Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Boiling Points, Reactivity, and Mechanisms of Substitution Reactions for Organic Compounds
Enviado por
Dayallini WinxDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Boiling Points, Reactivity, and Mechanisms of Substitution Reactions for Organic Compounds
Enviado por
Dayallini WinxDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Account for the following: 1) Halo alkanes have higher boiling point than the corresponding parent alkane.
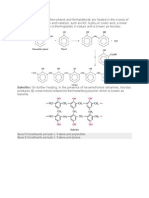
2) Boiling point of halo alkanes RI>RBr>RCl> RF 3) Boiling point of 1-Bromo butane >2-Bromo butane> 1-Bromo- 2-methyl propane> 2-Bromo- 2-methyl propane. 4) Melting point of p-Dichlo benzene is higher than its ortho and meta isomer. 5) Halo alkanes are polar in nature but sparingly soluble in water. 6) Iodo alkane can not be prepared by the reaction of alcohol with KI and sulphuric acid. Phosphoric acid is used in place of sulphuric acid. 7) Order of reactivity of alcohol with HX is tert alcohol> sec alcohol > primary alcohol.. 8) Halo arenes can not be prepared by treating phenol with HX or NaX in the presence of sulphuric acid. 9) Iodination of benzene is carried out in the presence of HIO3 or HNO3. 10) Propane on chlorination gives 2-chloro propane as a major product and not 1-chloro propane. 11) Kharasch effect is possible only with HBr and not with HCl and HI. 12) Alcohol reacts with thionyl chloride to give pure halo alkane. 13) Finkelstein reaction of halo alkane is carried out in the presence of dry acetone. 14) Order of reactivity of halo alkanes as per substitution bimolecular nucleophilic is primary halide > secondary halide>tertiary halide. 15) Order of reaction as per substitution unimolecular is tertiary halide>secondary halide >primary halide. 16) Benzylic halides and allylic halides are more reactive towards nucleophile than halo alkanes. 17) Chloro ethene is less reactive towards nucleophile than chloro ethane. 18) Halo arenes are less reactive towards nucleophile than halo alkanes. 19) SN1 mechanism is ruled out in the reaction of halo arenes with nucleophile. 20) Electron with drawing groups like NO2 at ortho and para position with respect to halogen facilitates nucleophillic substitution reaction. 21) Electron with drawing groups like NO2 at meta position with respect to halogen has no effect on nucleophillic substitution reaction. 22) Halo arenes are less reactive towards electrophile than benzene. 23) Although chlorine atom has electron with drawing effect electrophillic substitution occur at ortho and para position. 24) Order of reactivity of alkyl halide RI>RBr>RCl>RF 25) Halo alkanes react with KCN to give alkyl cyanide as a major product while it gives alkyl isocyanide as a major product with AgCN. 26) Halo alkanes give nitrito alkane with KNO2 while nitro alkane with AgNO2. 27) CH3I undergoes SN2 reaction faster than CH3Cl. . Account for the following: a) COH bond angle in alcohol is less than tetrahedral angle of 109.50 b) COC bond angle in ether is more than tetrahedral angle of 109.50 c) C-O bond length in phenol is less than that of alcohol. d) Phenol has lower dipole moment than alcohol. e) Phenol under goes electrophillic substitution at ortho and para position f) Alcohol acts as a bronsted acid as well as bronsted base. g) Phenol is more acidic than alcohol. h) Acidity of alcohol is primary alcohol>sec alcohol>tert alcohol. i) Basicity of alcohol is tert alcohol> sec alcohol>primary alcohol. j) In Williamsons synthesis sec and tert halide can not be used. k) para nitro phenol is less steam volatile than ortho nitro phenol. l) Presence of nitro group at ortho and para position makes phenol more acidic. m) Alcohols and phenols have higher boiling point. n) Boiling point of alcohol is higher than its isomeric ether. o) Boiling point of glycerol>ethylene glycol> ethanol. p) Grignard reagent is a versatile reagent in organic chemistry. q) Cresol is less acidic than phenol. r) In esterification reaction, water is removed as soon as it is formed. s) Order of reactivity of HX with alcohol is HI>HBr>HCl>HF t) Alcohol reacts with SOCl2 to give pure halo alkane. u) Ease of dehydration of alcohol is tert alcohol> sec alcohol>primary alcohol. v) Phenol and anisole undergoes bromination reaction even in the absence of halogen carrier. w) Methyl phenyl ether reacts with HI to give phenol and methyl iodide and not methanol and iodo benzene. x) Methoxy ethane reacts with HI to give methyl iodide and ethanol and not ethyl iodide and methanol. y) Tert butyl methyl ether reacts with HI to give tert butyl iodide and methanol and not not methyl iodide and tert butyl alcohol. z) Anisole undergoes electrophillic substitution at ortho and para position. aa) Boiling point of butan-1-ol is higher than tert butyl alcohol. bb) Alcohol, phenol and ether are soluble in water. cc) In the reaction between acid chloride and alcohol a small amount of pyridine is added. dd) Alcohol behaves as nucleophile as well as electrophile. ee) Water is a stronger acid than alcohol. Account for the following: a) Aldehyde and ketone are polar in nature. b) Aldehyde and ketones have higher boiling point than hydro carbons of comparable molar mass. c) Aldehyde and ketones have lower boiling point than alcohols of comparable molar mass. d) Ketone has higher boiling point than aldehyde of comparable molar mass. e) Oxidation of primary alcohol to aldehyde is carried out using PCC as an oxidizing agent. f) Rosenmund's reduction of acid chloride to aldehyde is carried out using quinoline and sulphur. g) Aldehyde is more reactive than ketone towards nucleophile. h) Butanone is less reactive than propanone. i) 2,2,6-Tri methyl cyclo hexanone is less reactive towards nucleophile than cyclo hexanone. j) Para nitro benzaldehyde is more reactive towards nucleophile than benzaldehyde. k) Para methyl benzaldehyde is less reactive towards nucleophile than benzaldehyde. m) Reaction of aldehyde with alcohol to give acetal is carried out in the presence of HCl(g). n) Formaldehyde and benzaldehyde undergoes cannizaro reaction and not aldol condensation. o) Acetaldehyde undergoes aldol condensation and not cannizaro reaction. p) Aromatic aldehyde and ketones undergoes electrophillic substitution at meta position. q) Carboxylic acid do not show the reactions of aldehyde and ketone though it has >C=O group. r) Carboxylic acid has higher boilimg point than aldehyde, ketone and alcohol of comparable molar mass. s) In semi carbazide, only one NH2 group is involved in the formation of semi carbazone. t) Aldehyde, ketone and carboxylic acid are soluble in water. u) In oxidation of primary alcohol to carboxylic acid is not carried out using acidified potassium dichromate. v) Carboxylic acid is more acidic than alcohol. w) Carboxylic acid is more acidic than phenol. x) Acidity of CCl3COOH>CHCl2COOH>CH2ClCOOH>CH3COOH. y) Acidity of FCH2COOH>ClCH2COOH>BrCH2COOH>I CH2COOH. z) a chloro propanoic acid is more acidic than chloro propanoic acid. aa) Acetic acid is less acidic than formic acid. bb) Pure acid halide is prepared by the reaction of carboxylic acid with thionyl chloride. cc) Carbon in carbonyl group of aldehyde and ketone acts as Lewis acid(electrophile) while oxygen acts as Lewis base ( nucleophile). dd) Benzoic acid does not undergo Friediel craft alkylation reaction. Account for the following: a) Methyl chloride reacts with AgNO2 to give nitro methane as a major product where as it gives nitrito methane as a major product with KNO2 b) C-N bond in aniline is shorter than in aliphatic amines. c) In ammonalysis of halo alkane , primary amine is the only product when large excess of ammonia is used while quaternary ammonium salt is the only product when halo alkane is in excess. d) Primary and sec amines have higher boiling point than tert amine. e) Amines have lower boiling point than alcohol of comparable molar mass. f) Amines are soluble in water. Solubility of amines p.amines>sec amines>tert amines g) Amines are less soluble in water than alcohol. h) Basicity of amines in aqueous solution is sec amine>tert amine>p.amine. i) Basicity of amines in vapor phase tert amine>sec amine>p.amine. j) Aniline is a weaker base than aliphatic amine. k) Electron repelling group at ortho and para position increases the basicity while electron with drawing group at ortho and para position decreases the density of aniline.
l) Ammonalysis of halo alkane is carried out in the presence of a base. m) Unlike alkylation of amines acylation stops after first styep. n) Tert amines do not react with acid derivatives. o) Aniline undergoes bromination even in the absence of halogen carrier. p) Nitration of aniline gives 47% meta nitro aniline. q) P-toluidine is more basic than aniline. r) Amines are less acidic than alcohol. s) Halo alkane reacts with KCN to give alkyl cyanide as a major product while it gives alkyl isocyanide as a major product with AgCN. t) Aniline do not undergo Friedel craft's reaction. u) Aniline can't be prepared by Gabriel pthalimide synthesis. v) ArN2X is more stable than RN2X at lower temperature. w) Aniline is a weaker base than ammonia. x) Order of basicity (C2H5)2NH>(C2H5)3N > C2H5NH2>NH3 y) Order of basicity (CH3)2NH>CH3NH2>(CH3)3N>NH3 Z) Bromination of aniline after acylation gives only para bromo aniline. aa) Sandmeyer reaction is prefered over Gatterman reaction to prepare halo arenes from aniline. bb) Ethyl amine is soluble in water but not aniline. cc) Aqueous solution of methyl amine with ferric chloride solution gives brown precipitate of ferric hydroxide.. dd) Gabriel pthalimide synthesis is prefered to prepare primary amine. ee) p-nitro aniline is less basic than aniline.
Você também pode gostar
- The Reaction Gives Pure Alkyl HalidesDocumento8 páginasThe Reaction Gives Pure Alkyl HalidesMohammed IliasAinda não há avaliações
- Alchohols Phenols and EthersDocumento5 páginasAlchohols Phenols and EthersPritika Yamini SaiAinda não há avaliações
- Carbonyl Compounds: Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento9 páginasCarbonyl Compounds: Aldehydes and KetonesCamille AdleAinda não há avaliações
- ReasoningDocumento4 páginasReasoningAayush MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Complete NCERT Revision Material for Class XII ChemistryDocumento14 páginasComplete NCERT Revision Material for Class XII ChemistryabiAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocumento11 páginasAlcohols Phenols and Ethersnm.ananya2008Ainda não há avaliações
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento4 páginasAldehydes and Ketonesnvmohankumar85Ainda não há avaliações
- A RX and ArXDocumento2 páginasA RX and ArXKeep Smiling with SanidhyaAinda não há avaliações
- ITL Public School Holiday Homework Class XII CHEMISTRYDocumento14 páginasITL Public School Holiday Homework Class XII CHEMISTRYNisith Kr DasAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers: ClassificationDocumento13 páginasAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers: ClassificationDUHA GORASHIAinda não há avaliações
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento159 páginasPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- CH 7 S Cbse BDocumento13 páginasCH 7 S Cbse BjsjsjskakkakoAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Notes On AlcoholsDocumento13 páginasRevision Notes On AlcoholsMuredzwa MuzendaAinda não há avaliações
- Haloalkanes - Class Assignmnt (23-24)Documento1 páginaHaloalkanes - Class Assignmnt (23-24)Gaurav Chauhan 4795Ainda não há avaliações
- Ald, Ket, CaDocumento17 páginasAld, Ket, CabharathAinda não há avaliações
- Hydroxyl Compounds: Alcohol & PhenolDocumento59 páginasHydroxyl Compounds: Alcohol & PhenolUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Formula Chapter10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento17 páginasChemistry Formula Chapter10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenessukhada34Ainda não há avaliações
- Functional Group Transformation NotebookDocumento78 páginasFunctional Group Transformation NotebookchedhedAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocumento50 páginasUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acidssukaina fatima100% (1)
- Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition ReactionsDocumento64 páginasChapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactionsaggelisgeorge8546Ainda não há avaliações
- Give ReasonsDocumento1 páginaGive Reasonsp2109760Ainda não há avaliações
- All ORGANIC Q ADocumento55 páginasAll ORGANIC Q AkunalAinda não há avaliações
- Things To Remember Only Alc Phe 2022-23Documento17 páginasThings To Remember Only Alc Phe 2022-23poornaAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry Revision Questions-1Documento3 páginasOrganic Chemistry Revision Questions-1jatin2006gamil.comAinda não há avaliações
- 1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocumento117 páginas1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsKRISHNARJUNA NAinda não há avaliações
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Class NotesDocumento19 páginasORGANIC CHEMISTRY Class NotesWolam guyAinda não há avaliações
- 12th Chemistry Practice Sheet Unit 11: Alcohol, Phenol & EtherDocumento5 páginas12th Chemistry Practice Sheet Unit 11: Alcohol, Phenol & EtherGLOBAL XAinda não há avaliações
- Note HaloalkanesDocumento7 páginasNote HaloalkanesNabin JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- 34 ch11Documento10 páginas34 ch11Mohammed IbrahimAinda não há avaliações
- WK7 - Halogenated HCDocumento10 páginasWK7 - Halogenated HCsam cuadraAinda não há avaliações
- Haloalkenes and Haloarenes 1Documento1 páginaHaloalkenes and Haloarenes 1nvmohankumar85Ainda não há avaliações
- Alcohol, Phenol and Ether MCQsDocumento22 páginasAlcohol, Phenol and Ether MCQsShypackofcheetosAinda não há avaliações
- Haloalkane and HaloareansDocumento16 páginasHaloalkane and HaloareansAbhianv Gupta100% (1)
- DocumentDocumento4 páginasDocumentAdil Nawaz KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Preparation and Properties of Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers and EpoxidesDocumento14 páginasPreparation and Properties of Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers and Epoxidesitsleochandu21Ainda não há avaliações
- Holidays HW Class XiiDocumento3 páginasHolidays HW Class XiiPoorvKumarAinda não há avaliações
- Aldehydes and Ketones Structure and ReactionsDocumento104 páginasAldehydes and Ketones Structure and ReactionsCharin Kadian75% (4)
- Important Order and Facts of Organic ChemistryDocumento6 páginasImportant Order and Facts of Organic ChemistryDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKAinda não há avaliações
- AK Alc PhenolDocumento3 páginasAK Alc PhenolFelix Joshua.B 10 BAinda não há avaliações
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocumento9 páginasAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsAnand RawatAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Test SeriesDocumento5 páginasAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Test SeriesCR foreverAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Notes On AlcoholsDocumento15 páginasRevision Notes On AlcoholsSUSHMAAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-10: Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento6 páginasCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-10: Haloalkanes and HaloarenesKrishna Moorthy RamaiahAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohol, Phenols and Ethers PDFDocumento13 páginasAlcohol, Phenols and Ethers PDFRahul JaiswalAinda não há avaliações
- Word Problems in Organic ChemistryDocumento70 páginasWord Problems in Organic ChemistryreghuuchihaAinda não há avaliações
- AreneDocumento37 páginasArene'Aqilah ZulkifliAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrocarbons (Hints)Documento2 páginasHydrocarbons (Hints)hchawla421Ainda não há avaliações
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento62 páginasCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesSubhabrata MabhaiAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 04Documento44 páginasChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 04Ng Swee Loong StevenAinda não há avaliações
- Hydroxy and Phenol Compounds TutorialDocumento6 páginasHydroxy and Phenol Compounds TutorialDomAinda não há avaliações
- Hand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocumento11 páginasHand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesLuisgarciaBerlangaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 11. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers One Mark QuestionsDocumento10 páginasUnit 11. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers One Mark QuestionsVedha GowdaAinda não há avaliações
- Halo NewDocumento10 páginasHalo NewMohammed IliasAinda não há avaliações
- SXHS XII (CHEM) P.T-2 Imp Questions 2023Documento7 páginasSXHS XII (CHEM) P.T-2 Imp Questions 2023sampritmodiAinda não há avaliações
- AldehydesDocumento18 páginasAldehydesVibhor KaushikAinda não há avaliações
- Derivatives of Aromatic HydrocarbonDocumento43 páginasDerivatives of Aromatic HydrocarbonShariar ShawoŋAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 7-10 SM Theory Book 2 EM For 2022GRDocumento19 páginasUnit 7-10 SM Theory Book 2 EM For 2022GRThilanka LiyanageAinda não há avaliações
- MDCAT 2022 HydrocarbonsDocumento41 páginasMDCAT 2022 Hydrocarbonszaka ullahAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsNo EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsAinda não há avaliações
- Ozone Layer DepletionDocumento2 páginasOzone Layer DepletionDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- HaleyDocumento48 páginasHaleyDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Independent HOUSE With 2 Car Parks: ToletDocumento2 páginasIndependent HOUSE With 2 Car Parks: ToletDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 MatricesDocumento66 páginasUnit 1 MatricesDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Office 2007 - Kgfvy 7733b 8wck9 Ktg64 Bc7d8Documento1 páginaMicrosoft Office 2007 - Kgfvy 7733b 8wck9 Ktg64 Bc7d8MădălinaAstancăiAinda não há avaliações
- Admision FAQ 14-15Documento5 páginasAdmision FAQ 14-15Dayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Term I Sanskrit FA Portions, Blue Print & Project Details FA I Review Test PortionsDocumento1 páginaTerm I Sanskrit FA Portions, Blue Print & Project Details FA I Review Test PortionsDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- AcDocumento1 páginaAcDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Rent A WifeDocumento117 páginasRent A WifeDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Novolac, Bakelite, Buna N and Buna S polymersDocumento1 páginaNovolac, Bakelite, Buna N and Buna S polymersDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Book 1Documento1 páginaBook 1Dayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- The 43-character concise title for the Sri Chakra Maha Mantra documentDocumento5 páginasThe 43-character concise title for the Sri Chakra Maha Mantra documentDayallini Winx100% (1)
- Rig VedaDocumento749 páginasRig VedaVikas RupareliaAinda não há avaliações
- Bionic Eye Research ProgressDocumento53 páginasBionic Eye Research ProgressElmin OmicAinda não há avaliações
- Bio MoleculesDocumento6 páginasBio MoleculesDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- D&FDocumento1 páginaD&FDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Book 1Documento1 páginaBook 1Dayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Readme 1Documento1 páginaReadme 1Jogn DebAinda não há avaliações
- Learn Hindi Through English Medium by Ratnakar NaraleDocumento21 páginasLearn Hindi Through English Medium by Ratnakar NaraleVijaya Manjoola50% (2)
- FromDocumento1 páginaFromDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:PDocumento16 páginasP:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:P:PDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Tremble in terror from shaking earthDocumento2 páginasTremble in terror from shaking earthDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Synopsis - Grade 12 Math Part I: Chapter 1: Relations and FunctionsDocumento24 páginasSynopsis - Grade 12 Math Part I: Chapter 1: Relations and FunctionsDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- ZXCVBNMDocumento25 páginasZXCVBNMDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- ZXCVBNMDocumento25 páginasZXCVBNMDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Black BananaDocumento3 páginasBlack BananaDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- AsdfghDocumento12 páginasAsdfghDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- What Are Antibiotics ?: Benefits and Side-Effects of AntibioticsDocumento3 páginasWhat Are Antibiotics ?: Benefits and Side-Effects of AntibioticsDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- ParliamentDocumento2 páginasParliamentDayallini WinxAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Classification of Hormones: Steroids, Peptides, Eicosanoids & MoreDocumento9 páginasChemical Classification of Hormones: Steroids, Peptides, Eicosanoids & Morevishal sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- SPESIFIKASI UMUM 2018 LAPIS RESAP PEREKATDocumento104 páginasSPESIFIKASI UMUM 2018 LAPIS RESAP PEREKATKadek SugiyonoAinda não há avaliações
- BioInfo2 Assignment - PythonDocumento11 páginasBioInfo2 Assignment - PythonJin YeowAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs 17Documento2.351 páginasDrugs 17Mohamed NizamAinda não há avaliações
- Carbohydrates PresentationDocumento60 páginasCarbohydrates PresentationRaagas, ChristianAinda não há avaliações
- Price List Pharma Per 1 Oktober 2020Documento2 páginasPrice List Pharma Per 1 Oktober 2020Geraldin ImawanAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocumento5 páginasCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesSIDHARTH SBAinda não há avaliações
- Pemakaian Obat RS Tahun 2020Documento20 páginasPemakaian Obat RS Tahun 2020ENDAH SANDIAHAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 18: Anticancer Agents (Part B) : Patrick: An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry 3eDocumento65 páginasChapter 18: Anticancer Agents (Part B) : Patrick: An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry 3eHussein Al-jmrawiAinda não há avaliações
- BCH301Documento19 páginasBCH301yabdallahAinda não há avaliações
- Identify and Describe Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins As Food Substances State The Chemical and Physical Properties of Different Food SubstancesDocumento18 páginasIdentify and Describe Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins As Food Substances State The Chemical and Physical Properties of Different Food SubstancesLunactic ThanosAinda não há avaliações
- Perception Test 4 Organic Chem Sem 2Documento5 páginasPerception Test 4 Organic Chem Sem 2gypsydavesbrotherAinda não há avaliações
- Price List SendDocumento19 páginasPrice List SendzakkykuAinda não há avaliações
- Ketoconazole: SampleDocumento7 páginasKetoconazole: SampleJuan PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Class 12 Chemistry - Key concepts on DNA structure and functionDocumento4 páginasClass 12 Chemistry - Key concepts on DNA structure and functionshamiksha dAinda não há avaliações
- Aldehydes & Ketones: Properties, Preparation and ReactionsDocumento45 páginasAldehydes & Ketones: Properties, Preparation and ReactionsShivam GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Polimer Dan Monomer Polimer Dan MonomerDocumento15 páginasPolimer Dan Monomer Polimer Dan MonomerarnizasanusiAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology (Biol. 1012) : Course Instructor: Kabeta LegeseDocumento48 páginasGeneral Biology (Biol. 1012) : Course Instructor: Kabeta LegeseKena MegersaAinda não há avaliações
- Quality Test For Amino AcidDocumento7 páginasQuality Test For Amino AcidNurmazillazainal100% (1)
- Invent A RioDocumento20 páginasInvent A RiojoseywilAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC & Nomenclature PDFDocumento6 páginasIUPAC & Nomenclature PDFjaspreet singh100% (1)
- Chemistry Lab Report - Reaction of AlcoholDocumento3 páginasChemistry Lab Report - Reaction of Alcoholans68% (40)
- Study Glycolysis TCA Gluconeogenesis Lipid Amino Acid MetabolismDocumento1 páginaStudy Glycolysis TCA Gluconeogenesis Lipid Amino Acid MetabolismVibhav SinghAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry-Alcohol, Phenol & Ether PDFDocumento10 páginasCBSE Class 12 Chemistry-Alcohol, Phenol & Ether PDFVaishnavi DurbadeAinda não há avaliações
- Commercial Invoice Delivery DetailsDocumento1 páginaCommercial Invoice Delivery DetailsMuhammad Ameer Hamza KayanAinda não há avaliações
- Enzyme Brochure Gen Chem PTDocumento2 páginasEnzyme Brochure Gen Chem PTAdrielAinda não há avaliações
- Poster de Las Vias Metabolicas.Documento2 páginasPoster de Las Vias Metabolicas.Moises RosalesAinda não há avaliações
- Final Report of The Amended Safety Assessment of Glyceryl LaurateDocumento40 páginasFinal Report of The Amended Safety Assessment of Glyceryl LaurateSam SonAinda não há avaliações
- (WORKSHEET) General Biology 1 2nd Quarter Activity 2 - LipidsDocumento2 páginas(WORKSHEET) General Biology 1 2nd Quarter Activity 2 - Lipidsaltheatoledo15Ainda não há avaliações
- Rubber Chemical Resistance ChartDocumento13 páginasRubber Chemical Resistance ChartQuality ControlAinda não há avaliações