Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Chapter 1
Enviado por
Renu Sekaran0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
14 visualizações16 páginasGas System Material and Components
Título original
chapter 1
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoGas System Material and Components
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
14 visualizações16 páginasChapter 1
Enviado por
Renu SekaranGas System Material and Components
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 16
LOGO
BKG3493 GAS SYSTEM
MATERIALS & COMPONENTS
CHAPTER 1
REVIEW OF GAS SYSTEMS
TOPIC OUTCOMES
At the end of this chapter you should be able to:
i) Explain the overview of gas industry in Malaysia
ii) Differentiate between NG, LPG and LNG supply
chains
iii) Explain the supply pressure and materials used
for transporting NG, LPG and LNG to the users
Worldwide Natural Gas Consumption
An increasing demand for natural gas as
a fuel as well as a feed for
petrochemical and chemicals plants
throughout the world.
Natural gas has played a major role in
meeting energy demand in North
America, Western and Eastern European
countries, and industrialized Asia due to
its availability and environmental
acceptance.
Advantages of using natural gas includes
abundance resources compared to
crude oil, most clean burning, efficient,
economic, etc.
Among the multinational companies in
gas (and oil) industry
Natural Gas Supply Chain
Offshore Exploration and
Production platforms
(Lawit, Jernih, Resak,
Duyong, Bekok, Sotong,
Guntong, and etc)
Gas Processing
Plants (A & B)
City Gate Odorizer Station
District Station
Area Station
Service Station
Subsea
Pipeline
PGU
Line
Feeder
Line
Regulating
Station
Service Station
Distribution
Line
Industrial/
Cogenaration
Commercial
Commercial
Residential
500-1000
psig
260 psig
60 psig
> 29 psig
Supply pressure
dictates the material
used for the pipeline!
LPG Supply Chain/ LPG Reticulation System
LPG Manifold
System
First Stage
Regulator
Second Stage
Regulator
LPG Bulk Storage
(60 to 80 psi)
Residential &
Commercial
Customers
5.0 psi 0.5 psi
LNG Supply Chain
Gas Field
Liquefaction Plant Shipping
Receiving Terminal
+
Re-gasification
Pipeline &
Distribution
Load Centers
Load Centers
Cryogenic condition mainly dictates the
materials used for piping and storage systems!
Gas Utilization Policy in Malaysia
In Peninsular Malaysia, natural gas and LPG are mainly utilized
for meeting continuous domestic demands from
residential/household, commercial and industrial users.
Domestic/household utilizations water heating and boiling,
cooking, drying and etc.
Commercial utilizations restaurants (heating and cooking),
hotels (heating, sauna, Jacuzzi), malls (heating, air
conditioning), and etc.
Industrial utilizations heating, production of steam, power
generations, NGV, feedstock for chemicals productions, and
etc.
In East Malaysia, particularly in Sarawak, natural gas is exported
in the form of LNG.
Peninsular Gas Utilisation (PGU) Project
Owned by Petronas Gas Berhad (PGB)
Started on 1983 and completed on 1999/2000
GPP A (1,2,3 & 4) and GPP B (5 & 6)
3 phases
Phase I from Kertih to Paka and to Kuantan
Phase II from Kuantan to Singapore and Klang (via
Segamat)
Phase III from Klang to Padang Besar
Parallel line act as loop
Gas Processing Plant and Gas Liquefaction
Plant
Produce treated natural gas (sales gas) to meet pipeline
requirements and customers specifications
Involve several processing steps such as gas dehydration, gas
sweetening, gas conditioning, dew point control, and etc.
In LNG production, raw natural gas must be treated to avoid
equipment plugging during liquefaction process.
Gas Processing Plant
GPP Capacity (mmscfd) Gas in
1 250 1984
2 250 1992
3 250 1992
4 250 1994
5 500 1998
6 500 1999
Gas Piping System in Malaysia
Gas Transmission System
Steel pipe with high tensile strength
Pipe diameter ranges from 24 inches to 36 inches
Pressure ranges from 500 psig to 1000 psig (3400-6900
kPa)
Capable of transporting large volume of gas
Comprise large compression station (such as in Segamat)
Gas distribution
Distribute gas to the customers/users
Gas users are from industrial, commercial and residential
System components
City Gates and Odorisation Station
District Station
Service Station
Piping comprises of
Feeder line (steel pipe)
Distribution line (steel pipe or PE pipe)
Service line (steel pipe or copper pipe)
Internal pipe (carbon steel or copper pipe)
Pipe size less than 24 inches
Operated by Gas Malaysia Sdn. Bhd (GMSB)
Gas Piping System in Malaysia
Codes and Standards
(Malaysian) Related
to Piping Materials
MS 930 Code of Standards for the Installation of Gas Piping
System and Appliances
MS 830 Code of Standards for the Storage, Handling and
Transportation of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)
Q & A
LIST DOWN
Characteristics of piped gas
Safety requirements in design,
construction and maintenance of LPG and
NG
www.themegallery.com
LOGO
Você também pode gostar
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Science Form 1Documento15 páginasScience Form 1Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- For Section A, Write Your Answer in The Answer Sheet Provided in Page 12Documento12 páginasFor Section A, Write Your Answer in The Answer Sheet Provided in Page 12Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Wesley Methodist School Klang MONTHLY TEST 1 (2019) Chemistry Form 4 Total: 50 MarksDocumento8 páginasWesley Methodist School Klang MONTHLY TEST 1 (2019) Chemistry Form 4 Total: 50 MarksRenu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocumento40 páginasCell As A Unit of LifeRenu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan (Subject: SCIENCE)Documento3 páginasLesson Plan (Subject: SCIENCE)Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Format 24-2 (Opal)Documento3 páginasLesson Plan Format 24-2 (Opal)Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Lesson Plan Format 27-1 (Opal)Documento4 páginasLesson Plan Format 27-1 (Opal)Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Intensive 4 Page 4Documento1 páginaIntensive 4 Page 4Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Intensive 4 Page 2Documento1 páginaIntensive 4 Page 2Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Lesson Plan (Subject: SCIENCE)Documento2 páginasLesson Plan (Subject: SCIENCE)Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
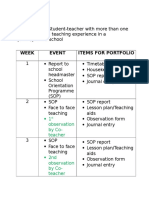
- MODE 1: For Student-Teacher With More Than One: 1 Observation by Co-TeacherDocumento4 páginasMODE 1: For Student-Teacher With More Than One: 1 Observation by Co-TeacherRenu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Lesson Plan Format 27-1Documento4 páginasLesson Plan Format 27-1Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- E E:sl: Et Isl If:: I Ii:i I Il", 3:p:r I Et:sfDocumento1 páginaE E:sl: Et Isl If:: I Ii:i I Il", 3:p:r I Et:sfRenu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Form 2 - Page 1Documento1 páginaForm 2 - Page 1Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Intensive 3 Page 2Documento1 páginaIntensive 3 Page 2Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- 1 PGDIPEDU (UAB) MyVLE Practicum SlideDocumento17 páginas1 PGDIPEDU (UAB) MyVLE Practicum SlideRenu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
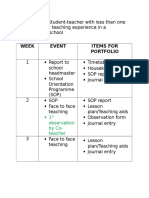
- MODE 2: For Student-Teacher With Less Than One: 1 Observation by Co-TeacherDocumento4 páginasMODE 2: For Student-Teacher With Less Than One: 1 Observation by Co-TeacherRenu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Form 1 Assessment OCTOBER 2015 Form 1 Science: (Duration: 25 Minutes)Documento8 páginasForm 1 Assessment OCTOBER 2015 Form 1 Science: (Duration: 25 Minutes)Renu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Chapter 2b Molecular Diffusion in LiquidDocumento12 páginasChapter 2b Molecular Diffusion in LiquidRenu SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)