Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
BICD 120 TA Handouts - 2009 - 001
Enviado por
Abraham WalkthewokDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
BICD 120 TA Handouts - 2009 - 001
Enviado por
Abraham WalkthewokDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
BICD 120 Fall 2009 TA: Abraham Tang
Section: Wednesday 2-2:50PM, HSS 2321 abraham.h.tang@gmail.com
OH: email for appointment http://plantbuddy.wordpress.com
Lecture 1
1. According to this class, what is the chemical equation that became possible as a
result of the photosynthetic prokaryotes?
2. According to this class, how many years took place until an important gas
became available for respiration as a result of the equation in the above
question? What was this important gas?
3. How much ATP is yielded in anaerobic growth? How much ATP is yielded in
aerobic growth?
4. What is the chemical equation for oxygen giving rise to the ozone?
5. According to this class, how did O2 and O3 allow evolution to progress?
Lecture 2
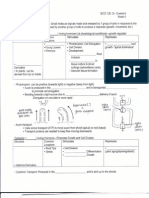
Cell Wall
1. Be able to identify the following: cell wall, plasma membrane, vacuole,
tonoplast membrane, chloroplast, cytoplasm.
2. What is the primary cell wall composed of? Do all plant cells have a primary
cell wall? Is it flexible or rigid? Can cells in this layer divide? (Note: No need to
memorize B 1-4 glucose, xylose, or galactourinase, just understand the concept
that plants use a variety of sugars for structural skeleton.)
3. What is the secondary cell wall composed of? Do all plant cells have a
secondary cell wall? Is it flexible or rigid? Can cells in this layer divide?
4. Be able to identify the following: primary cell wall, secondary cell wall, middle
lamella, plasmodesmata.
5. What happens to lignified cells when they are dehydrated or re-hydrated? What
happens to non-lignified cells when they are dehydrated or re-hydrated?
Plastids
1. What are the four characteristics that all plastids have? (Note: No need to
memorize the numbers in “70 copies of approximately 150kb.”)
2. What are the characteristics of the chloroplast? Be able to identify the following:
outer membrane, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid membrane.
3. There are 2 types of carotenoid pigments. B-carotenes (have/ do not have) –OH
hydroxyl groups in their structure. Xanthophylls (have/ do not have) –OH
hydroxyl groups in their structure.
4. Know the characteristics of and differences between the following plastids:
chloroplast, chromoplast, amyloplast, elaioplast.
5. Be able to reproduce the flowchart starting with the undifferentiated Proplastid,
ending with the different kinds of plastids the Proplastid could differentiate to.
Psalm 103:15 (NKJV)
As for man, his days are like grass;
As a flower of the field, so he flourishes.
Você também pode gostar
- US Navy Dentistry FlyerDocumento1 páginaUS Navy Dentistry FlyerAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Week BlankedDocumento3 páginasWeek BlankedAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Week 8 FullDocumento4 páginasWeek 8 FullAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Week 7 FullDocumento4 páginasWeek 7 FullAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Week 9 FullDocumento2 páginasWeek 9 FullAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Eudicot Flowers: GrassesDocumento12 páginasEudicot Flowers: GrassesAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Week BlankedDocumento3 páginasWeek BlankedAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Week 6 FullDocumento3 páginasWeek 6 FullAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- 2009 Abraham Handout Week 9-10Documento2 páginas2009 Abraham Handout Week 9-10Abraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Week BlankedDocumento3 páginasWeek BlankedAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Amanda's Handout Week 7Documento3 páginasAmanda's Handout Week 7Abraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Week 1 BlankDocumento3 páginasWeek 1 BlankAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Quicktime and A Tiff (Uncompressed) Decompressor Are Needed To See This PictureDocumento6 páginasQuicktime and A Tiff (Uncompressed) Decompressor Are Needed To See This PictureAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Week 3 BlankedDocumento4 páginasWeek 3 BlankedAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Week 2 BlankedDocumento3 páginasWeek 2 BlankedAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- BICD 120 TA Handouts - 2009 - 003Documento3 páginasBICD 120 TA Handouts - 2009 - 003Abraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- BICD 120 TA Handouts - 2009 - 003Documento2 páginasBICD 120 TA Handouts - 2009 - 003Abraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Abraham's Week 10 HandoutDocumento2 páginasAbraham's Week 10 HandoutAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Amanda's Handout Week 6Documento3 páginasAmanda's Handout Week 6Abraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Plantbio - Week9handout-2003Documento4 páginasPlantbio - Week9handout-2003Abraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Amanda's Week 5 HandoutDocumento2 páginasAmanda's Week 5 HandoutAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Three Ways To Support Your ParagraphsDocumento3 páginasThree Ways To Support Your ParagraphsAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Overview of The Neuron: Neurons Vs Somatic CellsDocumento10 páginasOverview of The Neuron: Neurons Vs Somatic CellsAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- Neural Communication Neural Communication: The SynapseDocumento9 páginasNeural Communication Neural Communication: The SynapseAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- The Brain Hypothesis The Neuron HypothesisDocumento10 páginasThe Brain Hypothesis The Neuron HypothesisAbraham WalkthewokAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Douglas I. Johnson (Auth.) - Bacterial Pathogens and Their Virulence Factors (2018, Springer International Publishing)Documento451 páginasDouglas I. Johnson (Auth.) - Bacterial Pathogens and Their Virulence Factors (2018, Springer International Publishing)Alvaro EstupiñánAinda não há avaliações
- Chilli Crop Improvement - Training - IIHRDocumento2 páginasChilli Crop Improvement - Training - IIHRVipasha Tanu RawatAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report # 1 - HOMEOSTASISDocumento17 páginasLab Report # 1 - HOMEOSTASISLaw Light50% (4)
- History of HLA PDFDocumento17 páginasHistory of HLA PDFeseAinda não há avaliações
- G10 Nervous System DLPDocumento5 páginasG10 Nervous System DLPBAD-E, JUSTINE ALEXIS BALBUENAAinda não há avaliações
- Protein Synthesis: How Do We Get Proteins From A Bunch of A's, T'S, C's and G's in DNA??Documento33 páginasProtein Synthesis: How Do We Get Proteins From A Bunch of A's, T'S, C's and G's in DNA??jodyjodzAinda não há avaliações
- The Storage of Tropical Agricultural Products: Agrodok 31Documento84 páginasThe Storage of Tropical Agricultural Products: Agrodok 31Seyha L. AgriFoodAinda não há avaliações
- Sexual and Asexual Reproduction QuizDocumento43 páginasSexual and Asexual Reproduction QuizNesel AlacarAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Biotechnology: A Resource Guide For Biotechnology Club SponsorsDocumento39 páginasMedical Biotechnology: A Resource Guide For Biotechnology Club Sponsorsim_mogerzAinda não há avaliações
- Ks3 Science Paper 57P2 2008Documento28 páginasKs3 Science Paper 57P2 2008odysseym1Ainda não há avaliações
- 6 (2016) Sustainable Valorisation of Seafood By-Products - Recovery of CollagenDocumento15 páginas6 (2016) Sustainable Valorisation of Seafood By-Products - Recovery of CollagenMaría Fernanda Moreno ValdésAinda não há avaliações
- Sponge Bob Genetics PracticeDocumento3 páginasSponge Bob Genetics Practiceapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Science: Second Quarter - Module 2Documento30 páginasScience: Second Quarter - Module 2Mujeres Virglius Pablius89% (9)
- Lesson Plan For Demo TeachingDocumento6 páginasLesson Plan For Demo Teachingjanice alquizar100% (6)
- Sts Finals NotesDocumento10 páginasSts Finals NotesRossy HidalgoAinda não há avaliações
- NLC Physio JULY 2023 McqsDocumento12 páginasNLC Physio JULY 2023 Mcqsshrey100% (1)
- Grouping Living OrganismsDocumento8 páginasGrouping Living OrganismsOsmany MadrigalAinda não há avaliações
- Crone Dahl 2012 NRNDocumento16 páginasCrone Dahl 2012 NRNFernandaAinda não há avaliações
- Borneo Adventure - Tours in Sabah, Sarawak & BruneiDocumento24 páginasBorneo Adventure - Tours in Sabah, Sarawak & BruneiBorneo Adventure100% (5)
- The Reproductive Ecology of Exotic Trachemys Scripta Elegans in An Invaded Area of Southern EuropeDocumento10 páginasThe Reproductive Ecology of Exotic Trachemys Scripta Elegans in An Invaded Area of Southern Europewijayanti chantikaAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Science & EngineeringDocumento38 páginasEnvironmental Science & EngineeringKailash KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Tropical Rainforest PlantsDocumento2 páginasTropical Rainforest PlantsGab PeñaAinda não há avaliações
- HPP Neuro Paper GraserDocumento12 páginasHPP Neuro Paper GraserCaro ErazoAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture On Science and Technology and Society Notes General Paper 2019Documento8 páginasLecture On Science and Technology and Society Notes General Paper 2019DLAinda não há avaliações
- Brock Biology of MicrooDocumento6 páginasBrock Biology of MicrooÇağla Koca100% (1)
- Pheromones Dogs PDFDocumento25 páginasPheromones Dogs PDFRayman RushAinda não há avaliações
- Glycogenesis and GlycogenolysisDocumento55 páginasGlycogenesis and Glycogenolysisclear mindAinda não há avaliações
- How To Write Discussions and Conclusions - PLOSDocumento10 páginasHow To Write Discussions and Conclusions - PLOSkarenAinda não há avaliações
- Erotic MassageDocumento2 páginasErotic MassageKarugu MartinAinda não há avaliações
- Crown-Of-Thorns Starfish and Coral Surveys Using The Manta Tow and Scuba Search TechniquesDocumento42 páginasCrown-Of-Thorns Starfish and Coral Surveys Using The Manta Tow and Scuba Search TechniquesCrassostrea GigasAinda não há avaliações