Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
ORTODONCIA
Enviado por
Sheylita Jesus CubillusDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ORTODONCIA
Enviado por
Sheylita Jesus CubillusDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
34.
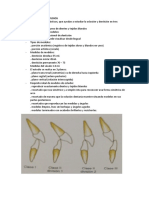
- MENCIONE LAS LLAVES DE LA OCLUSION -RELACION MOLAR -ANGULACION DE LAS CORONAS (MEDIO-DISTAL) -ROTACION
-INCLINACION DE LAS CORONAS DE LOS INCISIVOS (LABIO-LINGUAL) -DIASTEMAS -PLANOS DE OCLUSION (Curva de Spee)
35.- LEY DE WOLF. Cada cambio en forma y la funcin del hueso o solo en funcin es seguida por ciertos cambios por su arquitectura interna y igualmente por alteraciones secundarias definidas en su configuracin externa de acuerdo con leyes matemticas 36.- TEORIA SERVO SISTEMA PETROVICH Es la interacion entre factores causales y mecanimos de retroalimentacin que van a determinar el crecimiento craneofacial 37.- CLASIFICACION DE ANGLE CLASE I : Es cuando la cspide mesio vestibular del primer molar superior ocluye sobre la surco mesio vestibular del primer molar inferior CLASE II : Es cuando la cspide mesio vestibular del primer molar superior ocluye por mesial de la cspide medio vestibular de la primera molar inferior CLASE III : La cspide mesio vestibular de la primera molar superior ocluye por detrs de la cspide distal vestibular de la primera molar inferior 38.- IMPRESIN DE MODELOS EN ORTODONCIA. Se debe realizar la impresin con una cubeta profunda suficiente para la impresin del fondo de surco gingivolabial y gingivogeniano y se debe extender hasta las tuberosidad del maxilar y el trgono retromolar en la mandibula. Luego al momento de la impresin se debe de considerar la posicin del paciente y la preparacin del material en proporciones. 39.- OCLUSION NORMAL. - SALUD FISICA -SALUD Psquica
40.- QUE ES NORMAL. -Inclusion inferior (la arcada superior debe cubrir a la arcada inferior) - Llave premolar (En denticin permanente es mas diable que llave molar o canina) - Transpase horizontal y vertical posterior. -Forma oval (En la arcada superior o inferior)
41.-CARACTERISTICAS DE UNA OCLUSION NORMAL LIMITE: Finaliza con la erupcin del segundo molar OCLUSION MADURA: Cuando se tiene los 28 dientes (12 a 14 aos) MADURACION OCLUSAL: Ortodoncia (entre 12 a 16 aos) MADURACION ESQUELETICA: Hombre finaliza a los 18 y mujer a los 16 aos RAICES PARALELAS: Solo el 3% tiene oclusin perfecta o ideal
42.- CARABELLI CLASICA EN - Mordex Normalis -Mordex Rectus -Mordex Retrusus Mordex Tortuosus 43.- LISHER CLASIFICACION. NEUTROCLUSION - MESIOCLUSION -DISTOCLUSION 44.- CONUT REFIERE QUE LA MALOCLUSION PUEDE CLASIFICARSE EN - MALOCLUSION FUNCIONAL. -MALOCLUSION ESTRUCTURAL 45.- CLASIFICACION DE MALPOSICION MALPOSICION DE DIENTE AISLANTE PLANO SAGITAL MALPOSICION DE GRUPOS DE DIENTES PLANO TRANVERSAL ANOMALIAS OCLUSALES VERTICAL 47.- MENCIONE 5 PROPIEDADES DEL ALAMBRE IDEAL -BIOCONPATIBLE. -RESISTENTE A LA CORROSION -FLEXIBLES -ESTETICOS -AL RESISTENCIA A LA FRACTURA 48.- ETIOLOGIA DE LAS MALOCLUSIONES -HEREDITARIOS -CONGENITOS - ADQUIRIDOS 49.- EL RESPIRADOR BUCAL COMO INFLUYE EN LAS MALOCLUSIONES -MORDIDA ABIERTA. -MORDIDA CRUZADA UNILATERAL O BILATERAL -PROTUCION DE LOS INCISIVOS SUPERIORES -RETRUCCION DE LOS INCISIVOS INFERIORES 50.- CARACTERISTICAS DE UN SINDROME DE CLASE I -Cara masomenos armonica - relacin esqueltica clase I -Clase I dentaria -Neutrooclusion de Lisher. 51.- CARACTERISTICAS INTRAORALES DE UN SINDROME CLASE I -Apiamiento. Extrusin -mordida abierta 52.- CARACTERISTICAS DE UN SINDROME DE CLASE II/I EXTRAORAL -Dolicofacial -Perfil convexo -Labio superior incopetente, -El inferior interpuesto neutralizando el resalte INTRAORAL. -Clase II molar -Clase II canino -overjet marcado -Presenta mordida abierta -paladar profundo y estrecho 52.- CARACTERISTICAS DE UN SINDROME CLASE II/II -Extraoral: Braquifacial, perfil cncavo presenta gran tono muscular, buen sellado labial, son respiradores nasales y sonrisa gingival Intraoral: Incisivos centrales lingualizados, Incisivos laterales vestibularizados, gran sobre mordida, canino y molar clase II.
53.- SINDROME CLASE III -EXTRAORALES.-Tercio medio fecial refleja una discrepancia esqueltica maxilofacial, defisis del tercio medio fcial, regin infraorbitaria plana, protrucion mandibular 54.- SINDROME PLANO TRANSVERSAL -Mordida Cruzada(Cuando la mandibula esta sobre extendida y la maxila mas chica) -Mordida Tijera -Desviacin de la lnea media 55.- SINDROME PLANO VERTICAL -BIOTIPOS FACIALES. Mesofacial.- Dimension vertical y horizontal iguales Braquifacial.- Division Vertical y horizontal alteradas Dolicofacial.- Division vertical alta -MORDIDA ABIERTA -MORDIDA CRUZADA 56.- SINDROME DE APIAMIENTO -Primario.-Tamao diente mayor y hueso alveolar -Secundario.-Perdida temprana de temporals -Terciario.-Producto del crecimiento 57.- TEORIA METRIS FUNCIONAL (MOSS) El hueso del cartlago care de determinantes de crecimiento y crecen intrnsecamente por los tejidos asociados 58.- DESCRIBA LA TEORIA PRESION TENSION La alteracin de flujo sanguneo en el ligamento periodontal se debe a la presin mantenida y obliga al diente a cambiar de posicin compirmiendo unos puntos y tensando otros 59.-TEORIA PIEZO-ELECTRICA Es un estimulo importante en recontruccion y reparacin esqueltica Es un mecanismo por el cual la estructura osea se adapta a las demandas funcionales 60.- A QUE SE LE LLAMA MORDIDA CONTRUCTIVA Mejora las relaciones maxilares entre los tres planos del espacio
Você também pode gostar
- Clasificacion de La MaloclusiónDocumento44 páginasClasificacion de La MaloclusiónIván Meza Morales100% (2)
- Atm PDFDocumento64 páginasAtm PDFNolberth GuardadoAinda não há avaliações
- Prosto Anatomia PDFDocumento107 páginasProsto Anatomia PDFAllisonAinda não há avaliações
- Fracturas de Maxilar y MalarDocumento89 páginasFracturas de Maxilar y MalarSiluety BodyArtAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomía de Los MaxilaresDocumento27 páginasAnatomía de Los MaxilaresAna Maria Aznaran Perez100% (2)
- Conceptos de OclusionDocumento3 páginasConceptos de OclusiondanielaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomía Aplicada de Cabeza Ycuello 4 DR. CUBADocumento198 páginasAnatomía Aplicada de Cabeza Ycuello 4 DR. CUBAPatricia Garcia SaldarriagaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomia TopograficaDocumento25 páginasAnatomia TopograficaGustavo UribeAinda não há avaliações
- Resumen de Ortodoncia PARCIAL 2Documento5 páginasResumen de Ortodoncia PARCIAL 2Giancarlo Miguel Cordova MachucaAinda não há avaliações
- Alteraciones Del DesarrolloDocumento45 páginasAlteraciones Del DesarrolloJesus Castillo GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Musculo BuccinadorDocumento6 páginasMusculo BuccinadorMilagros Liz Mamani ChAinda não há avaliações
- Analisis de ModelosDocumento8 páginasAnalisis de ModelosAlejandro GarcíaAinda não há avaliações
- CLASE 3. Alteraciones-Del-DesarrolloDocumento45 páginasCLASE 3. Alteraciones-Del-DesarrolloANGEL JOSHIMAR LOPEZ SALAS100% (1)
- OclusiónDocumento56 páginasOclusiónerick ortegaAinda não há avaliações
- In Extenso Anatomia Quirurgica Cabeza y CuelloDocumento10 páginasIn Extenso Anatomia Quirurgica Cabeza y CuelloJorge Enrique TejadaAinda não há avaliações
- Patología de La EdentaciónDocumento20 páginasPatología de La EdentaciónJosé Francisco Reyes MosquedaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomía de La Boca DesdentadaDocumento35 páginasAnatomía de La Boca DesdentadaAra Tovar67% (3)
- Anato Era 1 - SuperiorDocumento23 páginasAnato Era 1 - SuperiorIvy Renon AlbuquerqueAinda não há avaliações
- Mehu108 - U6 - T11 - TRAUMATISMOS FACIALES, NARIZ Y EPISTAXISDocumento37 páginasMehu108 - U6 - T11 - TRAUMATISMOS FACIALES, NARIZ Y EPISTAXISMy MAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomia ProstodonciaDocumento4 páginasAnatomia ProstodonciaAline Y. SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Biomecanica AtmDocumento27 páginasBiomecanica AtmSTN2691Ainda não há avaliações
- ANTROPOMETRIADocumento88 páginasANTROPOMETRIAAksinia Navinta50% (2)
- 2 - MaxilofacialDocumento7 páginas2 - Maxilofacialesteban.bocanegraAinda não há avaliações
- Traumatismo FacialDocumento61 páginasTraumatismo FacialangelicaAinda não há avaliações
- Apuntes Cervical Ual Oficial 2023Documento35 páginasApuntes Cervical Ual Oficial 2023am2dr01Ainda não há avaliações
- Biomecanica de La AtmDocumento42 páginasBiomecanica de La AtmMilton SalazarAinda não há avaliações
- Maloclusiones TransversalesDocumento17 páginasMaloclusiones TransversalesDarlenne Román ChavezAinda não há avaliações
- Zona Anatomica-ProtesicaDocumento31 páginasZona Anatomica-ProtesicaFLOR DE MARIA DIAZ RAMIREZAinda não há avaliações
- Exploración IntraoralDocumento9 páginasExploración IntraoralMARIA LAURA RUIZ RODRIGUEZAinda não há avaliações
- ADENTDocumento5 páginasADENTJuliizz Thu LoQra Martiinezz50% (2)
- OrtognaticaDocumento20 páginasOrtognaticaFelipe Novoa OrellanaAinda não há avaliações
- Urgencias OdontologicasDocumento17 páginasUrgencias Odontologicaswq9d6pcs4pAinda não há avaliações
- Oclusión ResumenDocumento7 páginasOclusión ResumenDaniel EstrellaAinda não há avaliações
- Huesos de La Órbita OcularDocumento30 páginasHuesos de La Órbita OcularMaria Luisa Velarde Baltazar50% (2)
- Esqueleto Oseo de La CabezaDocumento31 páginasEsqueleto Oseo de La CabezaLuis Felipe CarrilloAinda não há avaliações
- Planos Terminales y Escalones en Denticic3b3n Primaria yDocumento17 páginasPlanos Terminales y Escalones en Denticic3b3n Primaria yRafael MacariAinda não há avaliações
- Copia de Carpeta OrtodonciaDocumento55 páginasCopia de Carpeta OrtodonciaJessica AlmadaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomia 1 Tarea #1Documento4 páginasAnatomia 1 Tarea #1J'sRodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Tema V - OrtodonciaDocumento6 páginasTema V - OrtodonciaMar RomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Clasificacion de Las MaloclusionesDocumento77 páginasClasificacion de Las MaloclusionesIsaias Hidalgo TarazonaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomia de La CaraDocumento52 páginasAnatomia de La CaraPatricia Diaz Villanueva100% (1)
- El Universo de La OclusiónDocumento10 páginasEl Universo de La OclusiónARUAL YESENIA VILLICANA GALLARDOAinda não há avaliações
- Esquemas Oclusales TrabajoDocumento6 páginasEsquemas Oclusales TrabajoDaniloEnriqueChavarriaMarinAinda não há avaliações
- Analisis de La OclusionDocumento13 páginasAnalisis de La OclusionRossy Stefania Rufino SaavedraAinda não há avaliações
- Tema 5 La OclusionDocumento5 páginasTema 5 La OclusionJorgeMtinezAinda não há avaliações
- Malformaciones de La Cabeza y El CuelloDocumento50 páginasMalformaciones de La Cabeza y El CuelloAlexis Jhair Bustamante VásquezAinda não há avaliações
- Anato - 10 Musculos de La CabezaDocumento26 páginasAnato - 10 Musculos de La CabezaMirllaNunesAinda não há avaliações
- Clase 2 de Operatoria (Preparaciones Cavitarias)Documento10 páginasClase 2 de Operatoria (Preparaciones Cavitarias)Yenni FrancoAinda não há avaliações
- Tema 13Documento3 páginasTema 13EstrellaAinda não há avaliações
- Fracturas Del Maxilar SuperiorDocumento10 páginasFracturas Del Maxilar SuperiorKatherine Chuchuca100% (1)
- Modulo de Sistema MuscularDocumento58 páginasModulo de Sistema MuscularNicole OrjuelaAinda não há avaliações
- TEORíA 3 HOMBRO - 20200317132739Documento41 páginasTEORíA 3 HOMBRO - 20200317132739LuigiZeladaNeyraAinda não há avaliações
- RSU Oclusion AlexDocumento14 páginasRSU Oclusion AlexAndrea SugashimaAinda não há avaliações
- PPR Tema 10 Prueba de La Estructura Metalica, Tema 11 Rim Raf PDFDocumento65 páginasPPR Tema 10 Prueba de La Estructura Metalica, Tema 11 Rim Raf PDFYaneth Cristina Morales BlasAinda não há avaliações
- Inroduccion CuelloDocumento16 páginasInroduccion Cuelloyoselin gonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- OCLUSIONDocumento21 páginasOCLUSIONbladetiger100% (1)
- Artrología Miembro SuperiorDocumento34 páginasArtrología Miembro SuperiorBrayan FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Las cadenas fisiológicas (Tomo V): Tratamiento del cráneo (Color)No EverandLas cadenas fisiológicas (Tomo V): Tratamiento del cráneo (Color)Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Los músculos: Anatomía clínica de las extremidades (Bicolor)No EverandLos músculos: Anatomía clínica de las extremidades (Bicolor)Nota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- PAE UCI AdrianaDocumento8 páginasPAE UCI AdrianaSheylita Jesus CubillusAinda não há avaliações
- Monografia de VoleyDocumento10 páginasMonografia de VoleyEdinson Perez43% (7)
- Uci Pae Distres RespirastorioDocumento23 páginasUci Pae Distres RespirastorioSheylita Jesus Cubillus100% (1)
- Repaso VacacionalDocumento37 páginasRepaso VacacionalSheylita Jesus CubillusAinda não há avaliações
- III BimestreDocumento69 páginasIII BimestreSheylita Jesus CubillusAinda não há avaliações
- Religion. IV BimDocumento22 páginasReligion. IV BimSheylita Jesus CubillusAinda não há avaliações
- QQQQQDocumento9 páginasQQQQQSheylita Jesus CubillusAinda não há avaliações
- Circulacion en Los AnimalesDocumento13 páginasCirculacion en Los AnimalesSheylita Jesus CubillusAinda não há avaliações
- Genu Varo Genu Valgo Verdadero y FalsoDocumento27 páginasGenu Varo Genu Valgo Verdadero y FalsoCintya Quispe Macedo100% (3)
- Muerte CerebralDocumento22 páginasMuerte CerebralPRE RESIDENTES 2017Ainda não há avaliações
- Tromboelastometria y TromboelastografíaDocumento11 páginasTromboelastometria y TromboelastografíaMarcela Sanchez Parra100% (2)
- Discapacidad MotrizDocumento36 páginasDiscapacidad MotrizReyna Torres IlaquitaAinda não há avaliações
- Ficha Tecnica DiamaxDocumento1 páginaFicha Tecnica DiamaxEMPREMEDI S.A.Ainda não há avaliações
- Artritis Reumatoide en Ovejas y CabrasDocumento8 páginasArtritis Reumatoide en Ovejas y CabrasVaCh DaVidAinda não há avaliações
- KmadurasDocumento5 páginasKmadurasRraulr RojasAinda não há avaliações
- Intoxicacion EstafilococicaDocumento11 páginasIntoxicacion EstafilococicaFranklin Carretero RojasAinda não há avaliações
- Guia Observación, Examen Práctico de Promoción.Documento2 páginasGuia Observación, Examen Práctico de Promoción.Carlos PrietoAinda não há avaliações
- FINAL Fisio General 2022Documento7 páginasFINAL Fisio General 2022Nadia AlbalatAinda não há avaliações
- DiagnósticoDocumento4 páginasDiagnósticosergioAinda não há avaliações
- Puntos de ApoyoDocumento4 páginasPuntos de Apoyoeve100% (2)
- Botiquín Primeros AuxiliosDocumento2 páginasBotiquín Primeros AuxiliosYoselin RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Taller Signos VitalesDocumento5 páginasTaller Signos VitalesKarol Arnedo MarinAinda não há avaliações
- SEMIOlOGIA RADIOLOGICA DEL TORAX-CLASE VI-1Documento76 páginasSEMIOlOGIA RADIOLOGICA DEL TORAX-CLASE VI-1Pedro CostaAinda não há avaliações
- Anamnesis Psicológica Niños ModificadoDocumento6 páginasAnamnesis Psicológica Niños ModificadoAnghel Luan Vera FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Traqueobronquitis ExposicionDocumento14 páginasTraqueobronquitis ExposicionJunior AguilarAinda não há avaliações
- 04 Vectores T. Cruzi (Triatominos) 2022Documento83 páginas04 Vectores T. Cruzi (Triatominos) 2022fioregleoneAinda não há avaliações
- Autopsia Verbal CacuDocumento7 páginasAutopsia Verbal CacuJuan J. LópezAinda não há avaliações
- Pasos NAR. DESDE PsicologiaDocumento2 páginasPasos NAR. DESDE PsicologiaAngela HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Gingivitis NoñosDocumento4 páginasGingivitis NoñosAlaín LeónAinda não há avaliações
- Obtencion de Materia Prima y NutraceuticosDocumento57 páginasObtencion de Materia Prima y NutraceuticosSara Rojas100% (2)
- ALUMBREDocumento4 páginasALUMBREDiegoAinda não há avaliações
- Pensamiento DistorsionadoDocumento4 páginasPensamiento DistorsionadoLizeth RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Cultura Fisica y Deporte para El Estado de Nayarit (Ley De)Documento32 páginasCultura Fisica y Deporte para El Estado de Nayarit (Ley De)Jose Luis OlimonAinda não há avaliações
- Ensayo de Aztecas J Mayas e Incas de Historia de La MedicinaDocumento4 páginasEnsayo de Aztecas J Mayas e Incas de Historia de La MedicinaPrueba Kskdk100% (2)
- Toxina Botulinica ADocumento5 páginasToxina Botulinica APavel LunaAinda não há avaliações
- Anotomia de Laringe y FaringeDocumento26 páginasAnotomia de Laringe y FaringeAna RuizAinda não há avaliações
- TinidanDocumento1 páginaTinidanJuan PerzAinda não há avaliações
- OsteomielitisDocumento33 páginasOsteomielitisDaniel Felipe Hoyos YepesAinda não há avaliações