Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013
Enviado por
Anthony ButlerDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013
Enviado por
Anthony ButlerDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ID:
NAME:
DATE:
CLASS:
Chapter 4 POGIL #1:Spring Scales
DIRECTIONS: Please complete the following questions. READ ALL DIRECTIONS and check in at
Before beginning activity, you should know that
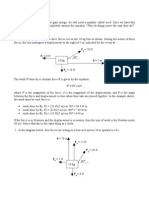
Tension occurs when atoms in a rope, or string, etc are not compressed, but stretched. A rope under tension twangs if you pluck it. On Earth, at sea level, a mass of 1kg = a weight of 9.8 N. The spring scales in this activity will simulate our ropes. The spring scales measure FORCE (in Newtons) Make sure you are looking at the NEWTON side of spring scales, not grams or pounds. You have one 1kg mass (weight of 9.8 N). This will be Nellie. You have 1 ruler. This will be your bar.(In #1, Nellie is NOT hanging from a barso dont use the ruler!) You also have string loops. These will attach the mass to ruler. See diagram below (Your only possible answers for #1-6 are 9.8 N, 4.9 N, and 3.3 Nyou will NOT get these exact readings, because the ruler and spring scales add additional weight to the whole system. However, you should choose the spring scale reading that is closest to 9.8 N, 4.9 N, and 3.3 N for your answers for #1-6.) This is for conceptual, simulation purposes only! Stop at stop sign!
Tension Activityrequires some imagination
DIRECTIONS for #1-6:
Using spring scales, bar, and Nellie, design simulation experiments to answer #1-4 Use what you have learned, your guided notes, supplemental text, and your MIND/common sense to solve for #5-6 (you cannot actually set these up) Your only possible answers for #1-6 are 9.8 N, 4.9 N, and 3.3 N. Stop at Stop Sign!
DIRECTIONS for #7-9: Read #7-8-9. Answer each question;use your Guided Notes, and what you
learned in the above activity to help you. **You are NOT using bars / rulers in this activity!**
Vector Addition of Forces
We just learned about vertically oriented spring scales/tensions. Now, lets learn about spring scales/tensions at an angle. 10. TRY THIS - Using your spring scales, string, and masses, design an experiment to answer the following scenario Which below objects spring scales will have LARGER READINGS? (you can circle answer)
Assume Nellie has the same weight in both pictures
11. Using your spring scales, string, and masses, design an experiment to answer the following scenario What happens to the spring scale readings as you increase the angle between the spring scales? (in other words, pull the spring scales away from each other, like what happened in #10) _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ True or False:The greater the angle BETWEEN the spring scales, the more tension the spring scales experience:_______________________ 12. Suppose you have 2 identical ropes. You suspend one VERTICALLY from a tree. You suspend another HORIZONTALLY between 2 trees. Then, YOU hang from each. a. Which rope is more likely to snap under your weight? ___________________________________________ b. Which rope experiences more tension?__________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ c. True or False: The more tension in a rope, the more likely it is to snap:_________________________
Chapter Review DIRECTIONS : Please READ each question and ANSWER in full.
You do not have to use complete sentences, but please BE COMPLETE in your explanations! THINK CAREFULLY! Question Your Answer 13. When a box of chocolate bars is in mechanical equilibrium - What can be correctly said about all forces that act on it? - Must the net for necessarily be zero? 14. Faina says that an object cannot be in mechanical equilibrium when only a single force acts on it? Do you agree or disagree? WHY? *Make sure you explain WHY you answered the way you did*
15. Justin sets a hockey puck sliding across the ice at a constant speed. Is the puck in equilibrium? Why or Why not?
*Assume ice means a frictionless surface
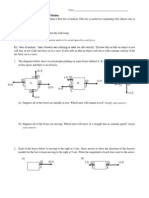
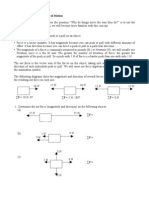
16. How many significant forces act on your physics book when it is at rest on a table? Identify the forces.
*Consider drawing a diagram to help you
17. Why Doesnt the support force that acts on a book resting on a table cause the book to rise from the table?
*Consider drawing a diagram to help you
18. Nicole stands in a bathroom scale and reads her weight. Does the reading change if she stands on one-foot instead of both feet?
19. Alyssa pulls horizontally on a create with a force of 200N, and it slides across the floor at a constant speed in a straight line. How much friction is acting on the create? 20. Lucy lightweight stands with one foot on the bathroom scale and her other foot on a second bathroom scale each scale reads 300N. What is Lucys weight?
*Consider drawing a diagram to help you
*Consider drawing a diagram to help you
21. Harry Heavyweight, who weighs 1200N stands on a pair of bathroom scales so that one scale reads twice as much. What are the scale readings?
*Consider drawing a diagram to help you
Você também pode gostar
- Torque POGIL and WebquestDocumento7 páginasTorque POGIL and WebquestSamuel Jay100% (1)
- Em SpectrumDocumento3 páginasEm SpectrumMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Relativistic EnergyDocumento4 páginasRelativistic EnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- GB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015Documento2 páginasGB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015api-261277442Ainda não há avaliações
- Temperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingDocumento3 páginasTemperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- AccelerationDocumento4 páginasAccelerationMark Prochaska100% (1)
- EnergyDocumento3 páginasEnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Third LawDocumento3 páginasNewton's Third LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Electric ForceDocumento4 páginasElectric ForceMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL - KinematicsDocumento4 páginasPOGIL - KinematicsmagiclcjAinda não há avaliações
- Voltage and ResistanceDocumento4 páginasVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Electric PowerDocumento4 páginasElectric PowerMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Work and PowerDocumento3 páginasWork and PowerMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Free Body DiagramsDocumento4 páginasFree Body DiagramsMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's First LawDocumento3 páginasNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Second LawDocumento5 páginasNewton's Second LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- POGIL: Force: Physics First NameDocumento2 páginasPOGIL: Force: Physics First NameMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Working and PowerDocumento4 páginasWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL: Length ContractionDocumento3 páginasPOGIL: Length ContractionMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Action and ReactionDocumento2 páginasAction and ReactionMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Electric ForcesDocumento4 páginasElectric ForcesMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Pogil Describing MotionDocumento2 páginasPogil Describing Motionapi-259781257100% (1)
- POGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSDocumento3 páginasPOGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSSharmet SolarzAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL Answer KeysDocumento15 páginasPOGIL Answer KeysHolden KodishAinda não há avaliações
- Heating and Phase ChangesDocumento4 páginasHeating and Phase ChangesMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Speed and VelocityDocumento4 páginasSpeed and VelocityMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Temperature and HeatingDocumento4 páginasTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Second LawDocumento4 páginasNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDocumento3 páginasPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Vector ComponentsDocumento4 páginasVector ComponentsMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyDocumento3 páginasMass Defect and Binding EnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- RC Circuit POGIL 2020Documento8 páginasRC Circuit POGIL 2020fnoschese-1Ainda não há avaliações
- POGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumDocumento5 páginasPOGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumsydAinda não há avaliações
- Universal GravitationDocumento3 páginasUniversal GravitationMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Accuracy and Precision POGILDocumento10 páginasAccuracy and Precision POGILmijaggiAinda não há avaliações
- AccelerationDocumento4 páginasAccelerationMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Accuracy Precision Mini POGIL, LabDocumento6 páginasAccuracy Precision Mini POGIL, LabAlistair Morgan100% (1)
- ScaleDocumento4 páginasScaleMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- AccelerationDocumento2 páginasAccelerationMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Pogil - Ke PeDocumento4 páginasPogil - Ke Peapi-259781257Ainda não há avaliações
- Academy For Allied Health Mr. J. Smith: Significant Figures in DataDocumento5 páginasAcademy For Allied Health Mr. J. Smith: Significant Figures in DataJSmithChemteachAinda não há avaliações
- Pogil Theories of UniverseDocumento3 páginasPogil Theories of UniverseChell Queentana FundaAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential Energy - HONORSDocumento3 páginasKinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential Energy - HONORSMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- 29 Electrochemical Cell Voltage - SDocumento4 páginas29 Electrochemical Cell Voltage - SLeia JonesAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyDocumento3 páginasKinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyMark Prochaska50% (2)
- Newton's Third LawDocumento3 páginasNewton's Third LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- POGIL - ThermodynamicsDocumento4 páginasPOGIL - ThermodynamicsMar0% (1)
- Atomic Structure and Quantum Theory POGILDocumento20 páginasAtomic Structure and Quantum Theory POGILmagiclcj100% (1)
- Momentum and ImpulseDocumento10 páginasMomentum and ImpulseYuniar AmaliaAinda não há avaliações
- VectorsDocumento2 páginasVectorsMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential EnergyDocumento3 páginasKinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential EnergyMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's First LawDocumento3 páginasNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Phase-Changes OriginalDocumento4 páginasPhase-Changes Originalapi-293306937Ainda não há avaliações
- 3 - Determining Activity SeriesDocumento5 páginas3 - Determining Activity Seriescarter0% (2)
- Newton's First LawDocumento4 páginasNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaAinda não há avaliações
- Ch06 ISMDocumento67 páginasCh06 ISMThai-Son LeAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 1922 – 1941: Including Presentation Speeches and Laureates' BiographiesNo EverandPhysics 1922 – 1941: Including Presentation Speeches and Laureates' BiographiesAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Equilibrium Chapter 2Documento16 páginasMechanical Equilibrium Chapter 2khalidsattarAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge Science Y7 Workbook + Worksheet Unit 9-10-11 StudentDocumento50 páginasCambridge Science Y7 Workbook + Worksheet Unit 9-10-11 StudentpettagscoAinda não há avaliações
- Become Your Own Balancing Act - Learn to Balance Everything from Brooms to Chairs on Your ChinNo EverandBecome Your Own Balancing Act - Learn to Balance Everything from Brooms to Chairs on Your ChinAinda não há avaliações
- Homework #3 TemplateDocumento18 páginasHomework #3 TemplateAnthony ButlerAinda não há avaliações
- (January 17) The Circular FlowDocumento9 páginas(January 17) The Circular FlowAnthony ButlerAinda não há avaliações
- Application For ValentineDocumento1 páginaApplication For ValentineAnthony ButlerAinda não há avaliações
- CP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Documento4 páginasCP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Anthony ButlerAinda não há avaliações
- Day 5 Snow Day Assignment 02 05 14aDocumento1 páginaDay 5 Snow Day Assignment 02 05 14aAnthony ButlerAinda não há avaliações
- Civil Liberties, Lincoln, The Civil WarDocumento3 páginasCivil Liberties, Lincoln, The Civil WarAnthony ButlerAinda não há avaliações
- 412 1238 1 PBJDocumento16 páginas412 1238 1 PBJAnthony ButlerAinda não há avaliações
- AP Unit 5 Optional Test Asdfessay, 2011-12Documento1 páginaAP Unit 5 Optional Test Asdfessay, 2011-12Anthony ButlerAinda não há avaliações
- American Lit (3) FasdfDocumento1 páginaAmerican Lit (3) FasdfAnthony ButlerAinda não há avaliações
- Life Sciences Grade 10 ATP 2024Documento19 páginasLife Sciences Grade 10 ATP 2024olwe149Ainda não há avaliações
- Dashboard Design Best PracticesDocumento43 páginasDashboard Design Best Practicesgabriel_babiano8003100% (4)
- 3107 Enthusiast Score Advanced Paper-2 (E+H) JADocumento56 páginas3107 Enthusiast Score Advanced Paper-2 (E+H) JAsonu goyalAinda não há avaliações
- Ha400 PDFDocumento1 páginaHa400 PDFZacharias Pavlos50% (2)
- Servo Motor Application: Assignment - 2Documento3 páginasServo Motor Application: Assignment - 2Smakshi ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle Alerts: Mona Lisa SahuDocumento35 páginasOracle Alerts: Mona Lisa Sahuanishokm2992Ainda não há avaliações
- AsdDocumento10 páginasAsdsalman khanAinda não há avaliações
- 03 Traversing Gear SlaveDocumento69 páginas03 Traversing Gear SlaveDeMen NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Model Selection StrategiesDocumento20 páginasModel Selection StrategiesIlinca MariaAinda não há avaliações
- BioavailabilityDocumento16 páginasBioavailabilityTyshanna JazzyNicole BariaAinda não há avaliações
- Noise in Fiber Optic Communication LinksDocumento14 páginasNoise in Fiber Optic Communication Linksian.maximillianAinda não há avaliações
- DLP Math 10 q1 Week 8 Day 1Documento16 páginasDLP Math 10 q1 Week 8 Day 1Henel Mar100% (1)
- AnswerDocumento51 páginasAnswersamAinda não há avaliações
- Art Appreciation Learning ModulesDocumento32 páginasArt Appreciation Learning ModulesJonah ChoiAinda não há avaliações
- 2003 831 01 - Fiber Optic AttenuatorDocumento51 páginas2003 831 01 - Fiber Optic AttenuatorchopanalvarezAinda não há avaliações
- TIMSS Booklet 1Documento11 páginasTIMSS Booklet 1Hrid 2Ainda não há avaliações
- Tesis de Pared de BloquesDocumento230 páginasTesis de Pared de BloquesRobert FinqAinda não há avaliações
- Sound Intensity Level CalculationDocumento10 páginasSound Intensity Level CalculationvenkateswaranAinda não há avaliações
- Os Module1Documento37 páginasOs Module1lingaraj_superstarAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Evaluation TechniquesDocumento6 páginasStructural Evaluation TechniquesMohan NaikAinda não há avaliações
- 支持允許多個 Vlan 的 Trunk 接口。: Techtalk/Td-P/58419Documento6 páginas支持允許多個 Vlan 的 Trunk 接口。: Techtalk/Td-P/58419000-924680Ainda não há avaliações
- Trane ComercialDocumento152 páginasTrane ComercialMartin Bourgon100% (2)
- Cytomat Software InformationDocumento34 páginasCytomat Software InformationCarlosReisAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile Communications: Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDocumento108 páginasMobile Communications: Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systemsradislamy-1Ainda não há avaliações
- Warn 2013-2014 Application GuideDocumento75 páginasWarn 2013-2014 Application Guideapi-238139220Ainda não há avaliações
- Actor-Network Theory and After - Jonh Law and John HassardDocumento14 páginasActor-Network Theory and After - Jonh Law and John HassardGabriel RomanAinda não há avaliações
- Working With Files and Directories: Chapter 11Documento62 páginasWorking With Files and Directories: Chapter 11Abdelahad SatourAinda não há avaliações
- M31M 1 1Documento13 páginasM31M 1 1DannyChaconAinda não há avaliações
- Sequencing Problems 1Documento24 páginasSequencing Problems 1Div SavaliyaAinda não há avaliações