Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#: in This Session, You Will Learn To
Enviado por
caininmeDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#: in This Session, You Will Learn To
Enviado por
caininmeDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Objectives
In this session, you will learn to:
Define abstraction and encapsulation
Implement encapsulation by using access specifiers
Use methods
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 1 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Introducing Abstraction and Encapsulation
Abstraction and encapsulation are important features of any
object-oriented programming language.
Abstraction involves extracting only the relevant information.
Encapsulation involves packaging one or more components
together.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 2 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Defining Abstraction
An automobile salesperson is aware that different people
have different preferences.
Some people are interested in the speed of a car, some in its
price, some in the engine, and the some in its style.
Although all of them want to buy a car, each of them is
interested in a specific attribute or feature.
The salesman knows all the details of a car, but he presents
only the relevant information to a potential customer.
As a result, a the salesman practices abstraction and presents
only relevant details to customer.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 3 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Defining Encapsulation
Encapsulation literally means ‘to enclose in or as if in a
capsule’.
Encapsulation is defined as the process of enclosing one or
more items within a physical or logical package.
It involves preventing access to nonessential details.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 4 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Implementing Encapsulation by Using Access Specifiers
An access specifier defines the scope of a class member.
A class member refers to the variables and functions in a
class.
A program can have one or more classes.
You may want some members of a class to be accessible to
other classes.
But, you may not want some other members of the class to
be accessible outside the class.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 5 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Types of Access Specifiers
C# supports the following access specifiers:
public
private
protected
internal
protected internal
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 6 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
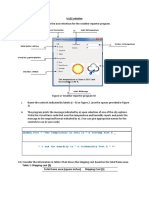
Demo: Calculating Area and Volume by Using Access
Specifiers
Problem Statement:
Write a program to calculate the area of a rectangle and a
square.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 7 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Using Methods
A method is a set of one or more program statements,
which can be executed by referring to the method name.
To use methods, you need to:
Define methods
Call methods
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 8 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Defining Methods
Defining a method means declaring the elements of its
structure.
Consider the syntax of defining a method:
<Access specifier> <Return Type> <Method
Name>(Parameter List)
{
Method Body
}
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 9 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Defining Methods (Contd.)
The elements of the method declaration include the method
name, the parameters list, the return type, and the method
body.
The following are the elements of a method:
Access specifier
Return type
Method name
Parameter list
Method body
Let us understand each of the element of the method
declaration.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 10 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Defining Methods (Contd.)
Defining a method means declaring the
This determines the
elements of its structure. extent to which a
Consider the syntax of defining avariable or method
method: can be accessed
<Access specifier> <Return Type> from another class.
<Method Name>(Parameter List)
{
Method Body
}
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 11 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Defining Methods (Contd.)
Defining a method means declaring the
A method can return
elements of its structure. a value of any type.
Consider the syntax of defining aIf the method is not
method: returning any value,
<Access specifier> <Return Type> use void as the
<Method Name>(Parameter List) return type.
{
Method Body
}
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 12 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Defining Methods (Contd.)
Defining a method means declaring the This is a unique
elements of its structure. identifier and is
Consider the syntax of defining a method: case-sensitive.
<Access specifier> <Return Type> The method name
<Method Name>(Parameter List) cannot be the
{ same as the
Method Body
variable name or
any other
}
non-method item
declared in the
class.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 13 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Defining Methods (Contd.)
Defining a method means declaring the This is used to
elements of its structure. pass and receive
Consider the syntax of defining a method: the data from a
<Access specifier> <Return Type> method. It is
<Method Name>(Parameter List) enclosed between
{ parentheses. The
Method Body
parentheses are
included even if
}
there are no
parameters.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 14 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Defining Methods (Contd.)
Defining a method means declaring the This contains the
elements of its structure. set of instructions
Consider the syntax of defining a needed to complete
method: the required activity.
<Access specifier> <Return Type>
<Method Name>(Parameter List)
{
Method Body
}
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 15 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Calling Methods
After defining the method, you can execute it by calling it.
You can call a method by using the name of the method.
The method name is followed by parentheses even if the
method call has no parameters, as shown in the following
example:
MethodName();
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 16 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Calling Methods (Contd.)
The following is an example of calling methods:
using System;
class Calculator
{
public int AddNumber(int num1, int num2)
{
int result;
result = num1 + num2;
return result;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 17 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Calling Methods (Contd.)
{
Calculator cal = new Calculator();
// The following statement is calling the
// AddNumber method and passing 10 and
// 20 as the parameter list.
int value=cal.AddNumber(10, 20);
Console.WriteLine("The result is
{0}", value);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 18 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Using Methods with Parameters
Methods can also be declared with parameters. Consider
the example of declared a method with parameters:
void DisplayResult (int result)
{
//…..
}
When the methods are declared with parameters, they
should be called with parameters. The methods with
parameters are called by passing the value using the
following mechanism:
Value
Reference
Output
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 19 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Using Methods with Parameters (Contd.)
Value: The parameters passed by value creates a separate
copy in the memory. The following example shows the
parameters passed by value:
void CalculateSum( int num1, int num2)
{
//…
}
void Accept()
{
int val1=10;
int val2=2;
CalculateSum(val1,val2);
}
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 20 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Using Methods with Parameters (Contd.)
Reference: The parameters passed by reference does not
creates a separate copy of the variable in the memory. A
reference parameter stores the memory address of the data
member passed. The following example shows the parameters
passed by reference:
void CalculateSum( ref int num1,ref int num2)
{
//…
}
void Accept()
{
int val1=10;
int val2=2;
CalculateSum( ref val1,ref val2);
}
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 21 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Using Methods with Parameters (Contd.)
Output: The output parameters are used to pass the value out
of the method. The following example shows the parameters
passed by reference:
void CalculateSum( ref int num1,ref int num2, out
int result)
{
result=num1+num2;
}
void Accept()
{
int val1=10;
int val2=2;
int recieveVal;
CalculateSum( ref val1,ref val2,out
recieveVal);
}
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 22 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Demo: Swapping Two Numbers by Using Methods with
Parameters
Problem Statement:
Write a program to swap two numbers by using reference type
parameters in a method.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 23 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Summary
In this session, you learned that:
Abstraction is the process of reducing information content in
order to retain only the relevant information for a particular
purpose.
Encapsulation is the process of hiding all the details of an
object that do not contribute to its essential characteristics.
An access specifier is used to determine whether any other
class or function can access the member variables and
functions of a particular class.
The public access specifier allows a class to expose its
member variables and member functions to other functions
and objects.
The private access specifier allows a class to hide its member
variables and member functions from other class functions and
objects.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 24 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Summary (Contd.)
The protected access specifier allows a class to hide its
member variables and member functions from other class
objects and functions, just like the private access specifier
while implementing inheritance.
A method is a set of one or more program statements that can
be executed by referring to the method name.
Defining a method means declaring the elements of its
structure.
The access modifiers that can be used with methods are
public, protected, internal, protected internal, and private.
Parameters allow information to be passed into and out of a
method. When you define a method, you can include a list of
parameters in parentheses.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 25 of 26
Object-Oriented Programming Using C#
Summary (Contd.)
Parameters can be passed by using any one of the following
parameters types:
Value
Reference
Output
Pass by value is the default mechanism for passing
parameters in C#.
A reference parameter is a reference to a memory location of a
data member.
Output parameters are like reference parameters, except that
they transfer data out of the method rather than into it.
The return statement is used to return the control to the caller.
Ver. 1.0 Session 4 Slide 26 of 26
Você também pode gostar
- Basic Programming ConstructsDocumento30 páginasBasic Programming ConstructsJanette Anne Reyes Macaraig100% (1)
- ICSE Class 10 Computer Application NotesDocumento42 páginasICSE Class 10 Computer Application NotesRishabh 24 Singh KshatriyaAinda não há avaliações
- OPC 10030 - UA Companion Specification For ISA-95 Common Object Model 1.00Documento128 páginasOPC 10030 - UA Companion Specification For ISA-95 Common Object Model 1.00Walker ReynoldsAinda não há avaliações
- Informatica Cloud Real Time Service Technology and Security OverviewDocumento16 páginasInformatica Cloud Real Time Service Technology and Security OverviewLakshminarayana SamaAinda não há avaliações
- M6 Act1Documento6 páginasM6 Act1KyleAinda não há avaliações
- Orca Share Media1667395632302 6993564170150144449Documento3 páginasOrca Share Media1667395632302 6993564170150144449Nor Jhon BruzonAinda não há avaliações
- Windows ProgrammingDocumento27 páginasWindows ProgrammingLyfe LernerAinda não há avaliações
- SSD3U2S3Documento66 páginasSSD3U2S3api-3728126Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 2Documento74 páginasUnit 2Akshay HariyaniAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Classes and ObjectsDocumento40 páginasIntroduction To Classes and ObjectsAdarsh DixitAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 - C# Class - MethodDocumento45 páginasLecture 2 - C# Class - MethodBob LongAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4: Methods and ConstructorsDocumento22 páginasUnit 4: Methods and ConstructorsMasautso ChiwambaAinda não há avaliações
- Declaring Methods: Module 03 (Working With Methods and Handling Exception)Documento11 páginasDeclaring Methods: Module 03 (Working With Methods and Handling Exception)Afid Md AzwadAinda não há avaliações
- In This Session, You Will Learn To:: ObjectivesDocumento20 páginasIn This Session, You Will Learn To:: ObjectivesTanvi SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Object Oriented ProgrammingDocumento18 páginasObject Oriented ProgrammingDuncan M Ng'endaAinda não há avaliações
- Delegates and EventsDocumento9 páginasDelegates and EventsRamya PrAinda não há avaliações
- Handout05 PDFDocumento9 páginasHandout05 PDFabibual desalegnAinda não há avaliações
- OOPJ-1.3 E-Learning PowerPoint TemplatesDocumento8 páginasOOPJ-1.3 E-Learning PowerPoint TemplatesHeer PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 3 Object Oriented Programming (Contd.) : What Is A Constructor?Documento4 páginasExperiment 3 Object Oriented Programming (Contd.) : What Is A Constructor?Mohammad RafaeAinda não há avaliações
- Module 5 Introduction To Object Oriented ProgrammingDocumento55 páginasModule 5 Introduction To Object Oriented ProgrammingStefano EdicAinda não há avaliações
- Ppt-Class and Objects in Java OOPDocumento67 páginasPpt-Class and Objects in Java OOPaasxdas100% (3)
- Presentation1 JAVADocumento20 páginasPresentation1 JAVAhacker worldAinda não há avaliações
- Object Oriented Programming PDFDocumento16 páginasObject Oriented Programming PDFEunice NjokiAinda não há avaliações
- 9.1. Overview and Types of Access Specifiers: PublicDocumento11 páginas9.1. Overview and Types of Access Specifiers: PublicjestinmaryAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture05 - ITE 5230Documento102 páginasLecture05 - ITE 5230Madhav ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Query and Classes and Methods in AX 2012Documento82 páginasQuery and Classes and Methods in AX 2012osamaanjumAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento45 páginasUntitledDzudzi ManyuhaAinda não há avaliações
- Glossary A... CDocumento7 páginasGlossary A... Cnuvvu_rojaAinda não há avaliações
- Using C# Reflection: Finding Types in A Running ProgramDocumento5 páginasUsing C# Reflection: Finding Types in A Running ProgramkannanbegclAinda não há avaliações
- JEDI Slides-Intro2-Chapter01-Review of Basic Concepts in JavaDocumento62 páginasJEDI Slides-Intro2-Chapter01-Review of Basic Concepts in JavaReina ReinzAinda não há avaliações
- ObjectDocumento68 páginasObjectKyle DalyAinda não há avaliações
- C# Programming: 3.0 Fundamentals IIDocumento10 páginasC# Programming: 3.0 Fundamentals IIbrianweldtAinda não há avaliações
- Objects and Classes: Object Oriented ProgrammingDocumento17 páginasObjects and Classes: Object Oriented ProgrammingDanita Ureta BalastaAinda não há avaliações
- Chap5-Methods in JavaDocumento2 páginasChap5-Methods in JavaVarsha KalagiAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 5Documento1 páginaAssignment 5Murali KarthikAinda não há avaliações
- 03 - C++ Notes PDFDocumento35 páginas03 - C++ Notes PDFZeeshanAinda não há avaliações
- Object Oriented Programming: Class, Objects and InheritanceDocumento18 páginasObject Oriented Programming: Class, Objects and InheritanceRajat SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Object Oriented Programming: Class, Objects and InheritanceDocumento18 páginasObject Oriented Programming: Class, Objects and InheritanceRajat SinghAinda não há avaliações
- M1 Chapter4Documento10 páginasM1 Chapter4Matt MurdockAinda não há avaliações
- Classes and Member Access ModifiersDocumento14 páginasClasses and Member Access ModifiersARVIND HAinda não há avaliações
- C OopsDocumento34 páginasC OopspkAinda não há avaliações
- Delegates (C# Programming Guide)Documento3 páginasDelegates (C# Programming Guide)Vishal PanwarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1. Introduction To: C# ProgrammingDocumento31 páginasChapter 1. Introduction To: C# ProgrammingJuan OrdoñezAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Method in JavaDocumento11 páginasWhat Is A Method in JavaM UsmithaAinda não há avaliações
- Howto Descriptor PDFDocumento8 páginasHowto Descriptor PDFAlisha AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Software Engineering Principles and Java Classes: Ias1223 Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocumento39 páginasSoftware Engineering Principles and Java Classes: Ias1223 Data Structures and AlgorithmsMuhammad HashimAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4: Writing ClassesDocumento45 páginasChapter 4: Writing ClassesMouhamad BazziAinda não há avaliações
- Object-Oriented Programming in ABAPDocumento61 páginasObject-Oriented Programming in ABAPJeeva DarlingAinda não há avaliações
- Descriptor Howto Guide: Guido Van Rossum and The Python Development TeamDocumento7 páginasDescriptor Howto Guide: Guido Van Rossum and The Python Development Teamaleks3Ainda não há avaliações
- Class12 Computer Science Basic Concepts of OOP Classes and ObjectsDocumento23 páginasClass12 Computer Science Basic Concepts of OOP Classes and ObjectsYogesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Good Startter PDFDocumento87 páginasGood Startter PDFFiya MalikAinda não há avaliações
- CC102 Lesson 6 Classes and MethodsDocumento35 páginasCC102 Lesson 6 Classes and MethodsBonjovie FaustoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2: Class and ObjectsDocumento8 páginasChapter 2: Class and ObjectsAdityaAinda não há avaliações
- Creating Aspects: Introducing AOPDocumento7 páginasCreating Aspects: Introducing AOPrakeshrfAinda não há avaliações
- (More Than One Answer Is Correct) : TAW10 2/2 ABAP Workbench FundamentalsDocumento24 páginas(More Than One Answer Is Correct) : TAW10 2/2 ABAP Workbench FundamentalsAdriana Matute MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- CC102 Lesson 6 Classes and MethodsDocumento35 páginasCC102 Lesson 6 Classes and MethodsBonjovie FaustoAinda não há avaliações
- C++ Viva Questions By:yatendra KashyapDocumento6 páginasC++ Viva Questions By:yatendra Kashyapyatendra kashyap78% (9)
- 06 Iec t1s1 Oops Session 08Documento24 páginas06 Iec t1s1 Oops Session 08ajay_anavAinda não há avaliações
- Descriptor Howto Guide: Guido Van Rossum and The Python Development TeamDocumento8 páginasDescriptor Howto Guide: Guido Van Rossum and The Python Development TeamPlesa AlexandruAinda não há avaliações
- Asp Oct 2013Documento8 páginasAsp Oct 2013Jainish ShahAinda não há avaliações
- C# Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo EverandC# Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- Updates of Jaiib May 2010 ExamDocumento1 páginaUpdates of Jaiib May 2010 ExamcaininmeAinda não há avaliações
- Updates of Jaiib May 2010 ExamDocumento1 páginaUpdates of Jaiib May 2010 ExamcaininmeAinda não há avaliações
- Object-Oriented Programming Using C#: in This Session, You Will Learn ToDocumento35 páginasObject-Oriented Programming Using C#: in This Session, You Will Learn TocaininmeAinda não há avaliações
- PROCALCITONINDocumento52 páginasPROCALCITONINcaininmeAinda não há avaliações
- 02 Iec t1s1 Oops Session 02Documento25 páginas02 Iec t1s1 Oops Session 02caininmeAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Iec t1s1 Oops Session 07Documento32 páginas05 Iec t1s1 Oops Session 07caininmeAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Iec t1s1 Oops Session 01Documento45 páginas01 Iec t1s1 Oops Session 01caininmeAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1ADocumento40 páginasLesson 1Arohitpr2007Ainda não há avaliações
- Exam - Questions SW EngDocumento20 páginasExam - Questions SW EngaliAinda não há avaliações
- CGM Practical File by Akshat AgrawalDocumento21 páginasCGM Practical File by Akshat AgrawalWWE OFFICAL MATCH CARDS.Ainda não há avaliações
- Slide 01Documento85 páginasSlide 01quyên nguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- CA3 QuestionDocumento1 páginaCA3 QuestionSukla BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento83 páginasChapter 6Thi Minh Dat (K17 HCM)Ainda não há avaliações
- Create Your Own Tab and Buttons in RevitDocumento14 páginasCreate Your Own Tab and Buttons in RevitRajaAinda não há avaliações
- Matplotlib ReferenceDocumento23 páginasMatplotlib Referencevyns amaliaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 6 - Flow Control InstructionsDocumento23 páginasCH 6 - Flow Control Instructionsapi-237335979Ainda não há avaliações
- Altera Nios II BSP SummaryDocumento12 páginasAltera Nios II BSP SummarywwasdAinda não há avaliações
- VB - Practical ProgramsDocumento109 páginasVB - Practical ProgramsFayaz khanAinda não há avaliações
- Is122 Solution: A) B) Form: Frmweather Label: LbltemperatureDocumento2 páginasIs122 Solution: A) B) Form: Frmweather Label: LbltemperatureStaygoldAinda não há avaliações
- GPT Use CasesDocumento6 páginasGPT Use CasesKshitij LauAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Tle As CSS10 Q3 WK2Documento3 páginasRevised Tle As CSS10 Q3 WK2Jonald SalinasAinda não há avaliações
- Dialog BoxesDocumento11 páginasDialog BoxesJvershaAinda não há avaliações
- SAP Activate Vs ASAP Methodology 1702436964Documento3 páginasSAP Activate Vs ASAP Methodology 1702436964karthikbjAinda não há avaliações
- 10g BIGFILE Type Tablespaces Versus SMALLFILE TypeDocumento8 páginas10g BIGFILE Type Tablespaces Versus SMALLFILE TypeejgonzalezpAinda não há avaliações
- Setting Up (35D) : Core Data Services-Based Extraction With SAP S/4HANA CloudDocumento28 páginasSetting Up (35D) : Core Data Services-Based Extraction With SAP S/4HANA CloudsreeAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Web Design and Applications: Lecture 4 ADocumento54 páginasIntroduction To Web Design and Applications: Lecture 4 Akelvin kadonyaAinda não há avaliações
- VLSI Design: SkillDocumento44 páginasVLSI Design: SkillPika ChuAinda não há avaliações
- Jim Wu's FPGA Blog - Memory Initialization MethodsDocumento1 páginaJim Wu's FPGA Blog - Memory Initialization Methodsganga_ch1Ainda não há avaliações
- A Beginner's Guide To Gambas PDFDocumento364 páginasA Beginner's Guide To Gambas PDFAnungAinda não há avaliações
- Internship Report Flutter DeveloperDocumento9 páginasInternship Report Flutter DeveloperGon FrecsAinda não há avaliações
- WebDocumento571 páginasWebFraz AlamAinda não há avaliações
- CSC108 Final 2010F PDFDocumento21 páginasCSC108 Final 2010F PDFexamkillerAinda não há avaliações
- Object Oriented Analysis and DesignDocumento57 páginasObject Oriented Analysis and DesignJoseph John100% (1)
- Java Programming - Module2021Documento10 páginasJava Programming - Module2021steven hernandezAinda não há avaliações
- How Can I Download, Install and Set Up SonicWall Analyzer On WindowsDocumento16 páginasHow Can I Download, Install and Set Up SonicWall Analyzer On WindowsNicu UdubasaAinda não há avaliações