Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
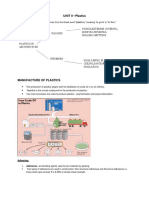
MInggu Ke-6 Plastic For Food Packaging
Enviado por
Mega OktafTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MInggu Ke-6 Plastic For Food Packaging
Enviado por
Mega OktafDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
4/11/2014
PACKAGING (VAI 226)
Week-6: Plastic for Food Packaging
INTRODUCTION
4/11/2014
PLASTIC: BASIC POLYMER
1. Polyolefins LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE, PP 2. Copolymers of ethylene EVA, EVOH
3. Substituted olefins
PS, PVC, PVdC 4. Polyesters PET 5. Polyamide (PA) 6. Regenerated cellulose film
PLASTICS: POLYOLEFINS
Polyethylene (PE) HDPE 940 kg/m3 LDPE < 915-939 kg/m3 Polypropylene (PP) 900 kg/m3 Permeability of polyolefins
High O2-permeability
Low H2O-permeability
4/11/2014
GAS BARRIER PROPERTIES
PLASTIC:POLYOLEFINS
LDPE (Low Density PolyEthylene) Excellent chemical resistance (e.g. acids) Sensitive to oils and greases Films and bottles (squeeze-bottles) Suitable for deep-freezing applications Excellent sealing properties: often used as outer layer of multi-layer films
50% cristallinity
4/11/2014
PLASTIC:POLYOLEFINS
HDPE (High Density PolyEthylene) 90% cristallinity (more linear structure than LDPE)
=> higher density than LDPE
=> less transparant than LDPE Better resistance to oils and greases than LDPE Films and bottles LLDPE (Low Linear Density Polyethylene) Similar molecular structure to HDPE More crystalline than LDPE (more linear)
PLASTIC:POLYOLEFINS
PP Good resistance to greases and chemicals High temperature stability Suitable for heat processes (e.g. microwave applications, sterilisation) Good gloss & high clarity => ideal for reverse printing Trays, closures, films (cast oriented form) Seal layer in retortable pouches, hot filled bottles and microwaveable packaging
4/11/2014
PLASTICS: COPOLYMERS OF ETHYLENE
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) VA => crystallinity => permeability and clarity
Mostly used in multi-layer applications
Three advantage over LDPE Heat sealing temperature is lower Barrier properties are better Excellent stretch properties Applications Stretch wrapping: replacing PVC Heat sealing layer for PET and BOPP films
PLASTICS: COPOLYMERS OF ETHYLENE
Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol (EVOH) Excellent processability on machines Superior barriers to gasses, odors and solvents Multi-layer applications (in many cases surrounded by polyolefins)!!! Hydrophilic => moisture absorption => barrier properties Ethylene => barrier properties and moisture barrier
4/11/2014
EVOH
Gambar struktur
PLASTICS: SUBSTITUTED OLEFINS
Polystyrene (PS) Amorphous structure different types Examples 1. High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) Adding synthetic rubbers during polymerization => brittleness of PS Thermoforming applications (cups for cream) 2. Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) PS foam Disposable packages (e.g. trays for meat and produce)
4/11/2014
PLASTICS: SUBSTITUTED OLEFINS
PolyVinylChloride (PVC) Largely amorphous polymer Permeability properties Water vapour barrier lower than polyolefins Gas barrier higher than polyolefins Applications 1. Film: e.g. stretch wrapping (+ stabilizers and plasticizers) Excellent gloss and transparency 2. Trays Environmental issues!
PLASTICS: SUBSTITUTED OLEFINS
PolyVinylidene Chloride (PVdC) Unique combination of low permeability to water vapournd gasses, odours, greases and alcohols Suitable for hot filling applications and retorting Component in multilayer barrier containers or films
4/11/2014
PLASTICS: POLYESTERS
Carbon-oxygen-carbon links 1. Poly(Ethylene Terephtalate) (PET) Bottles, films, trays Largely amorphous => excellent transparency Capacity to crystallize under certain controlled conditions (CPET) Preventing deformation during cooking and serving PET bottles Stretching: in biaxial orientation => good gas barrier => minimize bottle weights
PLASTICS: POLYAMIDE
Polyamide (PA) Also called nylons Mechanical strength (BOPA!) Good gas barrier properties (when dry!) Highly permeable to water vapor Excellent thermal stability
Applications
In combination with LDPE or EVA
4/11/2014
PLASTICS:REGENERATED CELLULOSE FILMS
Regenerated Cellulose Film (RCF) Also called cellophane Cellulose from wood, cotton, hemp Good gas barrier properties (when dry!) Often used in multi-layer film Recently: replaced by BOPP in many cases Twist wrapping of sweets
PLASTIC: MOST USED MATERIAL
Rigid sheets for thermoforming HIPS, HDPE, PP for bulk layers Flexible films LDPE, LLDPE Bottles PET, HDPE
Barrier layers
EVOH, PVdC
4/11/2014
PLASTIC: PERMEABILITY OF PLASTICS
Permeable to: Gases Water vapour Organic vapors Other low molecular weight compounds Permeability depends on: Packaging material itself Integrity of packages (including seals and closures!!!)
PLASTIC: MODIFICATION
Adding additives in plastics Co-extrusion, lamination, coating Orientation Metallization
10
4/11/2014
PLASTIC:MODIFICATION
Aim: improve different properties of the basic polymers to comply with the demands related to food packaging Example Orientation / crystallization Increase interaction between molecular strains => increase barrier properties Filling agents Decrease interaction between molecular strains => decrease barrier properties Also when H2O is absorbed (e.g. in O2-barrier in EVOH decreases due to absorption of H2O)
PLASTICS: ADDING ADDITIVES
Additive: an auxiliary ingredient enhancing the properties of the parent polymer without appreciably altering its chemical structure Food legislation: positive list! Types: Processing additives Flexibilizers Antiaging additives: for ex: UV stabiliser Surface property modifiers: antistatic and antifoaming agents Optical property modifiers: give colour Foaming agents: Active packaging technology
11
4/11/2014
CO-EXTRUSION, LAMINATION, COATING
Three methods to produce multilayer structures Co-extrusion: simultaneously extrude two or more different polymers, which fuse into one film/sheet Lamination: combining two or more different films/sheets (plastics or nonplastics) by means of adhesives and curing systems Coating: applying one or more layers of a fluid or melt to the surface of a material
12
Você também pode gostar
- Rizalda, Jocelyn Food PackagingDocumento10 páginasRizalda, Jocelyn Food PackagingAXI KAMIA IBALAinda não há avaliações
- E.G. E.G. E.G. E.G. I.E. Etc. Etc. E.GDocumento13 páginasE.G. E.G. E.G. E.G. I.E. Etc. Etc. E.GjoshigautaAinda não há avaliações
- 1) Plastics PackagingDocumento29 páginas1) Plastics Packaginglightbulboooo1Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of PlasticsDocumento2 páginasTypes of PlasticsMoniqueAinda não há avaliações
- Studies of Some Thermoplastic Resins Note - DR Akinsiku PDFDocumento12 páginasStudies of Some Thermoplastic Resins Note - DR Akinsiku PDFGlory Usoro100% (1)
- Guyana TFO PKG W'SHP Session 4 - Plastic FilmDocumento39 páginasGuyana TFO PKG W'SHP Session 4 - Plastic Filmaimy9006Ainda não há avaliações
- Flexible Package DesignDocumento98 páginasFlexible Package DesignBhupendra Singh100% (14)
- Fundamentals of Packaging-Ovop MalawiDocumento38 páginasFundamentals of Packaging-Ovop MalawiXerxa LinganAinda não há avaliações
- 04 Laminating-Adhesives Glasbrenner PDFDocumento28 páginas04 Laminating-Adhesives Glasbrenner PDFAlmoosawiAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic As A Packing MaterialDocumento53 páginasPlastic As A Packing MaterialPratyush SahooAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic PackagingDocumento47 páginasPlastic PackagingRajaSekarsajja100% (1)
- Plastic Bottles and Bottle CapsDocumento10 páginasPlastic Bottles and Bottle Capsikki kuroganeAinda não há avaliações
- Polymers and Polymerization: Identical RepeatingDocumento5 páginasPolymers and Polymerization: Identical RepeatingMax Yin [Student]Ainda não há avaliações
- Hds DDFDDocumento31 páginasHds DDFDGraizel Joy AndresAinda não há avaliações
- PolymersDocumento20 páginasPolymerslakshay ManglaAinda não há avaliações
- Polymer Chemistry For Packaging ApplicationsDocumento25 páginasPolymer Chemistry For Packaging ApplicationsdivyaAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic PackagingDocumento117 páginasPlastic PackagingAnthony Cruz0% (1)
- Plastics NotesDocumento5 páginasPlastics Noteskaviya barathyAinda não há avaliações
- PlaDocumento10 páginasPlaijat_Ainda não há avaliações
- Food Packaging PresentationDocumento52 páginasFood Packaging PresentationXaverius Quentin AntonAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic Polymers CompleteDocumento57 páginasPlastic Polymers CompleteMaria OzaoAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic As A Packaging Material: Dr. Anil PetheDocumento53 páginasPlastic As A Packaging Material: Dr. Anil PetheAnubhav UjlayanAinda não há avaliações
- Flexible PackagingDocumento16 páginasFlexible Packagingdreamwakeman100% (1)
- Plastics Thermoplastics Thermosetting: Rivera, Patrick Joshua D. Perez, JaysonDocumento13 páginasPlastics Thermoplastics Thermosetting: Rivera, Patrick Joshua D. Perez, Jaysonpatrick1101Ainda não há avaliações
- High Density PolyethyleneDocumento2 páginasHigh Density PolyethylenePhuoc TranAinda não há avaliações
- Polyethylene TerephthalateDocumento4 páginasPolyethylene TerephthalateClarisse Joyce GenerAinda não há avaliações
- Packaging Materials: Course: Epbm&Fq Course Incharge: V Sai KrishnaDocumento9 páginasPackaging Materials: Course: Epbm&Fq Course Incharge: V Sai Krishnasai krishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic Group 1Documento20 páginasPlastic Group 1DELA TORRE KAREN KAYE PABLEOAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic As A Packaging Material: Mrs. Kirteebala PawarDocumento53 páginasPlastic As A Packaging Material: Mrs. Kirteebala PawarJillianne JillAinda não há avaliações
- Shelf Plus 02Documento1 páginaShelf Plus 02Plymouth3DDesignAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic PackagingDocumento32 páginasPlastic PackagingKarthikeyan G100% (1)
- Barrierpropertiesoffilms0312 13324910000013 Phpapp02 120323032528 Phpapp02Documento51 páginasBarrierpropertiesoffilms0312 13324910000013 Phpapp02 120323032528 Phpapp02karismaAinda não há avaliações
- Polymers Used in Food Packaging: 10/30/2020 Erandika Bandara 1Documento41 páginasPolymers Used in Food Packaging: 10/30/2020 Erandika Bandara 1sumit kumarAinda não há avaliações
- PVC Compound Ingredients IdentificationsDocumento9 páginasPVC Compound Ingredients IdentificationsAhmed RaafatAinda não há avaliações
- Adhesive SelectionDocumento17 páginasAdhesive SelectionPubg fansAinda não há avaliações
- Synthetic PolymersDocumento68 páginasSynthetic Polymersdhong100% (1)
- Different Kinds of Plastic and Their Ability To Get RecycledDocumento8 páginasDifferent Kinds of Plastic and Their Ability To Get RecycledAayan KabraAinda não há avaliações
- Flexible PackagingDocumento15 páginasFlexible PackagingAngela GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Polymers Ref DEC 24Documento40 páginasPolymers Ref DEC 24Gowtham Kae KaeAinda não há avaliações
- POLYMERSDocumento26 páginasPOLYMERSnyoy yoyAinda não há avaliações
- Handout Packaging MaterialsDocumento15 páginasHandout Packaging MaterialsShahnasAinda não há avaliações
- Biodegradable Plastic Master Batch AdditiveDocumento6 páginasBiodegradable Plastic Master Batch AdditivePankaj KushwahaAinda não há avaliações
- PicklesDocumento11 páginasPickleschetanashetyeAinda não há avaliações
- Polyethylene (PE) : Plastics and Polymers PolymersDocumento8 páginasPolyethylene (PE) : Plastics and Polymers PolymersbabanAinda não há avaliações
- PlasticsDocumento13 páginasPlasticsshashi upadhyaAinda não há avaliações
- Polyethylene:: Structure of PE Monomer C H Structure of PolyethyleneDocumento10 páginasPolyethylene:: Structure of PE Monomer C H Structure of PolyethyleneRishikesh ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- IMP 9 PlasticsDocumento44 páginasIMP 9 PlasticspaulamarieestrellalengascoAinda não há avaliações
- Morris 2017Documento51 páginasMorris 2017farukh azeemAinda não há avaliações
- Production and Properties: Briquetting Plants in INDIADocumento9 páginasProduction and Properties: Briquetting Plants in INDIARobin SahaAinda não há avaliações
- PolymerProperties From CESDocumento23 páginasPolymerProperties From CESskc3128Ainda não há avaliações
- Ancillary Materials For Food Packaging: AdhesivesDocumento30 páginasAncillary Materials For Food Packaging: AdhesivesNikesh ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Ethylene Vinyl AcetateDocumento5 páginasEthylene Vinyl AcetateAli RazuAinda não há avaliações
- Polyethylene:: Structure of PE Monomer C H Structure of PolyethyleneDocumento4 páginasPolyethylene:: Structure of PE Monomer C H Structure of PolyethyleneRishikesh ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- PolyetheneDocumento11 páginasPolyetheneUshanth SivalingamAinda não há avaliações
- Lldpe Uhmwldpe Cpe Jan 2018Documento50 páginasLldpe Uhmwldpe Cpe Jan 2018Suchetha RajuAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic PipesDocumento44 páginasPlastic PipeskejspmAinda não há avaliações
- Waste Plactics To Useful Petroleum ProductsDocumento6 páginasWaste Plactics To Useful Petroleum ProductsNishant ChoubeyAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Packaging Technologies for Fruits and VegetablesNo EverandAdvanced Packaging Technologies for Fruits and VegetablesAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Packaging Technologies For Fruits and Vegetables: For Fruits and VegetablesNo EverandAdvanced Packaging Technologies For Fruits and Vegetables: For Fruits and VegetablesAinda não há avaliações
- Clear and Plastic Danger: The Alien in your KitchenNo EverandClear and Plastic Danger: The Alien in your KitchenNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Designing Plastic Products Injection MouldingDocumento123 páginasDesigning Plastic Products Injection MouldingSandeep PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Cat Stepn Components MS21266 BACG20Z Data SheetDocumento2 páginasCat Stepn Components MS21266 BACG20Z Data SheetFariz FadzuanAinda não há avaliações
- Up 2Documento3 páginasUp 2gaurang_12Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento1 páginaChapter 6Sayad H AbirAinda não há avaliações
- GeopipesDocumento9 páginasGeopipesRamesh GhaleAinda não há avaliações
- Adhesives - Cord Chemicals IncDocumento3 páginasAdhesives - Cord Chemicals IncEddie Resurreccion Jr.Ainda não há avaliações
- Astm D 3754Documento14 páginasAstm D 3754Rostarina AnggrainiAinda não há avaliações
- CALICO+ +Catalogo+2013+InglesDocumento213 páginasCALICO+ +Catalogo+2013+InglesOscar SpinningaliciaAinda não há avaliações
- DVS 2011 Table of ContentsDocumento8 páginasDVS 2011 Table of ContentsJennifer JenkinsAinda não há avaliações
- Polyuretddhane - Properties, Prddocessing, and Applicssations - MatmatchDocumento10 páginasPolyuretddhane - Properties, Prddocessing, and Applicssations - MatmatchEric LamAinda não há avaliações
- Joint Designs For Ultrasonic WeldingDocumento4 páginasJoint Designs For Ultrasonic WeldingitslowAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Weld JointDocumento3 páginasStandard Weld Jointtalparadipak100% (1)
- PPT Chandra AsriDocumento49 páginasPPT Chandra AsrianandaAinda não há avaliações
- TR-610 - Material Compatibility in Envirotemp Fluids-Gaskets & Polymers - April - 23 - 2015Documento11 páginasTR-610 - Material Compatibility in Envirotemp Fluids-Gaskets & Polymers - April - 23 - 2015rodineicarraroAinda não há avaliações
- Araldite Price List - InTERNAL FinalDocumento10 páginasAraldite Price List - InTERNAL FinalAashish PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Draft Soal US B Ing Kelas 9 TP 21 22Documento7 páginasDraft Soal US B Ing Kelas 9 TP 21 22Nizar Ridaus SyamsiAinda não há avaliações
- POLYMER TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS Polytechnic KeralaDocumento3 páginasPOLYMER TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS Polytechnic KeralaprasobhaAinda não há avaliações
- Plastics: Why Is Widely Used? Definition of TermsDocumento9 páginasPlastics: Why Is Widely Used? Definition of TermsrenaAinda não há avaliações
- Dragonox-1098: Pine Chemicals Polymer Additives Petrochemicals ProductsDocumento2 páginasDragonox-1098: Pine Chemicals Polymer Additives Petrochemicals ProductsXuân Giang NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- SBR General Introduction: HistoryDocumento3 páginasSBR General Introduction: Historyanvesha raoAinda não há avaliações
- Elastomeric Fibres - Fibres With Elastic CapabilityDocumento5 páginasElastomeric Fibres - Fibres With Elastic Capability9043785763Ainda não há avaliações
- Materials Used For Packaging of Pharmaceutical Products: PlasticDocumento8 páginasMaterials Used For Packaging of Pharmaceutical Products: PlasticAnuj ZanjurneAinda não há avaliações
- Reformer Welding Joint SummaryDocumento1 páginaReformer Welding Joint SummaryPraveen RANAAinda não há avaliações
- B62 0300 (Rev. B 2004.08) EN - THERMOPLASTIC, THERMOSETTING MATERIALS THERMOPLASTIC ELASTOMERS AND RUBBERS - CLASSIFICATIONDocumento20 páginasB62 0300 (Rev. B 2004.08) EN - THERMOPLASTIC, THERMOSETTING MATERIALS THERMOPLASTIC ELASTOMERS AND RUBBERS - CLASSIFICATIONDiego CamargoAinda não há avaliações
- Super GlueDocumento6 páginasSuper GlueMarcela Liliana MolnarAinda não há avaliações
- PolymersDocumento1 páginaPolymersqishyAinda não há avaliações
- Class 8 Science Worksheet CH - Synthetic MaterialsDocumento2 páginasClass 8 Science Worksheet CH - Synthetic MaterialsRiddhiAinda não há avaliações
- 3D Hubs CapabilitiesDocumento3 páginas3D Hubs CapabilitiesRR_scribdAinda não há avaliações
- SYBTech PO221 PC 01b Polymer Classification PPT 2020-07-28Documento29 páginasSYBTech PO221 PC 01b Polymer Classification PPT 2020-07-28Deep SinojiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Plastics Technology Practice PDFDocumento35 páginasPlastics Technology Practice PDFabi lash100% (1)