Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Thermodynamic Cycles Explained
Enviado por
Daniel Ortega100%(3)100% acharam este documento útil (3 votos)
2K visualizações1 páginaThe document discusses several thermodynamic cycles used in heat engines:
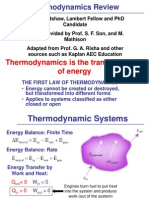
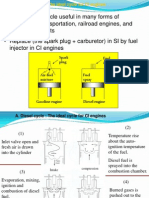
1) The Carnot, Diesel, and Otto cycles describe reciprocating engines and involve isentropic compression and expansion processes.
2) The Ericsson and Stirling cycles involve isothermal and constant pressure processes.
3) The Brayton cycle describes gas turbine engines with isentropic compression and expansion as well as constant pressure heat addition and rejection.
4) Specific heats, regeneration, compression and expansion efficiencies are also mentioned.
Descrição original:
A list of all the
Título original
Thermodynamics Formula Sheet
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThe document discusses several thermodynamic cycles used in heat engines:
1) The Carnot, Diesel, and Otto cycles describe reciprocating engines and involve isentropic compression and expansion processes.
2) The Ericsson and Stirling cycles involve isothermal and constant pressure processes.
3) The Brayton cycle describes gas turbine engines with isentropic compression and expansion as well as constant pressure heat addition and rejection.
4) Specific heats, regeneration, compression and expansion efficiencies are also mentioned.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
100%(3)100% acharam este documento útil (3 votos)
2K visualizações1 páginaThermodynamic Cycles Explained
Enviado por
Daniel OrtegaThe document discusses several thermodynamic cycles used in heat engines:
1) The Carnot, Diesel, and Otto cycles describe reciprocating engines and involve isentropic compression and expansion processes.
2) The Ericsson and Stirling cycles involve isothermal and constant pressure processes.
3) The Brayton cycle describes gas turbine engines with isentropic compression and expansion as well as constant pressure heat addition and rejection.
4) Specific heats, regeneration, compression and expansion efficiencies are also mentioned.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
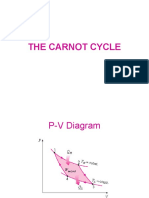
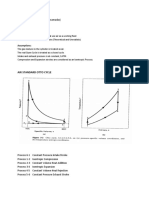
Carnot Cycle
Reciprocating Engines Compression ratio: Mean effective pressure:
Power:
Diesel Cycle
Otto Cycle
1-2 Isentropic compression 2-3 Constant-volume heat addition 3-4 Isentropic expansion 4-1 Constant-volume heat rejection
1-2 Isentropic compression 2-3 constant-pressure heat addition 3-4 Isentropic expansion 4-1 Constant-volume heat rejection
Cutoff ratio:
Compression efficiency
Expansion efficiency
Ericsson Cycle Process 1-2: Reversible isothermal compression.
Process 2-3: Constant pressure heat addition. Process 3-4: Reversible isothermal expansion. Process 4-1: Constant pressure heat rejection.
Stirling Cycle 1-2 isothermal expansion heat addition
P2=P3, P1=P4, = 1
2-3 const. vol. heat removal 3-4 isothermal compression 4-1 const. vol. heat addition
Brayton Cycle
1-2 Isentropic compression (in a compressor) 2-3 Constant-pressure heat addition 3-4 Isentropic expansion (in a turbine) 4-1 Constant-pressure heat rejection
Specific Heats:
Regeneration
Você também pode gostar
- Thermodynamics Formula SheetDocumento1 páginaThermodynamics Formula Sheetpoly WannaAinda não há avaliações
- Stirling and Ericsson Cycles 2016 PDFDocumento13 páginasStirling and Ericsson Cycles 2016 PDFArvin Loui Bascon100% (1)
- Sample Formula Sheet For ThermodynamicsDocumento2 páginasSample Formula Sheet For Thermodynamicsmicrop_aras100% (3)
- Thermo Formula SheetDocumento1 páginaThermo Formula SheetdoubletaprAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics FormulaeDocumento2 páginasThermodynamics FormulaeHelmi Hamzah100% (3)
- Thermodynamics - Formula SheetDocumento2 páginasThermodynamics - Formula SheetShaikh ZubairAinda não há avaliações
- Pressure and Thermodynamics FundamentalsDocumento2 páginasPressure and Thermodynamics FundamentalsPearl Alexandra FabitoAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamic Cheat SheetDocumento6 páginasThermodynamic Cheat SheetAnthony Rey100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Cheat SheetDocumento2 páginasThermodynamics Cheat SheetAlvin Tung Kwong Choong100% (2)
- Constant velocity formula sheet for physics formulasDocumento2 páginasConstant velocity formula sheet for physics formulassharon100% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics Equation Sheet FullDocumento5 páginasFluid Mechanics Equation Sheet FullZara ThomasAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Cycle BraytonDocumento15 páginasBasic Cycle BraytonMarin Andreea100% (1)
- Thermodynamics - Cheat SheetDocumento2 páginasThermodynamics - Cheat SheetJonathan0% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Formulae SheetDocumento4 páginasFluid Mechanics Formulae SheetBinay J Pande100% (1)
- Tutorial C5 AnswerDocumento7 páginasTutorial C5 AnswerAustin Phua Yun HockAinda não há avaliações
- Processes of Ideal GasDocumento14 páginasProcesses of Ideal GasKevin Baterina40% (5)
- Thermodynamics Fundamental Property RelationsDocumento36 páginasThermodynamics Fundamental Property RelationsnAinda não há avaliações
- L14 - Analyse Fanno flow conditions in adiabatic compressible pipe flowDocumento30 páginasL14 - Analyse Fanno flow conditions in adiabatic compressible pipe flowAitizaz KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering - Heat Transfer Formulas PDFDocumento2 páginasEngineering - Heat Transfer Formulas PDFharvey.denis75% (4)
- Thermodynamics II - LectureDocumento82 páginasThermodynamics II - LectureJohn Panopio100% (1)
- Cooling Electronics Heat TransferDocumento14 páginasCooling Electronics Heat Transferramy100% (2)
- ThermoDynamics Conversion TableDocumento1 páginaThermoDynamics Conversion Tablefrancisco69% (13)
- Thermodynamic FormulasDocumento17 páginasThermodynamic Formulasdaniebenade86% (28)
- Otto Cycle ProblemsDocumento4 páginasOtto Cycle ProblemsBipulBrahmaAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics Review of Energy Transfer and SystemsDocumento130 páginasThermodynamics Review of Energy Transfer and SystemsJaimin Joshi0% (1)
- Brayton Cycle PDFDocumento43 páginasBrayton Cycle PDFAdly_arkim100% (2)
- Heat and Mass Transfer NotesDocumento364 páginasHeat and Mass Transfer NotesPradeep KumarAinda não há avaliações
- ThermodynamicsDocumento341 páginasThermodynamicsjonathan2788100% (4)
- Gas Cycles Otto, Diesel, Dual CyclesDocumento43 páginasGas Cycles Otto, Diesel, Dual Cyclesprasad5034100% (1)
- Optics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Documento1 páginaOptics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Mark Riley100% (1)
- Diesel CycleDocumento20 páginasDiesel CycleShafiq ShapianAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics DefinitionsDocumento8 páginasThermodynamics Definitionsdaniebenade100% (1)
- Fluids Dynamics Formula SheetDocumento2 páginasFluids Dynamics Formula SheetMark Riley88% (8)
- Freezing of subcooled water and entropy changeDocumento3 páginasFreezing of subcooled water and entropy changeAchmad WidiyatmokoAinda não há avaliações
- The Carnot CycleDocumento9 páginasThe Carnot CyclePatrick Antonio Orge ChingAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 18 Solving Problem On Boiler Performance - Students - Vol 2Documento68 páginasLecture 18 Solving Problem On Boiler Performance - Students - Vol 2Dr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN100% (1)
- Important Trick To Remember All Thermodynamic Cycles For Oral ExamsDocumento11 páginasImportant Trick To Remember All Thermodynamic Cycles For Oral ExamsParikshit Ugale50% (2)
- Otto Diesel Dual Ideal Cycle - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Documento16 páginasOtto Diesel Dual Ideal Cycle - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Danang Wahdiat Aulia Ishaq0% (1)
- FiguresDocumento17 páginasFiguresMahmudul Hasan TanvirAinda não há avaliações
- Jabatan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Politeknik Sultan Azlan ShahDocumento24 páginasJabatan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Politeknik Sultan Azlan ShahAdid PunyaAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Power CyclesDocumento32 páginasGas Power CyclesZachary NgAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Combustion EngineDocumento5 páginasInternal Combustion EnginenidhidarklordAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamic CyclesDocumento32 páginasThermodynamic CyclessunitbhaumikAinda não há avaliações
- Ic Engine Ignou NotesDocumento16 páginasIc Engine Ignou NotesRakesh JhaAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics Cycles: Umar TariqDocumento16 páginasThermodynamics Cycles: Umar TariqHasib IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Air Standard CyclesDocumento28 páginasAir Standard CyclesAditya Krishnakumar100% (1)
- Deal With Systems That Produce Power in Which The Working Fluid Remains A Gas Throughout The Cycle, I.e., No Change in PhaseDocumento22 páginasDeal With Systems That Produce Power in Which The Working Fluid Remains A Gas Throughout The Cycle, I.e., No Change in PhasePushpa Mohan RajAinda não há avaliações
- Air Standard Cycles: What Is It?Documento13 páginasAir Standard Cycles: What Is It?Nobel Engzen Du BermoyAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Turbine Cycles ExplainedDocumento48 páginasGas Turbine Cycles ExplainedN S SenanayakeAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocumento51 páginasInternal Combustion EnginesJamesAinda não há avaliações
- Combustion Engine CyclesDocumento4 páginasCombustion Engine CyclesRiazAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Gas Power CyclesDocumento8 páginasAnalysis of Gas Power CyclesPradeep SandhalAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Combustion Engines: LecturDocumento32 páginasInternal Combustion Engines: LecturPuneet GargAinda não há avaliações
- Air Standed Cycles Lec-7Documento20 páginasAir Standed Cycles Lec-7pleasename1Ainda não há avaliações
- IC Engines 2012 Edition Theory & QuestionsDocumento178 páginasIC Engines 2012 Edition Theory & Questionskumarrohit91Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 4-2016 SchemeDocumento90 páginasModule 4-2016 SchemeRitwik AravindakshanAinda não há avaliações
- Different Cycle of IC EngineDocumento13 páginasDifferent Cycle of IC EngineTaslim AminAinda não há avaliações
- GDP Per Employed PersonDocumento8 páginasGDP Per Employed PersonDaniel OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- Control Systems TheoryDocumento331 páginasControl Systems Theorycorsairsan100% (1)
- Company ListDocumento5 páginasCompany ListDaniel OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- DictionaryDocumento167 páginasDictionaryDaniel OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- DictionaryDocumento167 páginasDictionaryDaniel OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- DictionaryDocumento167 páginasDictionaryDaniel OrtegaAinda não há avaliações