações
- Evolution Inner GameDocumento10 páginasEvolution Inner GamedocumentaryttAinda não há avaliações
- Suture TypesDocumento6 páginasSuture TypesJen Vizcarra CaminoAinda não há avaliações
- General Principles of Periodontal SurgeryDocumento20 páginasGeneral Principles of Periodontal SurgerysevattapillaiAinda não há avaliações
- Everything You Need to Know About Sutures and Suturing TechniquesDocumento65 páginasEverything You Need to Know About Sutures and Suturing TechniquesRicha Bhosale100% (2)
- SUTURE MATERIALS & TECHNIQUES: A GUIDEDocumento182 páginasSUTURE MATERIALS & TECHNIQUES: A GUIDESharmela BrijmohanAinda não há avaliações
- ASSESSMENT AND NURSING CARE PLANDocumento6 páginasASSESSMENT AND NURSING CARE PLANbjhilarioAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of PainDocumento31 páginasPathophysiology of PainJonniwal Sanusi100% (4)
- Types of SuturesDocumento7 páginasTypes of SuturesAngie Mandeoya100% (2)
- NCPDocumento3 páginasNCPbjhilarioAinda não há avaliações
- IncisionalDocumento50 páginasIncisionalelsayedsalemAinda não há avaliações
- Community Organizing Participatory Action ResearchDocumento3 páginasCommunity Organizing Participatory Action ResearchbjhilarioAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid EmergenciesDocumento23 páginasThyroid EmergenciesHeron BayaninAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Sutures: Absorbable vs Non-AbsorbableDocumento3 páginasTypes of Sutures: Absorbable vs Non-Absorbableruby cubionaAinda não há avaliações
- History of The Suture Personal Suture Preference Suture CharacteristicsDocumento33 páginasHistory of The Suture Personal Suture Preference Suture Characteristicsmob3Ainda não há avaliações
- Dental Management in Hematologic DisordersDocumento31 páginasDental Management in Hematologic DisordersdmdsahAinda não há avaliações
- Immunosero ReviwerDocumento73 páginasImmunosero ReviwerDarla YsavelAinda não há avaliações
- Sutures & Suturing: Dr. Sateessh Bhatele Oral & Maxillofacial SurgeryDocumento86 páginasSutures & Suturing: Dr. Sateessh Bhatele Oral & Maxillofacial SurgeryShalini SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Surgical Skills Pauline 1Documento84 páginasBasic Surgical Skills Pauline 1paulineAinda não há avaliações
- SUTURE Ethicon ManualDocumento48 páginasSUTURE Ethicon ManualRomulo BittencourtAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study For OligohydramniosDocumento7 páginasCase Study For Oligohydramniosbjhilario86% (14)
- Suture NeedlesDocumento12 páginasSuture NeedlesHenrietta GaviolaAinda não há avaliações
- Everything You Need to Know About Absorbable SuturesDocumento40 páginasEverything You Need to Know About Absorbable SuturesMehboob AlamAinda não há avaliações
- Sepsis Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 páginasSepsis Nursing Care Planbjhilario100% (1)
- Sepsis Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 páginasSepsis Nursing Care Planbjhilario100% (1)
- Suture and NeedlesDocumento5 páginasSuture and NeedlesMabesAinda não há avaliações
- Case StudyDocumento15 páginasCase Studybjhilario0% (2)
- Glossary Sutures Neu PDFDocumento32 páginasGlossary Sutures Neu PDFcesarcrrAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Veterinary SuturingDocumento24 páginasPrinciples of Veterinary Suturing115130100111015Ainda não há avaliações
- Suture Size: SmallestDocumento2 páginasSuture Size: SmallestGeraldine BirowaAinda não há avaliações
- Suture TypesDocumento2 páginasSuture TypesMahmoud SelimAinda não há avaliações
- SutureDocumento4 páginasSuturealaamorsyAinda não há avaliações
- 2014-08-13 Suture Presentation FINAL - SlidesDocumento13 páginas2014-08-13 Suture Presentation FINAL - SlidesMariana HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Eyeless NeedlesDocumento13 páginasTypes of Eyeless NeedlesClaudia AnissyaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Surgical Skills Pauline 1Documento68 páginasBasic Surgical Skills Pauline 1paulineAinda não há avaliações
- Sutures, Drains and TubesDocumento49 páginasSutures, Drains and Tubesshafic kamogaAinda não há avaliações
- 40 Complex Facial Reconstruction Aldona Jedrysiak, M.DDocumento6 páginas40 Complex Facial Reconstruction Aldona Jedrysiak, M.DAndini RomzaAinda não há avaliações
- Suture and Needles Nursing Lecture 1Documento8 páginasSuture and Needles Nursing Lecture 1ilovedaneAinda não há avaliações
- SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS & SUTURES GUIDEDocumento11 páginasSURGICAL INSTRUMENTS & SUTURES GUIDEAhmed Azmy AlgebalyAinda não há avaliações
- Interne Bedah Umum SuturematerialsDocumento31 páginasInterne Bedah Umum SuturematerialsAryantomo ArsadAinda não há avaliações
- Dressingandbandages 171203170738Documento38 páginasDressingandbandages 171203170738Marc Lester ObatononAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of excision Skin lesion and Wound ClosureDocumento10 páginasPrinciples of excision Skin lesion and Wound ClosureKhdhir M. SalemAinda não há avaliações
- Transfemoral Above Knee AmputationDocumento4 páginasTransfemoral Above Knee AmputationMarthaLhtAinda não há avaliações
- Everything You Need to Know About EpisiotomyDocumento23 páginasEverything You Need to Know About EpisiotomyCharisse Ann GasatayaAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacognosy Assignment (Dressings and Sutures) PDFDocumento5 páginasPharmacognosy Assignment (Dressings and Sutures) PDFMr.Shaz100% (1)
- SUTURESDocumento27 páginasSUTURESsncmanguiat.2202276.chasnAinda não há avaliações
- Umbilical Surgery in CalvesDocumento11 páginasUmbilical Surgery in CalvesguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Types of SuturesDocumento6 páginasTypes of SuturesLorina Lynne ApelacioAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Bontilao, Jimnah Rhodrick M. Level: 3-B Instructor in Charge: MRS. AISSA CARLIT Date Materials Checked: Date PerformedDocumento7 páginasName: Bontilao, Jimnah Rhodrick M. Level: 3-B Instructor in Charge: MRS. AISSA CARLIT Date Materials Checked: Date PerformedJimnah Rhodrick BontilaoAinda não há avaliações
- Cirugía Orejas Prominente - Mustardé 1967Documento5 páginasCirugía Orejas Prominente - Mustardé 196722omar22Ainda não há avaliações
- Suture Characteristics & TypesDocumento45 páginasSuture Characteristics & TypesJonathanDavid Contreras InfanteAinda não há avaliações
- Optimal Methods For Preparation and Immunostaining of Iris, Ciliary Body, and Choroidal WholemountsDocumento6 páginasOptimal Methods For Preparation and Immunostaining of Iris, Ciliary Body, and Choroidal WholemountsIlalang GurunAinda não há avaliações
- Snodgrass HypospDocumento11 páginasSnodgrass HypospRajarshi KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Selected Surgical Conditions of The Bovine Penis and PrepuceDocumento11 páginasSelected Surgical Conditions of The Bovine Penis and PrepuceAhmed Fittoh MosallamAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Sutures and LayersDocumento4 páginasTypes of Sutures and LayersChrizley Shawn DeroniaAinda não há avaliações
- Flora Belle ADocumento4 páginasFlora Belle AmmmgmgmAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical Suture Materials Are Used in The Closure of Most Wound Types. The Ideal SutureDocumento9 páginasSurgical Suture Materials Are Used in The Closure of Most Wound Types. The Ideal SutureToria053Ainda não há avaliações
- Perio 5Documento7 páginasPerio 5Meiz JaleelAinda não há avaliações
- Theatre and SuturingDocumento10 páginasTheatre and SuturingazilebongcloudinengenyiAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 2. Basic Hematological Methods of ExaminationDocumento9 páginasLesson 2. Basic Hematological Methods of ExaminationKhelly Joshua UyAinda não há avaliações
- Lateral Thigh and Anterolateral Thigh Free Tissue Transfer: Background, History of The Procedure, IndicationsDocumento12 páginasLateral Thigh and Anterolateral Thigh Free Tissue Transfer: Background, History of The Procedure, IndicationsNaenay WannatrakoolAinda não há avaliações
- In The Name of Ulla The Most Compassionate The Most MercifulDocumento28 páginasIn The Name of Ulla The Most Compassionate The Most MercifulHaqmal100% (1)
- Surgical Treatment of Diseases of The Maxillary SinusDocumento6 páginasSurgical Treatment of Diseases of The Maxillary SinusRaymund Niño BumatayAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Nursing 3Documento20 páginasAdvanced Nursing 3Justus NwakaAinda não há avaliações
- Subarachnoid Block TOTW 059 2007 PDFDocumento14 páginasSubarachnoid Block TOTW 059 2007 PDFilham fadlilahAinda não há avaliações
- AmputationDocumento40 páginasAmputationaeruginoAinda não há avaliações
- A Manual of the Operations of Surgery: For the Use of Senior Students, House Surgeons, and Junior PractitionersNo EverandA Manual of the Operations of Surgery: For the Use of Senior Students, House Surgeons, and Junior PractitionersAinda não há avaliações
- Fbao EdDocumento2 páginasFbao EdbjhilarioAinda não há avaliações
- Conversion TableDocumento3 páginasConversion TableAbi HabilingAinda não há avaliações
- DinnerDocumento2 páginasDinnerAbi HabilingAinda não há avaliações
- PharmaDocumento20 páginasPharmabjhilarioAinda não há avaliações
- BPNDocumento5 páginasBPNbjhilarioAinda não há avaliações
- Wesleyan University - Philippines: College of NursingDocumento1 páginaWesleyan University - Philippines: College of NursingbjhilarioAinda não há avaliações
- Meal PlanDocumento2 páginasMeal PlanBij HilarioAinda não há avaliações
- Fbao EdDocumento2 páginasFbao EdbjhilarioAinda não há avaliações
- BurnDocumento10 páginasBurnbjhilarioAinda não há avaliações
- 633760633489581250Documento42 páginas633760633489581250loulen2421Ainda não há avaliações
- G8 Science Q4 - Week 2 - MeiosisDocumento21 páginasG8 Science Q4 - Week 2 - MeiosisLeyannAinda não há avaliações
- L16 Animal Diversity 2Documento29 páginasL16 Animal Diversity 2shadoworacleAinda não há avaliações
- Week8-Deception Detection (Methods)Documento4 páginasWeek8-Deception Detection (Methods)Sahmin SaalAinda não há avaliações
- What Causes Chest Pain When Feelings Are Hurt - Scientific AmericanDocumento5 páginasWhat Causes Chest Pain When Feelings Are Hurt - Scientific AmericangprasadatvuAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Purulent Diseases of Fingers and HandDocumento23 páginasAcute Purulent Diseases of Fingers and Handluckyswiss7776848Ainda não há avaliações
- Strain SprainDocumento17 páginasStrain SprainPuterinugraha Wanca ApatyaAinda não há avaliações
- RH Isoimmunization (PritDocumento23 páginasRH Isoimmunization (PritmaezuAinda não há avaliações
- Transportation in Plants and AnimalsDocumento7 páginasTransportation in Plants and AnimalsDivyansh JhaAinda não há avaliações
- Mizuho Vascular (Transcranial) DopplerDocumento4 páginasMizuho Vascular (Transcranial) DopplersigmakarsaAinda não há avaliações
- Tetralogy of FallotDocumento3 páginasTetralogy of FallotKamal FauzeAinda não há avaliações
- Somatic HybridizationDocumento23 páginasSomatic HybridizationJan VivienelAinda não há avaliações
- A6. Karring T, Lang N, Löe H. The Role of Gingival Connective Tissue in Determining Epithelial Differentiation. J Perio Res 1975Documento12 páginasA6. Karring T, Lang N, Löe H. The Role of Gingival Connective Tissue in Determining Epithelial Differentiation. J Perio Res 1975Daniel CubasAinda não há avaliações
- Toxicokinetics & ToxicodynamicsDocumento31 páginasToxicokinetics & ToxicodynamicsWahyudin AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Carbohydrates PDFDocumento8 páginasCarbohydrates PDFWrigley PatioAinda não há avaliações
- Full Lab ReportDocumento5 páginasFull Lab ReportchampmorganAinda não há avaliações
- Duke University Nurse Anesthesia Program (Acct #7042) Montgomery, Kelly Barton (Semester 7) Is Logged inDocumento3 páginasDuke University Nurse Anesthesia Program (Acct #7042) Montgomery, Kelly Barton (Semester 7) Is Logged inkellyb11Ainda não há avaliações
- Nitrifying Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) Biofilm and Biomass Response To Long Term Exposure To 1 CDocumento10 páginasNitrifying Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) Biofilm and Biomass Response To Long Term Exposure To 1 CSyamsul Bahry HarahapAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Esr BT CTDocumento9 páginas6 Esr BT CTdlerAinda não há avaliações
- Histo Review 2Documento13 páginasHisto Review 2Coy NuñezAinda não há avaliações
- Kimia Kofaktor Dan KoenzimDocumento35 páginasKimia Kofaktor Dan KoenzimSuwahono, M.PdAinda não há avaliações
- Mahmoud Jamil Daher 16/02/2023 12:47 PM M 29/10/1985 16/02/2023 12:47 PM HAM / 00375052Documento1 páginaMahmoud Jamil Daher 16/02/2023 12:47 PM M 29/10/1985 16/02/2023 12:47 PM HAM / 00375052Mahmoud DaherAinda não há avaliações
- Kvpy SB SolutionsDocumento34 páginasKvpy SB Solutionsricky24x7Ainda não há avaliações
- Dermatic Effects PIP-MXDocumento2 páginasDermatic Effects PIP-MXtesiscbaAinda não há avaliações