Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Understanding Big O Notation and Time Complexity Analysis
Enviado por
Sally JarkasDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Understanding Big O Notation and Time Complexity Analysis
Enviado por
Sally JarkasDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Big O: A Review
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Carleton University
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Big O: Denition
O (g (n)) = {f (n) : there exists positive constants c and n0 such that f (n) cg (n) for all n n0 }
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Big O: Denition
O (g (n)) = {f (n) : there exists positive constants c and n0 such that f (n) cg (n) for all n n0 } Notice: O (g (n)) is a set of functions
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Big O: Denition
O (g (n)) = {f (n) : there exists positive constants c and n0 such that f (n) cg (n) for all n n0 } Notice: O (g (n)) is a set of functions
When we say f (n) = O (g (n)) we really mean f (n) O (g (n))
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Big O: Denition
O (g (n)) = {f (n) : there exists positive constants c and n0 such that f (n) cg (n) for all n n0 } Notice: O (g (n)) is a set of functions
When we say f (n) = O (g (n)) we really mean f (n) O (g (n)) E.g., n2 + 42n + 7 = O (n2 ) means:
The function f (n) = n2 + 42n + 7 is in the set O (n2 )
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
n2 + 42n + 7 = O (n2 )
n2 + 42n + 7 2n2 for all n 50
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002 Big O: A Review
Example
Prove n2 + 42n + 7 = O (n2 )
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Example
Prove n2 + 42n + 7 = O (n2 ) n2 + 42n + 7 n2 + 42n2 + 7n2 = 50n
2
for n 1
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Example
Prove n2 + 42n + 7 = O (n2 ) n2 + 42n + 7 n2 + 42n2 + 7n2 = 50n
2
for n 1
So, n2 + 42n + 7 50n2 for all n 1
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Example
Prove n2 + 42n + 7 = O (n2 ) n2 + 42n + 7 n2 + 42n2 + 7n2 = 50n
2
for n 1
So, n2 + 42n + 7 50n2 for all n 1 n2 + 42n2 + 7n2 = O (n2 ) [ c = 50, n0 = 1 ]
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Example
Prove 5n log2 n + 8n 200 = O (n log2 n)
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Example
Prove 5n log2 n + 8n 200 = O (n log2 n) 5n log2 n + 8n 200 5n log2 n + 8n 5n log2 n + 8n log2 n 13n log2 n
for n 2 (log2 n 1)
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Example
Prove 5n log2 n + 8n 200 = O (n log2 n) 5n log2 n + 8n 200 5n log2 n + 8n 5n log2 n + 8n log2 n 13n log2 n 5n log2 n + 8n 200 13n log2 n for all n 2
for n 2 (log2 n 1)
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Example
Prove 5n log2 n + 8n 200 = O (n log2 n) 5n log2 n + 8n 200 5n log2 n + 8n 5n log2 n + 8n log2 n 13n log2 n 5n log2 n + 8n 200 13n log2 n for all n 2 5n log2 n + 8n 200 = O (n log2 n) [ c = 13, n0 = 2 ]
for n 2 (log2 n 1)
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Some common relations
O (nc1 ) O (nc2 ) for any c1 < c2 For any constants a, b , c > 0, O (a) O (log n) O (nb ) O (c n )
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Some common relations
O (nc1 ) O (nc2 ) for any c1 < c2 For any constants a, b , c > 0, O (a) O (log n) O (nb ) O (c n ) These make things faster 2 log2 n + 2 = O (log n) n + 2 = O (n) 2n + 15n1/2 = O (n)
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Some common relations
O (nc1 ) O (nc2 ) for any c1 < c2 For any constants a, b , c > 0, O (a) O (log n) O (nb ) O (c n ) These make things faster 2 log2 n + 2 = O (log n) n + 2 = O (n) 2n + 15n1/2 = O (n) We can multiply these to learn about other functions, O (an) = O (n) O (n log n) O (n1+b ) O (nc n )
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Some common relations
O (nc1 ) O (nc2 ) for any c1 < c2 For any constants a, b , c > 0, O (a) O (log n) O (nb ) O (c n ) These make things faster 2 log2 n + 2 = O (log n) n + 2 = O (n) 2n + 15n1/2 = O (n) We can multiply these to learn about other functions, O (an) = O (n) O (n log n) O (n1+b ) O (nc n ) Examples: O (n1.5 ) O (n1.5 log n)
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002 Big O: A Review
An indulgence
In this course, we have seen expressions like O (n i )
Two argument function g (n, i ) = n i For the purposes of this course, we will take O (g (n, i )) to be O (g (n, i )) = {f (n, i ) : there exists positive constants c and n0 such that f (n, i ) cg (n, i ) for all n n0 and all valid arguments i }
For example (Lists) valid values of i are {0, . . . , n 1} or (sometimes) {0, . . . , n}
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Why Use big-O Notation?
Consider the following (simple) code:
for ( int i = 0; i < n ; i ++) { a[i] = i; }
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Why Use big-O Notation?
Consider the following (simple) code:
for ( int i = 0; i < n ; i ++) { a[i] = i; }
The running time is
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Why Use big-O Notation?
Consider the following (simple) code:
for ( int i = 0; i < n ; i ++) { a[i] = i; }
The running time is
1 assignment (int i = 0)
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Why Use big-O Notation?
Consider the following (simple) code:
for ( int i = 0; i < n ; i ++) { a[i] = i; }
The running time is
1 assignment (int i = 0) n+1 comparisons (i < n)
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Why Use big-O Notation?
Consider the following (simple) code:
for ( int i = 0; i < n ; i ++) { a[i] = i; }
The running time is
1 assignment (int i = 0) n+1 comparisons (i < n) n increments (i++)
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Why Use big-O Notation?
Consider the following (simple) code:
for ( int i = 0; i < n ; i ++) { a[i] = i; }
The running time is
1 assignment (int i = 0) n+1 comparisons (i < n) n increments (i++) n array oset calculations (a[i])
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Why Use big-O Notation?
Consider the following (simple) code:
for ( int i = 0; i < n ; i ++) { a[i] = i; }
The running time is
1 assignment (int i = 0) n+1 comparisons (i < n) n increments (i++) n array oset calculations (a[i]) n indirect assignments (a[i] = i)
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Why Use big-O Notation?
Consider the following (simple) code:
for ( int i = 0; i < n ; i ++) { a[i] = i; }
The running time is
1 assignment (int i = 0) n+1 comparisons (i < n) n increments (i++) n array oset calculations (a[i]) n indirect assignments (a[i] = i) = a + b (n + 1) + cn + dn + en, where a, b , c , d , and e are constants that depend on the machine running the code
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Why Use big-O Notation?
Consider the following (simple) code:
for ( int i = 0; i < n ; i ++) { a[i] = i; }
The running time is
1 assignment (int i = 0) n+1 comparisons (i < n) n increments (i++) n array oset calculations (a[i]) n indirect assignments (a[i] = i) = a + b (n + 1) + cn + dn + en, where a, b , c , d , and e are constants that depend on the machine running the code
Easier just to say O (n) (constant-time) operations
Pat Morin COMP2402/2002
Big O: A Review
Você também pode gostar
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesNo EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesNota: 1.5 de 5 estrelas1.5/5 (2)
- Principal Component Analysis 4 Dummies - Eigenvectors, Eigenvalues and Dimension Reduction - George DallasDocumento10 páginasPrincipal Component Analysis 4 Dummies - Eigenvectors, Eigenvalues and Dimension Reduction - George Dallasjlvn20Ainda não há avaliações
- Ring Homomorphisms Over Certain RingsDocumento122 páginasRing Homomorphisms Over Certain RingsUnos0% (1)
- Stochastic Processes NotesDocumento22 páginasStochastic Processes Notesels_872100% (1)
- Ensemble Average and Time AverageDocumento31 páginasEnsemble Average and Time Averageilg1Ainda não há avaliações
- Integration in Finite Terms - Maxwell RosenlichtDocumento11 páginasIntegration in Finite Terms - Maxwell RosenlichtAshish Kumar100% (1)
- MSMS-204: Pure Birth Process TheoryDocumento7 páginasMSMS-204: Pure Birth Process TheoryKIRAN DUBEYAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Birth DeathDocumento49 páginas2 Birth Deathsumit2560% (1)
- (Springer Series in Statistics) Jun Shao, Dongsheng Tu (Auth.) - The Jackknife and Bootstrap-Springer-Verlag New York (1995)Documento532 páginas(Springer Series in Statistics) Jun Shao, Dongsheng Tu (Auth.) - The Jackknife and Bootstrap-Springer-Verlag New York (1995)sherlockholmes108Ainda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Methods: Linear Algebra / Normed Spaces / Distributions / IntegrationNo EverandMathematical Methods: Linear Algebra / Normed Spaces / Distributions / IntegrationAinda não há avaliações
- Latin Squares: New Developments in the Theory and ApplicationsNo EverandLatin Squares: New Developments in the Theory and ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Nonlinear Programming and Process OptimizationDocumento224 páginasNonlinear Programming and Process OptimizationLina Angarita HerreraAinda não há avaliações
- Mohamad A Mehdi Conformal Mappings and ApplicationsDocumento53 páginasMohamad A Mehdi Conformal Mappings and Applicationsapi-363560361Ainda não há avaliações
- Filtering in the Frequency Domain Using Circulant MatricesDocumento48 páginasFiltering in the Frequency Domain Using Circulant MatricesManu PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics With Common Sense - David Kault (2003)Documento272 páginasStatistics With Common Sense - David Kault (2003)Mary Joyce RaymundoAinda não há avaliações
- Halmos - Problems As Heart of MathematicsDocumento7 páginasHalmos - Problems As Heart of MathematicsΧάρης ΦραντζικινάκηςAinda não há avaliações
- Computing Methods in Optimization Problems: Proceedings of a Conference Held at University of California, Los Angeles January 30-31, 1964No EverandComputing Methods in Optimization Problems: Proceedings of a Conference Held at University of California, Los Angeles January 30-31, 1964Ainda não há avaliações
- App.A - Detection and Estimation in Additive Gaussian Noise PDFDocumento55 páginasApp.A - Detection and Estimation in Additive Gaussian Noise PDFLê Dương LongAinda não há avaliações
- Total Domination Books PDFDocumento184 páginasTotal Domination Books PDFGuru Viswanathan75% (4)
- Final 12Documento11 páginasFinal 12heltaherAinda não há avaliações
- Monte Carlo Integration LectureDocumento8 páginasMonte Carlo Integration LectureNishant PandaAinda não há avaliações
- Prog Comp Func Lang PCFDocumento3 páginasProg Comp Func Lang PCFHgfghf GhfghgfAinda não há avaliações
- The Riccati EquationDocumento345 páginasThe Riccati EquationfisikaAinda não há avaliações
- Picks TheoremDocumento10 páginasPicks Theoremcbarraza77398100% (1)
- Efficient Mining of Frequent Patterns On Uncertain GraphsDocumento5 páginasEfficient Mining of Frequent Patterns On Uncertain GraphsRenowntechnologies VisakhapatnamAinda não há avaliações
- Homework 8 SolutionsDocumento4 páginasHomework 8 SolutionsMeezan ChandAinda não há avaliações
- Additional Exercises For Convex Optimization PDFDocumento187 páginasAdditional Exercises For Convex Optimization PDFCliffordTorresAinda não há avaliações
- Stochastic Modelling 2000-2004Documento189 páginasStochastic Modelling 2000-2004Brian KufahakutizwiAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Nonlinear Analysis: Proceedings of an International Conference on Applied Nonlinear Analysis, Held at the University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, Texas, April 20–22, 1978No EverandApplied Nonlinear Analysis: Proceedings of an International Conference on Applied Nonlinear Analysis, Held at the University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, Texas, April 20–22, 1978Ainda não há avaliações
- Random MatricesDocumento27 páginasRandom MatricesolenobleAinda não há avaliações
- MATH2045: Vector Calculus & Complex Variable TheoryDocumento50 páginasMATH2045: Vector Calculus & Complex Variable TheoryAnonymous 8nJXGPKnuW100% (2)
- EC 622 Statistical Signal ProcessingDocumento135 páginasEC 622 Statistical Signal Processingqwwq215Ainda não há avaliações
- r5210501 Probability and StatisticsDocumento1 páginar5210501 Probability and StatisticssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Notes on Linear Regression ModelsDocumento46 páginasNotes on Linear Regression Modelsken_ng333Ainda não há avaliações
- OnlineTut03 PDFDocumento10 páginasOnlineTut03 PDFMohd Nazri SalimAinda não há avaliações
- Legendre Polynomials ExplainedDocumento7 páginasLegendre Polynomials Explainedbraulio.dantas0% (1)
- FINA3010 Summary For Lecture 1,2Documento9 páginasFINA3010 Summary For Lecture 1,2Koon Sing ChanAinda não há avaliações
- Large Networks and Graph LimitsDocumento487 páginasLarge Networks and Graph Limitsanon020202100% (2)
- Linear Algebra FundamentalsDocumento94 páginasLinear Algebra Fundamentalspattrapong pongpattraAinda não há avaliações
- JaBuka TopologyDocumento131 páginasJaBuka TopologyGabriel Dalla VecchiaAinda não há avaliações
- STAT 1520 NotesDocumento61 páginasSTAT 1520 NotesnojnfoAinda não há avaliações
- Reductions, Recursion and Divide and Conquer: February 1, 2011Documento97 páginasReductions, Recursion and Divide and Conquer: February 1, 2011A.K. MarsAinda não há avaliações
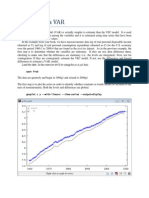
- Estimating a VAR Model in GRETLDocumento9 páginasEstimating a VAR Model in GRETLkaddour7108Ainda não há avaliações
- Lattice Solution PDFDocumento142 páginasLattice Solution PDFhimanshu Arya100% (1)
- MDM4U Online Culminating ActivityDocumento3 páginasMDM4U Online Culminating ActivityMarisaAinda não há avaliações
- Bob Coecke - Quantum Information-Flow, Concretely, AbstractlyDocumento17 páginasBob Coecke - Quantum Information-Flow, Concretely, AbstractlyGholsasAinda não há avaliações
- Topological Property - Wikipedia PDFDocumento27 páginasTopological Property - Wikipedia PDFBxjdduAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Statistical ThermodynamicsDocumento29 páginasIntroduction To Statistical ThermodynamicsYasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- Additional Exercises for Convex Optimization ProblemsDocumento232 páginasAdditional Exercises for Convex Optimization ProblemsShy PeachDAinda não há avaliações
- Matematika BookDocumento335 páginasMatematika BookDidit Gencar Laksana100% (1)
- Engineering Optimization: An Introduction with Metaheuristic ApplicationsNo EverandEngineering Optimization: An Introduction with Metaheuristic ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- FFTContent PDFDocumento8 páginasFFTContent PDFAaaaaAinda não há avaliações
- 4540 17 PDFDocumento274 páginas4540 17 PDFMichael PetersAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento3 páginasAssignment 1Sally JarkasAinda não há avaliações
- Cloud ComputingDocumento29 páginasCloud ComputingSrijan UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- Cloud ComputingDocumento29 páginasCloud ComputingSrijan UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- UML WorkshopDocumento1 páginaUML WorkshopSally JarkasAinda não há avaliações
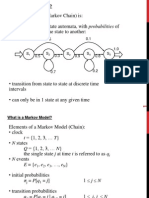
- HMMDocumento25 páginasHMMSally JarkasAinda não há avaliações
- Business Intelligence - Sally JarkasDocumento21 páginasBusiness Intelligence - Sally JarkasSally JarkasAinda não há avaliações
- HMMDocumento25 páginasHMMSally JarkasAinda não há avaliações
- Sally Jarkas-Business Intelligence (BI)Documento19 páginasSally Jarkas-Business Intelligence (BI)Sally JarkasAinda não há avaliações
- 16 Unique Innovative Ways To Market Your BusinessDocumento29 páginas16 Unique Innovative Ways To Market Your BusinessRupesh LimbaniAinda não há avaliações
- BAMBUDocumento401 páginasBAMBUputulAinda não há avaliações
- Core Strategy - Statement of Consultation February 2010Documento168 páginasCore Strategy - Statement of Consultation February 2010Aimee-NonaAinda não há avaliações
- Leader in Water Purification Systems RougingDocumento16 páginasLeader in Water Purification Systems RougingtomcanAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus Early Transcendentals 10th Edition Anton Solutions ManualDocumento35 páginasCalculus Early Transcendentals 10th Edition Anton Solutions Manualcrenate.bakshish.7ca96100% (16)
- Geo 2230 MJ 02Documento8 páginasGeo 2230 MJ 02Jason 402Ainda não há avaliações
- Win Server 2008 Manual Installation PDFDocumento20 páginasWin Server 2008 Manual Installation PDFFery AlapolaAinda não há avaliações
- Day Trading Money ManagementDocumento8 páginasDay Trading Money ManagementJoe PonziAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 The Nature of Strategic Management2Documento8 páginasModule 1 The Nature of Strategic Management2Julienne LobchoyAinda não há avaliações
- Municipal Tax Dispute Over Petroleum Refinery in PilillaDocumento5 páginasMunicipal Tax Dispute Over Petroleum Refinery in PilillaDaphne Jade Estandarte PanesAinda não há avaliações
- Delta Ia-Mds VFDB I TC 20070719Documento2 páginasDelta Ia-Mds VFDB I TC 20070719homa54404Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 ComplaintDocumento6 páginas1 ComplaintIvy PazAinda não há avaliações
- 40W 2.1CH Digital Audio Amplifier with EQDocumento4 páginas40W 2.1CH Digital Audio Amplifier with EQDylan Gonzalez VillalobosAinda não há avaliações
- CISSPDocumento200 páginasCISSPkumarAinda não há avaliações
- 2390A Series Spectrum AnalyzersDocumento6 páginas2390A Series Spectrum AnalyzersElizabeth FaulknerAinda não há avaliações
- IAS Physics SB1 Practs CP1 Student SheetDocumento3 páginasIAS Physics SB1 Practs CP1 Student Sheethussain azizAinda não há avaliações
- PahaDocumento2 páginasPahaSeyfeAlemayehuAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Jurnal Internasional (2019) PDFDocumento9 páginas2 Jurnal Internasional (2019) PDFDwi KrisnawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Deckers v. Comfy - Minute OrderDocumento2 páginasDeckers v. Comfy - Minute OrderSarah BursteinAinda não há avaliações
- 26-200 kVA BrochureDocumento16 páginas26-200 kVA Brochureargo kuncahyoAinda não há avaliações
- Politische StrategiesEnd 2012 de en FINALDocumento405 páginasPolitische StrategiesEnd 2012 de en FINALFomeAinda não há avaliações
- Work-Experience-Sheet CSC Form 212Documento5 páginasWork-Experience-Sheet CSC Form 212Marc AbadAinda não há avaliações
- Quickspecs: HP Proliant Dl980 Generation 7 (G7)Documento46 páginasQuickspecs: HP Proliant Dl980 Generation 7 (G7)nadiaAinda não há avaliações
- The Puppet Masters: How The Corrupt Use Legal Structures To Hide Stolen Assets and What To Do About ItDocumento284 páginasThe Puppet Masters: How The Corrupt Use Legal Structures To Hide Stolen Assets and What To Do About ItSteve B. SalongaAinda não há avaliações
- CJ718 Board Functional Test ProcedureDocumento13 páginasCJ718 Board Functional Test ProcedureYudistira MarsyaAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Accounting 1: Accounting Lab Module Uph Business SchoolDocumento36 páginasAdvanced Accounting 1: Accounting Lab Module Uph Business SchoolDenisse Aretha LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Ilo MLCDocumento66 páginasIlo MLCcarmenAinda não há avaliações
- Zkihel Ilaye Efera: EducationDocumento3 páginasZkihel Ilaye Efera: EducationezkihelAinda não há avaliações
- Construction Management System Final Year ReportDocumento53 páginasConstruction Management System Final Year ReportMebiratu BeyeneAinda não há avaliações
- 6Tdvfutfrfr-S: of ofDocumento2 páginas6Tdvfutfrfr-S: of ofhim vermaAinda não há avaliações
- IEEEDocumento15 páginasIEEELaharish GuntukaAinda não há avaliações