Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Capability Study With His To Gram Excel Template
Enviado por
nithyachatsuTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Capability Study With His To Gram Excel Template
Enviado por
nithyachatsuDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
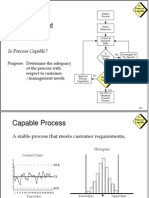
Conducting a Capability Study:
The purpose of a capability study is to estimate the process average and variation, relative to the specified tolerances. To begin a capability study, identify the product, the characteristic, the tolerances, and the measurement method. Capability studies are frequently performed using 30 consecutively-produced units. If the units for the study are not consecutive, note the times, groupings, and conditions under which the units were produced. Measure the units in time-order-produced if possible, to permit deeper investigation if desired. Enter the tolerance maximum (if applicable) and minimum (if applicable) on the form where shown. Characteristics with only a minimum tolerance are usually "higher is better" characteristics. Characteristics with only a maximum tolerance are usually "lower is better" characteristics. Characteristics with both a maximum and minimum tolerance are usually "nominal is best" characteristics. Some characteristics are special "closer to tolerance is better" characteristics. Examples are speed limits and gear diameters. Determine which direction the characteristic is supposed to be "better," to be able to interpret the capability study. Enter the 30 measurement readings on the form where shown. The template will automatically construct a histogram to visually estimate the shape of the process distribution, relative to the to Note the Cp ratio, which is the ratio of the tolerance width to the width of 6-sigma of process variation. A Cp of less than 1.33 signals trouble staying within the tolerance. A Cp greater than 2.0 signals a good potential to meet the to The Cp ratio is independent of the location of the process average. Processes with off-target averages can still score good Cp If the characteristic has only a one-sided tolerance, the Cp ratio does not apply. Note the Cpk, which is the distance from process average to closest tolerance, divided by 3-sigma. A Cpk of less than 1.33 signals trouble with exceeding the closest tolerance. A Cpk greater than 2.0 signals a good safety mar Both Cp and Cpk are estimates based on random sampling, and are subject to variation from one sample to another sample. Histogram distributions with unexpected shapes deserve investigation. Histograms with unexpected shapes can be caused by process average changes during production, mixing of two or more proc Process capability should be studied in coordination with process control (SPC) in order to evaluate both capability and stability Process capability estimates are misleading if the process is subject to significant special causes (changes in average or variat To avoid producing defects, the process needs BOTH capability AND stability.
to the specified tolerances. measurement method.
der which the units were produced.
characteristics. are speed limits and gear diameters. ret the capability study.
process distribution, relative to the tolerance limits.
ignals a good potential to meet the tolerances. get averages can still score good Cp ratios.
er than 2.0 signals a good safety margin to the closest tolerance. om one sample to another sample.
roduction, mixing of two or more processes, and many other causes. evaluate both capability and stability of the process. causes (changes in average or variation).
Capability Study Instructions: Re-name & save file, delete old data, enter Maximum, Minimum, and up to 30 data readings in Column "B" Part # or SKU#: 124789 Product name: Housing Characteristic name: Flange diameter Specification Maximum: Specification Minimum: Data Reading 1 Data Reading 2 Data Reading 3 Data Reading 4 Data Reading 5 Data Reading 6 Data Reading 7 Data Reading 8 Data Reading 9 Data Reading 10 Data Reading 11 Data Reading 12 Data Reading 13 Data Reading 14 Data Reading 15 Data Reading 16 Data Reading 17 Data Reading 18 Data Reading 19 Data Reading 20 Data Reading 21 Data Reading 22 Data Reading 23 Data Reading 24 Data Reading 25 Data Reading 26 Data Reading 27 Data Reading 28 Data Reading 29 Data Reading 30 Operation #: 20 Operation name: drilling Workstation #: 456123 Histogram Maximum: Coded data point: Histogram Minimum: 0.53096 10 Upper bound cell 20 10.5952381 Upper bound cell 19 0.5276 9.404761905 Upper bound cell 18 8.80952381 Upper bound cell 17 0.52424 8.214285714 Upper bound cell 16 10.5952381 Upper bound cell 15 0.52088 11.19047619 Upper bound cell 14 11.78571429 Upper bound cell 13 10.5952381 Upper bound cell 12 0.51752 11.19047619 Upper bound cell 11 10 Upper bound cell 10 0.51416 12.38095238 Upper bound cell 9 8.80952381 Upper bound cell 8 0.5108 9.642857143 Upper bound cell 7 11.78571429 Upper bound cell 6 11.19047619 Upper bound cell 5 0.50744 8.80952381 Upper bound cell 4 9.702380952 Upper bound cell 3 0.50408 10.29761905 Upper bound cell 2 8.214285714 Upper bound cell 1 0.50072 7.619047619 Lower bound cell 1 7.023809524 10.29761905 10.29761905 Average: 12.97619048 Standard Deviation: -296.547619 Upper 3 Sigma Value: -296.547619 Lower 3 Sigma Value: -296.547619 Cp Index: -296.547619 Cpk: -296.547619 Average to max Person: Shift: Date: 0.5318 0.4982 0.5318 0.53012 0.52844 0.52676 0.52508 0.5234 0.52172 0.52004 0.51836 0.51668 0.515 0.51332 0.51164 0.50996 0.50828 0.5066 0.50492 0.50324 0.50156 0.49988 0.4982 John Smith 1 1/10/05
0.529 0.501 0.515 0.516 0.514 0.513 0.512 0.516 0.517 0.518 0.516 0.517 0.515 0.519 0.513 0.5144 0.518 0.517 0.513 0.5145 0.5155 0.512 0.511 0.51 0.5155 0.5155 0.52
Count above 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 7 13 18 23 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25
Cell Midpoint 0.53096 0.52928 0.5276 0.52592 0.52424 0.52256 0.52088 0.5192 0.51752 0.51584 0.51416 0.51248 0.5108 0.50912 0.50744 0.50576 0.50408 0.5024 0.50072 0.49904
0.515096 0.002475964 0.522523893 0.507668107 1.884787421 1.871863165 0.013904
"# of Sigmas Capability": 2-tail PPM "Traditional": 1-tail PPM "Traditional": PPM "w/1.5 Sigma Shift":
5.6 0.019589323 0.009794662 19.30955567
Você também pode gostar
- Capability Study With His To Gram Excel TemplateDocumento3 páginasCapability Study With His To Gram Excel TemplateMelissa MurrayAinda não há avaliações
- Conducting A Capability StudyDocumento3 páginasConducting A Capability Studysubbu0815Ainda não há avaliações
- Process Capability and SPC : Operations ManagementDocumento43 páginasProcess Capability and SPC : Operations ManagementRahul KhannaAinda não há avaliações
- CpkGuide 0211 TECH1Documento11 páginasCpkGuide 0211 TECH1d_flamarich7358Ainda não há avaliações
- SAA ReportDocumento54 páginasSAA ReportSonny AguilarAinda não há avaliações
- CP and CPK SolutionDocumento5 páginasCP and CPK SolutionlawtonAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Note 8: Process Capability and Statistical Quality ControlDocumento46 páginasTechnical Note 8: Process Capability and Statistical Quality ControlVipin NairAinda não há avaliações
- SPCDocumento19 páginasSPCAmandeep SinghAinda não há avaliações
- 5.2 Process Capability Analysis Rev2ADocumento8 páginas5.2 Process Capability Analysis Rev2APollyAinda não há avaliações
- Six Sigma Vs TaguchiDocumento14 páginasSix Sigma Vs TaguchiemykosmAinda não há avaliações
- Process Capability: Chapter OutlineDocumento5 páginasProcess Capability: Chapter OutlineFernandoAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Data? Data Is A Set of Values of Subjects With Respect To Qualitative or Quantitative VariablesDocumento10 páginasWhat Is Data? Data Is A Set of Values of Subjects With Respect To Qualitative or Quantitative Variablesvinothkumar441Ainda não há avaliações
- CPK - Vs PPMDocumento21 páginasCPK - Vs PPMazadsingh1100% (1)
- SPC Basics: Presented By: Tariq KhurshidDocumento50 páginasSPC Basics: Presented By: Tariq Khurshidtkhurshid3997Ainda não há avaliações
- Study of Feasibility of Six Sigma Implementation in A Manufacturing Industry: A Case StudyDocumento5 páginasStudy of Feasibility of Six Sigma Implementation in A Manufacturing Industry: A Case StudyThasarathan RavichandranAinda não há avaliações
- Six Sigma STDocumento52 páginasSix Sigma STsaravanan tAinda não há avaliações
- SPC For Correlated Variables PDFDocumento15 páginasSPC For Correlated Variables PDFEdAinda não há avaliações
- Software Verification: ConclusionsDocumento5 páginasSoftware Verification: Conclusionsdcuong9gAinda não há avaliações
- SPC ForDocumento116 páginasSPC ForRohit JanardananAinda não há avaliações
- Process Capability Indices PDFDocumento6 páginasProcess Capability Indices PDFasamadhAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Control Chart For VariablesDocumento66 páginasChapter 3 Control Chart For VariablesRitam PalAinda não há avaliações
- Wave Soldering Thermal Profiling Management Improvement: Process Improvement Team ProjectDocumento26 páginasWave Soldering Thermal Profiling Management Improvement: Process Improvement Team ProjectLamjed WhibiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 of One - Theory of Control ChartDocumento36 páginasChapter 2 of One - Theory of Control ChartAmsalu SeteyAinda não há avaliações
- 6.4 Process CapabilityDocumento13 páginas6.4 Process CapabilitychuszAinda não há avaliações
- Control SystemDocumento10 páginasControl Systemrajeswari_ece07Ainda não há avaliações
- Process Capability: 99.73% of parts lie within the 6 σ limitsDocumento10 páginasProcess Capability: 99.73% of parts lie within the 6 σ limitsrm_muruganAinda não há avaliações
- Documento Sin NombreDocumento4 páginasDocumento Sin Nombregeoffreyporto6706Ainda não há avaliações
- 6e ControlchartsforvariablesDocumento39 páginas6e ControlchartsforvariablesdeepikaAinda não há avaliações
- Lean Six Sigma e SMCDocumento5 páginasLean Six Sigma e SMCzettiAinda não há avaliações
- Taguchi Method AssignmentDocumento6 páginasTaguchi Method AssignmentpuriAinda não há avaliações
- CPK Guide 0211 TECH1Documento11 páginasCPK Guide 0211 TECH1Mark LacroAinda não há avaliações
- Software Verification: ConclusionsDocumento5 páginasSoftware Verification: ConclusionsGeruEMAinda não há avaliações
- Process Capability - ToolDocumento26 páginasProcess Capability - ToolFouzan SoniwalaAinda não há avaliações
- The Quality Improvement Model: Is Process Capable?Documento19 páginasThe Quality Improvement Model: Is Process Capable?shafie_buangAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding How CP and CPK Are UsedDocumento4 páginasUnderstanding How CP and CPK Are UsedisotempAinda não há avaliações
- Someshewar Sahai Sinha 027 F13 SQCR Practical File 6.1,7.4,8.2,9.1,10.1-10.4 and 10.9Documento12 páginasSomeshewar Sahai Sinha 027 F13 SQCR Practical File 6.1,7.4,8.2,9.1,10.1-10.4 and 10.9PappuAinda não há avaliações
- Six Sigma Methods and Formulas For Successful Quality ManagementDocumento4 páginasSix Sigma Methods and Formulas For Successful Quality ManagementjesustorresAinda não há avaliações
- Basics of CapabilityDocumento18 páginasBasics of Capabilitymancheung6429Ainda não há avaliações
- Quick Guide To Precision Measuring Instruments: Catalog No. E11003Documento52 páginasQuick Guide To Precision Measuring Instruments: Catalog No. E11003Manz ManingoAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Experiments Via Taguchi Methods Orthogonal ArraysDocumento21 páginasDesign of Experiments Via Taguchi Methods Orthogonal ArraysRohan ViswanathAinda não há avaliações
- CPK GuidelinesDocumento2 páginasCPK GuidelinesNavnath Tamhane100% (1)
- Iso ManualDocumento9 páginasIso ManualSanjay MalhotraAinda não há avaliações
- Hygk307 ManualDocumento16 páginasHygk307 Manualkenlavie1Ainda não há avaliações
- 105 0002E CapabilityDocumento34 páginas105 0002E CapabilityFJNovaes454Ainda não há avaliações
- Thesis MsstateDocumento8 páginasThesis Msstatehollyhernandezdurham100% (2)
- Advanced Process CapabilityDocumento11 páginasAdvanced Process Capabilitycheqjieja100% (1)
- IE Lab ManualDocumento61 páginasIE Lab Manualniel upadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- Statistical Process ControlDocumento42 páginasStatistical Process ControlErick Bok Cang YeongAinda não há avaliações
- Ss Case StudyDocumento19 páginasSs Case StudyPriyaprasad PandaAinda não há avaliações
- Tensile Testing Basics Tips TrendsDocumento5 páginasTensile Testing Basics Tips TrendsJonathan Elias MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- A Guide To Process Capability (CP, CPK) and Process Performance (PP, PPK) - 1factoryDocumento8 páginasA Guide To Process Capability (CP, CPK) and Process Performance (PP, PPK) - 1factoryabhijit612Ainda não há avaliações
- Intro To DMAICDocumento40 páginasIntro To DMAICKool BhardwajAinda não há avaliações
- Managing the Testing Process: Practical Tools and Techniques for Managing Hardware and Software TestingNo EverandManaging the Testing Process: Practical Tools and Techniques for Managing Hardware and Software TestingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (8)
- Diagnosis and Robust Control of Complex Building Central Chilling Systems for Enhanced Energy PerformanceNo EverandDiagnosis and Robust Control of Complex Building Central Chilling Systems for Enhanced Energy PerformanceAinda não há avaliações
- Configuration Management for Senior Managers: Essential Product Configuration and Lifecycle Management for ManufacturingNo EverandConfiguration Management for Senior Managers: Essential Product Configuration and Lifecycle Management for ManufacturingAinda não há avaliações
- Six Sigma Green Belt, Round 2: Making Your Next Project Better than the Last OneNo EverandSix Sigma Green Belt, Round 2: Making Your Next Project Better than the Last OneAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Predictive Analytics with JMP, Third EditionNo EverandFundamentals of Predictive Analytics with JMP, Third EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Downloads - Questions & Answers - PDF FormatDocumento6 páginasDownloads - Questions & Answers - PDF FormatnithyachatsuAinda não há avaliações
- Auto Mouse ClickerDocumento5 páginasAuto Mouse ClickernithyachatsuAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring Your Process Capability: PreambleDocumento13 páginasMeasuring Your Process Capability: PreamblejayeshjpillaiAinda não há avaliações
- FL at Backs Hotfi X, FL at Backs No Hotfi X: ColoursDocumento2 páginasFL at Backs Hotfi X, FL at Backs No Hotfi X: ColoursnithyachatsuAinda não há avaliações
- Amount CalculatorDocumento9 páginasAmount CalculatornithyachatsuAinda não há avaliações
- Round Stones, Sew-On Stones, Fancy Stones, Buttons: ColoursDocumento2 páginasRound Stones, Sew-On Stones, Fancy Stones, Buttons: ColoursnithyachatsuAinda não há avaliações
- Capability Study With His To Gram Excel TemplateDocumento3 páginasCapability Study With His To Gram Excel TemplatenithyachatsuAinda não há avaliações
- Yearly Calendar Blue LandscapeDocumento1 páginaYearly Calendar Blue LandscapenithyachatsuAinda não há avaliações
- Audit Checklist (ISO) Internal AuditDocumento2 páginasAudit Checklist (ISO) Internal Auditnithyachatsu100% (1)
- Periodic TableDocumento13 páginasPeriodic TablenithyachatsuAinda não há avaliações
- Home Budget Worksheet: Income CategoriesDocumento3 páginasHome Budget Worksheet: Income CategoriesnithyachatsuAinda não há avaliações