Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Kingdom Monera & Protozoa
Enviado por
Anne Aguilar ComandanteDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Kingdom Monera & Protozoa
Enviado por
Anne Aguilar ComandanteDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
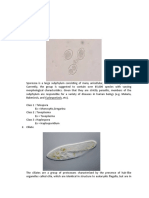
Kingdom: Monera Monerans are the oldest, the simplest and the most abundant organisms on earth.
They are named monera, which means alone. Monerans lack most of the organelles that other cell have. They exist a single cell and are very small. Their sizes range from 1 to 10 micrometers. Cell Nucleus: Prokaryotic Kingdom Monera is the only kingdom which has cells that has no membrane-bound nucleus , thus making them prokaryotic. Number of cells: Unicellular Monerans are single, and very small cells, thats why they are unicellular. Monerans are divided into two groups when it comes to food making. Some monerans make their food from chemicals like carbon dioxide and water. Some monerans must seek supplies of food like tissues, remains, and wastes of other living organisms.
Common groups . Archae Bacteria is a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon (sometimes spelled "archeon"). They have no cell nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles within their cells. Eubacteria are microscopic single-celled organisms. They are sometimes referred to as the true bacteria, differentiating them from Archaebacteria, similar organisms with some significant genetic and lifestyle differences. The vast majority of organisms we think of as bacteria are Eubacteria, with their Archean cousins preferring extreme living environments like nuclear power plants and hydrothermal vents. Protozoa - a diverse group of single-cell eukaryotic organisms, many of which are motile. Throughout history, protozoa have been defined as single-cell protists with animal-like behavior, e.g., movement.
Phyla and sub-phyla, classes and orders Schizophyta the former term for Cyanophyta. It is also known as blue-green algae, blue-green bacteria. It is a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through photosynthesis. Mastigophora - A superclass of the Protozoa characterized by possession of flagella. Ciliophora(Ciliates) - a group of protozoans characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagella but typically shorter and present in much larger numbers with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Sarcodina(Rhizopoda) - a superclass of Protozoa in the subphylum Sarcomastigophora in which movement involves protoplasmic flow, often with recognizable pseudopodia(false feet). Sporozoa - A subphylum of parasitic Protozoa, typically producing spores during the asexual stages of the life cycle. Sporozoans are types of animal-like protists. Many of them cause disease.
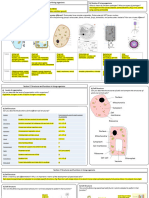
Kingdom: Protozoa Protozoa are single-celled eukaryotes (organisms whose cells have nuclei) that commonly show characteristics usually associated with animals, most notably mobility and heterotrophy.
Cell Nucleus: Eukaryotic Unlike Monerans, Protozoans has cells that has membrane-bound nucleus(organelles). Number of cells: Multicellular and Unicellular Protozoans has oraganisms that has single cells and multi cells. Protozoans has the same way of making their food like monerans, by chemicals or by supplies.
Common groups Algae - a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many distinct organs found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine forms are called seaweeds. Slime mold - a broad term describing protists that use spores to reproduce. They grow on decaying vegetation and in moist soil and have a similar but more advanced life cycle.
Phyla and sub-phyla, classes and orders Chlorophyta - a division of green algae, informally called chlorophytes. Myxomycophyta - An order of microorganisms, equivalent to the Mycetozoia of zoological classification.
Phaeophyta - Phaeophyta or brown algae are a group of autotrophic, multicellular organisms. The members of phaeophyta exhibit a characteristic greenish-brown color. The brown colored pigment is very important for the adaptation of phaeophyta in deep seas and oceans. Rodophyta the rodophyta or red algae is one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae, and also one of the largest, with about 5,0006,000 species of mostly multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Chrysophyta - chrysophytes, or golden algae, are common microscopic chromists in fresh water. Some species are colorless, but the vast majority are photosynthetic. As such, they are particularly important in lakes, where they may be the primary source of food for zooplankton. Pyrrophyta - a division of lower plants comprising unicellular and biflagellate algae that form starchy compounds.
Você também pode gostar
- The Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo EverandThe Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksAinda não há avaliações
- FUNGI AND PROTOZOA - BSEdIIIPDocumento57 páginasFUNGI AND PROTOZOA - BSEdIIIPKarl Francis GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Kingdom ProtistaDocumento6 páginasIntroduction To Kingdom ProtistaJersson JuarioAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom CompilationDocumento79 páginasKingdom CompilationPrayl Hope NapanoAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Kingdom of LifeDocumento12 páginas5 Kingdom of LifeDivyanshu AggarwalAinda não há avaliações
- MicroPara - ProtistDocumento101 páginasMicroPara - ProtistJannah Monaliza BambaAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom Protista NotesDocumento3 páginasKingdom Protista Noteshafizhusain0% (1)
- ProstistaDocumento40 páginasProstistaSyafiq AbeAinda não há avaliações
- Clasificacion de Los Seres Vivos en InglesDocumento16 páginasClasificacion de Los Seres Vivos en InglesPamelaMelissaManriqueGraosAinda não há avaliações
- Protista Written ReportDocumento8 páginasProtista Written ReportLance RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- JoannaDocumento4 páginasJoannapfaxawaiAinda não há avaliações
- Week Two Biology SS1Documento12 páginasWeek Two Biology SS1Oseni MuibaAinda não há avaliações
- Biological ClassificationDocumento54 páginasBiological ClassificationAyesha MahboobAinda não há avaliações
- MICROBESDocumento26 páginasMICROBESEA CatalanAinda não há avaliações
- NullDocumento9 páginasNullmephamangchokAinda não há avaliações
- Reading The Major Classification and Characteristics of ProtozoaDocumento4 páginasReading The Major Classification and Characteristics of ProtozoaLuis PadillaAinda não há avaliações
- ProstistaDocumento43 páginasProstistaNovelynLozano-EdrosoAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom MoneraDocumento21 páginasKingdom MoneraJohnrey CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- Unit:1 Kingdom Protista General Characters and Classification Upto Classes Locomotory Organelles and Locomotion in ProtozoaDocumento34 páginasUnit:1 Kingdom Protista General Characters and Classification Upto Classes Locomotory Organelles and Locomotion in ProtozoaEgga AndiniAinda não há avaliações
- Protozoa ManuscriptDocumento4 páginasProtozoa ManuscriptLuthfiyyah AnnisaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 (Biology)Documento12 páginasChapter 2 (Biology)MahendraKumarAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom ClassificationDocumento7 páginasKingdom ClassificationAdit KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Biological Classification Xi Chapter 2Documento29 páginasChapter 2 Biological Classification Xi Chapter 2manas100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Botany With Taxonomy: "Kingdom Protista and Algae"Documento10 páginasPharmaceutical Botany With Taxonomy: "Kingdom Protista and Algae"TheQueen SnobberAinda não há avaliações
- ClassificationDocumento3 páginasClassificationNamami DubeAinda não há avaliações
- Invertebrate Biology: by Jane YaweDocumento42 páginasInvertebrate Biology: by Jane YaweANYWAR SIMONAinda não há avaliações
- Science PRTDocumento11 páginasScience PRTTykes xiumAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom PlantaeDocumento14 páginasKingdom Plantaeazileinra OhAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 3 - Group 1 - The Cambrian Explosion and Protistan AncestryDocumento26 páginasChap 3 - Group 1 - The Cambrian Explosion and Protistan AncestryRachel TomlayenAinda não há avaliações
- Protozoa Tugas 1Documento5 páginasProtozoa Tugas 1De shila syailinda maulidaAinda não há avaliações
- Plant KingdomDocumento9 páginasPlant KingdomsanaullahAinda não há avaliações
- Protists FungiDocumento77 páginasProtists FungiEgga AndiniAinda não há avaliações
- Additional: By: Group 1Documento12 páginasAdditional: By: Group 1Wem Louie YapAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom ProtistaDocumento27 páginasKingdom ProtistaHELMA B. JABELLOAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom of Life Paprint PrasyaDocumento11 páginasKingdom of Life Paprint PrasyaZir AdaAinda não há avaliações
- Protists: Protista The Very FirstDocumento5 páginasProtists: Protista The Very FirstclaricejennAinda não há avaliações
- Eukaryotic MicroorganismDocumento11 páginasEukaryotic MicroorganismDency Mae AbreAinda não há avaliações
- Protista: The First EukaryotesDocumento102 páginasProtista: The First EukaryoteshannAinda não há avaliações
- 1.3. Classification of Living ThingsDocumento134 páginas1.3. Classification of Living ThingsLehn Cruz MiguelAinda não há avaliações
- MCB 206 Lecture NoteDocumento22 páginasMCB 206 Lecture NoteKelly KayodeAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdoms and DomainsDocumento19 páginasKingdoms and DomainsJonathan ZhangAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4: ProtistaDocumento8 páginasChapter 4: ProtistaNawal Che IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- ScienceDocumento8 páginasScienceCold CoockiesAinda não há avaliações
- Algae Are A Large and Diverse Group of Simple, Typically Autotrophicorganisms, RangingDocumento2 páginasAlgae Are A Large and Diverse Group of Simple, Typically Autotrophicorganisms, RangingSharina Eunice Lucas DalinAinda não há avaliações
- Biological ClassificationDocumento30 páginasBiological ClassificationSureshAinda não há avaliações
- Algae JupebDocumento6 páginasAlgae JupebDavid AsuquoAinda não há avaliações
- Rajkumar Class 11 Unit 1Documento21 páginasRajkumar Class 11 Unit 1asuhassAinda não há avaliações
- Biological ScienceDocumento21 páginasBiological Sciencehelperforeu100% (3)
- Biological ClassificationDocumento8 páginasBiological Classificationlpc4944Ainda não há avaliações
- Ciliates and Flagellates HardDocumento4 páginasCiliates and Flagellates HardLizaAinda não há avaliações
- Biodiversity and Classification 1Documento33 páginasBiodiversity and Classification 1api-202349222Ainda não há avaliações
- Living Organisms Have Evolved On The Earth Over Millions of Years. There Is A Vast Variety of Living OrganismsDocumento4 páginasLiving Organisms Have Evolved On The Earth Over Millions of Years. There Is A Vast Variety of Living OrganismsAchuth PradeepAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3 - ProtistaDocumento41 páginasLecture 3 - ProtistaLee KaiYangAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of MicroorganismsDocumento11 páginasClassification of Microorganismschinazomanyaora13Ainda não há avaliações
- Kingdom of Life Paprint JannaDocumento11 páginasKingdom of Life Paprint JannaZir AdaAinda não há avaliações
- 3A General - ClassificationDocumento10 páginas3A General - Classificationনাজমুল হক শাহিনAinda não há avaliações
- Group 6 Iyalyn Hannah ElishaDocumento25 páginasGroup 6 Iyalyn Hannah ElishaIrvin EcalnirAinda não há avaliações
- ZOO211 MATERIALS With IntroductionDocumento32 páginasZOO211 MATERIALS With IntroductionAdwale oluwatobi festusAinda não há avaliações
- Biological Classification: Name Anuj Class 11Documento19 páginasBiological Classification: Name Anuj Class 11Anuj MorAinda não há avaliações
- OBLIGATIONS and Contracts SyllabusDocumento4 páginasOBLIGATIONS and Contracts SyllabusAnne Aguilar ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- Web DesignDocumento12 páginasWeb DesignAnne Aguilar ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 The Doctrine of State ImmunityDocumento3 páginasChapter 4 The Doctrine of State ImmunityAnne Aguilar ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- Spanish Era-Japanese RegimeDocumento25 páginasSpanish Era-Japanese RegimeAnne Aguilar ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- HBO PerceptionDocumento4 páginasHBO PerceptionAnne Aguilar ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- Biography of Andres Bonifacio: Date Accessed: 11/25/13Documento9 páginasBiography of Andres Bonifacio: Date Accessed: 11/25/13Anne Aguilar ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- Performance Task Science 1Documento5 páginasPerformance Task Science 1Anne Aguilar ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- 3 "Behold, I Send My Messenger, and He Will Prepare The Way Before Me. and TheDocumento2 páginas3 "Behold, I Send My Messenger, and He Will Prepare The Way Before Me. and TheAnne Aguilar ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- Legis Meaning Law. The Term Law Refers To Statutes Which Are Written Enactments of TheDocumento1 páginaLegis Meaning Law. The Term Law Refers To Statutes Which Are Written Enactments of TheAnne Aguilar ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- AdviserDocumento1 páginaAdviserAnne Aguilar ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- Help Your Kids With ScienceDocumento258 páginasHelp Your Kids With ScienceThihaThant423191% (23)
- Unicellular and Multicellular OrganismDocumento14 páginasUnicellular and Multicellular OrganismDekfa MiefaAinda não há avaliações
- iGCSE-revision-mindmaps-new-specification-double-award ANSWERS Year 10 ModDocumento25 páginasiGCSE-revision-mindmaps-new-specification-double-award ANSWERS Year 10 Modlily wongAinda não há avaliações
- AlgaeDocumento10 páginasAlgaeapi-612669722Ainda não há avaliações
- Prescotts Microbiology 10Th Edition Willey Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento25 páginasPrescotts Microbiology 10Th Edition Willey Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFbob.morris579100% (14)
- IB HL BIO FULL NOTES (Onarıldı)Documento874 páginasIB HL BIO FULL NOTES (Onarıldı)Sıla DenizAinda não há avaliações
- Victory Elijah Christian College: First Monthly Test in Science 5Documento20 páginasVictory Elijah Christian College: First Monthly Test in Science 5Lucille Gacutan AramburoAinda não há avaliações
- Animal and Plant CellsDocumento3 páginasAnimal and Plant CellsKritzel Mae CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- 7.1.5 Unicellualr OrganismsDocumento9 páginas7.1.5 Unicellualr OrganismsA.K MonAinda não há avaliações
- Bio192 General Biology Practical Ii Summary 08024665051Documento45 páginasBio192 General Biology Practical Ii Summary 08024665051Brian CopperAinda não há avaliações
- SBI3U - Textbook Pages and WorksheetsDocumento12 páginasSBI3U - Textbook Pages and WorksheetsMinAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 2 Spec 1b Variety of Living OrganismsDocumento39 páginasLesson 2 Spec 1b Variety of Living OrganismsAditya MishraAinda não há avaliações
- HCCS BIOL 2320 Chapter 1 Lecture Notes 10eDocumento11 páginasHCCS BIOL 2320 Chapter 1 Lecture Notes 10eSridevi DinakaranAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2.1 Interactive Notes 2223Documento8 páginasUnit 2.1 Interactive Notes 2223thomasAinda não há avaliações
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocumento19 páginasProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellReanne MeregildoAinda não há avaliações
- Bato Balani Vol. 20 No. 1 SY 2000-2001Documento24 páginasBato Balani Vol. 20 No. 1 SY 2000-2001Annie MayAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 8 Biology Worksheet 1Documento5 páginasGrade 8 Biology Worksheet 1YonasAinda não há avaliações
- Origin of LifeDocumento14 páginasOrigin of Liferjpusung420Ainda não há avaliações
- Infection by Microorganisms Case Report by Slidesgo (Autosaved)Documento40 páginasInfection by Microorganisms Case Report by Slidesgo (Autosaved)farwanadeem0611Ainda não há avaliações
- SBT 2173: Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Elizabeth Mitaki Lesson 1Documento30 páginasSBT 2173: Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Elizabeth Mitaki Lesson 1Derrick kinyaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Microorganisms?: Microorganisms & Their Effects On Living ThingsDocumento4 páginasWhat Is Microorganisms?: Microorganisms & Their Effects On Living ThingsDevikha PeremelAinda não há avaliações
- DLP 1 Gen Bio Cell TheoryDocumento2 páginasDLP 1 Gen Bio Cell Theoryadrian nenengAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry (The Chemistry of Life)Documento8 páginasBiochemistry (The Chemistry of Life)kimashleymandronAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Virus and Bacteria PDFDocumento14 páginas1 Virus and Bacteria PDFLifw BellAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Taxonomy: DiversityDocumento12 páginasIntroduction To Taxonomy: DiversityRajesh Kumar GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4: ProtistaDocumento8 páginasChapter 4: ProtistaNawal Che IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1Documento65 páginasModule 1csksanjanaAinda não há avaliações
- 2.01 Introduction To Microbiology in Nursing and The MicroscopeDocumento5 páginas2.01 Introduction To Microbiology in Nursing and The MicroscopeNorhaifa Hadji EbrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom Classification 3Documento28 páginasKingdom Classification 3Merium FazalAinda não há avaliações
- Las q3 Week-2 Gen - Bio-1 Viros SnsDocumento10 páginasLas q3 Week-2 Gen - Bio-1 Viros SnsFranzhean Balais CuachonAinda não há avaliações