Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
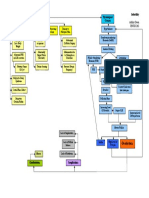
Sleep Apnea Concept Map
Enviado por
ashleydeanDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sleep Apnea Concept Map
Enviado por
ashleydeanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
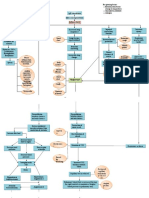
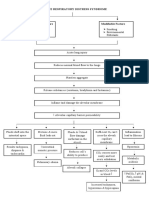
Risk Factors Physiological Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Changes
Ashley Dean
Abnormal Upper Abnormal Respiratory Obesity Sleep RNSG1263
Airway Structure Control Mechanism
Airway Muscles Relax
Nasal Obstruction Altered Tissue
& Muscle
Compliance Oropharynx Collapses Occluding Airway
Large Tonsils
& Adenoids
Reduction in Airway
Metabolic &
Endocrine Changes
Elongated during sleep
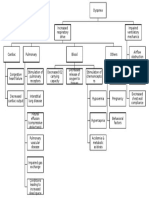
Soft Palette Decrease in O2 Moving Reduction of Gas Increase in CO2 Moving
Into Pulmonary Capillaries Exchange in Alveoli Out of Pulmonary Capillaries
Hypoxia Decrease in pCO2 In Blood
Decrease in pO2 In Blood
Stimulates Peripheral Chemoreceptors Stimulates Central Chemoreceptors
Send Excitatory Awakens Brain Sends Afferent Impulses to
Impulses to Medulla Medullary Inspiratory Neurons
Increases Ventilation
Airway Opens
Depressed Impotent Normal Respirations Resume
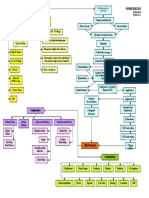
Irritable Moody
Increase in pO2 Decrease in pCO2
General Anesthesia
Problems Fall Back Asleep
Memory Problems Nocturia AMI
Medications Concerns Hyperventilation
Loss of Concentration Mood Swings Stoke
Sleep-deprived
Daytime Fatigue AM Headaches Hypertension Partners
Obstructive
Manifestations Complications Sleep Apnea
Você também pode gostar
- Obstructive Sleep ApneaDocumento15 páginasObstructive Sleep ApneaMushee01Ainda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology Tetanus FinalDocumento17 páginasAnatomy and Physiology Tetanus Finalfelicisimo039690175% (4)
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance Disorders WebDocumento36 páginasAssessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance Disorders WebStephKirstin Velasco Malapit100% (2)
- COPD Make-Up Assignment FINALDocumento9 páginasCOPD Make-Up Assignment FINALlmstar980% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans CVADocumento14 páginasNursing Care Plans CVAJaye DangoAinda não há avaliações
- Lumbar SpondylosisDocumento59 páginasLumbar SpondylosisKURBULDKAinda não há avaliações
- Narrative PathophysiologyDocumento18 páginasNarrative PathophysiologyNica Georgelle Maniego SamonteAinda não há avaliações
- Teaching Plan - CopdDocumento5 páginasTeaching Plan - Copdapi-363656404Ainda não há avaliações
- Multiple Sclerosis: Saadia Perwaiz, PT BSPT, M. Phil-MskDocumento39 páginasMultiple Sclerosis: Saadia Perwaiz, PT BSPT, M. Phil-MskArslan Aslam100% (2)
- Trigeminal NeuralgiaDocumento72 páginasTrigeminal NeuralgiaCocoMathewAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Sclerosis: Case Study by Trcoski ElenaDocumento43 páginasMultiple Sclerosis: Case Study by Trcoski ElenaElena TrcoskiAinda não há avaliações
- Brief Description: Pleural EffusionDocumento3 páginasBrief Description: Pleural EffusionJessica CatacutanAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocumento71 páginasDrugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDShabnam Binte AlamAinda não há avaliações
- Zoloft (Sertraline)Documento1 páginaZoloft (Sertraline)Adrianne BazoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan for Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocumento16 páginasNursing Care Plan for Peptic Ulcer DiseaseWardinatul ImanAinda não há avaliações
- ThyroidectomyDocumento52 páginasThyroidectomyWindelyn Gamaro100% (4)
- Patient Case Presentation: Headache: Migraine and Tension TypeDocumento31 páginasPatient Case Presentation: Headache: Migraine and Tension TypeKathleen B Baldado100% (3)
- Respiratory AlkalosisDocumento4 páginasRespiratory Alkalosismardsz100% (1)
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea - Pulmo LectureDocumento16 páginasObstructive Sleep Apnea - Pulmo LecturemandrakesMD0% (1)
- Pills ROWATINEXDocumento2 páginasPills ROWATINEXpbmlAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Ge Stimulations Mast Cell Degeneration Asthma AttackDocumento4 páginas1 Ge Stimulations Mast Cell Degeneration Asthma Attacknebbie06Ainda não há avaliações
- Ass Q ArdsDocumento1 páginaAss Q ArdsKristine MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Inp PathoDocumento1 páginaInp PathoNoveeAinda não há avaliações
- Culture and Sensitivity: InhalationDocumento3 páginasCulture and Sensitivity: Inhalationjamie carpioAinda não há avaliações
- Acid-Base Imbalances: Types, Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentsDocumento4 páginasAcid-Base Imbalances: Types, Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentsHenric CasimiroAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology DyspneaDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology DyspneaJoseph LimAinda não há avaliações
- Patho PneumoniaDocumento2 páginasPatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- 2020 - NEUR30002 - Lecture 28Documento48 páginas2020 - NEUR30002 - Lecture 28Neeraja MohanAinda não há avaliações
- Supplementary Material 1c Acute Respiratory FailureDocumento5 páginasSupplementary Material 1c Acute Respiratory FailureJanela Chriselle B. TICARAinda não há avaliações
- Woc Asma BronkialDocumento4 páginasWoc Asma Bronkialyedida susanaAinda não há avaliações
- Stroke PathophysioDocumento3 páginasStroke PathophysioKrystele CangaAinda não há avaliações
- ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) : EarlyDocumento1 páginaARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) : EarlyDora Elena HurtadoAinda não há avaliações
- Causes and Tests for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDSDocumento1 páginaCauses and Tests for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDSchristine louise bernardoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 22, Part DDocumento5 páginasChapter 22, Part Ddoris karimiAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumonia Concept Map - KPoindexterDocumento1 páginaPneumonia Concept Map - KPoindexterKatie_Poindext_5154100% (2)
- Shortness of BreathDocumento17 páginasShortness of BreathChingHuaAinda não há avaliações
- Managing Dyspnea: Understanding Causes and TreatmentsDocumento17 páginasManaging Dyspnea: Understanding Causes and TreatmentsChingHuaAinda não há avaliações
- IADVL Color Atlas of Dermatopathology - BookDocumento41 páginasIADVL Color Atlas of Dermatopathology - Book65gkenAinda não há avaliações
- Pathway Sop CerebriDocumento1 páginaPathway Sop CerebriFaris hakim100% (1)
- PATOFISIOLOGI TUMOR OTAKDocumento1 páginaPATOFISIOLOGI TUMOR OTAKPutri Dewi Arumsari100% (1)
- Pathway Sop CerebriDocumento1 páginaPathway Sop CerebriFaris hakimAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map Example 2Documento5 páginasConcept Map Example 2LorrieAinda não há avaliações
- Pa ThoDocumento3 páginasPa Thotammy_deguzman5223Ainda não há avaliações
- Respiratory FailureDocumento1 páginaRespiratory FailureKring-kring GereniaAinda não há avaliações
- Web of CautionDocumento2 páginasWeb of CautionSurya GexAinda não há avaliações
- Narrowed Blood Vessels and Stroke Nursing CareDocumento4 páginasNarrowed Blood Vessels and Stroke Nursing CareChelsyann FerolinoAinda não há avaliações
- ARDS ManagementDocumento4 páginasARDS ManagementJulyan ValenzaAinda não há avaliações
- RespiratoryDocumento1 páginaRespiratoryKhaled Abdel-saterAinda não há avaliações
- Pulmo Rehab 1 - MidDocumento16 páginasPulmo Rehab 1 - MidAlyssa RagasaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Foundations II: Caring for Clients with Oxygenation ProblemsDocumento4 páginasNursing Foundations II: Caring for Clients with Oxygenation ProblemsAlec Xavier MirandaAinda não há avaliações
- Hypoxia: Lori HolmesDocumento5 páginasHypoxia: Lori HolmesDanson Githinji EAinda não há avaliações
- Breathing Pattern Disorders Patient InformationDocumento7 páginasBreathing Pattern Disorders Patient InformationblackAinda não há avaliações
- Subjective Cues: Independent: On The: "Nahihirapa N Ako Huminga" AsDocumento5 páginasSubjective Cues: Independent: On The: "Nahihirapa N Ako Huminga" AsYessaminAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology & Concept Map: Precipitating FactorsDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology & Concept Map: Precipitating FactorsVanessa Rose Vargas0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderBlessyl Mae EstenzoAinda não há avaliações
- ABGs ManifestationsDocumento3 páginasABGs ManifestationsAnmari OnespinAinda não há avaliações
- Pathway PneumoniaDocumento1 páginaPathway PneumoniaFairuzAinda não há avaliações
- Pathphysiology of HPTN & Bone Metastasis Seondary To Stage 4 Malignant Pulmonary MassDocumento3 páginasPathphysiology of HPTN & Bone Metastasis Seondary To Stage 4 Malignant Pulmonary MassAnabel UnidaAinda não há avaliações
- Predisposing Factors: Age Neurological Condition Immunity Precipitating Factors: Smoking Environment LifestyleDocumento2 páginasPredisposing Factors: Age Neurological Condition Immunity Precipitating Factors: Smoking Environment LifestyleDavid RefuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map COPDDocumento2 páginasConcept Map COPDMatthew Frank Melendez QuerolAinda não há avaliações
- Pituitary Adenoma Concept MapDocumento1 páginaPituitary Adenoma Concept MapashleydeanAinda não há avaliações
- Osteoarthritis Concept MapDocumento1 páginaOsteoarthritis Concept Mapashleydean67% (3)
- Infertility Concept MapDocumento1 páginaInfertility Concept Mapashleydean0% (1)
- Hypertension Concept MapDocumento1 páginaHypertension Concept Mapashleydean100% (7)
- Bipolar Disorder Concept MapDocumento1 páginaBipolar Disorder Concept Mapashleydean100% (1)
- Degenerative Disc Disease Concept MapDocumento1 páginaDegenerative Disc Disease Concept MapashleydeanAinda não há avaliações
- Banco de Preguntas Parcial 1 InglesDocumento54 páginasBanco de Preguntas Parcial 1 InglesJoel GuallichicoAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory System Anatomy and FunctionDocumento7 páginasRespiratory System Anatomy and FunctionDaniel DanielAinda não há avaliações
- Measure Lung Volumes & Calculate Capacities Lab ReportDocumento6 páginasMeasure Lung Volumes & Calculate Capacities Lab ReportchairiziaAinda não há avaliações
- TSC - Common Sub H & H CHAP 1-5-1Documento86 páginasTSC - Common Sub H & H CHAP 1-5-1Manjot singh rainaAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumonia Case Study: Armed Forces of The Philippines Medical Center Medical Intensive Care UnitDocumento49 páginasPneumonia Case Study: Armed Forces of The Philippines Medical Center Medical Intensive Care UnitLei Ortega100% (1)
- Recognising Seriously Ill ChildrenDocumento12 páginasRecognising Seriously Ill ChildrenNurul Aulia AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Pulmonary Congestion Secondary To PneumoniaDocumento104 páginasPulmonary Congestion Secondary To PneumoniaAubrey Unique EvangelistaAinda não há avaliações
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Read and Answer The Questions in The Best Way You Can. Write The Letter of Your Answer On The Space Provided Before Each NumberDocumento4 páginasMULTIPLE CHOICE. Read and Answer The Questions in The Best Way You Can. Write The Letter of Your Answer On The Space Provided Before Each NumberLesley AntojadoAinda não há avaliações
- NANDA NursingDocumento11 páginasNANDA Nursingesteffie21Ainda não há avaliações
- Fluid Shifting and Electrolyte Shifting in Burn Injuries, Study GuideDocumento13 páginasFluid Shifting and Electrolyte Shifting in Burn Injuries, Study GuideNicole Williams86% (7)
- Case Study Final AsthmaDocumento6 páginasCase Study Final AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Ent SpecimenDocumento8 páginasEnt Specimen28bidishanathAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaDocumento5 páginasNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaKullin Rain100% (1)
- (Lung Biology in Health and Disease, V. 137) Richard D Bland - Jacqueline J Coalson-Chronic Lung Disease in Early Infancy-Marcel Dekker (2000)Documento1.080 páginas(Lung Biology in Health and Disease, V. 137) Richard D Bland - Jacqueline J Coalson-Chronic Lung Disease in Early Infancy-Marcel Dekker (2000)Uri MoraAinda não há avaliações
- Oxygen Therapy Powerpoint - Jan 2016 Student ViewDocumento47 páginasOxygen Therapy Powerpoint - Jan 2016 Student ViewMark Anthony AlcantaraAinda não há avaliações
- 2Documento78 páginas2api-3744136Ainda não há avaliações
- SuctioningDocumento23 páginasSuctioningrnrmmanphd100% (2)
- Pneumonia and TuberculosisDocumento18 páginasPneumonia and TuberculosisVincent QuitorianoAinda não há avaliações
- NANDA DefinitionDocumento5 páginasNANDA DefinitionAngel_Liboon_388Ainda não há avaliações
- RespiratorDocumento53 páginasRespiratorlianarodicaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocumento157 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsOliver Talip100% (1)
- Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDocumento4 páginasAssessment of Respiratory FunctionCristine Dominique E. DonaireAinda não há avaliações
- COPD Case PresentationDocumento78 páginasCOPD Case PresentationMaria Rogine ElopreAinda não há avaliações
- English VersionDocumento20 páginasEnglish Versionistinganatul muyassarohAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory SystemsDocumento4 páginasCirculatory SystemsMarielle GodoyAinda não há avaliações
- BurnsDocumento27 páginasBurnsThao TranAinda não há avaliações
- WK 4 Respiratory 2023Documento38 páginasWK 4 Respiratory 2023Basmala HebaAinda não há avaliações
- Pre-Op Preparation and Assessment of Pediatric PatientsDocumento62 páginasPre-Op Preparation and Assessment of Pediatric PatientsBedahanakugmAinda não há avaliações
- Syllab bscct1819-24102018Documento65 páginasSyllab bscct1819-24102018vasanthAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Newborns (RDSDocumento39 páginasUnderstanding Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Newborns (RDSMohammed BIen Manamba100% (2)