Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
2 9
Enviado por
Husna AdilaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
2 9
Enviado por
Husna AdilaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Forces in Equilibrium The principle of the forces in equilibrium states, When forces act upon an object , the object
t is said to be in a state of equilibrium when the resulting force acting on the object is zero ( no net force acting upon it) When the equilibrium is reached, then the object is in two states, that is (i) remains stationary (if the object is stationary) (ii) moves at a constant velocity ( if the object is moving) Based on , F = ma atau a = F m When the equilibrium of forces is achieved, then, F = 0 , hence a =0 Thus a = 0 , it means the object remains stationary or moves at a constant velocity. e!ton"s Third #a! of $otion ewton!s third law of motion states , "o every action there is an equal but opposite direction E%amples Forces in Equilibrium (a)
Wei&ht = ormal reaction (b)
Wei&ht = Tension (c)
Buoyant force = Wei&ht
(d)
Wei&ht = ormal reaction (e)
Wei&ht = ormal reaction 'ullin& force = Frictional force (f)
Wei&ht = #iftin& force (rivin& force = (ra&&in& force (g)
Wei&ht = ormal reaction En&ine thrust = )ir resistance * Frictional force
(h)
Buoyant force = Wei&ht of load * Wei&ht of helium &as T!o Forces in Equilibrium
' * +=0 We can re!ritten into ' = , + Example 1 #igure shows a stationary wooden bloc$ of mass % $g resting on a table&
'alculate (a) the weight of the wooden bloc$ (b) the normal reaction Solution
Three Forces in Equilibrium
' * + *-=0 When three forces in equilibrium the triangle of forces in one direction (in order) ()ample % "he following figure shows a steel sphere of mass *% $g suspended from a length of rope which is pulled to the side by a horizontal force of +& "he tension of another rope is &
(a) (b)
,raw a triangle of forces& 'alculate the value of (i) + (ii)
Solution
-esultant force #orce is a vector quantity and hence it has magnitude and direction& "wo or more forces which act on an object can be combined into a single force called the resultant force& -f two forces are in same line, vector addition is easy& We simply add the forces if both pull or push together. subtract them if one is in the opposite direction& -f they are at an angle, the resultant force can be determined by the triangle method and the parallelogram method&
Parallelogram method :
-n this method the tail of the first vector is joined to the tail of second vector and then draw a parallelogram& "he diagonal represents the resultant force& Triangle method:
-n this method the tip of the first vector is joined to the tail of second vector and then draw a line to complete the triangle& "he third side represents the resultant force& Example 3 #ind the resultant force for the following figure/0
Solution:
Example 4
"he figure shows a trolley is pulled by two forces What is the magnitude and the direction of the resultant force acting on the trolley& Solution
Example 5 #igure shows a boat is pulled by two forces& 'alculate the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the trolley&
Solution:
-esolution of forces 1 force can be resolved into two components, that is, (i) the horizontal component, #) and (ii) the vertical component , #y
F% = F cos q Fy = F sin q 2 2 q is an angle between the force # to the horizontal line the sign of the force depend on the quadrant where the force , # is placed
#or an object on a inclined plane, the weight,W of the object can be resolved into two components . (i) parallel to inclined plane, 1 (ii) perpendicular to inclined plane,3
) = W sin q B = W .os q
Example 6 #ind the values of 4) and 4y for the following figures&
Solution:
Example 7
#igure shows a stationary wooden bloc$ of mass 56 g which is placed on a inclined plane that is at an angle of 76 o to the horizontal& What is the magnitude of the weight parallel to the inclined plane& /olution0
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- English (Reading, Writing)Documento8 páginasEnglish (Reading, Writing)Husna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- 4 5817800830434148958 PDFDocumento1 página4 5817800830434148958 PDFHusna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- Readind Writing GrammarDocumento8 páginasReadind Writing GrammarHusna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- List of Registered Participants (Rero Educators Conference)Documento3 páginasList of Registered Participants (Rero Educators Conference)Husna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- Book 5: Magnetcode For 2-Axis Robot ArmDocumento41 páginasBook 5: Magnetcode For 2-Axis Robot ArmHusna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- Example Paper 3Documento1 páginaExample Paper 3Husna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- Gravitational ForceDocumento4 páginasGravitational ForceHusna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- MODULE 7-The Straight LinesDocumento15 páginasMODULE 7-The Straight LinesHusna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- Latest F4STDocumento4 páginasLatest F4STHusna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- Meaning of Shape: Return To TutorialDocumento1 páginaMeaning of Shape: Return To TutorialHusna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- The Effect of ForcesDocumento1 páginaThe Effect of ForcesHusna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
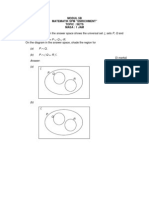
- The Venn Diagram in The Answer Space Shows The Universal Set, Sets P, Q and The Universal Set On The Diagram in The Answer Space, Shade The Region ForDocumento9 páginasThe Venn Diagram in The Answer Space Shows The Universal Set, Sets P, Q and The Universal Set On The Diagram in The Answer Space, Shade The Region ForHusna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- 2.2 Menganalsis Gerakan Graf ( /20 X 100 %)Documento6 páginas2.2 Menganalsis Gerakan Graf ( /20 X 100 %)Husna AdilaAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- p135w11 Lecture Notes v1.0 PDFDocumento406 páginasp135w11 Lecture Notes v1.0 PDFFiras HarithAinda não há avaliações
- Kin ENGDocumento25 páginasKin ENGLakshyaAinda não há avaliações
- Notes On Partial Differential Equations (Theory)Documento129 páginasNotes On Partial Differential Equations (Theory)Elhibari OthmaneAinda não há avaliações
- Boson Algebra As A Symplectic Clifford AlgebraDocumento12 páginasBoson Algebra As A Symplectic Clifford AlgebraHong Shen LiuAinda não há avaliações
- Unit I: Electromagnetic TheoryDocumento139 páginasUnit I: Electromagnetic TheoryDependra SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Emtl Unit1 PDFDocumento49 páginasEmtl Unit1 PDFnelapatikoteswarammaAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions Manual Continuum Mechanics Lai 4th EdittionDocumento246 páginasSolutions Manual Continuum Mechanics Lai 4th Edittiondiego_dave89% (18)
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocumento7 páginasNewton's Laws of MotionwolfretonmathsAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus 15 SyllabusDocumento3 páginasCalculus 15 SyllabusSooraj VSAinda não há avaliações
- Class XI PHYSICS - Class Assignment TOPIC: - Vector ProductDocumento2 páginasClass XI PHYSICS - Class Assignment TOPIC: - Vector Productsudir_phyAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions Manual PDFDocumento964 páginasSolutions Manual PDFfwalker2013100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Solution - Matlab Programming With Applications For EngineersDocumento7 páginasChapter 2 Solution - Matlab Programming With Applications For EngineersCarolMichalskiAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Characteristics of Linear Asynchronous Motor: A. Boudiaf, Z. Aissani, A. BentriouDocumento4 páginasMechanical Characteristics of Linear Asynchronous Motor: A. Boudiaf, Z. Aissani, A. BentriouTarak BenslimaneAinda não há avaliações
- 1100 PDF-How To Solve 2 Dimension Relative Velocity ProblemsDocumento7 páginas1100 PDF-How To Solve 2 Dimension Relative Velocity ProblemsAfia S HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Module Checklist - Mechanics - Grade 12Documento7 páginasModule Checklist - Mechanics - Grade 12api-257324866Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsDocumento37 páginasChapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsTutor_KLAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Quantities, Units and MeasurementDocumento8 páginasPhysical Quantities, Units and Measurementmanya mustafaAinda não há avaliações
- Applications of Linear Algebra in Game Development2Documento8 páginasApplications of Linear Algebra in Game Development2VARANGANTI HARI PRATAP GOUTHAM 17110168Ainda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics, Turbulent Flow and Turbulence ModelingDocumento247 páginasFluid Mechanics, Turbulent Flow and Turbulence ModelingAhmad GhafouriAinda não há avaliações
- Flow,: Power Requirement, and Pressure Distribution of Fluid in A Screw ExtruderDocumento6 páginasFlow,: Power Requirement, and Pressure Distribution of Fluid in A Screw ExtruderLê Văn HòaAinda não há avaliações
- AHP Supply Chain ManagementDocumento6 páginasAHP Supply Chain Managementsajesh nairAinda não há avaliações
- Methods of Problem Solving in KinematicsDocumento7 páginasMethods of Problem Solving in KinematicsVikram AdityaAinda não há avaliações
- Angular MomentumDocumento10 páginasAngular MomentumKlarence Medel PacerAinda não há avaliações
- Delhi Public School-Bopal, Ahmedabad Assignment Class: XII Vector Algebra Level 1Documento2 páginasDelhi Public School-Bopal, Ahmedabad Assignment Class: XII Vector Algebra Level 1DevanshGanganiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2Documento27 páginasChapter 2Mainul Islam 312Ainda não há avaliações
- Ultra-Small-Angle Neutron Scattering With Azimuthal AsymmetryDocumento10 páginasUltra-Small-Angle Neutron Scattering With Azimuthal AsymmetryKarthikPrakashAinda não há avaliações
- Cauchy's Stress Theorem-Stress Tensor-The State of Stress at A Point PDFDocumento8 páginasCauchy's Stress Theorem-Stress Tensor-The State of Stress at A Point PDFonnly1964Ainda não há avaliações
- NUST Engineering 2 1Documento28 páginasNUST Engineering 2 1d3d3dAinda não há avaliações
- 2K MethodDocumento5 páginas2K MethodLind D. QuiAinda não há avaliações