Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Psychart Software
Enviado por
OmarZSharafDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Psychart Software
Enviado por
OmarZSharafDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
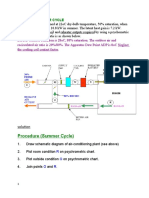
Examples on using Psychart
-- The digital psychrometric software
Basics of Air Conditioning Systems
Properties of the moist air
1. Moist air at standard atmospheric pressure
(Patm) is at 20 degree C dry-bulb
temperature (Tdb) and 50 % relative
humidity (RH). What is the humidity ratio
(absolute humidity, AH), degree of
saturation (DOS), dew point temperature
(Tdp), enthalpy (h), and wet bulb
temperature (Twb) of the moist air ?
Set the atmospheric pressure
Patm
Properties of the moist air
2. Continuing with problem 1, what is the wet
bulb depression (WBD) and what is the
vapor pressure deficit (VPD) ?
WBD = Tdb Twb = 20 13.79
= 6.21 deg. C
VPD = Pws Pw = 2.339 1.169
= 1.17 kPa
Dry-bulb temperature (T
db
) and relative
humidity (RH) in greenhouse
Tdb, deg.C
RH
min
(Activate fogging
system if below this
value)
Proper RH
RH
max
(severe
disease problem
might occurred if
higher than this
value)
15 - 50 % 73
20 46 64 80
25 60 73 86
30 70 80 89
VPD is a better index
Vapor Pressure Deficit
VPD
VPD too large
(activate fogging
system)
Proper VPD
range
VPD too low
(good for bacterial)
(activate heating or
dehumidification)
VPD too low
(might cause
severe disease
problem)
1.25
kPa
0.85
kPa
< 0.45
kPa
< 0.20
kPa
T, RH and VPD in a Greenhouse located in
Taiwan
Temperature,
deg.C
Relative humidity, %
VPD, kPa
Properties of the moist air
3. Fill the following blanks.
#1 #2 #3 #4
Atmospheric pressure, kPa
101.325 101.325 101.325 89.874
Dry-bulb T, deg.C
20 20 -10 20
Relative humidity, %
50 80 50 50
Humidity ratio, kg/kg
Dew point T, deg.C
Wet bulb T, deg.C
Specific volume, m
3
/kg
A bug was found in the software.
Twb should vary according to Patm.
Psychrometric Process
4. Determine the final state of moist air
originally at 20 deg.C and 50 % relative
humidity if 10 kJ are removed from 1.2 kg
of the air.
Answer to Problem 4
A T = q/(Ma*Cp)=(-10 kJ)/(1.2 kg*1.006 kJ/kg.K)= -8.28 K
The final dry bulb T will be 20 8.28 = 11.72 deg.C if this is a
sensible heating process.
The dew point T of moist air at initial state = 9.15 deg.C
The final dry bulb T > the dew point T of initial state, this is a
sensible cooling process.
A h =q/Ma = (-10 kJ)/(1.2 kg) = - 8.333 kJ/kg
The initial h = 38.5 kJ/kg
The final h = 38.545 8.333 = 30.212 kJ/kg
The initial dew point T = final dew point T.
Final state can be found based on final Tdb and Tdp, or
Tdb and h, or Tdp and h
State 2 was determined based on Tdb and H
H = 38.545 8.333 = 30.212 kJ/kg
Diff. of Tdp should be 0.
State 2 was determined based on Tdb and Tdp
AH = 8.591 kJ/kg which is a little bit off from 8.33
kJ/kg, also Diff. of AH should be 0.
Psychrometric Process
5. Determine the final state of moist air
originally at 20 deg.C and 50 % relative
humidity if 20 kJ are removed from 1.2
kg of the air.
Answer to Problem 5
A T = q/(Ma*Cp)=(-20kJ)/(1.2kg*1.006kJ/kg.K)= -16.56 K
The final T will be 20 16.56 = 3.44 deg.C if this is a
sensible heating process.
The dew point T of moist air at initial state = 9.1 deg.C
The final dry bulb T < dew point at initial state, this is a
cooling with condensation/dehumidification
process.
The final relative humidity is 100 %.
A h =q/Ma = (-20 kJ)/(1.2 kg) = - 16.66 kJ/kg
The initial h = 38.545 kJ/kg
The final h = 38.545 16.66 = 21.885 kJ/kg
State 2 can be determined based on RH and H,
however, this software does not provide this option.
We need to use trial and error method on Tdb of
state 2 to derive AH = -16.66 kJ/kg..
Psychrometric Process
6. Greenhouse in tropical and subtropical regions
often encounter high humidity problem. For
some floral industries, dehumidifier is used in the
greenhouses. Assuming the night time Tdb and
RH in a 3 m height 1000 m
2
greenhouse before
turn on the dehumidifier is 18 degree C, 91 %
respectively. After turn on the dehumidifier for a
while, the Tdb remain the same and RH drop to
80 %. How much water was removed from the
moist air inside this greenhouse ?
Answer to Problem 6
Before use
Specific volume = 0.8404 m
3
/kg
AH = 0.0117 kg vapor/kg dry air
After use
AH = 0.0103 kg vapor/kg dry air
Difference in AH
AH
1
AH
2
= 0.0014 kg vapor/kg dry air
Air volume 1000 x 3 = 3000 m
3
Air weight = 3000 / 0.8404 = 3569.7 kg
Total water condensed = 3569.7 * 0.0014 =
4.997 kg
Psychrometric Process
7. Air at 30 deg.C and 60% relative humidity
in a growth chamber is cycled past the
cooling coils and is returned back to the
chamber at a temperature of 15 deg.C.
Determine the psychrometric properties of
the air after it is cooled, the sensible and
latent heat removed, and the water vapor
condensed per kg of dry air moved past
the coils.
Growth Chamber
30 deg.C
60 % relative humidity
Cooler
15 deg.C
29.16 kJ/kg is the total heat removed, including
the sensible heat and the latent heat.
15.378 kJ/kg is the sensible heat removed
13.782 kJ/kg is the latent heat removed
0.0054 kg/kg dry air is the amount of water removed
13.782/ 2428.4 = 0.00567 kg/kg dry air is the amount
of water removed based on H
fg
.
Psychrometric Process
8. When ambient conditions are 35 deg.C and 25
% relative humidity, (a). determine the dry bulb
temperature to which ventilation air could be
cooled if drawn through an evaporative cooler
with an efficiency of 75%. (b). Calculate how
much water must be added to each cubic meter
of the air drawn through the cooler. (c). Redo
problem 7(a) with the ambient conditions at 35
deg.C and 80 % relative humidity.
Answer to problem 8
(a). At the given condition:
Tdb = 35 deg.C
RH = 25 % (Very dry weather)
Answer
Twb = 20.15 deg.C
WBD = 35 20.15 = 14.85 deg.C
AT = 0.75 * WBD = 11.13 deg.C
Final T = 35 11.13 = 23.87 deg.C
WBD
Answer to problem 8
(c). At the given condition:
Tdb = 35 deg.C
RH=80 % (Regular humid weather)
Answer
Twb = 31.64 deg.C
WBD = 35 31.64 = 3.36
AT = 0.75 * WBD = 2.52 deg.C
Final T = 35 2.52 = 32.48 deg.C
WBD
Answer to problem 8
(b). At initial conditions,
Tdb = 35 deg.C
RH = 25 %
Answer
the specific volume is 0.8853 m
3
/kg, humidity ratio is
0.0088 kg/kg of dry air.
At wet bulb of 20.15 and dry bulb of 23.87, the
humidity ratio is 0.0132 kg/kg of dry air.
A cubic meter of air will contain 1 m
3
/0.8853 m
3
/kg =
1.13 kg.
The change of humidity ratio is 0.0132 0.0088 =
0.0044 kg/kg dry air.
Thus, the total water gained by each cubic meter of
outdoor air will be 1.13 kg * 0.0044 kg/kg = 0.005 kg.
A small bug was found in the software.
Both Twb should be the same.
Psychrometric Process
9. A ventilation system for a calf nursery
draws 1 m
3
/s of air from the nursery,
exhausts 0.2 m
3
/s of the air to the outside,
and replaces the exhausted air with fresh
air. Air in the nursery is at 20 deg.C and 50
% relative humidity, and outdoor air is at 5
deg.C and 80 % relative humidity.
Determine properties of the mixed air
when it is returned to the nursery.
Calf Nursery
20 deg.C,
50 % relative humidity
Mixing
chamber
Outdoors
5 deg.C
80 % relative humidity
0.2 m
3
/s
1 m
3
/s
#1 #2 #3
T, deg.C 5 20 16.86 (cal.)
RH, % 80 50 53.37 (psychart)
V, m3/s 0.2 0.8 0.999
v, m3/kg 0.7935 0.8402 0.83
M, kg/s 0.252 0.952 1.204
W, kg/kg 0.0043 0.0073 0.0066 (cal.) / 0.0064 (psychart)
h, kJ/kg 15.859 38.545 33.796 (cal.) / 33.054 (psychart)
W
3
= (M
1
*W
1
+M
2
*W
2
)/(M
1
+M
2
)
h
3
= (M
1
*h
1
+M
2
*h
2
)/(M
1
+M
2
)
T
3
= (M
1
*T
1
+M
2
*T
2
)/(M
1
+M
2
)
State 3
| |
2 1
2 1
2
(
+
length
M M
M
| |
2 1
2 1
1
(
+
length
M M
M
Psychrometric Process
10. You are designing an evaporative cooling system to
ventilate a controlled environment, totally enclosed,
poultry house in a hot and dry climate.
Summer design weather conditions for your location
are 40 degree C Tdb and 20 % RH.
75 m
3
/s of outdoor air will be drawn by the evaporative
cooling system (75% efficiency) and 15 m
3
/s of outdoor
air will be drawn into the house through infiltration.
The birds in the house are expected to produce 250
kW of total heat of which 40% is latent heat. Determine
a) the psychrometric properties of the air mixed by air through
evaporative cooling pad and air through infiltration.
b) the psychrometric properties of the exhausted air.
c) the volumetric flow rate of air exhausted from the house.
d) the rate (L/s) at which water must be supplied to the evaporative
cooling pads by a water pump. When a (water flow/evaporation
rate) ratio of 3 is desire.
75 m
3
/s
4
3
1
2
15 m
3
/s
Evaporative
cooler
infiltration
Poultry
House
State 1
State 2
State 3
= 16.66, = 86.3, = 102.96 kg/s
T
3
= ( * T
1
+ * T
2
) / = 28.69 deg. C
W
3
=( * W
1
+ * W
2
) / = 0.0137 kg/kg
Zoom out
1
M
-
1
M
-
1
M
-
2
M
-
2
M
-
2
M
-
3
M
-
3
M
-
3
M
-
= 75 m
3
/s
v
2
= 0.8689 m
3
/kg
= 86.3 kg/s
4 3
1
2
= 15 m
3
/s
v
1
= 0. 9003 m
3
/kg
= 16.66 kg/s
Evaporative
cooler
infiltration
Poultry
House
T
1
= 40 deg. C
RH
1
= 20 %
W
1
= 0.0092 kg/kg
T
2
= 26.51 deg. C
RH
2
= 67.1 %
W
2
= 0.0146 kg/kg
T
3
= 28.69 deg. C
W
3
= 0.0137 kg/kg
= 102.96 kg/s
100 kW latent
150 kW
sensible heat
AT = 150 / ( * Cp) = 150 /
(102.96*1.006) = 1.448 deg. C
h
fg
= 2501 2.42 * (28.69+1.448)
= 2428 kJ/kg
AW= 100 / ( * h
fg
) = 100 /
(102.96 * 2428) = 0.0004 kg/kg
T
4
= T
3
+ AT = 28.69 + 1.448
= 30.138 deg. C
W
4
= W
3
+ AW = 0.0137 +
0.0004 = 0.0141 kg/kg
3
M
-
1
M
-
2
M
-
M
-
M
-
1
V
-
2
V
-
Zoom in to the limit.
State 3
State 4
s m
M V
M M
/ 47 . 90 8787 . 0 * 96 . 102 *
3
4
4 4
3 4
= = =
=
- -
- -
v
The volumetric flow rate
and properties of states 3 and 4
the rate (L/s) at which water must
be supplied to the cooling pad =
3 * (0.0146 0.0092) * 75 /
0.9003 = 1.3495 kg /s
Reference
Albright, L.D. 1990. Chapter 2
Psychrometrics. Environment Control for
Animals and Plants. An ASAE Textbook.
ASAE, St. Joseph, MI, USA.
Você também pode gostar
- Chapter 08Documento15 páginasChapter 08Jap Ibe86% (7)
- Sample Problems in Industrial Plant Design Pumps and CompressorsDocumento26 páginasSample Problems in Industrial Plant Design Pumps and CompressorsSdhfdh Hdfhd100% (1)
- Example 1Documento10 páginasExample 1karrar AilAinda não há avaliações
- Example1. Air at 12°C DBT and 85% RH Is To Be Brought To 36°C DBT and 23.2°C WBTDocumento33 páginasExample1. Air at 12°C DBT and 85% RH Is To Be Brought To 36°C DBT and 23.2°C WBTAhmed QasimAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8Documento6 páginasChapter 8Paulo AzañeroAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionNo EverandAdvanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionAinda não há avaliações
- The Psychrometric Chart: Theory and Application: Perry Peralta NC State UniversityDocumento50 páginasThe Psychrometric Chart: Theory and Application: Perry Peralta NC State UniversityAlaeddin Guner RodopAinda não há avaliações
- Week 6, 7 & 8: Methods of Handling Supply AirDocumento30 páginasWeek 6, 7 & 8: Methods of Handling Supply AirMariel MirafloresAinda não há avaliações
- Evaporative Cooling Technical Handbook - MuntersDocumento20 páginasEvaporative Cooling Technical Handbook - MuntersradiopascalgeAinda não há avaliações
- Hvac Rpoblems NewDocumento20 páginasHvac Rpoblems NewGrace Joy CariAinda não há avaliações
- Psychrometric Problems Air Conditioning System DesignDocumento11 páginasPsychrometric Problems Air Conditioning System DesignSaurabh SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Psychrometry Part-2Documento11 páginasPsychrometry Part-2Tushar Sharma100% (1)
- Preliminary Design of Air Conditioning System: TitleDocumento28 páginasPreliminary Design of Air Conditioning System: TitleFikri RahimAinda não há avaliações
- DocumentDocumento5 páginasDocumentveronicafind0% (1)
- DocumentDocumento5 páginasDocumentadithimatekk 99Ainda não há avaliações
- Hvac Lab 3Documento24 páginasHvac Lab 3Crystian Kobee EmpeynadoAinda não há avaliações
- Cooling Tower Refrigeration CapacityDocumento28 páginasCooling Tower Refrigeration Capacityboj VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- SH - No.1 ACDocumento3 páginasSH - No.1 ACيوسف عبيد خليفةAinda não há avaliações
- امثلةعلى الدورة الشتويةDocumento7 páginasامثلةعلى الدورة الشتويةkarrar AilAinda não há avaliações
- Psychrometric ChartDocumento50 páginasPsychrometric ChartVishal Mehta100% (2)
- Psychometric ChartDocumento50 páginasPsychometric Chartjunior alfredoAinda não há avaliações
- Psychrometry and Wetted-Surface Heat TransferDocumento16 páginasPsychrometry and Wetted-Surface Heat TransferLaurence Lee AdventoAinda não há avaliações
- ProblemsDocumento94 páginasProblemscatudalbryanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3-2Documento48 páginasChapter 3-2AHMEDAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 08Documento14 páginasChapter 08Gianne Karl AlmarinesAinda não há avaliações
- Drying Operation: Meika Syahbana RusliDocumento69 páginasDrying Operation: Meika Syahbana RusliFrida GinaAinda não há avaliações
- Drying Operation GuideDocumento54 páginasDrying Operation GuideMuhammad Sa'duddinAinda não há avaliações
- Basic State Values of Matter: Example 1.1Documento27 páginasBasic State Values of Matter: Example 1.1Warren CabunyagAinda não há avaliações
- Psychrometry ProblemsDocumento33 páginasPsychrometry Problems19R21A0334 MATTA SHASHANKAinda não há avaliações
- Psychrometric Chart NotesDocumento50 páginasPsychrometric Chart NotesMohammed MudassirAinda não há avaliações
- Mollie ChartDocumento15 páginasMollie ChartKriz EarnestAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Thermodynamics Question BankDocumento27 páginasEngineering Thermodynamics Question BankManideep DuggiAinda não há avaliações
- A Stream of Warm Air With A DryDocumento3 páginasA Stream of Warm Air With A DryRey Niño GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Design ConsiderationsDocumento6 páginasDesign ConsiderationssatyacvaAinda não há avaliações
- Rajarshi Rananjay Sinh Institute of Management and TechnologyDocumento3 páginasRajarshi Rananjay Sinh Institute of Management and TechnologyVinod yadavAinda não há avaliações
- 9.0 Coldstorage Principle of PsychrometricsDocumento90 páginas9.0 Coldstorage Principle of PsychrometricsSweekar KhadkaAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocumento3 páginasDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringJames Patrick TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Psych ExercisDocumento2 páginasPsych ExercisJohn Jonel CasupananAinda não há avaliações
- Problems and SolutionsDocumento37 páginasProblems and Solutionsalfrinjarj100% (2)
- Air CndtoningDocumento34 páginasAir Cndtoningsusanooabc100% (9)
- PeraltaDocumento51 páginasPeraltafortes_76635895Ainda não há avaliações
- HWSolutions PDFDocumento42 páginasHWSolutions PDFJames AhnAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Internal Heat GainDocumento15 páginas1-Internal Heat GainWunNa100% (1)
- Assignment Thermal 2015Documento22 páginasAssignment Thermal 2015Syafiq MazlanAinda não há avaliações
- Me40 Final Exam PracticeDocumento4 páginasMe40 Final Exam Practicegrinci76Ainda não há avaliações
- Weather Studies: The Commonwealth and International Library: Rural and Environmental Studies DivisionNo EverandWeather Studies: The Commonwealth and International Library: Rural and Environmental Studies DivisionAinda não há avaliações
- Total Energy: International Series in Heating, Ventilation and RefrigerationNo EverandTotal Energy: International Series in Heating, Ventilation and RefrigerationAinda não há avaliações
- Phase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringNo EverandPhase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringAinda não há avaliações
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 8, Slice 3 "Destructors" to "Diameter"No EverandEncyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 8, Slice 3 "Destructors" to "Diameter"Ainda não há avaliações
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportAinda não há avaliações
- Performance Model of Shams I Solar Power PlantDocumento9 páginasPerformance Model of Shams I Solar Power PlantOmarZSharafAinda não há avaliações
- Exergy Analysis of Parabolic Trough Sola PDFDocumento8 páginasExergy Analysis of Parabolic Trough Sola PDF11751175Ainda não há avaliações
- Theoretical Investigation of The Efficiency of A U-Tube Solar Collector Using Various NanofluidsDocumento11 páginasTheoretical Investigation of The Efficiency of A U-Tube Solar Collector Using Various NanofluidsOmarZSharafAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Transfer Enhancement in Parabolic Trough Collector Tube Using Al2O3-synthetic Oil NanofluidDocumento9 páginasHeat Transfer Enhancement in Parabolic Trough Collector Tube Using Al2O3-synthetic Oil NanofluidOmarZSharafAinda não há avaliações
- Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of The Thermal Performance of A Double Exposure Flat-Plate Solar CollectorDocumento14 páginasTheoretical and Experimental Investigation of The Thermal Performance of A Double Exposure Flat-Plate Solar CollectorOmarZSharafAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of Efficiency of Flat-Plate Solar Collectors Using Neural Network ApproachDocumento7 páginasDetermination of Efficiency of Flat-Plate Solar Collectors Using Neural Network ApproachOmarZSharafAinda não há avaliações
- Mishra2015 Thermal Modeling and Development of Characteristic EquationsDocumento12 páginasMishra2015 Thermal Modeling and Development of Characteristic EquationsNurCholisAinda não há avaliações
- Comparison of Selective Transmitters For Solar Thermal ApplicationsDocumento11 páginasComparison of Selective Transmitters For Solar Thermal ApplicationsOmarZSharaf100% (1)
- Tutorial 1Documento3 páginasTutorial 1Muhammad AriffAinda não há avaliações
- Drying - 5 - 29 Oct 2020 PDFDocumento25 páginasDrying - 5 - 29 Oct 2020 PDFshubhamAinda não há avaliações
- Equilibrium Between Phases of MatterDocumento411 páginasEquilibrium Between Phases of MatterJonatas LopesAinda não há avaliações
- University of Zakho College of Engineering Mechanical DepartmentDocumento9 páginasUniversity of Zakho College of Engineering Mechanical DepartmentDler SabryAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics Lecture 23Documento1 páginaThermodynamics Lecture 23Templa KentAinda não há avaliações
- HW 01 SolutionDocumento6 páginasHW 01 SolutionPotatoes123Ainda não há avaliações
- Experiment #2 HinchleyDocumento5 páginasExperiment #2 HinchleyTalha AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Hs diagramHDstaaendeDocumento5 páginasHs diagramHDstaaendevjakovljevicAinda não há avaliações
- Best Practices For Condensing Boilers: Technical FeatureDocumento8 páginasBest Practices For Condensing Boilers: Technical FeatureSantiago DuranAinda não há avaliações
- Absolute Humidity TableDocumento1 páginaAbsolute Humidity Tablerajib0403050cuetAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Rep - Experiment 1Documento6 páginasLab Rep - Experiment 1Clifford Dwight Ricanor100% (1)
- Chapter 7 - Phase Equilibrium of One ComponentDocumento24 páginasChapter 7 - Phase Equilibrium of One ComponentPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNAinda não há avaliações
- Cet-Iv - MCQDocumento6 páginasCet-Iv - MCQRohit Ramesh KaleAinda não há avaliações
- BEE Best Practice Manual - HVAC ChillersDocumento69 páginasBEE Best Practice Manual - HVAC ChillersHubert BonamisAinda não há avaliações
- Ekvi ManualDocumento46 páginasEkvi ManualAlexander LymarAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1-Thermal-ExpansionDocumento14 páginasModule 1-Thermal-ExpansionHazel A. BelloAinda não há avaliações
- Extra Titration Practice Problems SolutionsDocumento6 páginasExtra Titration Practice Problems SolutionsAnna BoyajyanAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Thermodynamics Question BankDocumento6 páginasApplied Thermodynamics Question BankHema3110100% (1)
- General Chemistry 2 Las Week 2c February 20 2024Documento7 páginasGeneral Chemistry 2 Las Week 2c February 20 2024Denisse OrigAinda não há avaliações
- Innovative Design - BATSIO & Night Sky CoolingDocumento6 páginasInnovative Design - BATSIO & Night Sky CoolingpeterhwilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- HEAT TRANSFER COURSE COVERS KEY TOPICSDocumento34 páginasHEAT TRANSFER COURSE COVERS KEY TOPICSSiskal DdAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Transfer Through Composite MaterialsDocumento10 páginasHeat Transfer Through Composite MaterialsAkash GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- 2-1435-36 Chapter 6 Chemical Equilibrium Solved Problem 0Documento5 páginas2-1435-36 Chapter 6 Chemical Equilibrium Solved Problem 0Minh ThungoAinda não há avaliações
- Basics of InfraredDocumento58 páginasBasics of InfraredConstantyn_FrederikAinda não há avaliações
- ReviewerDocumento30 páginasReviewerAriel Mark PilotinAinda não há avaliações
- P1 - 1 - Transfer of Energy QsDocumento9 páginasP1 - 1 - Transfer of Energy QsTim Lawrence50% (2)
- Heating & Cooling Load Calculation Program - CLTD/CLF/SCL MethodDocumento43 páginasHeating & Cooling Load Calculation Program - CLTD/CLF/SCL MethodSenthilnathanAinda não há avaliações
- NILE UNIVERSITY LAB REPORT ON pH OF MUDDocumento14 páginasNILE UNIVERSITY LAB REPORT ON pH OF MUDDivine DanrimiAinda não há avaliações
- Home Work1Documento3 páginasHome Work1kixyo100% (1)
- Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Chapter NotesDocumento6 páginasChemistry Equilibrium MCQs Chapter NotesAmina Khan100% (3)