Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Astronomy Sawah
Enviado por
Jessica AngelinaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Astronomy Sawah
Enviado por
Jessica AngelinaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ISLAMIC/ARABIC ASTRONOMY
RIHAB SAWAH
MCCA-MCGE Title VI-A Year Two North Africa
Na e! Rihab Sawah Colle"e! Moberly area Community College Co#r$e Title a%& N# 'er! PHY 262 - Introduction to Astronomy Mo&#le Title
Islamic/Arabic Astronomy
Se e$ter Offere&( )eli*er+ Metho&$( E%roll e%t
his module will be used in online astronomy courses o!!ered in summer" !all and s#ring semesters as well as traditional in-class astronomy courses o!!ered in !all and s#ring semesters$ he #ro%ect will be launched in summer 2&&'$ he module will be in!used throughout the course material where it !its with other to#ics in the curriculum$ A(erage enrollment in those classes is )*-2+ students$
Co#r$e O',ecti*e$
In a ty#ical introductory astronomy course there is usually a cha#ter on the history o! astronomy$ Almost all astronomy te,tboo-s co(er ancient .ree- astronomy then %um# to the Renaissance" o(erloo-ing about *&& years o! astronomical de(elo#ments /during the Islamic era0*th through )+th centuries1 that #a(ed the way !or the Renaissance" and contributed to the science in ways we still use today$ his module will not only in!use the course with an additional global com#onent" it will introduce the ma%or Islamic astronomical contributions during medie(al time$ It will guide students through (arious acti(ities that would enable them to learn the !ollowing2 )$ 2$ he language o! science during the Islamic era0Arabic0 that introduced star names still in use today$ he de(elo#ments in mathematical astronomy that #a(ed the way !or Co#ernicus3s wor-$ his will introduce im#ortant Islamic astronomers such as alusi and Ibn al-Shatir whose wor- was a ste##ing stone !or Co#ernicus3s mathematical model o! the hea(ens$ he origin o! the obser(atory as a research institution$ 6bser(ational instruments used by Muslim astronomers such as astrolabes" s#herical astrolabes" 7uadrant" se,tants and armillaries$ 8ew and more accurate astronomical tables by Muslim astronomers that re#laced the .ree- Almagest$
4$ 5$ +$
ISLAMIC/ARABIC ASTRONOMY 6$
RIHAB SAWAH
he history o! the 24$+o a,ial tilt o! #lanet 9arth that we still use today )5&& years a!ter its calculation by Muslim astronomers$ :$ he brightest su#erno(a recorded in human history in )&&6 /S8)&&61$ Accurate record o! this su#erno(a was #ro(ided by Ibn Ridwan !rom 9gy#t$ *$ he e,#lanation to the ;Moon Illusion< /Ibn al-Haytham or Alhacen1$ '$ he e,#lanation o! how rainbows !orm /al-=arisi1$ )&$ 8ames o! craters on the moon that are named a!ter Muslim astronomers !or their contribution to the science o! astronomy$ /e$g$ Alha>en crater" 8asireddin crater" Abul!eda crater" etc$1
Narrati*e )e$cri-tio% a%& Ba$ic O#tli%e
Students will be introduced to Islamic astronomy through a guided PowerPoint #resentation which will lay the !oundation !or !uture student wor-$ he PowerPoint is designed to introduce them to the conce#t o! Islamic?Arabic astronomy and to gi(e them a !la(or o! some the material they will be researching later$ he material included could be used in both in-class and online !ormat$ @hen class discussion is called !or" it would be re#laced by online hreaded Aiscussions to create a similar discussion en(ironment in the class$ Most o! the wor- will be #roduced by students as they do research to address the to#ics #resented to them /see Student Assignments1$
St#&e%t A$$i"% e%t$
)$ Arabic was the language o! science during the medie(al times re!erred to as the .olden Age o! Islam /!rom 622 B )5'2 AA1$ It was a time o! ama>ing scholarshi# and research shared by Muslims" Christians and Cews in the Islamic 9m#ire$ he Islamic 9m#ire s#anned !rom western India in the east" to western A!rica in the west" including the #art o! S#ain -nown then as Andalusia /Islamic S#ain1$ he de(elo#ments in science included di!!erent !ields such as mathematics" astronomy" #hysics" medicine" #harmacy" chemistry" engineering" and many more$ hese ad(ancements in the sciences gradually reached the rest o! 9uro#e /through Islamic S#ain and Italy1 and brought about the age -nown as the Renaissance$ Since all scienti!ic boo-s in the Islamic 9m#ire were documented in Arabic" Arabic words made their way into other languages$ here are o(er 4&&& words in the 9nglish language that are o! Arabic origin$ =ind ten 9nglish words in astronomy that are o! Arabic origin$ Dist the meaning o! the words and the original Arabic word they are deri(ed !rom$ 2$ 8icholas Co#ernicus introduced to astronomy a new model o! the hea(ens -nown as the heliocentric model /where he held the Sun in a !i,ed #osition rather than 9arth1$ Co#ernicus3s heliocentric system was not born in isolation rather it was the integration o! many (iews" models and theorems that had #receded and greatly
ISLAMIC/ARABIC ASTRONOMY
RIHAB SAWAH
in!luenced its author$ He was moti(ated by the !laws he disco(ered in the Ptolemaic .ree- astronomical models to de(elo# a new system !ree o! such inadmissible mista-es$ He de(elo#ed a mathematically harmonious system in a sense that he eliminated the arbitrary mathematical re#resentations o! the Ptolemaic .ree- system$ It was this mathematical harmony that made Co#ernicus3s wor- credible in the eyes o! his colleagues in the )6th century /not that he held the Sun !i,ed1$ Some o! those im#ortant in!luences on Co#ernicus3s mathematical models can be seen in the Islamic astronomical #resence in the theorems he used$ his demonstrates the centrality and the degree o! assimilation o! these theorems and models in his wor-$ wo im#ortant Muslim astronomers are im#ortant in relation to Co#ernicus2 al- usi and Ibn al-Shatir$ Research the connections between the two Muslim astronomers and Co#ernicus" and write a #a#er in which you discuss the im#ortance o! the wor- o! al- usi and Ibn alShatir as a ste##ing stone !or the de(elo#ment o! mathematical astronomy$ 4$ 6bser(atories are used today as international research institutions around the globe$ hey o!!er scientists o##ortunities to do collaborati(e wor- in astronomy$ @rite a #a#er in which you research the earliest international obser(atory that was set u# as a research institution$ Auring which era was it builtE @hat was its nameE @ho was its !ounderE @ho were its #atronsE @hat #ur#ose did this institution ser(e besides obser(ing the stars and #lanetsE @hat other obser(atories were modeled a!ter this great oneE How did Islamic obser(atories in!luence the course o! astronomy research until our modern timesE 5$ Dist at least three obser(ational instruments used by Muslim astronomers during the Middle Ages" and brie!ly e,#lain how they are used$ +$ he one im#ortant astronomical table the Muslims inherited !rom the .ree-s a!ter they translated all o! .ree- science to Arabic was the wor- by the .ree- scientist Ptolemy$ he boo- became -nown by its translated Arabic name" Almagest$ Dater Muslim astronomers" using more accurate obser(ational instruments they built" !ound many errors in the astronomical tables o! the Almagest$ hey com#iled new data based on their new and more accurate obser(ations o! the stars and #lanets$ Soon a!ter that" those new tables re#laced the Almagest due to their higher accuracy$ Aiscuss two such Islamic astronomical tables" the name o! the astronomer who made those new astronomical obser(ations" and the location and year they were #ublished$ he ancient .ree- astronomers had disco(ered the a,ial tilt o! #lanet 9arth$ heir obser(ations #roduced a calculation o! the tilt o! 25 o$ oday" we -now that the tilt o! our #lanet3s a,is is e,actly 24$+o$ Research the history o! the 24$+o a,ial tilt o! #lanet 9arth that we still use today )5&& years a!ter its calculation$ =ind out which time #eriod and where astronomers made this calculation$
6$
ISLAMIC/ARABIC ASTRONOMY :$
RIHAB SAWAH
he brightest su#erno(a recorded in human history in )&&6 /S8)&&61$ Research the astronomer who #ro(ided an accurate record o! this su#erno(a$ @hat was his nameE @here and when did he li(eE he #henomenon commonly -nown as the ;Moon Illusion< is when the !ull moon a##ears (ery large near the hori>on as it is rising" then a##ears smaller once it has ascended higher in the s-y$ 9,#lain this #henomenon" and #ro(ide the name o! the scientist who !irst e,#lained this ;Moon Illusion<$ @here and when did he li(eE
*$
'$ 9,#lain how rainbows !orm /white light !rom the Sun s#reading into all the (isible colors1$ @hat was the name o! the scientist who !irst #ro(ided a satis!actory e,#lanation o! rainbowsE @here and when did he li(eE )&$ he moon is hea(ily cratered$ Many o! the moon3s craters are named a!ter scientists who contributed to the science o! astronomy$ Many o! those craters are named a!ter Muslim astronomers$ =ind three craters on the moon named a!ter three Muslim astronomers$ @hat are their namesE @hat was their contribution to the science o! astronomyE
O*erall A$$e$$ e%t
Students will #roduces two #a#ers in this module" and eight discussion to#ics$ he #a#ers would be turned in !or grading$ Howe(er" the eight discussion to#ics would be used !or short one-minute re#orting in class /or as a hreaded Aiscussion in the online astronomy courses1$ he #a#ers and discussion to#ics would constitute F)5 o! students3 grade$ he two #a#ers would ma-es :F o! the total class grade" and the discussion to#ics the other :F$ I will also use the itle GI-A 9ntry?9,it Classroom Assessment" and will administer it be!ore and a!ter the in!usion o! the module$
E*al#ati%" St#&e%t$ Wor. o% A$$i"% e%t$
he #a#ers must #ortray student -nowledge in the research to#ic and re!lect their e!!ort in !ind the in!ormation needed$ It will be assigned a grade based on the #resentation and the com#leteness o! the material$ he discussion to#ics would be graded based on student #re#aredness and o(erall -nowledge o! the sub%ect assigned to them !or research$
Tech%olo"+ Nee&$
Instructor needs to ha(e PowerPoint ca#abilities /com#uter and o(erheard #ro%ector1 and Internet access$
ISLAMIC/ARABIC ASTRONOMY
RIHAB SAWAH
Re$o#rce$ for St#&e%t$
Al-Hassani" Salim $ S$ 1001 Inventions: Muslim Heritage in our World. HI2 =oundation !or Science" echnology and Ci(ili>ation" 2&&:$ J.oldstein" Kernard$ Copernicus and the rigin o! his Heliocentric "niverse. Cournal !or the History o! Astronomy2 44 /2&&21 ##$ 2)'-4+ .oldstein" homas$ #a$n o! Modern %cience. Koston2 Houghton" Mi!!lin" )'*&$ Hayes" Cohn$ &he 'enius o! Arab Civili(ation: %ource o! )enaissance. 8ew YorHni(ersity Press" )':+$ JHartner"@illy$ ;Copernicus* the Man* the Wor+* and Its History"< Proceedings o! the American Philoso#hical Society )):" no$ 6 /)':41" ##$ 5)4-522$ JIennedy" 9$ S$ ;,ate Medieval -lanetary &heory"< Isis" +:" no$ 4 /)'661$ JIennedy" 9$ S$ Koo- re(iew o! ;&he bservatory in Islam and Its -lace in the 'eneral History o! the bservatory by Aydin %ayili"< Isis" +4" no$ 2 /)'621$ Ihaleel" Iasem$ %cience in the .ame o! 'od$ Ku!!alo .ro(e2 Inowledge House" 2&&4$ JRoberts" Gictor$ &he %olar and ,unar &heory o! Ibn al/%hatir: A -re/Copernican Copernican Model. Isis2 5* /)'+:1 ##$ 52*-42$ Sabra" Abdelhamid I$ &he 0nterprise o! %cience in Islam: .e$ -erspectives. Cambridge2 MI Press" 2&&4$ JSaliba" .eorge$ An bservational .oteboo+ o! a &hirteenth/Century Astronomer$ Isis :5 /)'*412 4** - 5&)$ Saliba" .eorge$ A History o! Arabic Astronomy: -lanetary &heories during the 'olden Age o! Islam$ 8ew Yor-2 8YH Press" )''5$ Saliba" .eorge$ )ethin+ing the )oots o! Modern %cience: Arabic %cienti!ic Manuscripts in 0uropean ,ibraries$ Center !or Contem#orary Studies" .eorgetown Hni(ersity" )'':$ Saliba" .eorge$ Whose %cience is Arabic %cience in )enaissance 0urope1 htt#2??www$columbia$edu?Lgas)?#ro%ect?(isions?case)?sci$)$html" )'''$ JSaliba" .eorge$ 'ree+ Astronomy and the Medieval Arabic &radition. American Scientist$ Culy-August 2&&2246&-46:
ISLAMIC/ARABIC ASTRONOMY
RIHAB SAWAH
JSaliba" .eorge$ ;)evisiting the Astronomical Contacts 2et$een the World o! Islam and )enaissance 0urope: &he 2y(antine Connection"< 6ccult Sciences in Ky>antium" ed$ Paul Magdalino" Maria Ma(roudi" Da Pomme AM6r" 2&&6$ Saliba" .eorge$ Islamic %cience and the Ma+ing o! the 0uropean )enaissance$ Cambridge2 he Massachusetts Institute o! echnology Press" 2&&:$ Saudi Aramco @orld Maga>ine$ %cience in al/Andalus$ www$saudiaramcoworld$com" Al-Andalus" Com#ilation Issue$ Saudi Aramco @orld Maga>ine$ &he %cholar3s %upernova$ www$saudiaramcoworld$com" Culy-August 2&&6$ Saudi Aramco @orld Maga>ine$ )ediscovering Arabic %cience$ www$saudiaramcoworld$com" May-Cune 2&&:$ Sayili" Aydin$ &he bservatory in Islam and its -lace in the 'eneral History o! the bservatory$ An-ara2 Nr- arih Iurumu KasOme(i" )'6&$
J Articles to be #ro(ided to students electronically /attached1$
ISLAMIC/ARABIC ASTRONOMY
RIHAB SAWAH
Re$o#rce$ /$e& for )e*elo-i%" Mo&#le
Al-Hassani" Salim $ S$ 1001 Inventions: Muslim Heritage in our World. HI2 =oundation !or Science" echnology and Ci(ili>ation" 2&&:$ .oldstein" Kernard$ Copernicus and the rigin o! his Heliocentric "niverse. Cournal !or the History o! Astronomy2 44 /2&&21 ##$ 2)'-4+ .oldstein" homas$ #a$n o! Modern %cience. Koston2 Houghton" Mi!!lin" )'*&$ Hayes" Cohn$ &he 'enius o! Arab Civili(ation: %ource o! )enaissance. 8ew YorHni(ersity Press" )':+$ Hartner"@illy$ ;Copernicus* the Man* the Wor+* and Its History"< Proceedings o! the American Philoso#hical Society )):" no$ 6 /)':41" ##$ 5)4-522$ Iennedy" 9$ S$ ;,ate Medieval -lanetary &heory"< Isis" +:" no$ 4 /)'661$ Iennedy" 9$ S$ Koo- re(iew o! ;&he bservatory in Islam and Its -lace in the 'eneral History o! the bservatory by Aydin %ayili"< Isis" +4" no$ 2 /)'621$ Ihaleel" Iasem$ %cience in the .ame o! 'od$ Ku!!alo .ro(e2 Inowledge House" 2&&4$ Roberts" Gictor$ &he %olar and ,unar &heory o! Ibn al/%hatir: A -re/Copernican Copernican Model. Isis2 5* /)'+:1 ##$ 52*-42$ Sabra" Abdelhamid I$ &he 0nterprise o! %cience in Islam: .e$ -erspectives. Cambridge2 MI Press" 2&&4$ Saliba" .eorge$ An bservational .oteboo+ o! a &hirteenth/Century Astronomer$ Isis :5 /)'*412 4** - 5&)$ Saliba" .eorge$ A History o! Arabic Astronomy: -lanetary &heories during the 'olden Age o! Islam$ 8ew Yor-2 8YH Press" )''5$ Saliba" .eorge$ )ethin+ing the )oots o! Modern %cience: Arabic %cienti!ic Manuscripts in 0uropean ,ibraries$ Center !or Contem#orary Studies" .eorgetown Hni(ersity" )'':$ Saliba" .eorge$ &he rigin and #evelopment o! Arabic %cienti!ic &hought* 4Arabic5 $ Debanon2 Kalamand Hni(ersity" Center !or Christian Islamic Studies" )''*$ Saliba" .eorge$ Whose %cience is Arabic %cience in )enaissance 0urope1 htt#2??www$columbia$edu?Lgas)?#ro%ect?(isions?case)?sci$)$html" )'''$
ISLAMIC/ARABIC ASTRONOMY
RIHAB SAWAH
Saliba" .eorge$ &he Astronomical Wor+ o! Mu3ayyad al/#in al/"rdi: A &hirteenth Century )e!orm o! -tolemaic Astronomy* 67itab al/Hay3ah8$ Keirut2 Center !or Arab Hnity Studies" 2&&)$ Saliba" .eorge$ 'ree+ Astronomy and the Medieval Arabic &radition. American Scientist$ Culy-August 2&&2246&-46: Saliba" .eorge$ ;)evisiting the Astronomical Contacts 2et$een the World o! Islam and )enaissance 0urope: &he 2y(antine Connection"< 6ccult Sciences in Ky>antium" ed$ Paul Magdalino" Maria Ma(roudi" Da Pomme AM6r" 2&&6$ Saliba" .eorge$ Islamic %cience and the Ma+ing o! the 0uropean )enaissance$ Cambridge2 he Massachusetts Institute o! echnology Press" 2&&:$ Saudi Aramco @orld Maga>ine$ %cience in al/Andalus$ www$saudiaramcoworld$com" Al-Andalus" Com#ilation Issue$ Saudi Aramco @orld Maga>ine$ &he %cholar3s %upernova$ www$saudiaramcoworld$com" Culy-August 2&&6$ Saudi Aramco @orld Maga>ine$ )ediscovering Arabic %cience$ www$saudiaramcoworld$com" May-Cune 2&&:$ Sayili" Aydin$ &he bservatory in Islam and its -lace in the 'eneral History o! the bservatory$ An-ara2 Nr- arih Iurumu KasOme(i" )'6&$
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Lunch 2Documento1 páginaLunch 2Jessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Monthly Sales Report TemplateDocumento1 páginaMonthly Sales Report TemplateShady R. NicolasAinda não há avaliações
- Profit and Loss Forecast v1.0Documento4 páginasProfit and Loss Forecast v1.0Jessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Budget Worksheets For A Restaurant 12 Month BudgetDocumento5 páginasSample Budget Worksheets For A Restaurant 12 Month BudgetBabyBabyAngel100% (1)
- Cash Flow Worksheet: Cash in (Record When Actually Recieved)Documento53 páginasCash Flow Worksheet: Cash in (Record When Actually Recieved)Jessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Years Stavanger Northumbria Alberta Oldenburg Ljubljana TotalDocumento2 páginas3 Years Stavanger Northumbria Alberta Oldenburg Ljubljana TotalJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- CDL v8Documento16 páginasCDL v8Jessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Cashflow Statement SampleDocumento9 páginasCashflow Statement SampleJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- HargaDocumento30 páginasHargaSyarifudinAinda não há avaliações
- Brosur Channel ReloadDocumento2 páginasBrosur Channel ReloadJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Elcomreload: Tata Cara Transaksi Acs Pulsa (Format SMS)Documento5 páginasElcomreload: Tata Cara Transaksi Acs Pulsa (Format SMS)Jessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Duties: Pilotage: Eta: Etd: Port: - Pilot: +pilotDocumento2 páginasDuties: Pilotage: Eta: Etd: Port: - Pilot: +pilotJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Pricelist Rudi ModivDocumento4 páginasPricelist Rudi ModivJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Master List RevDocumento1.329 páginasMaster List RevJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Greenschool Donation Payments MethodDocumento1 páginaGreenschool Donation Payments MethodJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- AirDocumento3 páginasAirJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Pulsa DoanDocumento2 páginasPulsa DoanJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- 0293daftar Billing Provider - IndDocumento2 páginas0293daftar Billing Provider - IndAndhika Hantyo PermadiAinda não há avaliações
- Inspect 050114Documento116 páginasInspect 050114Jessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Price List 07 03 13Documento8 páginasPrice List 07 03 13Jessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- National Combustion Turbine List: Region 9 - CaliforniaDocumento1 páginaNational Combustion Turbine List: Region 9 - CaliforniaJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Chity AlDocumento318 páginasChity AlJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- OAP Database 8 2011Documento97 páginasOAP Database 8 2011Jessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Compressed Air Best Practice ToolDocumento17 páginasCompressed Air Best Practice TooljokishAinda não há avaliações
- Laporan Curah Hujan 2011Documento15 páginasLaporan Curah Hujan 2011Jessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Calc CACDocumento5 páginasCalc CACJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- APSAWC201213Documento92 páginasAPSAWC201213Jessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Seperate List of Recognised J.B Schools in TRIPURA (As On 31-08-2013)Documento134 páginasSeperate List of Recognised J.B Schools in TRIPURA (As On 31-08-2013)Jessica Angelina100% (1)
- SumatraDocumento34 páginasSumatraJessica AngelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Rab MasterDocumento71 páginasRab MasterFrengky MaskAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- NC1 AC Contactor, 9 95A: Contactors ContactorsDocumento2 páginasNC1 AC Contactor, 9 95A: Contactors ContactorsYamendra GurungAinda não há avaliações
- Fema 310Documento12 páginasFema 310Anil BasnetAinda não há avaliações
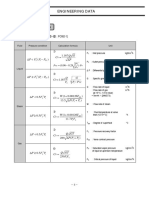
- Engineering Data: 2. CV CalculationDocumento1 páginaEngineering Data: 2. CV Calculationdj22500Ainda não há avaliações
- Bantilan Maureen Lhee RDocumento8 páginasBantilan Maureen Lhee RAlexa Anne Louise BercillaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson4 1515Documento14 páginasLesson4 1515gm hashAinda não há avaliações
- Poetics: Ester Van Laar, Alexander J.A.M. Van Deursen, Jan A.G.M. Van Dijk, Jos de HaanDocumento14 páginasPoetics: Ester Van Laar, Alexander J.A.M. Van Deursen, Jan A.G.M. Van Dijk, Jos de HaanViveka AshokAinda não há avaliações
- FZ1 Parts CatalogDocumento78 páginasFZ1 Parts CatalogAntonis Fotis100% (1)
- Equinoxes and Solstices: UttarayanamDocumento2 páginasEquinoxes and Solstices: UttarayanamRahul SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Thing in Itself Kantian: AnstoßDocumento1 páginaThing in Itself Kantian: Anstoßwhynotbequiet23Ainda não há avaliações
- A-W and A-F Oil SeparatorsDocumento1 páginaA-W and A-F Oil SeparatorstribleprinceAinda não há avaliações
- 67 - Es - Ut Republic Csalamade BooDocumento47 páginas67 - Es - Ut Republic Csalamade BooTyler LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Antennas and Wave Propagation - Nov - 2015Documento8 páginasAntennas and Wave Propagation - Nov - 2015Jyothi SamanthulaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Manual 10: Z-Transform and Inverse Z-Transform Analysis ObjectiveDocumento7 páginasLab Manual 10: Z-Transform and Inverse Z-Transform Analysis ObjectiveSyed Waqas ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Pertemuan 1 - Verb, Noun, Adjective and AdverbDocumento6 páginasPertemuan 1 - Verb, Noun, Adjective and AdverbHaris PambudiAinda não há avaliações
- Probability and Statistics Ii Assignment I July 2019 PDFDocumento3 páginasProbability and Statistics Ii Assignment I July 2019 PDFDanielAinda não há avaliações
- Mae 1202: Aerospace Practicum: Lecture 4: Introduction To Basic Aerodynamics 3Documento38 páginasMae 1202: Aerospace Practicum: Lecture 4: Introduction To Basic Aerodynamics 3زهديابوانسAinda não há avaliações
- I. Company Data 1.1. Company ProfileDocumento19 páginasI. Company Data 1.1. Company ProfileMhy AcajaAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 6 - MCQ Separation of SubstancesDocumento4 páginasCBSE Class 6 - MCQ Separation of Substancesvinod1577100% (1)
- Anti FoundationalismDocumento4 páginasAnti FoundationalismKostasBaliotisAinda não há avaliações
- SQAAU SM Assignment BriefDocumento10 páginasSQAAU SM Assignment BriefJamil NassarAinda não há avaliações
- Werling Optimal Trajectory Generationfor Dynamic Street Scenariosina Frenet FrameDocumento8 páginasWerling Optimal Trajectory Generationfor Dynamic Street Scenariosina Frenet FramehugoAinda não há avaliações
- Probability spaces and σ-algebras: Scott SheffieldDocumento12 páginasProbability spaces and σ-algebras: Scott SheffieldRikta DasAinda não há avaliações
- Boolean Operations in 3D - AutoCAD 2016 Tutorial and VideosDocumento19 páginasBoolean Operations in 3D - AutoCAD 2016 Tutorial and VideosRohit Chandrakant SalveAinda não há avaliações
- CSR of Pidilite PDFDocumento2 páginasCSR of Pidilite PDFtarang keraiAinda não há avaliações
- Service and Technology Marketing Service and Technology MarketingDocumento27 páginasService and Technology Marketing Service and Technology MarketingVinudeep MalalurAinda não há avaliações
- Enabling Secure Broadband Access Anywhere Anytime Access Anywhere, AnytimeDocumento4 páginasEnabling Secure Broadband Access Anywhere Anytime Access Anywhere, AnytimeEmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- Sharp Service Manual Models Lc-40sh340k and Lc-40sh340e With Chassis 17mb60Documento106 páginasSharp Service Manual Models Lc-40sh340k and Lc-40sh340e With Chassis 17mb60murtibing100% (1)
- MC68 HC05 B4 UDocumento253 páginasMC68 HC05 B4 Uflo724Ainda não há avaliações
- Please Complete The Information Requested Below: COMPANY NAME: X2 Logics Staffing Solution, IncDocumento2 páginasPlease Complete The Information Requested Below: COMPANY NAME: X2 Logics Staffing Solution, Incwasim riyazAinda não há avaliações
- Metaphor-Spatiality-Discourse - 10-11 July 2020 - Programme - FINALDocumento6 páginasMetaphor-Spatiality-Discourse - 10-11 July 2020 - Programme - FINALkostyelAinda não há avaliações