Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Some Important Reasoning Based Questions of Organic Chemistry
Enviado por
Sourajit MukherjeeDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Some Important Reasoning Based Questions of Organic Chemistry
Enviado por
Sourajit MukherjeeDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
SOME IMPORTANT REASONING BASED QUESTIONS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
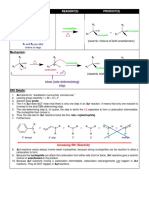
1. Chlorobenzene is less reactive than chloromethane. Ans. In chlorobenzene, each carbon atom of benzenering is sp2 hyridised and is electron withdrawing. Chlorine atom donates a lone pair of electron and acquire positive charge. The negative charge is delocalised on ortho and para position by resonance.
C-Cl bond acquires partial double bond character and is 169 pm as compared to 17.0 pm in chloromethane where C atom is sp3 hybridised. So larger amount of energy is required to break C-Cl bond in chlorobenzene and therefore is less reactive than haloalkane towards nucleophilic substitution reaction. 2. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanide as main product while AgCN form isocyonide.
Ans. KCN is, predominantly ionic compound and provide cyanide ion : C N in solution. The attack mainly takes place through lone pair of electron on carbon atom due to high electron density and not through nitrogen atom since C-C bond is more stable than C-N bond. AgCN: is mainly a covalent compound therefore, nitrogen donates electron pair forming isocyanide as the main product. 3. Grignard Reagent is prepared under anhydrous conditions. Ans. In Grignard Reagent, the carbon-magnesium covalent bond is highly polar with carbon atom of alkyl or aryl group withdrawing electrons from electropositive magnesium and magnesium halogen bond is also ionic
R Mg X . So Grignard reagent is highly reactive, and react with any
source of proton to give hydrocarbons. 176 [XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
R Mg X + H2O RH + Mg(OH)X 4. Wurtz Reaction is carried in dry ether.
Ans. CH3 Br 2Na Br dry other CH3CH3 2NaBr Sodium metal is sensitive towards air and moisture forming :
4Na O2 2Na2 O 2Na 2H2O 2NaOH H2
So reaction is carried in dry ether to avoid air and moisture. 5. SN1 reactions are favoured in protic solvent.
Ans. It involves C-X bond breakage for which the energy required is obtained through solvation of halide ion with the protons of protic solvent like H2O, alcohol etc. 6. Tertiary halides donot undergo SN2 mechanism.
Ans. In SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks to the carbon atom from the opposite side of halide atom. Three alkyl groups cause a steric hinderance to the approach of nucleophile. 7. Phenol is acidic in nature. In phenol each atom of benzene ring is sp2 hybridised and is electron withdrawing. Oxygen atom donates a pair of electron to the ring and acquire positive charge which facilitate the donate ion of proton.
The Phenoxide ion (conjugate base) is stabilised by resonance (PKa).
8.
Which is more acidic, p-nitrophenol or phenol? Explain why?
Ans. p-nitrophenol is more acidic. Any electron withdrawing group like NO 2 withdraws the electron density away from oxygen atom of phenoxide ion and this results in further delocalisation of negative charge and stabilisation 177 [XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
of phenoxide ion. Hence, electron withdrawing groups favour the ionisation of subsituted phenol to give more and more of H+ ions. 9. Cresol (C6H5OCH3) is less acidic than phenol.
Ans. Cresol is less acidic than phenol. Any electron releasing group like - CH3, releases the electron density over oxygen atom and destabilises it resulting in decrease in ionisation of cresol. So cresol is less acidic than phenol. 10. Ethers are insoluble in water.
Ans. Ethers cannot form Hydrogen bonds with water because it is less polar than water and cannot break hydrogen bonds formed between H2O molecules. 11. Boiling points of ethers are lower than isomeric alcohols.
Ans. Boiling points of ethers are lower than isomeric alcohols due to lack of intermolecular hydrogen bonding in ethers whereas alcohol molecules are associated through strong hydrogen bonds. 12. Ethers are polar in nature even if both alkyl groups are identical.
Ans. Ethers have non-linear structure. Each of the two C-O bonds are polar. Net dipole moment is the vector sum of dipole moments of both the bond dipoles.
13.
o-nitrophenol is steam volatile while p-nitrophenol is not.
o-nitrophenol is steam volatile due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding while p-nitrophenol is less volatile due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding. 14. Phenyl methyl ether reacts with HI to form phenol and methyl iodide not iodobenzene and methanol.
178
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
(a)
In phenyl methyl ether, the carbon atoms of phenyl group are sp2 hybridised and there is a partial double bond character in phenyl carbon-oxygen bond. Hence, C6H5O bond is stronger than CH3O. Therefore, the attack of I on the alkyl carbon of C6H5OH3C occurs and breaks the CH3O-bond to form phenol and iodomethane. Benzene ring offers a steric hinderance to I- to attack at C6H5O bond.
(b) 15.
Aldehydes are more reactive towards nucleophiles than ketones. (a) Sterically, the presence of two large substituents in ketones hinders the approach of nucleophile to carbonyl carbon as compared with aldehydes having only one such substituent. The two alkyl groups in ketones are electron releasing and release the electron density over carbonyl carbon, thus reduces the electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon more effectively than in aldehyde which has only one alkyl group.
(b)
16. Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2,2,6-trimethyl cyclohexanone does not.
+
Ans.
(a)
The three methyl groups are electron releasing and increase the electron density over carbonyl carbon atom thus reduces its electrophilicity. Three methyl groups causes steric hinderance to nucleophilic attack the carbonyl carbon of >C=group.
(b) 17.
There are two - NH2 groups in semicorbazide but only one is involved in the formation of semicorbozones.
Ans. >C = O + H2 N NHCONH2 >C=NNHCONH2 The lone pair of electrons on NH2 nearer to is delocalised over oxygen atom and therefore, this NH2 group is not available as mucleophile 179 [XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
H2N C = N NH2 The NH2
group not involved in resonance, will act as a nucleophile. 18. During the preparation of an ester from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, ester is removed as fast as it is formed.
H RCOOR1 H2O Ans. RCO OH H OR1
Both esterification and hydrolysis of ester are catalysed by acid, the reaction is reversible and an equilibrium is established, so ester or water is removed to favour the forward reaction, as per Le Chateliers principle. 19. Ans. pKa of chloroacetic acid is less than that of acetic acid or chloroacetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
+H
Any electron releasing group like CH3 increases the electron density over carboxylate anion (COO). The stability of the conjugate base is reduced and hence, H + cannot be donated easily. Thus, it decreases the acid strength of carboxylic acid. Any electron withdrawing group like Cl, F, NO2 etc. withdraws the electron density away from COO and spreads it and thus stabilises the carboxylate ion by delocalisation of negative charge. Thus, it increases the acid strength of carboxylic acid. 20. Amines are higher boiling compounds than hydrocarbons but lower boiling than alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
Ans. Boiling points of amines and alcohols are higher than those of hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding in amines and alcohols.
180
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
Hydrogen bonds in amines are weaker than those present in alcohols. This is because oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen, so boiling points of amines are lower than those of alcohols of comparable molecular masses. The intermolecular forces in hydrocarbons are weak van der Waals forces due to which hydrocarbons have lower boiling points than amines or alcohols. 21. Boiling point of isomeric tertiary amines are lower than those of primary amines.
Ans. Boiling points of isomeric tertiary amines are lower than those of primary amines due to the lack of intermolecular hydrogen bonding which exists in primary amines. 22. Observed Kb order is : (C2H5)2NH<(C2H5)3N<C2H5NH2<NH3 (CH3)2NH>CH3NH2>(CH3)N>NH3 Ans. (a) In gaseous phase, where solvent factor is missing, larger the number of electron releasing groups, more basic is the amine (positive inductive effect) as they release the electron cloud over N-atom and lone pair of electrons can be donated easily. The Kb order should be: teritary amine > secondary amine > primary amine. (b) In aqueous phase, the substituted ammonium cations get stabilised not only by electrons releasing effect of alkyl groups (+I) but also by solvation with water molecules via hydrogen bonding. In case the alkyl group is bigger than CH3 group, there will be steric hinderance to Hbonding resulting in less stabilisation of substituted ammonium cation. Combining these factors (i) Inductive effect stabilisation of substituted ammonium cations via H-bonding. (ii) steric hinderance of bigger alkyl group to H-bonding. The order of basic strength is as given above. 23. Aniline is a weaker base than CH3NH2.
Ans. In aniline, each C-atom of benzene ring is sp2 hybridised and is electron withdrawing. Nitrogen atom donates a lone pair of electrons to the ring and acquire (+) charge. The negative charge is delocalised on ortho and para position by resonance.
181
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
So due to delocalisation, the lone pair of electrons on benzene ring is not avai l abl e f or donat i on and t heref ore, ani l i ne i s w eaker base t han C H 3NH2 where CH3 is an electron releasing group and increases electron availability on N-atom which can be donated easily. 24. Methylamine in water react with ferric chloride to precipitate hydrated ferric oxide.
Ans. Methylamine in water behaves as a base to form OH- ions which react with FeCl3 to form hydrated ferric oxide.
+
25.
NH2 is ortho and para directing in aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions but aniline on nitration give a substantial amount of meta-nitro aniline.
Ans.
In strongly acidic medium aniline is protonated to form anilinium ion
NH3 in which NH3 group acts as meta directing.
+ + +
+
182
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
26.
Aniline does not undergo FriedelCraft reaction.
Ans. Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Craft reaction due salt formation with aluminium chloride, the Lewis acid, which is used as catalyst. Due to this, N-atom of aniline acquires positive charge and hence, it acts as strong deactivating group for further reaction.
27.
Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by Gabriels phthalamide synthesis.
Ans. Aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction with the anion formed by phthalamide because of partial double bond character of CX bond of aryl halide. 28. Although chlorine atom is an electron withdrawing group yet it is ortho and para directing in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
Ans. Please see Page 306, NCERT Part II. 29. Phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structure than carboxylate ion but carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
Ans. The phenoxide ion has non-equivalent resonance structures in which negative charge is at less electronegative carbon atom of phenoxide ion. The carboxalate ion has two equivalent resonance structures in which negative charge is more effectively delocalised over two electronegative oxygen atoms. In phenoxide ion, the negative charge is less effectively delocalised over one oxygen atom and less electronegative carbon atom of phenoxide ion. Thus, the carboxylate ion is more stabilised than phenoxide ion. Therefore, carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols.
183
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
Lucas Test is based on Kinetics of the reaction. 3 alcohols react at the fastest rate.
(3 alcohol)
(2 alcohol)
(1 alcohol)
Reagent
Reagent
184
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
and heat
(yellow ppt.)
(CHI3)
and heat s p
and heat
6.
[Fe(C6H5O)6] + 3Cl (Violet colour)
+3Br
3HBr
185
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
( CH3CH(OH)CH3
[XII Chemistry]
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
and heat
(CHI3)
186
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
a(
(CHI3) of Cu2O
and heat
(CHI3)
(CHI3)
COONa
formic (HCOOH acid
acetic acid
(aq)
187
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
C6H5SO2Cl + H2NC6H5
OH
C6H5SO2 NHC6 H5
NaOH
C6H5SO2 N Na C 6H 5
188
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
Aniline
Methylamine (CH3NH2)
+ heat
of Cu2O (Ag)
189
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII 2013 # Question Organic Chemistry *3rd
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
MOST FREQUENTLY ASKED REASONING BASED AND DISTINCTION BASED QUESTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes. Give two reasons. KCN reacts with haloalkanes to form alkyl cyanide as a main product while AgCN forms isocynamide as main product. Although chlorine is an electron withdrawing group, yet is ortho and paradirecting in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. The presence of an electron withdrawing like NO 2 at ortho and parapositions increases the reactivity of haloarenes. A SN2 reaction proceeds with complete stereo-chemical inversion while SN1 reaction proceeds with racemisation. Wurtz reaction is carried out in dry ethereal medium. Grignard reagent should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. tert-Butyl chloride reacts with aqueous NaOH by SN1 mechanism while n-Butyl chloride reacts with SN2 mechanism. SN1 reactions are favoured in protic solvent. Phenol is acidic in nature. p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol. p-cresol is less acidic than phenol. Boiling point of ethers are lower than isomeric alcohols. Ethers having two identical alkyl groups are polar in nature. o-nitrophenol is steam volatile while p-nitrophenol is not. Phenyl methyl ether reacts with HI to form phenol and methyl iodide and not iodibenzene and methanol.
190
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII*2013-addition QP-1*3rd print
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31.
Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophilic attack. Cyclohexanone form cyanohydrin in good hexanone does not. yield but 2,2,6-trimethleylo-
There are two NH2 groups in semicasbazide (H2N NH CONH2) but only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones. Although phenoxide ion (C6H5O) has more number of resonaling structure than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acids is a stronger acid than phenol. pKa of acetic acid is more than that of chloroacetic acid. 4-Nitrobenzoic acid is stronger acid than benzoic acid but 4-methoxybezoic acid is weaker acid than benzoic acid. Formic acid is stronger acid than benzoic acid. FCH2COOH is stronger acid than ClCH2COOH. Aniline is weaker base than cylohexylamine or an alkylamine. CH3 NH2 or RNH2 reacts with aq. FeCl3 to precipitate hydrated ferric oxide (Fe2O3 xH2O). NH2 group is ortho - and para - directing in aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction but aniline on nitration gives substantial amount of m-nitroaniline. Aniline like phenol does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction. Aromatic amines cannot be prepared by Gabriels phthalimide synthesis CH3NH2 or CH3CH2NH2 is soluble in water but aniline is not. The decreasing order of basic strength in gas phase is (C 2H5)3N (C2H5)2NH
>
> C2H5NH2 but in aqueous medium the correct decreasing order is (C2H5)2NH > (C2H5)3N > C2H5NH2
32. 33. 34. The decreasing order of basic strength in aqueous medium is (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N pKb of aniline is more than that of methylamine. CH3NH2 has more boiling point than (CH3)3N but has less boiling point than CH3OH.
191
[XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII*2013-addition QP-1*3rd print
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
Distinction - Based Questions
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. Chloroethane and Chlorobezene Cyclohexyl Chloride and Chlorobenzene Benzyl Chloride and Chlorobenzene Allyl Chloride and Vinyl chloride. Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) and isopropyl alcohol (propan-2-ol) Isopropyl alcohol and tert-butyl alcohol. Phenol and ethyl alcohol. Phenol and cyclohexyl alcohol. Acetaldehyble and acetone. Formaldehyde and acetaldehyde Ethanal and benzaldehyde Acetophenone and benzophenone Pentan-2-one and penton-3-one Formic acid and formadehyde. Formic acid and acetic acid. Acetone and acetic acid. Primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Methylamine and dimethylamine Dimethylamine and trimethylamine Aniline and cyclohexylamine Aniline and benzylamine Phenol and aniline. Acetone and acetic acid Acetic acid and ethylacetate Methylacetate and ethylacetate Phenol and acetic acid. 192 [XII Chemistry]
Twinklegraphics*chemistry-XII*2013-addition QP-1*3rd print
Você também pode gostar
- Reasoning Qns With Answers - Haloalkanes&Haloarenes 2Documento8 páginasReasoning Qns With Answers - Haloalkanes&Haloarenes 2tanishka0307Ainda não há avaliações
- Notes Organic Chemistry and AlkanesDocumento17 páginasNotes Organic Chemistry and Alkanessrk78Ainda não há avaliações
- Reactions of Alkenes: CC HX C HX C Markovnikov's OrientationDocumento8 páginasReactions of Alkenes: CC HX C HX C Markovnikov's OrientationMarc RitzAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Organic ChemistryDocumento90 páginasRevised Organic ChemistryMinh TieuAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohols & Phenols:: GeneralizationsDocumento27 páginasAlcohols & Phenols:: GeneralizationsdoudoudoudouAinda não há avaliações
- Haloalkanes PDFDocumento6 páginasHaloalkanes PDFthc8477Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 20 & 21 - Wade - NDDocumento93 páginasChapter 20 & 21 - Wade - NDyonggyeAinda não há avaliações
- Romatic Ydrocarbons: CH CH CH C HDocumento7 páginasRomatic Ydrocarbons: CH CH CH C HMukesh BishtAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry-JeeDocumento33 páginasOrganic Chemistry-JeeRamesh Babu GarlapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocumento99 páginasAlcohols, Phenols and EthersSanya VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Reduction Agents Organic ChemistryDocumento55 páginasReduction Agents Organic ChemistryvgvijuAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition ReactionsDocumento64 páginasChapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactionsaggelisgeorge8546Ainda não há avaliações
- Welcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvansDocumento22 páginasWelcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvanseraborAinda não há avaliações
- Skoog: CHM 414: Analytical ChemistryDocumento2 páginasSkoog: CHM 414: Analytical ChemistryCapsanneAinda não há avaliações
- Aromatic Compounds and Uses of BenzeneDocumento44 páginasAromatic Compounds and Uses of BenzenePaarijat DubeyAinda não há avaliações
- HYDROCARBONS Plusone HssliveDocumento13 páginasHYDROCARBONS Plusone HssliveAthulRKrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- Electron Delocalization and ResonanceDocumento9 páginasElectron Delocalization and ResonanceMariana LizethAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohols-Phenols and EthersDocumento16 páginasAlcohols-Phenols and EthersTr Mazhar PunjabiAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry Problem SetDocumento10 páginasOrganic Chemistry Problem SetBermonica Alvior SatuitoAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohol, Phenol, and Ethers:: "Their Structures, Physical Properties and Nomenclature"Documento33 páginasAlcohol, Phenol, and Ethers:: "Their Structures, Physical Properties and Nomenclature"AmanAinda não há avaliações
- Caieee04fisica PDFDocumento15 páginasCaieee04fisica PDFRafaelAinda não há avaliações
- ALKANES2Documento41 páginasALKANES2Shiki Asagami BrunestedAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 - Alkene ReactivityDocumento23 páginasChapter 8 - Alkene ReactivitySimran DhunnaAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chem U-2 AlcoholDocumento33 páginasOrganic Chem U-2 Alcoholsinte beyuAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1Documento11 páginasLecture 1Fang GaoAinda não há avaliações
- Reactions of AlcoholsDocumento49 páginasReactions of AlcoholsayushAinda não há avaliações
- Ether: Navigation Search AetherDocumento7 páginasEther: Navigation Search AetherMuhammad Wahyu Nugraha0% (1)
- 15 - Aldehyde and KetonesDocumento66 páginas15 - Aldehyde and KetonesIrfan Raza100% (1)
- CH 19-AminasDocumento40 páginasCH 19-Aminasmelg16Ainda não há avaliações
- Organic ChemistryDocumento14 páginasOrganic ChemistryStuteeAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperconjugation, The Anomeric Effect, and More: Chem 206 D. A. EvansDocumento12 páginasHyperconjugation, The Anomeric Effect, and More: Chem 206 D. A. Evansomkar9996767Ainda não há avaliações
- Preparations of Tetraamminecopper IIDocumento13 páginasPreparations of Tetraamminecopper IIJOHANA ARAUZAinda não há avaliações
- 100 Organic Reagentspptx - 230327 - 085539 PDFDocumento15 páginas100 Organic Reagentspptx - 230327 - 085539 PDFHeera MeenaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocumento29 páginasChapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionAnonymous Ngsu7C4aAinda não há avaliações
- Cy 101 Uv-Vis and Ir NewDocumento66 páginasCy 101 Uv-Vis and Ir NewSomesh MohapatraAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 - Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes PDFDocumento40 páginasChapter 7 - Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes PDFSam0% (1)
- Determination of o of Chromium Using Tanabe-Sugano DiagramDocumento2 páginasDetermination of o of Chromium Using Tanabe-Sugano DiagramDozdiAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Problems On Addition Reactions To Alkenes With AnswersDocumento4 páginasPractice Problems On Addition Reactions To Alkenes With AnswersSangetha ChelladoraiAinda não há avaliações
- Qoii0708 CO 17 TIFDocumento34 páginasQoii0708 CO 17 TIFLovely Joysweet100% (2)
- HW1 Solns KineticsDocumento10 páginasHW1 Solns Kineticsapb91781Ainda não há avaliações
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento159 páginasPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 Dir+eff++keyDocumento1 páginaOrganic Chemistry Midterm 1 Dir+eff++keyNorma Leticia RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Aromatic Cmpds AnskeyDocumento6 páginasAromatic Cmpds AnskeyAaron LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 Organic Chemistry ReactionsDocumento9 páginasUnit 5 Organic Chemistry ReactionsRobbing_Hood100% (1)
- CH 44 Organic Reactions - Supp Ex 1 (Updated)Documento4 páginasCH 44 Organic Reactions - Supp Ex 1 (Updated)伊貝P-Ainda não há avaliações
- T1-1 TDocumento30 páginasT1-1 TFRENCHONLYAinda não há avaliações
- Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Documento52 páginasStructure and Synthesis of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- CARBONYL CONDENSATION REACTIONS 2 (10 Mei 2013)Documento34 páginasCARBONYL CONDENSATION REACTIONS 2 (10 Mei 2013)Mammy Nya AllyaAinda não há avaliações
- ALKANESDocumento73 páginasALKANESChona TuyAinda não há avaliações
- Set3ans 10Documento5 páginasSet3ans 10amalinaishahAinda não há avaliações
- Important Order and Facts of Organic ChemistryDocumento6 páginasImportant Order and Facts of Organic ChemistryDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKAinda não há avaliações
- AP Ch. 12-13 Kinetics & Equilibrium Review AnswersDocumento35 páginasAP Ch. 12-13 Kinetics & Equilibrium Review AnswersRucar Rad0% (1)
- CH 8 Handouts (All)Documento34 páginasCH 8 Handouts (All)Ryan MaAinda não há avaliações
- Thermochemistry Answers RemovedDocumento11 páginasThermochemistry Answers Removedapi-327309463Ainda não há avaliações
- Organic Chem Midterm 1mech++keyDocumento1 páginaOrganic Chem Midterm 1mech++keyNorma Leticia RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Answer: (A) and (B)Documento18 páginasAnswer: (A) and (B)Germaine Manangan100% (1)
- Exp.06 Preparation of P-Bromo AcetanilideDocumento3 páginasExp.06 Preparation of P-Bromo AcetanilideAnanda VijayasarathyAinda não há avaliações
- Organic ChemistryDocumento25 páginasOrganic ChemistryhimanisinghbasnalAinda não há avaliações
- CHEMISTRY Part 2 Guess Paper 2023Documento14 páginasCHEMISTRY Part 2 Guess Paper 2023hassan932Ainda não há avaliações
- Organohalogen NotesDocumento76 páginasOrganohalogen NotesBella HannaAinda não há avaliações
- CM134-1L Experiment 2.1Documento8 páginasCM134-1L Experiment 2.1Christian JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Chm125 Lab Manual Okt 2022Documento25 páginasChm125 Lab Manual Okt 2022FiqajasmeAinda não há avaliações
- Spsc-Testing Service-Umerkot, 4TH Self - Assessment (Mcat)Documento45 páginasSpsc-Testing Service-Umerkot, 4TH Self - Assessment (Mcat)Ab Hadi100% (1)
- 2423 e 3Documento21 páginas2423 e 3Abdel Rahman MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- CHE1C1BDocumento4 páginasCHE1C1BSheila MuniandyAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrogen Reduction Cobalt-Chromium Spinel Oxides. Stoichiometric Cobalt ChromiteDocumento6 páginasHydrogen Reduction Cobalt-Chromium Spinel Oxides. Stoichiometric Cobalt ChromiteDuongAinda não há avaliações
- SN1 SN2Documento54 páginasSN1 SN2Feby Shyntia AfirantiAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Principal of Organic ChemistryDocumento69 páginasBasic Principal of Organic Chemistry1MS19CH049100% (1)
- Experiment 8 Classification of Organic Halides Formal ReportDocumento5 páginasExperiment 8 Classification of Organic Halides Formal ReportRoxine Florentino56% (9)
- Reaction Flashcards (Substitution and Elimination) PDFDocumento5 páginasReaction Flashcards (Substitution and Elimination) PDFArjun GandotraAinda não há avaliações
- TUGAS Organic Synthesis-1Documento28 páginasTUGAS Organic Synthesis-1Dia N SariAinda não há avaliações
- GS2011 QP BiologyDocumento16 páginasGS2011 QP Biologyvishnukesavieam1Ainda não há avaliações
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes GoodDocumento21 páginasHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes GoodAnitesh DharamAinda não há avaliações
- Organic ReactionsDocumento73 páginasOrganic ReactionsKrishnaah Doraj100% (1)
- Halogen DerivativesDocumento71 páginasHalogen Derivativesdevrarimanish72Ainda não há avaliações
- 56 5 3 ChemistryDocumento24 páginas56 5 3 ChemistrygettotonnyAinda não há avaliações
- Alkyl Halides PDFDocumento66 páginasAlkyl Halides PDFAhmed Sideeg83% (6)
- Isomerism: Definition-Structural Isomers: Same Molecular Formula Different Structures (Or Structural Formulae)Documento13 páginasIsomerism: Definition-Structural Isomers: Same Molecular Formula Different Structures (Or Structural Formulae)Pedro Moreno de Souza100% (1)
- Substitution ReactionsDocumento39 páginasSubstitution ReactionsAnil Kumar KadianAinda não há avaliações
- Ans & Sol - Chemistry (Class XII) - 28!02!2023Documento20 páginasAns & Sol - Chemistry (Class XII) - 28!02!2023sharanakash06Ainda não há avaliações
- #Aromatic Compound - 1Documento127 páginas#Aromatic Compound - 1shoaib1985100% (1)
- 07 Organic Mechanisms EDEXCELDocumento29 páginas07 Organic Mechanisms EDEXCELRach3chAinda não há avaliações
- IB Chem2 5 Assess T10Documento3 páginasIB Chem2 5 Assess T10Trúc Hồ100% (2)
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction (SN2) - 1Documento19 páginasNucleophilic Substitution Reaction (SN2) - 1Ramesh KatkamAinda não há avaliações
- 4 CBSQDocumento11 páginas4 CBSQShauryaAinda não há avaliações
- The Complete Book of EcstacyDocumento56 páginasThe Complete Book of EcstacyMagikFungus86% (7)
- Mock Test-Solutions & Halogen DerivativesDocumento3 páginasMock Test-Solutions & Halogen Derivativesshreyaraghuwanshi16Ainda não há avaliações
- Carbocations & CarbanionDocumento41 páginasCarbocations & CarbanionMuttu MAinda não há avaliações