Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
E Comm - Unit 3
Enviado por
prashanttendolkar0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
125 visualizações8 páginase commerce
Título original
e-comm_unit-3
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoe commerce
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
125 visualizações8 páginasE Comm - Unit 3
Enviado por
prashanttendolkare commerce
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 8
MBA-II, EBF (FT-204C) Unit-3, Study material compiled by Prof.
Vanita Joshi, SOM, SIMS, Indore
1
UNIT - 3
Electronic Payment System
Contents
What is E-payment?
Types of E-payment Systems
Digital Token-based Electronic Payment Systems
Smart Cards & Electronic Payment Systems
Credit Card-based Electronic Payment Systems
Risk & Electronic Payment Systems
Designing Electronic Payment System
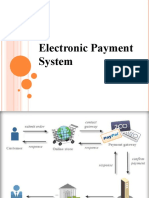
What is E-payment ?
E-payment systems is the mechanism of transferring money over the Internet
and technology used in this transfer is called as EFT.
EFT defined as any transfer of fund initiated through an e-terminal, telephonic
instrument, or computer or magnetic tape to order, instruct or authorize a financial
institution to debit or credit an account.
It is mostly used for Business to business (B2B) commerce where companies
doing business together tend to use electronic data interchange (EDI) system to
send each other bills and notices of payment.
E-Payment
Advantages of E-Payment
Increase payment efficiency
Reduce transaction costs
Enable trade in goods and services of very low value
Increase convenience of making payments
Payment can be made swiftly and remotely using various devices
Can be used for
e-commerce / e-Trade
For other purposes like paying bills, taxes, etc
Information
$
Products/services
online
offline
MBA-II, EBF (FT-204C) Unit-3, Study material compiled by Prof. Vanita Joshi, SOM, SIMS, Indore
2
Categories of EFT
Banking and financial payments
* Large-scale or wholesale payment
* Small scale or retail payment
* Home banking
Retailing payments
* Credit cards
* Debit cards
On-line electronic commerce payments
* Token-based payment system
~ Electronic cash
~ Electronic checks
~ Smart cards or debit cards
* Credit card-based payment systems
~ Encrypted credit cards
~ Third-party authorization numbers
Main factors when selecting e-payment method
Availability (bank system, laws and regulations)
The consideration of size and type of business, type of a target group of
consumers, types of products and services.
The ability to provide security against fraudulent activity
Being cost effective for low value transaction fees
Being protective of the privacy of the users
Easy to use, and being convenient for purchasing on the web based e-business
Token-based E-Payment Systems
Electronic tokens are the new financial instruments which are in the form of electronic
cash/money or checks.
Electronic tokens are same as cash that is backed by bank. They are of three types:
1. Cash or real-time ( e-cash)
2. Debit or Prepaid (smart cards, e-purses)
3. Credit or Postpaid (credit/debit cards, e-checks)
E-cash
Electronic cash is a consumer-oriented electronic payment. Though it replaces the cash
but still cash is quite dominant form of payment for three reasons:
1. Lack of trust in banking system
2. Inefficient clearing and settlement of non-cash transaction
3. Negative real interest rates paid on bank deposit
Advantages of cash over credit cards
It is negotiable
Cash is a legal tender
Cash is a bearer instrument
It need require bank account to operate
No risk on the part of acceptor that the medium of exchange may not be good
MBA-II, EBF (FT-204C) Unit-3, Study material compiled by Prof. Vanita Joshi, SOM, SIMS, Indore
3
Properties of e-cash
E-cash must have following four properties:
Monetary values:
Interoperability
Retrievability
Security
E-cash in Action
E-cash based on cryptographic systems called digital signature
This method involves pair of two numeric keys (very large number or integer)
that work in tandem (cycle): one for encoding and another for decoding.
Message encoded with one numeric key can only be decoded with other numeric
key and none other.
The encoding key is kept private while the decoding key is made public.
E-checks
E-checks are another form of electronic tokens.
A new electronic version of paper check. E-check is an instruction to a financial
institution to pay a given amount of money to the payee.
It is a specially formatted email message sent over the Internet. It contains as the
same information as on paper based check.
Check service providers
PayByCheck (http://www.paybycheck.com)
CyberSource (http://cybersource.com)
Transaction Payment Sequence in E-check system
Bank
Payer Payee
Transfer e-check
Forward e-check for
payer authentication
Deposit
e-check
Accounting Server
Bank
MBA-II, EBF (FT-204C) Unit-3, Study material compiled by Prof. Vanita Joshi, SOM, SIMS, Indore
4
Transaction Payment Sequence in E-check system
Buyer must register with third party account server using electronic check.
On receiving the check, the seller presents it to accounting server for verification
and payment.
The accounting system verifies the digital signature on the check.
Properly signed and endorsed checks can be electronically exchanged between
financial institutions through electronic clearing house.
Advantages of E-Check
They work in the same way as traditional checks.
E-checks are suited for micro payments.
Eliminate the need for expensive process reengineering and taking advantage of
the banking industry.
Financial risk is assumed by accounting server.
E-checks create a float through third-party accounting server. They make money
out of buyers and sellers transaction by providing deposit account.
Difference b/w EFT and E-check
In E-Cheque, electronic versions of the cheque are issued, received & processed.
So, payee issues an E-Cheque for each payment.
In EFT transfer automatic withdrawals are made for monthly bills or other fixed
payments; no cheques are issued.
Smart cards
A smart card is a plastic card with an embedded microchip containing information
about you.
A smart card can store about 100 times the amount of information that a magnetic
strip plastic card can store.
A smart card contains private user information, such as financial facts, private
encryption keys, account information, credit card numbers, health insurance
information, etc.
So far not successful in U.S., but popular in Europe, Germany, Singapore and
Japan to pay for public phone call, transportation.
Mondex Smart Card
Holds and dispenses electronic cash (Smart-card based, stored-value card)
Developed by MasterCard International
Requires specific card reader, called Mondex terminal, for merchant or customer
to use card over Internet
Supports micropayments and works both online and off-line at stores or over the
telephone
Secret chip-to-chip transfer protocol
Loaded through ATM
ATM does not know transfer protocol; connects with secure device at
bank
MBA-II, EBF (FT-204C) Unit-3, Study material compiled by Prof. Vanita Joshi, SOM, SIMS, Indore
5
Mondex Smart Card Processing
Mondex Smart Card
Disadvantages
Card carries real cash in electronic form, creating the possibility of theft
No deferred (overdue) payment as with credit cards - cash is dispensed
immediately
Types of Smart cards
Smart cards are basically of two types:
1. Relationship-based Smart Cards
2. Electronic Purses and Debit Cards
Relationship-based Smart Cards
It is the enhancement of existing card services that offer customers far better options like:
1. Access to multiple accounts (debit, credit, e-cash) on one card.
2. Offer various functions ( cash access, bill payment, balance inquiry, fund transfer)
3. Multiple access options at multiple location using multiple access device (ATM,
PC, PDA or screenphone etc)
Electronic Purses and Debit Cards
Electronic Purses or E- wallet are the smart cards embedded with programmable
microchip that store sum of money instead of cash.
Once a purse is loaded with money it require card reader vending machine which verifies
its authenticity .Then after amount is deducted from balance.
It shows the remaining balance on the card hence eliminate the small bill in busy stores.
E-wallets when depleted can be recharged with money .
MBA-II, EBF (FT-204C) Unit-3, Study material compiled by Prof. Vanita Joshi, SOM, SIMS, Indore
6
Credit cards-based e-payment system
Credit Cards
A credit card is a small plastic card issued to users dealing in e-commerce. Most
credit cards are the same shape and size, as specified by the ISO 7810 standard.
A credit card is different to a debit card in that it does not remove money from
the user's account after every transaction. In the case of credit cards, the issuer
lends money to the consumer (or the user) to be paid to the merchant.
Credit cards-based e-payment system
Customers who purchase any goods send their credit card details to the service provider
involved and the credit card organization will handle this payment.
Online credit card payment has following categories:
1. Payment using plain credit card details
2. Payments using encrypted credit card details
3. Payment using third-party verification
Entities involved in Credit card Transaction
Consumer (Buyer or Card holder)
Merchant (Seller)
Card Issuer (Consumers Bank)
Acquirer or Principal (Merchants Bank)
Card Association (Visa, Master Card etc)
Third party processor
How an Online Credit Transaction Works
Encryption and Credit cards
Encryption process starts when credit card information is entered into a browser and sent
securely over network between buyer to seller.
Encryption process includes following steps:
1. Customer presents his credit card information securely to merchant.
2. Merchant validates the authenticity of card holder
3. Merchant relays this information to its bank or on-line card processor.
MBA-II, EBF (FT-204C) Unit-3, Study material compiled by Prof. Vanita Joshi, SOM, SIMS, Indore
7
4. The bank relays the information to customers bank for authorization approval
5. The customers bank returns the credit card , charge authentication and
authorization to the merchant
Processing Payment with Encrypted
Third-party authorization and Credit cards
In third party processing, consumer register with third party on the internet to verify e-
microtransaction.
The companies providing third party payment service on internet are:
http://www.fv.com ( First Virtual)
http://www.openmarket.com
http://www.2checkout.com/
http://www.paypal.com/
Payment can be made by credit card via clearing house.
Online Third-Party Processor (OTPPs) has following steps for buying information
online.
1. Consumer registers for an OTPP a/c that is backed by credit card.
2. To purchase customer request merchant by her OTPP account no.
3. Merchant then contact the OTPP payment server with customers account no.
4. OTPP payment server verifies the customers account no. for vender (merchant)
& checks for sufficient funds.
5. OTPP server send a message to buyer that can be responded back by buyer as ;
yes/agree; No/disagree; fraud.
6. If OTPP gets Yes from customer, merchant is informed & then customer is
allowed to download material.
MBA-II, EBF (FT-204C) Unit-3, Study material compiled by Prof. Vanita Joshi, SOM, SIMS, Indore
8
Online Payment Processing using a Third-party Processor
Risk in using Credit cards
Customer uses a stolen card or account number to fraudulently purchase goods or
service online.
Many people who will be on the Internet have not even had their first Web
experience.
Hackers find the ways into an e-commerce merchants payment processing
system and then issue credits to hacker card account numbers.
Many users are also likely to be younger and have less access to credit and debit
cards
Many purchases they make will be micropayments.
Credit cards cannot be used for large sums of B2B transactions
Customer falsely claims that he or she did not receive a shipment
Limitations of Online Credit Card Payment Systems
Security neither merchant nor consumer can be fully authenticated.
Cost for merchants, around 3.5% of purchase price plus transaction fee of 20-
30 cents per transaction.
People living in rural areas dont have same access to computers and Internet that
others do.
Social equity many people do not have access to credit cards (young and old
age), disabled, individuals who are not computer savvy and individuals who
cannot afford cards ( poor credit risk).
Designing Electronic Payment Systems
Following criteria should be satisfied while designing any new E-payment System:
1. Privacy 6. Pricing
2. Security 7. Standards
3. Intuitive Interface
4. Database Integration
5. Brokers
Você também pode gostar
- Review of Some Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersNo EverandReview of Some Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Some Online Payment Providers Services: Best Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersNo EverandEvaluation of Some Online Payment Providers Services: Best Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment SystemsDocumento8 páginasElectronic Payment SystemsAbhishek NayakAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment System111Documento43 páginasElectronic Payment System111negirakes100% (1)
- Slow For Micro Payments and Produce High Transaction Costs For Processing Them. Therefore, New Processing Cost, and Widely AcceptableDocumento10 páginasSlow For Micro Payments and Produce High Transaction Costs For Processing Them. Therefore, New Processing Cost, and Widely AcceptableAakash RegmiAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-5 E-Commerce Electronic Payment System SRGDocumento33 páginasUnit-5 E-Commerce Electronic Payment System SRGLuitel ShaneAinda não há avaliações
- Unit III Final ECOMDocumento17 páginasUnit III Final ECOMsar leeAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - 2 - Electronic Payment SystemDocumento67 páginasUnit - 2 - Electronic Payment Systemvisdag100% (2)
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento23 páginasElectronic Payment System741Mohd Saif AnsariAinda não há avaliações
- E Payments Modes and MethodsDocumento52 páginasE Payments Modes and MethodsHarshithAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment System: Presented byDocumento43 páginasElectronic Payment System: Presented bysheetal28svAinda não há avaliações
- E Payment SystemDocumento56 páginasE Payment SystemAnkiTwilightedAinda não há avaliações
- ECOM Unit 3Documento29 páginasECOM Unit 3kunchala_veniAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-3 Electronic Payment SystemDocumento12 páginasUnit-3 Electronic Payment SystemNezuko KamadoAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Electronic Payment SystemsDocumento20 páginasTypes of Electronic Payment SystemsRushyanth VattikondaAinda não há avaliações
- E-COMMERCE - Unit-2Documento19 páginasE-COMMERCE - Unit-2Kalyan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- E Payment SystemsDocumento8 páginasE Payment SystemsAlex MianoAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento21 páginasElectronic Payment SystemHaidarAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment System: Presented By: Richa Somvanshi (85) Sachin Goel (68) Sahar AiromDocumento43 páginasElectronic Payment System: Presented By: Richa Somvanshi (85) Sachin Goel (68) Sahar AiromSiti Zalikha Md JamilAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-III: Types of Electronic Payment SystemsDocumento8 páginasUnit-III: Types of Electronic Payment SystemsUmam AfzalAinda não há avaliações
- E-Commerce & Web designing-IIDocumento10 páginasE-Commerce & Web designing-IISatya SaiAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento47 páginasElectronic Payment SystemMilan Jain100% (1)
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento20 páginasElectronic Payment SystemThe PaletteAinda não há avaliações
- E Money and e Payment System 1 1Documento114 páginasE Money and e Payment System 1 1Aman SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Online Payment SystemDocumento30 páginasOnline Payment SystemDjks YobAinda não há avaliações
- E Marketing Unit 2 e ComDocumento18 páginasE Marketing Unit 2 e ComjayAinda não há avaliações
- E Payment 120927112113 Phpapp02Documento38 páginasE Payment 120927112113 Phpapp02sagarg94gmailcomAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento20 páginasElectronic Payment SystemAanchal GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment Systems (Eps)Documento16 páginasElectronic Payment Systems (Eps)Navneet VishnoiAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento5 páginasElectronic Payment SystemSwati HansAinda não há avaliações
- .. CSE CSO5185Notes-11Documento2 páginas.. CSE CSO5185Notes-11mahesh_gottapuAinda não há avaliações
- Im Mini ProjectDocumento10 páginasIm Mini Projectsrividya balajiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-6 Electronic Payment PDFDocumento40 páginasChapter-6 Electronic Payment PDFSuman BhandariAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5Documento19 páginasLecture 5Muhammad Mubshar NazirAinda não há avaliações
- E CommerceDocumento25 páginasE CommerceShruti SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 03: Electronic Payment System: By: Diwakar UpadhyayaDocumento67 páginasChapter 03: Electronic Payment System: By: Diwakar UpadhyayaBibek karnaAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento30 páginasElectronic Payment SystemSONAL RATHIAinda não há avaliações
- Unit3e PaymentsDocumento53 páginasUnit3e PaymentsKavitha PalaniAinda não há avaliações
- Unit III EpsDocumento45 páginasUnit III Epsaditi pandeyAinda não há avaliações
- E Payment SystemsDocumento17 páginasE Payment SystemsdeekshaAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 3 E-COMM NotesDocumento13 páginasUNIT 3 E-COMM NotesVikash kumarAinda não há avaliações
- E PaymentDocumento15 páginasE PaymentRohan KirpekarAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Electronic Payment SystemsDocumento39 páginas4 Electronic Payment SystemsYashasweeAinda não há avaliações
- IDM - E-Commerce - Payment Systems & SEODocumento33 páginasIDM - E-Commerce - Payment Systems & SEOBhaswati PandaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3Documento23 páginasUnit 3Mahesh NannepaguAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment SystemsDocumento36 páginasElectronic Payment SystemsSaurabh G82% (11)
- Epayment SeminarDocumento5 páginasEpayment Seminardheeraj_ddAinda não há avaliações
- Group 2 - Various Forms of E - BankingDocumento12 páginasGroup 2 - Various Forms of E - BankingTrinidad, Ma. AngelicaAinda não há avaliações
- E Payment System Assign PDFDocumento9 páginasE Payment System Assign PDFShafique Ahmed ArainAinda não há avaliações
- MisDocumento3 páginasMisDevanshi AroraAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic PaymentsDocumento41 páginasElectronic PaymentsJohnkandruAinda não há avaliações
- E PaymentDocumento8 páginasE PaymentPrashant SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Payment System: Amit Kumar Nayak Roll No:29401 Regd No:1005105001Documento17 páginasElectronic Payment System: Amit Kumar Nayak Roll No:29401 Regd No:1005105001Amit Kumar NayakAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 7Documento31 páginasTopic 7LucyChanAinda não há avaliações
- CH-6 E MarketingDocumento17 páginasCH-6 E Marketingabdelamuzemil8Ainda não há avaliações
- Electronic PaymentDocumento81 páginasElectronic Paymentarya manchandaAinda não há avaliações
- E Commerce PresentationDocumento30 páginasE Commerce PresentationRajiv Ranjan100% (1)
- E-Commerce and Its Application: Unit-IVDocumento37 páginasE-Commerce and Its Application: Unit-IVVasa VijayAinda não há avaliações
- Cyber Unit 2 Lecture 4Documento21 páginasCyber Unit 2 Lecture 4VijayAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Some Online Banks, E-Wallets and Visa/Master Card IssuersNo EverandEvaluation of Some Online Banks, E-Wallets and Visa/Master Card IssuersAinda não há avaliações
- Bill of Lading - 2023-11-17T111055.919Documento1 páginaBill of Lading - 2023-11-17T111055.919Lissa PerezAinda não há avaliações
- ASME B16-48 - Edtn - 2005Documento50 páginasASME B16-48 - Edtn - 2005eceavcmAinda não há avaliações
- Online Declaration Form 1516Documento2 páginasOnline Declaration Form 1516AlcaAinda não há avaliações
- Michael Fine Disciplinary ComplaintDocumento45 páginasMichael Fine Disciplinary ComplaintAnonymous 2NUafApcVAinda não há avaliações
- A. Abstract: "Same-Sex Adoption Rights"Documento12 páginasA. Abstract: "Same-Sex Adoption Rights"api-310703244Ainda não há avaliações
- Evolution of Hotel Management Agreements and Rise of Alternative AgreementsDocumento14 páginasEvolution of Hotel Management Agreements and Rise of Alternative AgreementsSharif Fayiz AbushaikhaAinda não há avaliações
- Britannia: Business Conduct (COBC) For Its Employees. This Handbook Covers The CodeDocumento17 páginasBritannia: Business Conduct (COBC) For Its Employees. This Handbook Covers The CodevkvarshakAinda não há avaliações
- CHAP - 02 - Financial Statements of BankDocumento72 páginasCHAP - 02 - Financial Statements of BankTran Thanh NganAinda não há avaliações
- Arcelor MittalDocumento4 páginasArcelor Mittalnispo100% (1)
- As 1816.1-2007 Metallic Materials - Brinell Hardness Test Test Method (ISO 6506-1-2005 MOD)Documento3 páginasAs 1816.1-2007 Metallic Materials - Brinell Hardness Test Test Method (ISO 6506-1-2005 MOD)SAI Global - APACAinda não há avaliações
- Rizzo v. Goode, 423 U.S. 362 (1976)Documento19 páginasRizzo v. Goode, 423 U.S. 362 (1976)Scribd Government DocsAinda não há avaliações
- 409-Prohibiting Harassment Intimidation or Bullying Cyberbullying Sexting Sexual Harassment StudentsDocumento8 páginas409-Prohibiting Harassment Intimidation or Bullying Cyberbullying Sexting Sexual Harassment Studentsapi-273340621Ainda não há avaliações
- 2013 Annual ReportDocumento100 páginas2013 Annual ReportFederal Reserve Bank of St. LouisAinda não há avaliações
- Language in India: Strength For Today and Bright Hope For TomorrowDocumento24 páginasLanguage in India: Strength For Today and Bright Hope For TomorrownglindaAinda não há avaliações
- Mindanao Pres Co. v. City Assessors G.R. No. L-17870Documento2 páginasMindanao Pres Co. v. City Assessors G.R. No. L-17870Liam LacayangaAinda não há avaliações
- Consti - People Vs de LarDocumento1 páginaConsti - People Vs de LarLu CasAinda não há avaliações
- Tcode GTSDocumento28 páginasTcode GTSKishor BodaAinda não há avaliações
- GM 4Q W4Documento24 páginasGM 4Q W4Charmaine GatchalianAinda não há avaliações
- Borromeo v. DescallarDocumento2 páginasBorromeo v. Descallarbenjo2001Ainda não há avaliações
- Fuji v. Espiritu - CaseDocumento21 páginasFuji v. Espiritu - CaseRobeh AtudAinda não há avaliações
- Mohnish Pabrai - ChecklistDocumento1 páginaMohnish Pabrai - ChecklistCedric TiuAinda não há avaliações
- United States v. Mark Bowens, 4th Cir. (2013)Documento6 páginasUnited States v. Mark Bowens, 4th Cir. (2013)Scribd Government DocsAinda não há avaliações
- Solved Consider The Apple Computer Trade Example Given in Section 19 5 NowDocumento1 páginaSolved Consider The Apple Computer Trade Example Given in Section 19 5 NowM Bilal SaleemAinda não há avaliações
- BL-5-Negotiable Instruments ActDocumento46 páginasBL-5-Negotiable Instruments ActAbhishekAinda não há avaliações
- Spicer: Dana Heavy Tandem Drive AxlesDocumento34 páginasSpicer: Dana Heavy Tandem Drive AxlesPatrick Jara SánchezAinda não há avaliações
- Reodica Vs Court of AppealsDocumento2 páginasReodica Vs Court of AppealsChaoSisonAinda não há avaliações
- Ballard County, KY PVA: Parcel SummaryDocumento3 páginasBallard County, KY PVA: Parcel SummaryMaureen WoodsAinda não há avaliações
- 25 RESA vs. MO 39Documento37 páginas25 RESA vs. MO 39George Poligratis Rico100% (2)
- Sapbpc NW 10.0 Dimension Data Load From Sap BW To Sap BPC v1Documento84 páginasSapbpc NW 10.0 Dimension Data Load From Sap BW To Sap BPC v1lkmnmkl100% (1)
- Public OfficerDocumento12 páginasPublic OfficerCatAinda não há avaliações