Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Importance of The Constituents in Toothpaste (Dentifrice) .: 1-Detergent (1-2%)
Enviado por
2oclockTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Importance of The Constituents in Toothpaste (Dentifrice) .: 1-Detergent (1-2%)
Enviado por
2oclockDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SITI FATIMAH BINTI MOHD KAMAL
3
RD
YEAR MALAYSIAN DENTISTRY
(DENTAL PUBLIC HEALTH)
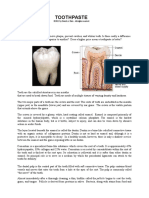
IMPORTANCE OF THE CONSTITUENTS IN TOOTHPASTE (DENTIFRICE).
1-Detergent (1-2%)
Detergents create foam and loosen plaque and other debris from the tooth surface. Principal
examples are sodium lauryl sulphate and sodium N-lauroyl sarcosinate.
2-Cleaning & Polishing materials (abrasive) (50%)
Most brands contain at least 50 percent abrasives. It is one of the most important ingredient to
remove food particles remaining on the teeth. These insoluble particles help remove plaque
from the teeth. The removal of plaque and calculus helps minimize cavities and periodontal
disease. High levels of abrasives may not be a good thing, since they can harm your teeth
sensitive by weakening enamel. It's preferable to use toothpaste with a gentle abrasive. The
right concentration of baking soda works best to clean stains of teeth.
3-Binder (1%)
It serves to prevent separation of ingredients in toothpaste. Materials used include sodium
alginate. Binders are hydrophilic colloids which disperse or swell in the presence of water and
are used to stabilise toothpaste formulations by preventing the separation of the solid and
liquid phases. Examples of binding agents used in toothpaste include the natural gums (arabic,
karaya and tragacanth), the seaweed colloids (alginates, Irish moss extract and gum
carrageenan) and synthetic celluloses (carboxymethyl cellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose), with
the latter now being used increasingly for economic reasons.
4-Humectants (10-30%)
It give toothpaste its texture as well as retain moisture of the paste. Humectants are used in
dentifrices to prevent loss of water and subsequent hardening of the paste when it is exposed
to air. The most commonly used humectants are glycerol and sorbitol.
5-Flavoring
It serves to provide aroma and flavor in paste and avoid feeling of nausea. In addition, to
increase the freshness of toothpaste. Peppermint oil, spearmint, cinnamon, wintergreen and
menthol are among the many different flavourings used.
6-Water (20-42%)
To help keep it from drying out.
7- Fluoride and other therapeutic agents
The majority of toothpastes combine the caries protection of fluoride with other therapeutic
agents to control plaque, tartar and gum disease. The inclusion of antibacterial agents can help
individuals improve their plaque control. Many toothpastes include triclosan, which has been
shown to offer a clinically useful improvement in gum health. Other pastes specifically target
"tartar" (hardened plaque) and use phyrosphosphate to inhibit the mineralisation of dental
plaque and hence the buildup of tartar (calculus).
8- Preservatives, Sweetener and Coloring Agent.
Preservatives (0.05-0.5%)
to help prevent microorganisms from growing on the organic binders and humectants,
certain preservatives are added. These may include sodium benzoate, methyl paraben,
and ethyl paraben. Between the three common preservatives, sodium benzoate is the
safest. Some natural toothpaste use citric acid. Too much citric acid may cause side
effects such as stomach cramps, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting.
Sweetener
to improve the taste of toothpaste, especially those containing the horrible taste of
sodium lauryl sulfate, such sweeteners as saccharin, stevia or xylitol are added. The best
form is xylitol, since it does have many benefits for a healthy mouth, as stated earlier.
Coloring agents
artificial dyes and coloring agents are not uncommon in most commercial toothpaste.
Titanium dioxide may also be used to make toothpaste white. Its best to avoid
toothpaste with artificial dyes and colorings.
9- Therapeutic dentifrices have a drug of chemical agent added for a specific
preventive or treatment.
Você também pode gostar
- Toothpaste - WikipediaDocumento46 páginasToothpaste - WikipediaKarthi NatarajaAinda não há avaliações
- ToothpasteDocumento15 páginasToothpastesuraj hanvateAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Working ?Documento19 páginasWhat Is Working ?shrustipatilAinda não há avaliações
- Shortcut Pharmacy: DentrificesDocumento10 páginasShortcut Pharmacy: DentrificesNidhi SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Trends Html#Ixzz1Czrko1HyDocumento8 páginasTrends Html#Ixzz1Czrko1HyRajen ManjhAinda não há avaliações
- Thao Tran, Sean Gillespie, Von KaukeanoDocumento14 páginasThao Tran, Sean Gillespie, Von KaukeanoTri NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- DentifriceDocumento26 páginasDentifricePharmacistBDAinda não há avaliações
- Toothpastes-WPS OfficeDocumento4 páginasToothpastes-WPS Office8t8w2nqy9dAinda não há avaliações
- TheoryDocumento4 páginasTheoryNIRANJANAAinda não há avaliações
- Project of ToothpasteDocumento5 páginasProject of ToothpastesridharsudharsanAinda não há avaliações
- Aluminum Hydroxide Calcium Carbonate Calcium Hydrogen Phosphates Silicas Zeolites HydroxyapatiteDocumento2 páginasAluminum Hydroxide Calcium Carbonate Calcium Hydrogen Phosphates Silicas Zeolites HydroxyapatiteImtiazUddinAinda não há avaliações
- History of ToothpasteDocumento3 páginasHistory of ToothpasteE. SubinAinda não há avaliações
- Toothpaste: Stannous Fluoride Sodium Fluoride Sodium Monofluorophosphate Hydrated SilicaDocumento3 páginasToothpaste: Stannous Fluoride Sodium Fluoride Sodium Monofluorophosphate Hydrated SilicaAmit SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- ToothpasteDocumento2 páginasToothpastebabeAinda não há avaliações
- IngredientsDocumento3 páginasIngredientsSaif ShamsAinda não há avaliações
- Agents Used For Oral HygieneDocumento8 páginasAgents Used For Oral HygieneHamid IftikharAinda não há avaliações
- AdamDocumento6 páginasAdammaantom3Ainda não há avaliações
- Dental ProductsDocumento62 páginasDental Productsapi-38318790% (1)
- Project On ToothpasteDocumento8 páginasProject On ToothpasteRushabh DoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Hygiene ProductDocumento43 páginasOral Hygiene Productfafyfskhan251kmfAinda não há avaliações
- Dental ProductsDocumento22 páginasDental ProductsAbdur Raquib100% (1)
- Piyush ProjectDocumento20 páginasPiyush ProjectVishwjeet Kumar ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Dental ProductsDocumento41 páginasDental Productsbrotycoccus.brauniiAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Ions in The ToothpasteDocumento10 páginasAnalysis of Ions in The ToothpasteKalika SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Hygiene ProductsDocumento20 páginasOral Hygiene ProductsAnoosha FarooquiAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Hygiene ProductsDocumento8 páginasOral Hygiene ProductsMr.ShazAinda não há avaliações
- MouthwashDocumento13 páginasMouthwashheaven.protikAinda não há avaliações
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento14 páginasNew Microsoft Word DocumentPriybrat SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Nilesh Toothpaste SynopsisDocumento6 páginasNilesh Toothpaste SynopsiskarulalpatidarAinda não há avaliações
- Page 10 - ToothpasteDocumento2 páginasPage 10 - ToothpasteHitesh AnandAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry ProjectDocumento12 páginasChemistry ProjectUtkarsh Tak75% (4)
- It Is Vital For Every Human Being To Take Good Care of Their TeethDocumento36 páginasIt Is Vital For Every Human Being To Take Good Care of Their TeethMusadaq ManzoorAinda não há avaliações
- Page 12-16 ComponentsDocumento6 páginasPage 12-16 ComponentsHitesh AnandAinda não há avaliações
- Dental ProductsDocumento17 páginasDental Productsade safitri100% (1)
- ToothpasteDocumento7 páginasToothpasteheaven.protikAinda não há avaliações
- Oral HygieneDocumento13 páginasOral HygieneBilal AqeelAinda não há avaliações
- Top 10 Best Toothpaste Brands in The World - EditedDocumento4 páginasTop 10 Best Toothpaste Brands in The World - EditedUzair SoomroAinda não há avaliações
- Dental PreparationsDocumento17 páginasDental PreparationsAG STXLEZAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Unit 4 Dental Products Pharmaceutical Chemistry PDF Notes-NoteskartsDocumento6 páginasChapter 3 Unit 4 Dental Products Pharmaceutical Chemistry PDF Notes-Noteskartsabhay sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Investigatory ReportDocumento16 páginasChemistry Investigatory ReportYash SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Hygiene 2 LESSON INGDocumento25 páginasOral Hygiene 2 LESSON INGAbdullah Seckin ErtugrulAinda não há avaliações
- Contact Allergy To (Ingredients Of) Toothpastes: Anton de Groot, MD, PHDDocumento20 páginasContact Allergy To (Ingredients Of) Toothpastes: Anton de Groot, MD, PHDervinstyaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Investigatory Project (Analysis of Toothpastes)Documento24 páginasChemistry Investigatory Project (Analysis of Toothpastes)Yash Sisodia33% (3)
- Composition of Ion in ToothpasteDocumento30 páginasComposition of Ion in Toothpastedibashkumar7896Ainda não há avaliações
- Product: Toothpaste: Brand: ColgateDocumento15 páginasProduct: Toothpaste: Brand: ColgateYash ParekhAinda não há avaliações
- Healthy Teeth Are Important To Your Health Power PointDocumento3 páginasHealthy Teeth Are Important To Your Health Power PointNevena DimitrijevicAinda não há avaliações
- Amity Institute of Pharmacy: B. Pharm., Semester One Pharmacy Dr. Pawan Kumar PorwalDocumento25 páginasAmity Institute of Pharmacy: B. Pharm., Semester One Pharmacy Dr. Pawan Kumar Porwalpawankumar guptaAinda não há avaliações
- As Additives In: Making ToothpasteDocumento26 páginasAs Additives In: Making ToothpasteJocelyn NagalizaAinda não há avaliações
- Mouthwash Infographic (Information) What Is Mouthwash?: Types of Mouthwash Cosmetics MouthwashDocumento4 páginasMouthwash Infographic (Information) What Is Mouthwash?: Types of Mouthwash Cosmetics MouthwashEdrick G. EsparraguerraAinda não há avaliações
- Natural Teeth WhiteningDocumento18 páginasNatural Teeth WhiteningMusaeb Shaikh100% (1)
- Dentalpharmacology1 130726101143 Phpapp02Documento44 páginasDentalpharmacology1 130726101143 Phpapp02Malatesh Sudharshan100% (1)
- Aim Is To Find The Determination of Contents of Tooth PowderDocumento4 páginasAim Is To Find The Determination of Contents of Tooth PowderHargur Bedi71% (7)
- Determination of Contents of Tooth Powder: Investigatory Project in ChemistryDocumento16 páginasDetermination of Contents of Tooth Powder: Investigatory Project in ChemistrySHIVEN KAMALAinda não há avaliações
- Dentifrice Fricare Your TeethDocumento4 páginasDentifrice Fricare Your Teethprabhanshusrivastava2Ainda não há avaliações
- CHEMISTRYDocumento20 páginasCHEMISTRYDev SonarAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Hygiene Maintenance - Dr. NadeemDocumento41 páginasOral Hygiene Maintenance - Dr. NadeemSuresh HaldipurAinda não há avaliações
- Baking Soda For TeethDocumento9 páginasBaking Soda For Teethkata OmoiAinda não há avaliações
- Dent Rific EsDocumento28 páginasDent Rific Essamm123456Ainda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Toothpaste Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12Documento20 páginasAnalysis of Toothpaste Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12Prakhar Joshi100% (1)
- Tooth Regrowth: Natural Methods to Remineralize, Restore and Repair Your Teeth and Gums at HomeNo EverandTooth Regrowth: Natural Methods to Remineralize, Restore and Repair Your Teeth and Gums at HomeNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- 257 2110 1 PBDocumento5 páginas257 2110 1 PB2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Dental HistoryDocumento6 páginasMedical Dental History2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- 332 340Documento9 páginas332 3402oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Dental Terms 2Documento34 páginasIntroduction To Dental Terms 22oclockAinda não há avaliações
- 7 - The Nature of The CementoDocumento1 página7 - The Nature of The Cemento2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Original Research Innovative MegafillersDocumento4 páginasOriginal Research Innovative Megafillers2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- List of Egypt Public Holidays 2013Documento2 páginasList of Egypt Public Holidays 20132oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Updating Medical HistoryDocumento2 páginasUpdating Medical History2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Nadeau UrbanIndianHealthConferenceDocumento36 páginasNadeau UrbanIndianHealthConference2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Dental Alloys Used in ProsthodonticsDocumento11 páginasDental Alloys Used in ProsthodonticsShufeiAinda não há avaliações
- RM ClinicalAuditTool Medical HistoryDocumento1 páginaRM ClinicalAuditTool Medical History2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- 18711Documento8 páginas187112oclockAinda não há avaliações
- CH 50Documento19 páginasCH 502oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Considerations Regarding The Methods Used For The Assessment of Castability of Dental Casting Alloys Marius Bibu Carmen Simion Valentin Petrescu Toderita NemesDocumento6 páginasConsiderations Regarding The Methods Used For The Assessment of Castability of Dental Casting Alloys Marius Bibu Carmen Simion Valentin Petrescu Toderita Nemes2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Medical History: Pediatric DentistryDocumento2 páginasMedical History: Pediatric Dentistry2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Dentifrices - An Update: Robin Davies, Crispian Scully, Antony J. PrestonDocumento7 páginasDentifrices - An Update: Robin Davies, Crispian Scully, Antony J. Preston2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- File 57711Documento13 páginasFile 577112oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Toothpaste IngredientsDocumento10 páginasToothpaste Ingredients2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- TocDocumento16 páginasToc2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Gingival Retraction Methods in Fixed Prosthodontics A Systematic ReviewDocumento7 páginasGingival Retraction Methods in Fixed Prosthodontics A Systematic ReviewNofal Mundathodu100% (2)
- DentistryToday August 2010Documento1 páginaDentistryToday August 20102oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Medical History FormDocumento2 páginasMedical History Form2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Local and Systemic Influences in Peridontal DiseaseDocumento10 páginasLocal and Systemic Influences in Peridontal Disease2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Ijld Lta SP Sept 11 ( (New) )Documento8 páginasIjld Lta SP Sept 11 ( (New) )2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- A To Z Orthodontics MCQDocumento112 páginasA To Z Orthodontics MCQUjjwal Pyakurel100% (4)
- Medical History FormDocumento2 páginasMedical History Form2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter37 Periodontal Dis94Documento13 páginasChapter37 Periodontal Dis942oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Medical History FormDocumento1 páginaMedical History Form2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Pontic PreparationDocumento2 páginasPontic Preparation2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- The Dentin-Enamel Junction-A Natural, Multilevel InterfaceDocumento8 páginasThe Dentin-Enamel Junction-A Natural, Multilevel Interface2oclockAinda não há avaliações
- Muscle InjuryDocumento33 páginasMuscle InjuryYuNa YoshinoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Refraction ManagementDocumento8 páginasRefraction ManagementRaissaAinda não há avaliações
- For Wastewater Systems: BioaugmentationDocumento3 páginasFor Wastewater Systems: BioaugmentationPalak AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?: Joint HypermobilityDocumento4 páginasWhat Is Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?: Joint HypermobilityisisjadidAinda não há avaliações
- Online Pharmacy in Indonesia - 2019Documento33 páginasOnline Pharmacy in Indonesia - 2019Yayuk Abay TambunanAinda não há avaliações
- Management of Perioperative ArrhythmiasDocumento51 páginasManagement of Perioperative ArrhythmiasAbhishek LonikarAinda não há avaliações
- Psychoanalytic TherapyDocumento28 páginasPsychoanalytic Therapyapi-3704513100% (3)
- Ciroza Si Sindromul de Activitate MezenchimalaDocumento29 páginasCiroza Si Sindromul de Activitate MezenchimalaClaudiu ValentinAinda não há avaliações
- Janeth Cardiovascular ExamDocumento10 páginasJaneth Cardiovascular ExammatthewandmaverickjeAinda não há avaliações
- Alzheimer's Disease: Roehampton UniversityDocumento10 páginasAlzheimer's Disease: Roehampton UniversityOnly LonlyAinda não há avaliações
- Medical NegligenceDocumento10 páginasMedical Negligence18532 AYUSH SUNDARKA100% (1)
- DLL Tle-He 6 q2 w6Documento4 páginasDLL Tle-He 6 q2 w6Meera Joy Deboma Blanco91% (11)
- Quality Control Lecture 1Documento18 páginasQuality Control Lecture 1AhmedEidAinda não há avaliações
- Growth Plate InjuriesDocumento10 páginasGrowth Plate InjuriesraissanindyaAinda não há avaliações
- Presbyopia: Care of The Patient WithDocumento34 páginasPresbyopia: Care of The Patient Withbebek sakitAinda não há avaliações
- Urin The Miracle DrugDocumento2 páginasUrin The Miracle DrugDina Malisa Nugraha, MDAinda não há avaliações
- PerforationsDocumento5 páginasPerforationsMariusNOAinda não há avaliações
- CV UpdateDocumento3 páginasCV Updateapi-350983586Ainda não há avaliações
- Person Centered TherapyDocumento16 páginasPerson Centered TherapyAldrinBalitaAinda não há avaliações
- MetaanalysisDocumento12 páginasMetaanalysisAhmed BadrAinda não há avaliações
- Reduced Fare Program For People With DisabilitiesDocumento4 páginasReduced Fare Program For People With DisabilitiesN SAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To Psychology UnitsDocumento38 páginasIntro To Psychology Unitsapi-325580763Ainda não há avaliações
- Ssri Presentation - 674 - Final2Documento52 páginasSsri Presentation - 674 - Final2api-289842236100% (1)
- National Mediclaim Policy PDFDocumento19 páginasNational Mediclaim Policy PDFTanmoy Pal ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Culture Bound SyndromesDocumento14 páginasCulture Bound SyndromesLinda MathewAinda não há avaliações
- Over Dentures Jan 2012Documento40 páginasOver Dentures Jan 2012Mohsin HabibAinda não há avaliações
- IVTDocumento6 páginasIVTpatzieAinda não há avaliações
- Updated 10-16-14 Quick Reference Guide Digital Npuap Epuap Pppia 16oct2014Documento75 páginasUpdated 10-16-14 Quick Reference Guide Digital Npuap Epuap Pppia 16oct2014Anonymous kZQet6QA100% (1)
- Cordis Case Study PDFDocumento29 páginasCordis Case Study PDFsingh242Ainda não há avaliações
- MDRTB Case StudyDocumento35 páginasMDRTB Case StudyFejlean Angelica AntineoAinda não há avaliações