Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
VEH-MB-ML320-ESP-W163 ESP Part1 PDF
Enviado por
d9dDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
VEH-MB-ML320-ESP-W163 ESP Part1 PDF
Enviado por
d9dDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1
ESP
Electronic Stability Program
327 HO 05 ESP (WJB,GC) 02-26-04
Starting MY1996
2
Objectives
At the end of this presentation, you should be able to:
1. Explain the function of and purpose for ESP
2. Describe the customer interface with ESP
3. List the hydraulic and electronic components used for ESP
4. Describe the ESP build up, holding and reduction control
modes
These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check for revised or updated information.
To help avoid personal injury to you or others, and to avoid damage to the vehicle on which you are working, you must always ref er to the latest Mercedes -Benz Technical Publication and follow all
pertinent instructions when testing, diagnosing or making repair.
Illustrations and descriptions in this training reference are based on preliminary information and may not correspond to the final US version vehicles. Refer to the official introduction manual and WIS
when available. Copyright Mercedes-Benz USA, LLC, 2004
WIS document numbers shown apply to WIS Version USA/CDN at date of writing.
Reproduction by any means or by any information storage and retrieval system or translation in whole or part is not permitted wi thout written authorization from Mercedes -Benz USA, LLC or it's
successors. Published by Mercedes -Benz USA, LLC Printed in U. S.A.
3
Contents
Purpose of ESP 4
Driving with ESP 7
ESP Electronic components 9
Six ESP control modes 19
Diagnosing Included ESP Functions 23
Other Functions Related to ESP 24
ESP block diagram 25
4
Purpose of ESP
1. Prevent oversteer and
understeer
2. Increase safety by
providing stability
It does this by applying the
appropriate brake(s)
5
Advantages
Improved starting and acceleration capability
Improved stability when:
braking
accelerating
coasting
cornering
Shortens stopping distances in corners or on slippery surfaces
Informs driver of slippery conditions
ABS, ASR, EBR and ESP functions are combined in one control unit
ABS, ASR, EBR and ESP basic components are combined in one hydraulic
unit
6
Improved Braking Stability
Additional ESP system sensors provide for further
enhanced braking stability.
7
Driving with ESP
Warning lamp flashes when ESP operates.
The throttle control portion of ESP can be
switched off with ESP OFF rocker switch.
This will illuminate the warning lamp continuously.
(may provide better traction in deep snow or when
snow chains are mounted)
8
Understeer and Oversteer
ESP monitors the vehicles traction and handling, using sensors to
detect wheel speed, understeer and oversteer
Understeer Oversteer
Vehicle does not turn as sharply as
desired. The vehicle seems to plow
straight ahead. ESP will brake the
inside rear wheel.
Vehicle turns in more sharply than
desired. The rear of the vehicle
swings outward. ESP will brake the
outside front wheel.
9
ESP Electronic Components
A1e17 ABS malfunction indicator lamp
A1e41 ESP and ABS warning lamp
A1p13 Multifunction display
A7/3n1 SBC control module
B24/15 Lateral acceleration and yaw rate
sensor
N47-5 ESP, BAS and SPS control module
N49 Steering angle sensor
N72/1s1 ESP OFF switch
X11/4 Diagnostic data link connector
10
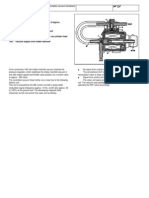
Steering Angle Sensor (N49)
N80 - Steering
column module
A45 - SRS &
horn clock spring
Signals the desired steering angle to ESP.
ESP also recognizes cornering by monitoring
input from the 2 front wheel speed sensors.
W220 shown
Front wheels must be
straight when removing
and installing A45
11
Early Version Steering Angle Sensor (N49)
a
b
b - 8 apertures
& barriers
arranged in a
specific pattern
a 9 evenly
spaced light
emitting diodes
(LEDs)
Must be re-initialized after the battery is disconnected,
because N49 has a T.30 power connection.
12
Late Version Steering Angle Sensor (N49)
W220 Shown
Screw
N80 = Steering column module
25
ESP Block Diagram
Front VSS
Terminal 61
Stop lamp switch
Data Link (X11/4)
CAN-C (VSS)
Rear VSS
Circuit 31
Power
N47/
Return pump Relay
K40/
Hydraulic control
unit A7/
Parking Brake sw. ESP warning lamp
ESP MIL
ABS MIL
Lateral Sensor
Steering Angle
Pressure Sensor
Yaw Sensor
13
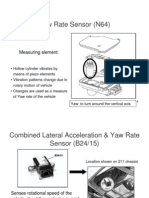
Lateral Acceleration Sensor (B24/2)
H
a
l
l
s
e
n
s
o
r
M
a
g
n
e
t
i
c
m
a
s
s
Produces a signal corresponding to the cornering forces.
Você também pode gostar
- VEH-MB-ML320-brakes-W163 BAS PDFDocumento15 páginasVEH-MB-ML320-brakes-W163 BAS PDFd9d100% (1)
- Mercedes Benz & Dodge Sprinter CDI 2000-2006 Owners Workshop ManualNo EverandMercedes Benz & Dodge Sprinter CDI 2000-2006 Owners Workshop ManualNota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (2)
- VEH-MB-ML320-ESP-W163 ESP Part2 PDFDocumento12 páginasVEH-MB-ML320-ESP-W163 ESP Part2 PDFd9dAinda não há avaliações
- SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission - 6R80 2012 F-150 Workshop Manual General ProceduresDocumento3 páginasSECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission - 6R80 2012 F-150 Workshop Manual General ProceduresPriscilla Kelly Freitas dos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- A32 GiDocumento49 páginasA32 GiLevin Tan HtAinda não há avaliações
- Avensis 2006 tns600Documento19 páginasAvensis 2006 tns600Expobiro Srbija100% (1)
- Efi System SQR780R CHERY QQDocumento65 páginasEfi System SQR780R CHERY QQGregory Subero100% (1)
- Steering Column Switch PDFDocumento26 páginasSteering Column Switch PDFDaniel OlariAinda não há avaliações
- 2005-Nissan-XTrail - ManuálDocumento256 páginas2005-Nissan-XTrail - ManuálHana Horáková100% (3)
- TATA Indica Owners Manual & Servie BookDocumento164 páginasTATA Indica Owners Manual & Servie BookPedro Zabala100% (1)
- P1012-Fuel Pump Delivery Pressure Too High: Theory of OperationDocumento2 páginasP1012-Fuel Pump Delivery Pressure Too High: Theory of OperationYovani AcevedoAinda não há avaliações
- 13 Re Russia-Kd 6B3 WM PDFDocumento636 páginas13 Re Russia-Kd 6B3 WM PDFIgor LukAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Calefaccion y A.Acondicionado Chevrolet Captiva 2006-10 PDFDocumento148 páginasManual Calefaccion y A.Acondicionado Chevrolet Captiva 2006-10 PDFskpppAinda não há avaliações
- Distributor Installation: Crankshaft Position Sensor RemovalDocumento2 páginasDistributor Installation: Crankshaft Position Sensor RemovalKeyboardMan1960Ainda não há avaliações
- Isuzu KB 1993-1996 TF140 Diesel PDFDocumento1.610 páginasIsuzu KB 1993-1996 TF140 Diesel PDFAndriatsitohaina Rabenaivo100% (1)
- 2007 Honda Civic Hatchback Owners Manual (Australian, Type R)Documento509 páginas2007 Honda Civic Hatchback Owners Manual (Australian, Type R)pblazevski_1100% (3)
- Brake Control PDFDocumento410 páginasBrake Control PDFClod HopperAinda não há avaliações
- Range Rover P38 Diesel EngineDocumento5 páginasRange Rover P38 Diesel EngineJoao Miguel Bernardo SaraivaAinda não há avaliações
- Цепи D4CBDocumento21 páginasЦепи D4CBКонстантин ДубенкоAinda não há avaliações
- 1 3Documento34 páginas1 3Gabriel BalcazarAinda não há avaliações
- LSD Manual PDFDocumento13 páginasLSD Manual PDFHector Muñoz SepulvedaAinda não há avaliações
- Charging For Toyota Land CruiserDocumento16 páginasCharging For Toyota Land CruiserAbu AliAinda não há avaliações
- Oil Control Valve 1zzfeDocumento1 páginaOil Control Valve 1zzferrtteam100% (3)
- Convenience Electronics Polo 9N 1,4 TDI PD 2002 55 KW AMFDocumento12 páginasConvenience Electronics Polo 9N 1,4 TDI PD 2002 55 KW AMFflorea tulituAinda não há avaliações
- Totota AygoDocumento318 páginasTotota AygoOlsi QinamiAinda não há avaliações
- Z Injector - Types - Nippon Denso 2Documento2 páginasZ Injector - Types - Nippon Denso 2joeAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Engine Controls TDV6 2.7Documento10 páginasElectronic Engine Controls TDV6 2.7elisei sorinAinda não há avaliações
- A760E Auto Trans - InstallationDocumento7 páginasA760E Auto Trans - InstallationJohn Locke100% (1)
- Nissan Almera II Hatchback (N16) 1.8 16V (2002) (Petrol)Documento4 páginasNissan Almera II Hatchback (N16) 1.8 16V (2002) (Petrol)theshitAinda não há avaliações
- Steering InitializationDocumento87 páginasSteering Initializationomanstar120% (2)
- Wiring Diagram HFM-SFI Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection - Ignition SystemDocumento8 páginasWiring Diagram HFM-SFI Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection - Ignition SystemStefanAinda não há avaliações
- Panasonic Lumix DMC-FZ50 Service ManualDocumento69 páginasPanasonic Lumix DMC-FZ50 Service Manualdasxax100% (1)
- 10 - Timing Chain - Installation PDFDocumento11 páginas10 - Timing Chain - Installation PDFbakriramzi100% (2)
- Ssang Young Rex TonDocumento14 páginasSsang Young Rex TonHri Vitalion100% (2)
- Mitsubishi Engine F9Q Series Workshop ManualDocumento48 páginasMitsubishi Engine F9Q Series Workshop ManualAlexandru sAinda não há avaliações
- BMW 318i - 318is - 325i - 325is (E36) 1993 Electrical Wiring DiagramsDocumento334 páginasBMW 318i - 318is - 325i - 325is (E36) 1993 Electrical Wiring DiagramsJose Calero PonsAinda não há avaliações
- Hybrid2009 SKBDocumento6 páginasHybrid2009 SKBsovon adhikaryAinda não há avaliações
- Automatic Transaxle Manual PDFDocumento429 páginasAutomatic Transaxle Manual PDFJeff UptagrafftAinda não há avaliações
- Smart Forfour 454-6Documento1 páginaSmart Forfour 454-6yamegAinda não há avaliações
- Phun Xang Dien Tu p1 8097Documento351 páginasPhun Xang Dien Tu p1 8097Đức Hòang100% (1)
- Hybrid 06Documento0 páginaHybrid 06Jorge Eduardo Diaz ValenzuelaAinda não há avaliações
- Customer Experience Center 1-800-331-4331: Quick Reference GuideDocumento30 páginasCustomer Experience Center 1-800-331-4331: Quick Reference GuideNaveed Gondal100% (1)
- X431 Pro Aus Help FileDocumento49 páginasX431 Pro Aus Help FilePrinto Simbolon100% (2)
- Ethos User ManualDocumento60 páginasEthos User Manual2791957Ainda não há avaliações
- Workshop ManualDocumento1.782 páginasWorkshop ManualgiuseppeAinda não há avaliações
- 1999 Isuzu Rodeo UE US Version Service Manual 2Documento2.613 páginas1999 Isuzu Rodeo UE US Version Service Manual 2Matt WillisonAinda não há avaliações
- 2uztrd PDFDocumento33 páginas2uztrd PDFbob loblawAinda não há avaliações
- Toyota - Land Cruiser 200 SpecificationsDocumento1 páginaToyota - Land Cruiser 200 SpecificationsJulius SamboAinda não há avaliações
- Steering SystemDocumento60 páginasSteering SystemAngga Budi PratamaAinda não há avaliações
- 8d22de PDFDocumento299 páginas8d22de PDFA-t HectorAinda não há avaliações
- Renault FluenceDocumento36 páginasRenault FluenceOdagescu StefanAinda não há avaliações
- Common Rail System (CRS) : Subaru Ee20 EngineDocumento47 páginasCommon Rail System (CRS) : Subaru Ee20 Engineleonardo medina100% (1)
- Apex'i RSM ManualDocumento47 páginasApex'i RSM Manualallenchen777Ainda não há avaliações
- Diesel+code+toyota+ PDFDocumento10 páginasDiesel+code+toyota+ PDFKumar HemrajAinda não há avaliações
- D.C. Powered Timing Light Model 161.2158 for 12 Volt Ignition Systems Sears Owners ManualNo EverandD.C. Powered Timing Light Model 161.2158 for 12 Volt Ignition Systems Sears Owners ManualAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Stability Program Starting Model Year 1996Documento25 páginasElectronic Stability Program Starting Model Year 1996Ozgean SeitomerAinda não há avaliações
- Bendix ® Gen 4 TM and Gen 5 TMDocumento48 páginasBendix ® Gen 4 TM and Gen 5 TMMarcialCastroLeonidasAinda não há avaliações
- General Removal and InstallationDocumento54 páginasGeneral Removal and InstallationKelvis RojasAinda não há avaliações
- Anti Lock Brake System Tata Motors Information PDFDocumento16 páginasAnti Lock Brake System Tata Motors Information PDFValBMSAinda não há avaliações
- Power SteeringDocumento10 páginasPower Steeringjohari23Ainda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 High Oil ConsumptionDocumento3 páginasVEH MB ML320 High Oil Consumptiond9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-ML320-Fill Power Steering Pump and BleedDocumento2 páginasVEH-MB-ML320-Fill Power Steering Pump and Bleedd9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-ML320-Fuel Filter & Line UpgradeDocumento3 páginasVEH-MB-ML320-Fuel Filter & Line Upgraded9dAinda não há avaliações
- Veh MB Ml320 Oil SludgeDocumento2 páginasVeh MB Ml320 Oil Sludged9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB TRANS 722.6 Transmission DTB Connector LeakDocumento2 páginasVEH MB TRANS 722.6 Transmission DTB Connector Leakd9dAinda não há avaliações
- Veh MB Ml320 Reset FssDocumento1 páginaVeh MB Ml320 Reset Fssd9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 EFI Purge Control Valve FunctionDocumento1 páginaVEH MB ML320 EFI Purge Control Valve Functiond9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 ETC Control Module, LocationDocumento1 páginaVEH MB ML320 ETC Control Module, Locationd9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 OIL DTB Air Intake SealDocumento1 páginaVEH MB ML320 OIL DTB Air Intake Seald9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 ETC Control Module, TaskDocumento2 páginasVEH MB ML320 ETC Control Module, Taskd9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 Fuel Vent Valve FunctionDocumento1 páginaVEH MB ML320 Fuel Vent Valve Functiond9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-TRANS-722.6-Transmission Troubleshooting For Leaks PDFDocumento1 páginaVEH-MB-TRANS-722.6-Transmission Troubleshooting For Leaks PDFd9d100% (1)
- VEH MB ML320 Oil Sludging 1Documento3 páginasVEH MB ML320 Oil Sludging 1d9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 Fuel Vent Valve PositionDocumento1 páginaVEH MB ML320 Fuel Vent Valve Positiond9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-ML320-W163 Climate Control (2002-05) Part1 PDFDocumento6 páginasVEH-MB-ML320-W163 Climate Control (2002-05) Part1 PDFd9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 EFI Throttle Valve Actuator FunctionDocumento1 páginaVEH MB ML320 EFI Throttle Valve Actuator Functiond9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-ML320-Egr-Exhaust Gas Recirculation Vacuum Transducer, FunctionDocumento1 páginaVEH-MB-ML320-Egr-Exhaust Gas Recirculation Vacuum Transducer, Functiond9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 EFI Pedal Value Sensor DesignDocumento1 páginaVEH MB ML320 EFI Pedal Value Sensor Designd9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-ML320-Fuel-Activated Charcoal Canister Shutoff Valve PositionDocumento1 páginaVEH-MB-ML320-Fuel-Activated Charcoal Canister Shutoff Valve Positiond9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 Upgraded Fuel LinesDocumento1 páginaVEH MB ML320 Upgraded Fuel Linesd9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-TRANS-722.6-limp Home Mode ETC Code P0715 PDFDocumento1 páginaVEH-MB-TRANS-722.6-limp Home Mode ETC Code P0715 PDFd9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-ML320-W163 Climate Control (2002-05) Part2 PDFDocumento15 páginasVEH-MB-ML320-W163 Climate Control (2002-05) Part2 PDFd9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH MB ML320 Fuel Sensor FailureDocumento2 páginasVEH MB ML320 Fuel Sensor Failured9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-TRANS-722.6-limp Home Mode ETC Code P0748-763 PDFDocumento1 páginaVEH-MB-TRANS-722.6-limp Home Mode ETC Code P0748-763 PDFd9dAinda não há avaliações
- R&I Pilot Bushing in Electrohydraulic Controller UnitDocumento2 páginasR&I Pilot Bushing in Electrohydraulic Controller Unityopmail555Ainda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-TRANS-722.6-limp Home Mode ETC Code P0730 PDFDocumento1 páginaVEH-MB-TRANS-722.6-limp Home Mode ETC Code P0730 PDFd9dAinda não há avaliações
- VEH-MB-TRANS-722.6-Limp Home Mode ETC Code P0700 - 2Documento1 páginaVEH-MB-TRANS-722.6-Limp Home Mode ETC Code P0700 - 2d9dAinda não há avaliações
- Audi PDFDocumento2 páginasAudi PDFManuel CostaAinda não há avaliações
- MB Atego 1529 4x2 Australien enDocumento2 páginasMB Atego 1529 4x2 Australien enPrem KumarAinda não há avaliações
- 7FB10Documento38 páginas7FB10Ionut GrozaAinda não há avaliações
- Triber AccessoriesDocumento3 páginasTriber AccessoriesPiyush Kumar SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Replacement Parts Import Catalogue 2020 - 2022Documento85 páginasReplacement Parts Import Catalogue 2020 - 2022nomaan0411100% (1)
- Volvo Обьемы жидкостейDocumento2 páginasVolvo Обьемы жидкостейРуденко РоманAinda não há avaliações
- Continental Timing Belt InstallationDocumento4 páginasContinental Timing Belt InstallationStuart WickensAinda não há avaliações
- TIA Katipunan Ch4Documento2 páginasTIA Katipunan Ch4Rannie Waji AyaayAinda não há avaliações
- Memo Gidley, Memo Gidley. Karting - Everything You Need To Know PDFDocumento136 páginasMemo Gidley, Memo Gidley. Karting - Everything You Need To Know PDFTraveller100% (1)
- JLG 1044c 54 Telehandler Parts ManualDocumento20 páginasJLG 1044c 54 Telehandler Parts Manualcathy100% (54)
- SWOT Analysis of Honda CityDocumento2 páginasSWOT Analysis of Honda CityRahul GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- 315 TransmissionDocumento2 páginas315 Transmissionhernan dueñasAinda não há avaliações
- Ride Height General Procedures PDFDocumento2 páginasRide Height General Procedures PDFMichael HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Catalogo Grua Link Belt 8065Documento2 páginasCatalogo Grua Link Belt 8065Raul LalindeAinda não há avaliações
- Manitou MT 932 EASY (EN)Documento2 páginasManitou MT 932 EASY (EN)ManitouAinda não há avaliações
- Chery LP Setiembre 2023Documento1 páginaChery LP Setiembre 2023johaira.cmAinda não há avaliações
- Calculation of Seasonal Correction FactorDocumento3 páginasCalculation of Seasonal Correction FactorartiAinda não há avaliações
- Adam Jee Revo ProjectDocumento17 páginasAdam Jee Revo ProjectAbdul Jalil TahirAinda não há avaliações
- Insignia PDFDocumento60 páginasInsignia PDFdavidninrio0% (1)
- Complete Vehicles Ec Certificate of ConformityDocumento2 páginasComplete Vehicles Ec Certificate of ConformityJery 3250% (2)
- Sonic HoodDocumento3 páginasSonic HoodJeff95TAAinda não há avaliações
- A Study To Measure Satisfaction Level of Swift Car OwnersDocumento56 páginasA Study To Measure Satisfaction Level of Swift Car OwnersVeeresh NaikarAinda não há avaliações
- Producer Series Build Model ModelyearDocumento45 páginasProducer Series Build Model ModelyearJimmy BobbyAinda não há avaliações
- SKF Differential CatalogDocumento238 páginasSKF Differential CatalogKHAinda não há avaliações
- Owner's Manual: Öhlins Shock Absorber TPX/TTX44 AutomotiveDocumento13 páginasOwner's Manual: Öhlins Shock Absorber TPX/TTX44 AutomotiveMauricio Xavier OjedaAinda não há avaliações
- Sport Stroller Instructions Philandteds 20150820 8209-01Documento44 páginasSport Stroller Instructions Philandteds 20150820 8209-01Herczku AnnamáriaAinda não há avaliações
- Brochure Scania Construction PDFDocumento21 páginasBrochure Scania Construction PDFMioMaulenovo100% (1)
- Product Recommendation Renault Kerax Kerax 400 (1999-2001)Documento6 páginasProduct Recommendation Renault Kerax Kerax 400 (1999-2001)tonnyAinda não há avaliações
- Citroen C4 Picasso Datasheet PDFDocumento2 páginasCitroen C4 Picasso Datasheet PDFisidroAinda não há avaliações
- Adam Rocks-Price GuideDocumento29 páginasAdam Rocks-Price GuidekarambaAinda não há avaliações