Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ece203 Modulation-Techniques Eth 1.20 Ac29
Enviado por
netgalaxy2010Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ece203 Modulation-Techniques Eth 1.20 Ac29
Enviado por
netgalaxy2010Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ECE203 Version No.: Prerequisite: 1.
20
Modulation Techniques
L T P C 3 0 2 4
ECE101 Electron Devices and Circuits
Objectives: To introduce the elements of communication systems, describe the generalized block diagram and the types of communication systems. To discuss the concepts of noise, noise voltage, noise temperature, SNR of various modulation schemes. To explain the need for modulation and describe the concepts behind the CW, PM, Angle modulation techniques. To illustrate and explain various pulse modulation techniques Expected Outcome: 1. Analyze the effects of noise in CW &angle modulation 2. Demonstrate the generation and detection of amplitude and angle modulation techniques 3. Identify and compare different pulse modulation techniques Unit I Introduction to Communication System Need and Importance of Communication, Elements of Communication System, Generalized block diagram of communication system, Role of each block (information source, transmitter, channel/communication media, receiver).Types of communication systems- Simplex and Duplex systems, Analog and digital systems, Applications of Electronic Communications, Electromagnetic Spectrum used in communication and various frequency bands, Concept of bandwidth. Unit II Amplitude Modulation Need for modulation amplitude modulation frequency spectrum Power relation different types of modulators SSB and VSB modulation and demodulation. AM transmitters Block diagram functions of each block high level transmitters- Problems. Unit III Angle Modulation Principle of frequency and phase modulation Relation between FM and PM waves Bandwidth of FM Narrow band wide band FM Generation of FM wave Direct and Indirect methods FM transmitters Block diagram functions of each block- Problems. Unit IV Noise, Detection and Receivers Noise in communication and types of noise (External and Internal), Noise voltage, Signal-tonoise ratio, Noise figure, Noise temperature. Noise in CW modulation systems: Receiver model, signal to noise ratio (SNR), noise figure, noise temperature, noise in DSB-SC, SSB, AM & FM receivers, pre-emphasis and de-emphasis Detection Diode detectors Synchronous detection FM detectors slope detectors Phase discriminators Ratio detectors. Receiver different types super hetero dyne receivers Block diagram Choice of IF and Oscillator frequencies Tracking alignment AVC, AFC Receiver characteristics.
Proceedings of the 29th Academic Council [26.4.2013]
320
Unit V Pulse Modulation Systems Sampling theorem Pulse amplitude modulation Channel bandwidth for PAM detection of PAM signals Pulse width modulation generation of PWM and PPM conversion of PWM to PPM detection of PWM and PPM TDM & FDM, problems related to TDM & FDM. Textbooks 1. G. Kennedy, Electronic Communication Systems, McGraw Hill, 2006. 2. Roddy and Coolen, Electronic Communication, Prentice Hall of India, 2005. Reference Books 1. Taub and Schilling, Principles of Communication Systems, McGraw Hill, 2007. 2. Wayne Tomasi, Electronic Communications Systems Fundamentals Through advanced, 5th Edition, Pearson Education, 2005. 3. Wayne Tomasi, Electronic Communications Systems Fundamentals Through advanced, 4th Edition, Pearson Education, 2007. Mode of Evaluation: CAT- I & II, Quizzes, Assignments/ other tests, Term End Examination.
ECE203 List of Experiments: 1. Amplitude modulation 2. Amplitude demodulation 3. Frequency modulation 4. Frequency demodulation 5. Pulse amplitude modulation 6. Pulse width modulation 7. Mixer 8. Pre-emphasis 9. De-emphasis 10. Sample and Hold Circuit.
Modulation Techniques Lab
11. Noise calculation in AM receiver using MATLAB. 12. Noise calculation in FM receiver using MATLAB.
Proceedings of the 29th Academic Council [26.4.2013]
321
Você também pode gostar
- Zoo Animals Coloring BookDocumento58 páginasZoo Animals Coloring BookMadalina LacatusuAinda não há avaliações
- Mwita 03 PH DDocumento385 páginasMwita 03 PH DKaran ChaudhryAinda não há avaliações
- A Dream English BookDocumento9 páginasA Dream English BookAristanti WidyaningsihAinda não há avaliações
- Fashion Coloring Pages Volume 1Documento90 páginasFashion Coloring Pages Volume 1Magda BaloiAinda não há avaliações
- Ijbbs 12-11831 PDFDocumento11 páginasIjbbs 12-11831 PDFnetgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Back To School Interlined Paper PDFDocumento1 páginaBack To School Interlined Paper PDFnetgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- My Alphabet Animals Coloring EbookDocumento27 páginasMy Alphabet Animals Coloring EbookgatirahmanahAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Picture Dictionary PDFDocumento2 páginasSpring Picture Dictionary PDFnetgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- My Angels PDFDocumento36 páginasMy Angels PDFnetgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Mcs Ls SylbsDocumento11 páginasMcs Ls SylbsdukerexAinda não há avaliações
- Cinco de Mayo Interlined Paper PDFDocumento1 páginaCinco de Mayo Interlined Paper PDFnetgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Harriet Kawesa.kDocumento106 páginasHarriet Kawesa.kDr-Shefali GargAinda não há avaliações
- Apple Interlined Paper PDFDocumento1 páginaApple Interlined Paper PDFnetgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Ijsrp p1751 PDFDocumento7 páginasIjsrp p1751 PDFnetgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- SBR 2007 April-160-175 PDFDocumento17 páginasSBR 2007 April-160-175 PDFnetgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Ece207 Analog-Electronic-Circuits Eth 1.20 Ac29Documento2 páginasEce207 Analog-Electronic-Circuits Eth 1.20 Ac29netgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Faa 53 PDFDocumento6 páginasFaa 53 PDFnetgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- 2012 White Paper On Rewards and RecognitionDocumento30 páginas2012 White Paper On Rewards and RecognitionVishnuSimmhaAgnisagarAinda não há avaliações
- Ece206 Signals-And-systems TH 1.20 Ac29Documento2 páginasEce206 Signals-And-systems TH 1.20 Ac29netgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- 233-Concept Note - Incentive SystemsDocumento25 páginas233-Concept Note - Incentive SystemstemekeAinda não há avaliações
- Carolina Mikander - MotivationDocumento51 páginasCarolina Mikander - MotivationFlorrie MitreaAinda não há avaliações
- Ece205 Electrical-And-electronic-measurements TH 1.20 Ac29Documento1 páginaEce205 Electrical-And-electronic-measurements TH 1.20 Ac29netgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Ece204 Analog-circuit-Design Eth 1.10 Ac29Documento2 páginasEce204 Analog-circuit-Design Eth 1.10 Ac29netgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Ece202 Transmission-lines-And-fields TH 1.00 Ac16Documento1 páginaEce202 Transmission-lines-And-fields TH 1.00 Ac16netgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Ece201 Probability Theory and Random Process TH 1.10 Ac29Documento2 páginasEce201 Probability Theory and Random Process TH 1.10 Ac29netgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Ece106 Embedded-c-And-linux TH 1.00 Ac29Documento1 páginaEce106 Embedded-c-And-linux TH 1.00 Ac29netgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Ece104 Discrete Time Systems and Processing TH 1.00 Ac22Documento2 páginasEce104 Discrete Time Systems and Processing TH 1.00 Ac22netgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Ece105 Network-Analysis TH 1.00 Ac29Documento2 páginasEce105 Network-Analysis TH 1.00 Ac29netgalaxy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- DB Operations and NoiseDocumento79 páginasDB Operations and NoisePatrick BelenAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Telecommunications 1Documento34 páginasFundamentals of Telecommunications 1hvrkAinda não há avaliações
- ChigoDocumento104 páginasChigoClaudio Ferreira100% (1)
- MS 2066Documento16 páginasMS 2066Anonymous xokGtxhAinda não há avaliações
- Hitachi Package Oil Free BEBICON G2 SeriesDocumento15 páginasHitachi Package Oil Free BEBICON G2 SeriesSilk RoadAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Corrosion TestingDocumento11 páginasLaboratory Corrosion TestingAnil Kumar TAinda não há avaliações
- Cbe Auger Care and Maintenance ManualDocumento26 páginasCbe Auger Care and Maintenance ManualKrishna Bhanu SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Unit I DC Corrected Version-LibDocumento32 páginasUnit I DC Corrected Version-LibpanthamangalamAinda não há avaliações
- Tapco Mix100 Service Manual Metal Power JackDocumento18 páginasTapco Mix100 Service Manual Metal Power JackRamiro GarAinda não há avaliações
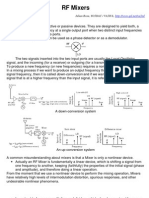
- RF Mixers: RF Mixers Are 3-Port Active or Passive Devices. They Are Designed To Yield Both, ADocumento13 páginasRF Mixers: RF Mixers Are 3-Port Active or Passive Devices. They Are Designed To Yield Both, ARiho Reinhold100% (1)
- IUG Communications Course OverviewDocumento32 páginasIUG Communications Course OverviewbalkyderAinda não há avaliações
- Nbsir73 333Documento460 páginasNbsir73 333Iliuta JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Image Processing 07 Image Restoration Noise RemovalDocumento53 páginasDigital Image Processing 07 Image Restoration Noise Removallakshmi2612Ainda não há avaliações
- AudioSystemComponents Serv EDocumento160 páginasAudioSystemComponents Serv Ebvogeler4007Ainda não há avaliações
- BS EN 12668-1 - InstrumentsDocumento46 páginasBS EN 12668-1 - InstrumentsRenier Koen100% (2)
- Satellite Lab ManualDocumento29 páginasSatellite Lab Manualaduvey0% (1)
- 07bDocumento30 páginas07bJorge A. Perez YebraAinda não há avaliações
- Unit6-DETECTION AND ESTIMATION PDFDocumento24 páginasUnit6-DETECTION AND ESTIMATION PDFAdal ArasuAinda não há avaliações
- AFCI Technical White PaperDocumento16 páginasAFCI Technical White PaperSon NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Channel Multiplexing Bandwidth Data Rateand CapacityDocumento9 páginasChannel Multiplexing Bandwidth Data Rateand CapacitysamiAinda não há avaliações
- Information Theory & Source CodingDocumento14 páginasInformation Theory & Source CodingmarxxAinda não há avaliações
- Sound Multiplex Demodulator IC For TV in The North American MarketDocumento11 páginasSound Multiplex Demodulator IC For TV in The North American MarketmellamofelipemcAinda não há avaliações
- Antennas & Wave Propagation: B.Tech (Iii Year - I Sem)Documento144 páginasAntennas & Wave Propagation: B.Tech (Iii Year - I Sem)Jayant Kumar AryaAinda não há avaliações
- Strahlenfolter Stalking - TI - Mind Control, Electronic Attack, Unusual, Strange Device TypesDocumento31 páginasStrahlenfolter Stalking - TI - Mind Control, Electronic Attack, Unusual, Strange Device TypesWirklichkeit-kommtAinda não há avaliações
- Tbm859cf PDFDocumento18 páginasTbm859cf PDFCarlos ParapeAinda não há avaliações
- Lab BerDocumento3 páginasLab Berfernando lindeAinda não há avaliações
- Channel Capacity NotesDocumento26 páginasChannel Capacity NotesLOmesh SaHuAinda não há avaliações
- CT Whitepaper Stellar DetectorDocumento8 páginasCT Whitepaper Stellar DetectorsitalekshmiAinda não há avaliações
- Am Am: QRP QRPDocumento6 páginasAm Am: QRP QRPagama1188Ainda não há avaliações
- Advanced Electronic Communications Systems Wayne Tomasi Sixth Edition Advanced Electronic ...Documento66 páginasAdvanced Electronic Communications Systems Wayne Tomasi Sixth Edition Advanced Electronic ...Kevin Valenzuela100% (1)