Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Project On HR Outsourcing On Various Functions in It Industrya
Enviado por
nikhincc0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
256 visualizações97 páginasproject on hr outsourcing on various functions in it industrya
Título original
project on hr outsourcing on various functions in it industrya
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoproject on hr outsourcing on various functions in it industrya
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
256 visualizações97 páginasProject On HR Outsourcing On Various Functions in It Industrya
Enviado por
nikhinccproject on hr outsourcing on various functions in it industrya
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 97
A Study on
THE IMPACT OF HR OUTSOURCING ON VARIOUS HR FUNCTIONS
WITH REFERENCE TO IT INDUSTRY
Submitted In Patia! Fu!"i!!ment #" t$e A%ademi% Re&uiement'
F# t$e A(ad #" t$e De)ee
O"
MASTER OF *USINESS ADMINISTRATION
*ANGA+ORE UNIVERSITY
Submitted *,
NIRVAN
REG NO- ./S0CMA.11
Unde t$e Guidan%e #"
D2 0AVITHA DESAI
ACHARYA INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT 3 SCIENCES
4
't2
C#''5 4
't2
Sta)e5 Peen,a Indu'tia! Aea5
*an)a!#e678..79
:../ ; :.44
1
DEC+ARATION
I, NIRVAN, hereby declare that this dissertation titled, THE IMPACT OF HR
OUTSOURCING ON VARIOUS HR FUNCTIONS WITH REFERENCE TO
IT INDUSTRY, is based on original project study conducted by me under the
guidance of D2 0AVITHA DESAI.
This has not been submitted earlier for the award of any other Degree / Diploma by
Bangalore University or any other University.
P!a%e- *an)a!#e <NIRVAN=
Date- 1
t$
Ma, :.44 REG NO- ./S0CMA.11
2
ACHARYA INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT 3 SCIENCES
4't2 C#''5 4't2 Sta)e5 Peen,a Indu'tia! Aea5
*an)a!#e678..79
CERTIFICATE FROM THE GUIDE
ertified that this dissertation titled THE IMPACT OF HR OUTSOURCING
ON VARIOUS HR FUNCTIONS WITH REFERENCE TO IT INDUSTRY
is based on an original project study conducted by NIRVAN, of !
th
"emester #B$
under my guidance.
This dissertation has not formed the basis for the award of any other
Degree/Diploma by Bangalore University or any other University.
P!a%e- *an)a!#e
Date- 1
t$
Ma, :.44 <D2 0AVITHA DESAI=
3
ACHARYA INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT 3 SCIENCES
4't2 C#''5 4't2 Sta)e5 Peen,a Indu'tia! Aea5
*an)a!#e678..79
CERTIFICATE FROM THE CO++EGE
ertified that this dissertation titled %THE IMPACT OF HR OUTSOURCING
ON VARIOUS HR FUNCTIONS WITH REFERENCE TO IT INDUSTRY&
is based on the study conducted by NIRVAN of !th "emester #B$ under the
guidance of D2 0AVITHA DESAI2
This dissertation is based on the original project study undergone and has not
formed the basis for the award of any other degree/diploma by Bangalore
University or any other University.
D2 0a>it$a De'ai D20e#n G2 Redd,
PROFESSOR M*A5 RESIGTRAR AIMS PRINCIPA+5 AIMS
P!a%e- *an)a!#e P!a%e- *an)a!#e
Date- 1
t$
Ma, :.44 Date- 1
t$
Ma, :.44
4
CERTIFICATE OF APPROVA+
This dissertation report of NIRVAN titled THE IMPACT OF HR
OUTSOURCING ON VARIOUS HR FUNCTIONS WITH REFERENCE TO
IT INDUSTRY is approved in 'uality and form and has been found to be fit for
the (artial )ulfilment of the *e'uirements of *an)a!#e Uni>e'it, for the $ward
of Degree of Ma'te #" *u'ine'' Admini'tati#n.
INTERNA+ GUIDE E?TERNA+ E?AMINERS
Name- D2 0AVITHA DESAI 42Name-
Si)natue- Si)natue-
Date- 1
t$
Ma, :.44 Date-
:2 Name-
Si)natue-
Date-
5
AC0NOW+EDGEMENT
)irst of all, I bow my head with full devotion, dedication, faith + gratitude to the omnipotent,
omnipresent, omniscient and $lmighty ,od for showering his unconditional blessings upon me
as a result of which I am able to complete this project well in time.
I would li-e to convey my deep and profound sense of gratitude, than-fulness and obligation to
my learned and self.esteemed guide D20a>it$a De'ai5 P#"2 M*A De@t2 and Re)i'ta5
AIMS5 for her untiring help, constant encouragement and learned suggestions. /ocabulary fails
to e0press my feelings, emotions and thoughts towards her greatness + -indness which she
e0pressed towards me. Instead of her e0tremely busy and e0haustive schedule, she always spared
her valuable time and guided me accordingly. "he stood li-e a beacon1s light to sail in the
uncharted sea of my dissertation project.
I would li-e to e0press my sincere than-s + gratefulness to all my respondents who helped me
with their learned, e0perienced and valuable feedbac- by answering the 'uestionnaire of my
research topic which wor-ed as the foundation stone to build this project.
I am e0tremely than-ful to 2onourable P#"20e#n G2 Redd,, Pin%i@a! 3 CEO AIMS, who
has provided me with all the re'uired facilities to carry out the present research wor- according
to the norms of Bangalore University and by nurturing my s-ills to e0ecute the re'uirements.
I e0press my sincere regards, respect and than-fulness to P#"2 Ran)anat$an 0i'$na Ra#5
P#)am Die%t#5 M*A De@atment, who always supported me with his fatherly love +
affection. I pay my sincere regards and than-fulness to all the respected teachers of #B$ Dept.
+ all the faculty members of $I#" particularly to P#"2Na)aaAan 3 D2*$at$a 02A for their
valuable suggestions and blessings. I e0press my special than-s to our COO5 M2Pi,anandan
Redd, for his effective support, sympathy, love and affection throughout the course of studies at
6
$I#". I would also li-e to than- our 3ibrarian #a1am + all the library staff for their co.
operation while collecting the relevant literature on the subject.
I bow my head in the lotus feet of my respected "at$e P#"2 <D2= D$am RaA Sin)$ 4,old
#edallist5, 60.2.7.D, (.,. Dept. of 8ayachi-itsa, 3uc-now University, 3uc-now and my
respected + loving m#t$e D2San)eeta Sin)$ 4,old #edallist5 60.$ssociate (rofessor, (.,.
Dept. of 8ayachi-itsa, 3uc-now University, 3uc-now who always stood with me in my difficult
times and always taught me the lesson from a famous 'uotation, %Ai'e 5 A(aBe and 't#@ n#t
ti!! t$e )#a! i' a%$ie>edC& by S(ami Vi>eBananda who had been a great saint and visionary.
3astly I bow my head down to earth with full faith, honour + devotion in the lotus feet of my
honourable ,urudev H2H S(ami Sub#d$ananda Saa'(ati for his continuous spiritual
enlightment and divine blessings.
7
TA*+E OF CONTENTS
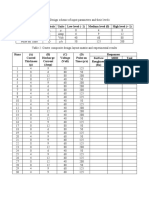
S2 N#2 TIT+E Pa)e N#2
4 INTRODUCTION 4 ; 41
9.9 I:T*7DUTI7: T7 T26 *6"6$*2 T7(I 9 ; <
9.< T26 T267*6TI$3 $"(6T" 7) T26 *6"6$*2 T7(I
= ; >
9.= T26 "UB?6T B$8,*7U:D 7) T26 *6"6$*2 T7(I > ; 99
9.! 7UT"7U*I:, 9<
9.! B6 "(6I)I $B7UT 2* 7UT"7U*I:, 9< ; 9!
: RESEARCH METHODO+OGY 47 ; :.
<.9 I:T*7DUTI7: 9@
<.< "T$T6#6:T 7) T26 (*7B36# 9@
<.= *6/I6A 7) 3IT6*$TU*6 9@ ; 9B
<.! 7B?6TI/6" 7) T26 "TUDC 9D
<.@ "7(6 7) T26 "TUDC 9D
<.> *6"6$*2 D6"I,: 9D
<.B "$#(3I:, (3$: 9E
<.D T773" )7* D$T$ 7336TI7: 9E
<.E T773" )7* D$T$ $:$3C"I" 9E
<.9F 3I#IT$TI7:" 7) T26 "TUDC <F
<.99 3$C7UT 7) 2$(T6*" <F
D INDUSTRY PROFI+E :4 ; D.
=.9 2* 7UT"7U*I:, I:DU"T*C <9 ; <=
=.< T26 B(7 I:DU"T*C <! ; <>
=.= I:DU"T*C (*7)I36 7) "7)TA$*6 + IT I:DU"T*C <> ; =F
1 DATA ANA+YSIS 3 INTERPRETATION D4 ; 79
!.9 Department and Designation (rofile of the respondents =9 ; =<
!.< Cears of Aor- 60perience of the respondents == ; =!
!.= $ppro0imate 2* strength in the organiGation =@
!.! *esponse of the organiGations towards 2* outsourcing =>
8
!.@ $ppro0imate no. of people outsourced by various organiGations =B ; =D
!.> #ajor 2* functions outsourced by various organiGations =D ; !9
!.B Important reasons for outsourcing 2* functions by various organiGations !9 ;!=
!.D Important factors for choosing a third party supplier for 2* outsourcing !! ; !@
!.E 7pinions on different aspects of 2* outsourcing in relation to various 2*
functions.
!> ; !B
!.9F Type of the legal service agreement standard included in 2* 7utsourcing
ontract
!B ; !D
!.99 2* )unctions Ahich $re :ot 7utsourced 7r Being 7utsourced 6ither (artially
or ompletely
!E ; @<
!.9< 7pinion about the impact of 2* 7utsourcing on various 2* attributes @< ; @=
!.9= 7pinion about 7utsourcing 7ptions with *eference To organiGational 2*
(olicies, (ractices + Talent :eeds of IT Industry
@! ; @@
!.9! 7pinion of 2* #anagers on whether 2* 7utsourcing may help to reduce the
*ate of $ttrition in IT 7rganiGations
@>
!.9@
7pinion of 2* #anagers on how well have your 2* outsourced functions
fulfilled their objectives
@B ; @D
7 SUMMARY OF FINDINGS 7/ ; 8:
@.9 )indings about different aspects of 2* outsourcing @E
@.< )indings about important reasons for 2* 7utsourcing >F
@.=
)indings about important factors responsible towards choosing a third party
supplier for 2* 7utsourcing. >F
@.!
)indings about major 2* functions being outsourced in the Indian industry
either completely or partially >9
@.@
)indings about the impact of 2* outsourcing on various 2* functions + on the
effectiveness of the 2* department. >9
@.> )indings about the co.relation between 2* 7utsourcing + IT industry ><
@.B )indings about the effectiveness of 2* function that is being outsourced. ><
8 SUGGESTIONS AND CONC+USIONS 8D ; 88
*I*+IOGRAPHY
/
9
ANNE?URE 4. ; 4.
10
+IST OF TA*+ES
TA*+E
NO2
TIT+E OF TA*+ES
PAGE
NO2
!.9 Department and Designation (rofile of the respondents =9
!.< Cears of Aor- 60perience of the respondents ==
!.= $ppro0imate 2* strength in the organiGation =@
!.! *esponse of the organiGations towards 2* outsourcing =>
!.@ $ppro0imate no. of people outsourced by various organiGations =B
!.> #ajor 2* functions outsourced by various organiGations =D
!.B Important reasons for outsourcing 2* functions by various organiGations !9
!.D Important factors for choosing a third party supplier for 2* outsourcing !!
!.E 7pinions on different aspects of 2* outsourcing in relation to various 2*
functions.
!>
!.9F Type of the legal service agreement standard included in 2* 7utsourcing
ontract
!B
!.99 2* )unctions Ahich $re :ot 7utsourced 7r Being 7utsourced 6ither (artially
or ompletely
!E
!.9< 7pinion about the impact of 2* 7utsourcing on various 2* attributes @<
!.9= 7pinion about 7utsourcing 7ptions with *eference To organiGational 2*
(olicies, (ractices + Talent :eeds of IT Industry
@!
!.9! 7pinion of 2* #anagers on whether 2* 7utsourcing may help to reduce the
*ate of $ttrition in IT 7rganiGations
@@
!.9@ 7pinion of 2* #anagers on how well have your 2* outsourced functions
fulfilled their objectives
@B
11
+IST OF GRAPHS
GRAPH
NO2
TIT+E OF GRAPH
PAGE
NO2
!.9 Department and Designation (rofile of the respondents =<
!.< Cears of Aor- 60perience of the respondents ==
!.= $ppro0imate 2* strength in the organiGation =@
!.! *esponse of the organiGations towards 2* outsourcing =>
!.@ $ppro0imate no. of people outsourced by various organiGations =B
!.> #ajor 2* functions outsourced by various organiGations =E
!.B Important reasons for outsourcing 2* functions by various organiGations !<
!.D Important factors for choosing a third party supplier for 2* outsourcing !!
!.E 7pinions on different aspects of 2* outsourcing in relation to various 2*
functions.
!>
!.9F Type of the legal service agreement standard included in 2* 7utsourcing
ontract
!D
!.99 2* )unctions Ahich $re :ot 7utsourced 7r Being 7utsourced 6ither (artially
or ompletely
@F
!.9< 7pinion about the impact of 2* 7utsourcing on various 2* attributes @<
!.9= 7pinion about 7utsourcing 7ptions with *eference To organiGational 2*
(olicies, (ractices + Talent :eeds of IT Industry
@!
!.9! 7pinion of 2* #anagers on whether 2* 7utsourcing may help to reduce the
*ate of $ttrition in IT 7rganiGations
@>
!.9@ 7pinion of 2* #anagers on how well have your 2* outsourced functions
fulfilled their objectives
@B
12
E?ECUTIVE SUMMARY
This Dissertation titled THE IMPACT OF HR OUTSOURCING ON VARIOUS HR
FUNCTIONS WITH REFERENCE TO IT INDUSTRY is based on an original study
conducted by me 4Ni>an5 of 1t$
semester #B$, student of $charya Institute of #anagement +
"ciences under the guidance of D20a>it$a De'ai5 A%$a,a In'titute #" Mana)ement 3
S%ien%e' *an)a!#e5 De@t2 #" M*A.
2* outsourcing is an accepted managerial tool for re.structuring and re.focusing the way an
organiGation does business. It is proved to be the catalyst for organiGations to drive
standardiGation of 2* policies and practices. 2* outsourcing is a boon for enhancing various
organiGational capacities and for overall improvement of different 2* )unctions of different
organiGations according to their various needs + re'uirements. It is an e0cellent tool for
completing the different tas-s, objectives and needs for which it has been assigned.
2* 7utsourcing + IT industries are inter.related and both are benefitted by mutual co.ordination
+ co.operation. The problem of %$ttrition& is very well managed with the help of 2*
outsourcing in IT industry. #id.mar-et, or medium.siGed, organiGations find 2*7 very
attractive because of the economic, strategic, operational, technology and ris- management
benefits.
2*7 is a comprehensive solution that impacts process, technology and people. Therefore, 2*7
re'uires more thoughtful approaches to managing change, as well as an e0perienced partner.
:avigating through the uncertainty leaves most 2* leaders reaching out to providers for help
because, in their words, Hwe donIt -now what we donIt -now.H 60perienced providers are well.
positioned to share their proven e0pertise and the best practices that will ensure success.
2*7 has the ability to impact the entire organiGation . far beyond the 2* department . with a
reach that is often underestimated. )rom -ey sta-eholders, such as an e0ecutive who can benefit
from better information about the wor-force, to the hourly wor-er who will interact with 2* in a
whole new way, 2*Is management of the 2*7 transition process will determine how each of its
constituencies responds to a new world of wor-.
#a-ing the decision to outsource human resource processes is a major step for many
organiGations. 7nce a company has decided to outsource one or more human resource processes
and has selected a vendor, the ne0t major tas- is to implement an effective outsourcing
arrangement. Thus my study helped me to get a clear picture of 2* 7utsourcing in the Indian
onte0t along with its future and feasibility.
13
CHAPTER-1
Introduction
14
C$a@te64
INTRODUCTION
424 INTRODUCTION TO THE RESEARCH TOPIC
42424 O>e>ie( #" HR Out'#u%in)
2* outsourcing is a process in which a company uses the services of a third party to ta-e care of
its 2* functions. $ company may outsource a few or all of its 2* related activities to a single or
combination of service provides located in offshore destinations li-e India, hina, (hilippines,
etc. In this sense the 2* outsourcing service providing firms or 2* outsourcing company can be
divided into four categories depending on the services they offer as, (67s 4professional
employer organiGation5, B(7s 4business process organiGation5, $"(s 4application service
providers5, or e.services. In these categories the (67s are the ones that assume full responsibility
of a companyIs 2* functions where as others such a B(7s, $"(s and e services provide web
based 2* solutions li-e database maintenance, 2* data warehousing, maintaining records,
developing and maintaining 2* softwareIs etc.
9
2* outsourcing is a viable choice for small to mid.siGed businesses loo-ing to limit staffing
burdens while maintaining high.'uality human resources functions. 2* is a comple0 and
specialiGed field that performs necessary services for businesses with employees, but the cost of
hiring 'ualified 2* personnel may not always ma-e financial sense. 7utsourcing 2* functions
can provide the services and highly trained professionals that businesses need, often with
significant cost savings over hiring full.time 2* staff.
4242: Fun%ti#n
The primary function of human resources is to manage and provide everyday personnel services.
)rom employee benefits management, payroll and administration, recruiting and hiring, training
and organiGational development, employment law and regulatory compliance, human resources
is a full.time job that re'uires specialiGed training and on.going education. 2* outsourcing firms
provide a full range of vital services to businesses that canIt afford a dedicated human resources
staff or choose not to maintain 2* functions in house.
4242D *ene"it'
1
*ef.9. %"ociety 7) 2* #anagement. 7utsourcing "urvey *eport about 2* 7utsourcing& By
$le0ey 8lementive
15
)or business owners and managers attempting to fulfil 2* roles, performing human resources
functions can ta-e away from running the business. The allure of outsourcing non.core business
functions such as 2* is that it allows the company to concentrate on its main business goals,
leaving other tas-s to the specialists. 2* outsourcing firms are e0perienced in implementing the
most efficient and cost.effective methods and practices and may be able to provide benefits,
payroll and other services at a lower cost than a company would on its own.
42421 Se>i%e +e>e!'
2* outsourcing companies generally offer different service levels..including a la carte, bundled
or all.inclusive services..depending on your particular needs and budget. Cou can contract
human resources outsourcing firms for a specified period of time, use then on an as.needed basis
or contract them for specific one.time or occasional projects. $uthoring employee handboo-s
and creating administrative systems and compensation programs are a few e0amples of project.
based 2* outsourcing services.
42427 C#'t and Va!ue
$side from staffing, there are costs associated with the setup of an 2* department. "oftware,
filing and information.gathering and storage systems, policy and procedure creation, and
implementing the 2* program itself cost time and money. Ahen you factor in all variables of
setting up and maintaining an in.house 2* department, there is no guarantee that the department
will run effectively. Ahen a business outsources 2* services, all the systems, processes and
personnel are in place, providing a value.added element to the e'uation.
42428 P#"e''i#na! Em@!#,e O)aniEati#n'
$nother outsourcing option that involves handing over the 2* duties along with the employees
is called a (67 4professional employer organiGation5. In a (67, the outsourcing firm becomes
the legal employer, handling payroll, benefits, insurance and other employee relationsJ it leases
the employees bac- to the company. 6mployees generally enjoy better benefits because of group
rates, and the scenario allows business owners to concentrate solely on company goals rather
than personnel issues. "ome companies may also enjoy ta0 benefits and will save on wor-erIs
compensation and unemployment insurance because employees are the responsibility of the
(67.
42: THE THEORETICA+ ASPECTS OF THE RESEARCH TOPIC
16
42:24 Human Re'#u%e Out'#u%in)
The increasing focus on 2*Is contribution to the performance of the wider business has led to
more emphasis on cost reduction. 2*7 has grown out of this debate . from re.engineering and
cost reduction on the one hand to a potential transformational capacity on the other. 2*7 is an
evolving industry and can be defined as the purchasing by an organiGation of on.going 2*
services from a third.party provider that it would otherwise normally provide for itself. 2*7 is a
strategic tool aimed primarily at chief e0ecutives. Though organisations may have different
strategies and performance models, all will relate in some way to 2*7. These can involve the
followingK
Ca@abi!it,K for any organiGation where there is a need to either improve or ac'uire 2*
capability
S%a!eK providing for large organisations with @F,FFF or more employees well.delivered
2* administration and services . and to justify the return on investment.
Te%$n#!#),K for most organisations where technology can be ac'uired and leveraged
through shared services or outsourcing
<
.
42:2: HRO @#>ide'
Ahile 2*7 providers may seem to offer little that is different between them, differences do
occur in their siGe, culture, 2*7 methodology and trac- record. 2owever, they offer their
services in three distinct ways.
"ingle.service or transactional solutions for a particular 2* activity
#ultiple 2* services as part of a large.scale deal
Transformational deals which radically change the purpose and role of 2*
Three different types of providers are active in the 2*7 mar-et . pure 2*7 specialists, Business
/ 2* transformation firms and 2* process technology suppliers.
2
*ef.<. %7utsourcing the 2* )unction. (ossibilities + (itfalls& a report by $nthoy 2es-eth on
behalf of "trategic Dimensions $ssociate, orporate *esearch )orum 4*)5
17
42:2D Se!!in) @#int' #" HRO
2*7 providers use these main selling points.
Increased efficiency of 2* with estimated cost savings of up to @FL.
Increased effectiveness of 2* through operational improvements.
Improved strategic focus from 2* on business goals.
The role of 2*7 in transforming the performance of 2* and the business.
Ahile many 2*7 users can point to improvements in the first two points, evidence is lac-ing for
the impacts on strategic focus and business performance. This is a major problem for the 2*7
industry.
42:21 State)i% debate' a#und HRO
These debates are on.going in 2* outsourcing among user . or prospective buyer .
organiGations, providers, 2*7 advisers and academics.
The future purpose and contribution of 2* because of the possibilities of functions being
transformed, or part.outsourced, through 2*7 deals.
The strategic and management comple0ities of 2*7 deals, especially so.called Mmega.
deals1.
Deciding what is Mcore1 and Mnon.core1 in 2* ; the critical competencies to be retained
versus peripheral activities that might be outsourced.
The difficulty that 2* has in assuming more strategic or value adding roles after
implementing 2*7.
The position of offshoring as it affects 2*7 decisions and raises emotive issues such as
job losses and redeployment.
The challenges of trying to manage 2* process delivery on a global scale and across
different cultures.
The 2*7 debate ultimately turns on the perceived 'uality of, and returns from, investments in
the 2* function. Those organiGations under pressure to reduce costs are more li-ely to consider
outsourcing at least part, if not all, of their 2* administration.
18
42:27 T$e "utue #" HR
2* itself is also loc-ed in a debate over its future. Though some organiGations have evidence
that the function is an integral part of its capability to deliver business success, many view 2* as
7ver.resourced
Inefficient
/ulnerable to the cost reduction possibilities of 2*7.
2* outsourcing raises 'uestions over 2*1s future s-ills, capabilities and career paths. Its
developments are creating pressures for practitioners to shift from being reactive and
administrative problem.solvers to more proactive, value.driven Mbusiness partners1.
42:28 S$aed 'e>i%e'
*esearch revealed much discussion about the definitions and position of shared services. )or our
purposes, it is defined as the transfer or insourcing of 2* services and their resources to a
separate unit within the business . and often with a separate (+3 system. "hared services is
often adopted by organiGations who are against outsourcing as a matter of principle . but still
see- some of the transformational and streamlining advantages connected with outsourcing.
$lternatively, some organiGations use shared services as a halfway house to prepare the specific
lines of 2* they intend to outsource.
42:2F T$e HRO !#)i%
:o amount of preparation, however e0tensive, can safeguard outsourcing deals completely.
3eaders need to clarify what their core logic is for creating value by demonstrating the
following.
2ow 2*7 can enable the organiGation to meet the re'uirements of its sta-eholders . be
they internal 4employees5 or e0ternal 4customers5.
2ow outsourcing will transform the way the 2* function wor-s in a radical and
sustainable way.
19
rucially, how transforming the 2* function will influence the planning, operations and
performance re'uired by the business model.
42:29 Mana)in) t$e tan'iti#n
In some organiGations, 2*7 is a-in to changing the engine while the plane is still in the air
which is a potentially catastrophic e0ercise. The conse'uences of 2*7 must be thought through
. before agreeing a contract. 2anding over single, multiple or all 2* service processes represents
for many organiGations their first e0perience of comple0 projects . project management is a
critical 2* capability for 2*7 to wor- well. $ successful transition minimiGes employee angst .
but botched handovers could have longstanding repercussions on relationships with providers,
employees, other sta-eholders and corporate image.
42:2/ G#>enan%e #" HRO @e"#man%e
#anaging and measuring performance after 2* outsourcing is pivotal to the relationship
between 2*7 client and provider. (erformance measurement in 2*7 traditionally concerns the
following.
6fficiencyK mainly through cost reductions.
6ffectivenessK through improved service outcomes against criteria in service level
agreements 4"3$s5.
TransformationK indicators of deeper change at the level of the organiGation, its
employees, systems . and at intangible levels.
"trategic governanceK evaluating the management of performance . including the
decision rights, rules and agreed management processes defined with and before
providers are engaged.
42D THE SU*GECT *AC0GROUND OF THE RESEARCH TOPIC
42D24 Im@a%t #" HR Out'#u%in) #n *u'ine'' Pe"#man%e
20
2uman resources outsourcing evolved from hiring payroll processing companies in the 9EEFs to
delegating tas-s previously performed by human resources assistants and specialists, such as
recruiting, coordinating benefits and handling unemployment claims. "ome small businesses
outsource entire human resources departmental functionsJ however, many companies outsource
singular processes.
42D2: Out'#u%in) HR P#%e''e'
"mall businesses to large corporations decide for one reason or another that outsourcing human
resources functions is a way to improve efficiency and minimiGe staffing costs. 3arge
organiGations that employ thousands of people may find itIs simpler to outsource a process, such
as payroll, rather than employ two to three payroll cler-s and purchase sophisticated technology
than engage the services of a company that focuses entirely on processing payroll. "mall
companies might decide that outsourcing human resources processes is more cost.effective and
efficient than creating a human resources department while the business is focused on other
projects associated with starting a new business. HInc.H magaGine contributor (riya ,anapati says
data from 6verest *esearch Institute in Dallas suggests a significant percentage of small
businesses are finding human resources outsourcing is the answer to avoiding labor costs and
e0pensive technology. H2* outsourcing among small businesses has gone up considerablyK 7f
the >@ 2* outsourcing deals between 9EED and mid.<FF!, that the report analyGed, =B involved
small businesses,H ,anapati writes. The growth rate of 2* outsourcing is li-ely to increase as
more small businesses focus on their product and service offerings instead of staffing an in.
house human resources department.
=
42D2D HRO E""e%t #n *u'ine'' Pe"#man%e
3
*ef.=. %$ 2andboo- of 2* management practices, D
th
edition <FF<, by #. $rmstrong.
21
Business performance is an important consideration when small business owners weigh the pros
and cons of 2*7. 7ne school of thought is that a small business can focus its energy and
e0penditures on developing the product it sells. This enables a small company to allocate its
resources to areas that include engineering and research and development, instead of recruiting
staff, maintaining personnel files and other human resources tas-s. The other school of thought
has more to do with human capital and talent..a small business owner may find herself without
the talent she needs to build an efficient human resources department. In this case, 2*7 resolves
the dilemma small business owners face during the search for an in.house human resources
e0pert. In the first scenario, a small business directing its focus on product design and sales may
determine the e0pense of 2*7 can be easily justified by more attention given to product sales. $
small business that doesnIt have the re'uisite talent to lead a human resources department can
justify the e0pense of 2*7 by the confidence in the level of competency 2*7 companies offer.
42D21 C#ntinued Im@a%t #n *u'ine'' Pe"#man%e
Ahen small businesses initially utiliGe 2*7 services for transactional processes, the selection of
a strategic human resources leader can become a priority. The search for human resources
administrative practitioners without e0pertise in 2* strategic management can then ta-e a
bac-seat for now. $n 2* strategic partner should be the first hired for development of a human
resources department. 7utsourcingInformationTechnology.com editor Beth *osenthal observes,
H"mall.to.medium businesses may have a hard time recruiting highly s-illed staffers without the
benefits they e0pect. 7utsourcing allows "#Bs to offer benefits typically available only at
bigger companies.H Upon ma-ing the decision to outsource 2* functions while you build a
successful, profitable company, you can resume your search for an 2* e0ecutive. 7nce your
company carves a position in the mar-et with your product offering, your e0ecutive leadership
team..including your human resources e0ecutive..can then begin to wor- collaboratively to form
a full.service human resources department and bring in.house those previously outsourced
functions. "till, you may discover that outsourcing some human resources functions is in the best
interest of the company. $s your business grows, resources committed to 2*7 may turn into a
wise, long.term decision that improves the services your human resources department can
provide to its internal customers, your employees.
42D27 C$##'in) HR Out'#u%in) Se>i%e'
There are numerous 2* outsourcing services that you can consider and it is sometimes very
difficult to properly -now what to choose. Cou need to properly understand everything involved
22
and in order to do this it is your responsibility to be informed at all times. Ae basically have two
main types of 2* 7utsourcing "ervicesK ore 2uman *esources and Talent $dministration.
42D28 C#e HR Out'#u%in) Se>i%e'
Ae are using the term %ore human resources& because in this case we are tal-ing about those
services that are crucial for most companies out there. Ae are dealing with ! core 2*
outsourcing servicesK
(ayroll $dministration ; This includes everything related to payrolls from filing ta0es to
managing the payroll of special projects.
Benefits $dministration ; This is a little more difficult to understand for some owners as
most believe there is no need for such a department. "uch 2* outsourcing services
include pensions, share plans and even welfare. "igning a contract is not always enough
to handle employee benefits in time
Aor-force $dministration ; These 2* outsourcing services are the foundation of a good
human resources management plan. Ae are tal-ing about employee data management,
relations, disciplinary services, unemployment administration and a lot more. This is the
one core 2* service that most people outsource.
3eave $dministration ; Cour employees will ta-e leaves of absence as they are entitled
to do so in some cases. 7n the other hand, there might also be leaves that are not good for
the company. $ good management of leaves is needed in order to -eep a close grasp on
human resources and employee satisfaction.
42D2F Ta!ent Admini'tati#n HR Out'#u%in) Se>i%e'
Ahen it comes to the talent you have on board, you want all people to feel good and always
-now that they will get compensation for what they do. In this case we have ! main talent
administration 2* outsourcing services that you can choose fromK
9. *elocation and 2andling $ssignments ; 2* outsourcing services can manage everything
involved from travel assistance to the entire program development.
<. (erformance #anagement and Training ; Cour employees need to be monitored so that
you -now their performance levels at all times. $lso, you do want to -now when training
is needed and want someone to do it properly. 2* outsourcing services can deliver.
=. *ecruiting $dministration ; It is usually 'uite hard to hire new staff. Cou lose a lot of time
going through /s and handling interviews. This is the one talent administration 2*
23
outsourcing service that can really offer benefits. These firms can handle all your hiring
needs and you will not lose a second. Cou can ma-e sure that the best people are always
hired and this is something that you really want to have incorporated. 6ven if you do not
use 2* outsourcing services for full talent administration, we recommend that you at
least consider recruiting administration.
!. ompensation $dministration ; This includes a lot of math. It is needless to say that a lot
of time is wasted in monitoring the compensations you would need to pay someone. $
good 2* outsourcing service will use various methods to -eep control of everything from
ta-ing surveys to e0ecutive administration.
2* outsourcing services can bring in a lot of benefits especially when we consider management.
It is crucial that human resources are properly handled in every single company out there. $
failure to do this can lead to loss of time and money. To ma-e it even worse, an improper
management can cause your employees to not wor- at their full potential. This is e0actly why
you should use 2* outsourcing services if you cannot properly handle this operation.
42D29 *ene"it' #" HR Out'#u%in)
2* outsourcing has really become a worldwide phenomenon. Ae see more companies doing it
daily and this can only bring in benefits. The problem is that few people really -now what 2*
outsourcing means. Ae have seen a lot of company owners that thought that only tal-ing to a
company to loo- for some staff for them was human resources outsourcing. 6ven this process is
not really 2* outsourcing in some circumstances. Before you thin- about the benefits of 2*
outsourcing you really need to understand what this concept means. 7nly after that can we
properly understand the benefits offered. Through the outsourcing of some or all core human
resources functions a company is almost immediately able to cut costs and minimiGe the time
that is needed for them to perform properly. In the last few years we saw that the common 2*
tas-s that are outsourced are payroll administration, attendance trac-ing, time trac-ing, ta0 filing
and ta0 payments. The tric-y subject stands in the fact that human resources are now viewed at a
much larger scale than they were in the past. Internal human resources departments are bigger
and have a more important role in a company. This immediately translates in an increase of costs
in maintaining and even implementing 2* functions internally. The good news stands in the fact
that companies are now available to outsource a part of their 2* tas-s or even all of them to a
specialiGed 2* outsourcing provider. This practice does save both time and costs.
Ae can also say that besides the two benefits of 2* outsourcing mentioned above, a company
will also have others that they should consider. Through 2* outsourcing they can focus their
efforts on more business oriented tas-s and they can get rid of a lot of activities that are difficult
24
to manage and consume a lot of time. Through 2* outsourcing you can be sure that your
employees are always receiving the best possible in class human resources services. This
includes retirement plans, rewards programs, recognition programs and health benefits. $ll this
is obtained at lower costs than ever before. To ma-e everything even better, 2* outsourcing
providers also bring in a lot of support and e0perience when dealing with comple0 issues that
might appear. If a company cannot have its own 2* in.house department it should definitely opt
for 2* outsourcing.
42D2/ T$e HR Out'#u%in) P#%e''
$ny organiGation ma-ing a significant commitment to 2*7 is ma-ing a decision with far.
reaching implications.not just for 2*, but for the entire organiGation. )or this reason, it is crucial
that all sta-eholders involved in the 2*7 process be involved from the outset and that there is
clarity in relation to the goals and objectives that the organiGation e0pects to achieve. $s a
starting point, a multi.departmental steering team, consisting of representatives of all potential
users of the service provider, should be formed and convened. Ideally, 2* will either lead the
decision.ma-ing process or be crucial to it. 7ther -ey members of the steering team should
include high.level managers and e0ecutives with a vested interest in all aspects of human capital
asset management and its return on investment, including operations, information systems
technology, finance, accounting and logistics. The goals and e0pectations of the outsourcing
process should be developed and defined in a detailed project plan.
42D24. T,@e' #" HR Out'#u%in)
In the past, 2* outsourcing was thought of as hiring a vendor to provide a service. Aith the new
focus on outsourcing, there is more of an opportunity to partner with the vendor to provide the
service on a longer term basis rather than just a one.time vendor contract. 2* outsourcing can
includeK
Di'%ete 'e>i%e'- In this instance, one element of a business process or a single set of high.
volume repetitive functions is outsourced to a third.party administrator. 60amples of discrete
services could include the annual open enrollment process, fle0ible spending accounts or
employee bac-ground chec-s.
Mu!ti6@#%e'' 'e>i%e'- The complete outsourcing of one or more functional human resource
processes would be an e0ample of multi.process outsourcing 4also called blended services5. $s
such, the outsourcing of either health and welfare benefits administration or defined retirement
25
plan to a third.party administrator would be an e0ample of multi.process or blended services
outsourcing.
T#ta! HR #ut'#u%in)- Total 2* outsourcing represents the transfer of the majority of 2*
services to a third party, to include recruitment, payroll, 2*I", benefits, compensation and
communications, as well as the transition of 2* management and staff. 2owever, 2* e0ecutive
management would normally remain in place within the organiGation, along with strategic
planning related to people management and other -ey 2* functions at the discretion of
management.
421 OUTSOURCING
The performance by outside parties, on a recurring basis, of tas-s that would otherwise be
performed in.house.
42124 Ot$e De"initi#n'
4212: In '#u%in) ; This refers to when companies loo- at their pool of employees to find those
who may be tapped to do certain needed jobs. They may offer these employees e0tra training or
they may merely find the employees that already possess the s-ills to ta-e on specialty wor-.
4212D O"" '$#in) . 7ff shoring simply means having the outsourced business functions done in
another country. )re'uently, wor- is off shored in order to reduce labor e0penses. 7ther times,
the reasons for off shoring are strategic .. to enter new mar-ets, to tap talent currently
unavailable domestically or to overcome regulations that prevent specific activities domestically.
42121 C# '#u%in) ; o sourcing is where a business function is performed by both internal staff
and e0ternal resources, such as consultants or outsourcing vendors, with specialiGed -nowledge
of the business function.
42127 Out @!a%ement . 7utplacement is a term used to describe the efforts made by a downsiGing
company to help its redundant employees through the redundancy transition and help them re.
orientate to the job mar-et. $ consultancy firm usually provides the outplacement services.
26
427 *E SPECIFIC A*OUT HR OUTSOURCING
7utsourcing contract negotiations re'uire very specific tas- and service.level descriptions, and
defining the why, what, who, where, when and what if can clarify things significantlyK
42724 Need "# Out'#u%in)
The decision to outsource is based on two business factorsK value proposition and mar-et.based
outsourcing. The most common value proposition is reducing cost savings. 7ther value
propositions include increasing operational efficiency, improving customer service, improving
employee satisfaction, growing revenue or reducing capital e0penditures. #ar-et.based
outsourcing is a comparison between internal s-ills and abilities and the capabilities of providers
in the mar-etplace. The decision to outsource is based on whether an e0ternal provider can do
the job better, cheaper or faster.
4272: Out'#u%ed Fun%ti#n'
ustomers can determine what to outsource by having a clear idea of the most common
performance management functions. (erformance management functions can be segmented into
user.centric processes and management.centric processes. User.centric processes include
individual performance objective management, individual performance evaluation, competency
mapping, self.paced e.learning and decision support, and career planning. #anagement.centric
processes include organiGational performance management, compensation management,
assessment management, learning management and training administration, and succession
planning. In general, all of the user.centric performance management processes lend themselves
to automation and outsourcing. #anagement.centric performance management functions also
can be outsourced. 3earning management and assessment management, in particular, lend
themselves to outsourcing. "ince vendors specialiGe in one or more of these functions, customers
can map the functions they intend to outsource to the capabilities of the vendor. This ma-es the
vendor selection process relatively straightforward.
!
4
*ef.!. %Theory to design successful outsourcing relationships& by #.". 3ogan 4<FFF5
27
4272D T,@e' #" Out'#u%in) Patne'
$ccording to a <FF! study by the ,artner ,roup, there are three types of outsourcing partnersK
application service providers 4$"(s5, traditional e0ternal service providers and business process
outsourcing 4B(75 companies. It is common for companies to have all three types of
relationships and several outsourcing partners. $n $"( hosts the technology and the services
appear to employees li-e an internal function. $ traditional e0ternal service provider brands the
service as its own, but the customer still controls deliverables. $ B(7 %owns& the entire business
process and has near.complete control, often called %end.to.end outsourcing.& It also has to be
decided that who will manage the outsourcers from the inside.
42721 W#B @!a%e #" t$e Out'#u%e
7utsourcers are not always physically located outside your company1s facilities. 7ccasionally
companies prefer a representative of the outsourcing firm to be present on.site. But it is far more
li-ely that outsourcers will wor- outside the buyer1s physical facility. #any governments have
passed or are drafting laws governing the offshoring of business, so it is prudent to chec-
e0isting regulations prior to engaging an offshore outsourcer. Defining where the outsourced
personnel will wor- is an important legal aspect of the outsourcing agreement.
42727 Duati#n #" t$e Out'#u%ed P#Ae%t
"pecifically defining service milestones is crucial to both the customer and the outsourcer.
Business.process cycles are always time.bound, and customers and outsourcers ali-e are always
constrained by time. Defining these time.bound constraints in terms of deliverables and
milestones is a strong point of outsourcing firms since milestones map directly to payment
cycles. ustomers should be willing to as- themselves, %Ahat is driving the dateN& Dates are
sometimes set by internal priorities 4hard dates5, but often dates can be fle0ible. Being fle0ible
about time constraints allows teams to proactively deal with unanticipated challenges.
42728 Pe%auti#n' "# P#''ib!e Futue P#b!em'
28
%60pect the une0pected& is a good motto to have on an outsourcing project. 60perienced
outsourcers will probably want to put a change management clause in the contract. This is
because they -now from e0perience that business needs change and it happens all the time.
$nswering 'uestions to such problems will result in development of specific goals that can be
used to develop measurable performance e0pectations and contractual obligations.
29
CHAPTER-2
Research
Methodology
30
C$a@te6:
RESEARCH METHODO+OGY
:24 INTRODUCTION
7utsourcing is an accepted management tool for restructuring and refocusing the way an
organiGation does business. It challenges management to build a more fle0ible organiGation
centred on the core competencies of the business. In ma-ing the determination that a business
has more to gain by having certain Hnon.coreH aspects of the business outsourced to a third.
party service provider, the organiGation transfers responsibility for one or more activities or
functions that would normally be performed in.house to a 'ualified vendor, for a specified
period of time and at a negotiated fee, in accordance with terms stipulated in a service level
agreement 4"3$5. In essence, the organiGation is ma-ing a decision to send certain parts of
the business out to a provider whose Hcore competencyH is that part of the business.
:2: STATEMENT OF THE PRO*+EM
To study the impact of 2uman *esource 7utsourcing on the effectiveness of the 2*
functions in Indian industry. Transitioning to an outsourcing arrangement can pose a uni'ue
set of ris-s that must be proactively managed, given the comple0ities associated with
transferring significant operational processes to a vendor while maintaining on.going service
to internal customers.
:2D REVIEW OF +ITERATURE
Rea!iEin) t$e >i'i#n #" HRO b, Na$a@iet5 G2 and G$#'$a!5 S2 <4//9=2 S#%ia! %a@ita!5
inte!!e%tua! %a@ita!5 and t$e #)aniEati#na! ad>anta)e5 A%adem, #" Mana)ement
Ab'ta%t
HAhat is our vision for the company five years after 2*7 implementation, and how do we get
thereNH The real opportunity e0ists for those companies that as- themselves these important
'uestions at the outset. 7f course, each adopterIs vision for the company five years from initial
transition will differ. Ahen 2* partners with a provider that has deep 2* e0pertise, it is better
able to move to transform and focus on strategic, high.return initiatives such as succession plan,
organiGation design, team effectiveness, leadership development, talent management,
performance management and development planning. The most successful change management
programs enable the 2*7 adopter to achieve the goals that they set out to achieve . without
running the ris- of allowing fate to ta-e over.
31
HRO %$an)e mana)ement- S,'temati% eHe%uti#n #" a 'tate)i% de%i'i#n b, Wi!!%#%B'5
+2P25 and 0en T2 <4//F=2 IT Out'#u%in) a' State)i% Patnein)
Ab'ta%t
If leveraged effectively, 2*7 can prove to be the catalyst for organiGations to Drive
standardiGation of 2* policies and practices. It ,ives 2* leaders more capacity to focus on
organiGational development, change management and e0ecutive coaching as underpinnings of
how 2* and business leaders wor- together. Increase 2*Is value to the organiGation by
supporting its focus on strategic opportunities. Ideally, change management begins as early as
the presale relationship, when a vendor conducts analysis and due diligence to understand an
organiGationIs uni'ue re'uirements. $n e0perienced vendor will help 2* leaders ma-e internal
communications around 2*7 e0ploration purposeful, productive and tailored to the employerIs
culture.
HR *PO di>e' and in$ibit#' b, *#nda#uB5 T2V25 Rue!5 H2G2M5 T$e Intenati#na!
G#una! #" Human Re'#u%e Mana)ement <:../=2
Ab'ta%t
The belief that outsourcing can cut costs attracts enterprises to 2* B(7 li-e moths to a flame.
3i-e the moths, these enterprises can become enlightened, but they can also get burnt.
6nlightenment comes when the enterprise see-ing to cut costs discovers other beneficial
outcomes that outsourcing can provide, such as the ability to focus on the core business and
improve service levels. ompanies turn to process outsourcing for a variety of reasons. They
include high cost of transactions, too much time spent on daily operations, high cost of
upgrading applications, disintegrated processes, difficulty in hiring or retaining process staff and
lac- of timely or accurate reports. Begin with the end in mind. Determine the capabilities that the
enterprise needs to align the wor-force with business strategy. Then, build the portfolio of
applications to meet this vision. 8eep in mind the strategy and direction of the enterprise1s core
integrated 2*#" provider when ma-ing the niche solution vs. integrated solution decision.
Trust, openness, autonomy, strategic collaboration, pro.activity, benchmar-ing and career
development are some other buGGwords prevalent in the field of 2*. The main issue according to
me is building self.regard. 7f late, driving the new economy organiGations in frenGy is the
growing malaise of the Mrate of employee turnover,1 which I felt can be correlated to low self.
esteem. It is thus worthwhile to ta-e a deep loo- into this concept and its implications in both
individual and corporate conte0ts.
32
HRO C$an)e Mana)ement- Emba%e S,'temati% A@@#a%$e' t# Tan'"#min) HR in t$e
Mid6MaBet b, M%Fa!an5 F2W2 and N#!an5 R2+2 <4//7=2 H#( t# mana)e an IT
#ut'#u%in) a!!ian%e2
Ab'ta%t
The adoption of end.to.end human resource outsourcing 42*75 is a strategic decision that offers
tremendous opportunity for medium.siGed organiGations. 2owever, itIs critical that the
organiGation use systematic approaches to build support for the new direction . approaches that
use communication to build momentum and e0citement among employees and 2* staff, and
training to ensure that the solution delivers the desired results. Ahile many 2*7 adopters say
that they view this level of attention to change management as an important option, without the
right focus or dedicated resources, change management often falls by the wayside.
Thoughtful, disciplined approaches to introducing 2*7 into the companyIs e0isting environment
are not something thatIs just Hnice to do.H They help focus on the people.related issues of an
outsourcing decision and enable employers and their provider partners to build a stronger
relationship that helps ensure a successful rollout. $s part of an on.going process, they also
enable 2* to better manage its relationships and interactions with internal customers and
sta-eholders, and successfully realiGe the organiGationIs longer.term vision of transformation
through 2*7.
S#me Mea'ue' t# Rai'e t$e M#ti>ati#n +e>e!' #" Em@!#,ee' b, 0en5 T2 and *!#i'5 02
<:..:=2 N#m de>e!#@ment in #ut'#u%in) e!ati#n'$i@2
Ab'ta%t
*ecogniGing the contributions of outstanding achievers will induce others to try hard. riteria for
selecting outstanding achievers should be transparent. 6ffective 2* measures in the areas of
training, career development etc. e'uip the wor-force better and also increase their self.esteem
and morale. The need of the hour is not only to enable the employees to grow in the Mlearning
organiGations1, the concept of which is fast attaining celebrity status in this age of -nowledge
economy, but also to ta-e care that the employee has substantial self.esteem. Aithout this all the
retention policies of the organiGations will meet a sorry fate.
33
:21 O*GECTIVES OF THE STUDY
To study the different aspects of 2* outsourcing
To study the important reasons for 2* 7utsourcing
To study the important factors responsible towards choosing a third party supplier for
2* 7utsourcing
To study the major 2* functions being outsourced in the Indian industry either
completely or partially
To study the impact of 2* outsourcing on various 2* functions + on the
effectiveness of the 2* department
To study the co.relation between 2* 7utsourcing + IT industry
To study the effectiveness of 2* function that is being outsourced
:27 SCOPE OF THE STUDY
The scope of study includes the following pointsK
To e0plore the different possibilities about 2* outsourcing and its various aspects
To e0plore the impact of 2* outsourcing on various 2* functions
To e0plore the possibilities of co.relation between 2* 7utsourcing + IT
To e0plore the future possibilities of 2* 7utsourcing
:28 RESEARCH DESIGN
*esearch design is a detailed blue print used to guide the research study towards its
objectives. Descriptive research has been used for this study. The major purpose of
descriptive research is description of the state of affairs, as it e0ists as present. This means
as-ing 'uestions to people who are believed to possess the desired information. It measures
the magnitude of people1s -nowledge, attitudes and opinion towards the present research
study.
34
*esearch design simply means a search for facts + answers to 'uestions and solutions to the
problems. It is a prospective investigation. *esearch is a systematic and logical study of an
issue or problem through scientific method.
:2F SAMP+ING P+AN
Sam@!in) Met$#d
Sim@!e and#m 'am@!in) is used which is the simplest met$#d of sampling for social
researches. It is used in simple e0periments that re'uire a single sample to be ta-en from a
given population or a representative sample frame. The people in the sample frame must all
be accessible and available. It is used when the target group is sufficiently large.
Sam@!e uni>e'e
The sample universe is comprised of the 2* managers and employees wor-ing in IT
companies in both services and manufacturing sector in India.
Sam@!e 'iEe
The sample siGe is restricted to 9FF respondents due to time constraint.
:29 TOO+S FOR DATA CO++ECTION
S#u%e' O" data %#!!e%ti#n
(rimary data is collected through 'uestionnaires and secondary data is collected through
enterprise portals and websites related 2* outsourcing and also through various journals,
magaGines and related boo-s.
:2/ TOO+S FOR DATA ANA+YSIS
Data $nalysis has been done with the use of statistical tools and results are presented through
tables, charts and graphs. "imple percentage method is used to analyGe and interpret the data.
The analyGed + interpreted data is presented in the form of tables, charts + graphs.
Tab!e'- . (resentation of data in vertical column + horiGontal rows.
Ga@$'- . ,raph is a pictorial representation of the data.
35
:24. +IMITATIONS OF THE STUDY
The sample which we too- does not represent the whole population as the numbers of
respondents were very less
The limited e0perience was another constraint on the 'uality of the research
*espondents were from specific areas and did not cover the whole of India
"ample siGe is small because of time constraint
The primary data is based on the 'uestionnaires which can be influenced by personal
bias and subjective for individuals
:244 +AYOUT OF CHAPTERS
C$a@te 46 INTRODUCTION
This chapter includes the theoretical aspect of the study and introduction
to the research topic. It also discusses about the subject bac-ground of the
research which has been carried out.
C$a@te :6 RESEARCH METHODO+OGY
This chapter includes the brief introduction, statement of the problem,
review of literature, objectives of the study, scope of the study, research
design, sampling plan, Tools for data collection, tools for data analysis,
limitations of the study and layout of chapters.
C$a@te D6 INDUSTRY PROFI+E
This includes brief introduction about the outsourcing practices and their
results in 2* sector.
C$a@te 16 DATA ANA+YSIS AND INTERPRETATION
It includes $nalysis and interpretation of data. $nalysis is carried on by
preparation of Tables, ,raphs and harts.
C$a@te 76 FINDINGS AND SUGGESTION
36
It contains the "ummary of findings and "uggestion. This chapter gives
summary of findings of the study along with the suggestion.
C$a@te 86 CONC+USION
This chapter gives conclusion of the study.
CHAPTER-3
Industry Profile
37
CHAPTER6D
INDUSTRY PROFI+E
D24 HR OUTSOURCING INDUSTRY
D2424 REASONS FOR STRONG OUTSOURCING INDUSTRY
:owadays 2* outsourcing is really something that is needed for most small to medium siGed
companies. This is mainly because everybody is doing it and the benefits that are gained from
doing this cannot be achieved if it is handled internally. 2* outsourcing is really strong at the
moment and there is no sign that this will change in the immediate future. The sheer benefits that
can be obtained cannot be ta-en lightly.
The main reason for which 2* outsourcing is needed at the moment is the fact that most
companies cannot do it properly alone. It is very hard to stay up to date with all the regulations
that have to be considered and the possible employee benefits that should implemented. Through
2* outsourcing we can easily avoid any problem and we can ma0imiGe the time we have to
dedicate to those business functions that are actually generating us profit.
The 2* outsourcing industry is useful because it can help to -eep the 2* functions in control at
all the times. If a good 2* provider is hired it can basically solve all the problems related to 2*.
$lso, if some problems still appear it is the responsibility of the provider to deal with them. Thus
we can basically shift responsibilities to gaining time and money. "o there is no reason why the
2* outsourcing industry would not continue to be strong in the years to come as long as such
benefits e0ist.
D242:SOME FACTS A*OUT HR OUTSOURCING INDUSTRY
38
@DL of companies outsource some 2* function
E9L of companies with O9 billionP annual revenues are now considering 2*7
2*7 grew <DL from second half of <FF! to first half of <FF@
N#teK "2*# 2uman *esource 7utsourcing "urvey *eportK
$lmost > out of 9F organiGations practice 2* 7utsourcing but 9/= of organiGations did not
outsource any function Q of organiGations partially outsource an 2* function 4organiGation
co.manages function with vendor5
HRO MaBet
In ne0t @ years, global spending on 2*7 will double ; from O!F billion to ODF billion
)rom <FF< to <FF!, 9!L increase in large firms that would consider 2*7
onsulting and Training
D242D FACTORS HAMPERING HRO INDUSTRY
ost factor + onfidentiality
The fear of losing jobs
3oss of sensitive information to public/competition
6thics and 'uality of outsourcing vendors
(ossibility of security breaches
ost.benefit e'uation not clear
3ac- of psychological acceptance
D2421 DOMINANT TRENDS IN MAIN HR OUTSOURCING INDUSTRY SEGMENTS-
39
onsultants
$dministrative ; service providers
Technology enablers
ustomiGing imported software products remains an issueK supply oriented rather than
demand based customiGation
D2427 HR OUTSOURCING COMPANY SERVICE TYPES
$n 2* outsourcing company can be divided basically into four categories as (67s, B(7s,
$"(s, or e.services based on the type of service it offers.
D2428 PEO <PROFESSIONA+ EMP+OYER ORGANIIATIONS=
$ (67 or $ (rofessional 6mployer 7rganiGation is the one that ta-es full responsibility of your
companyIs human resources management. $nother outsourcing option that involves handing
over the 2* duties along with the employees is called a (67 4professional employer
organiGation5. In a (67, the outsourcing firm becomes the legal employer, handling payroll,
benefits, insurance and other employee relationsJ it leases the employees bac- to the company.
6mployees generally enjoy better benefits because of group rates, and the scenario allows
business owners to concentrate solely on company goals rather than personnel issues. "ome
companies may also enjoy ta0 benefits and will save on wor-erIs compensation and
unemployment insurance because employees are the responsibility of the (67.
D242F *PO <*USINESS PROCESS OUTSOURCING=
The new buGG word IB(7I seems to be everywhere now a dayR 6ver wondered what is B(7N 3et
us e0plainK B(7 has e0panded sounds as Business (rocess 7utsourcing and can be aptly defined
as the act of utiliGing the services of a third party by a company in order to perform its bac-
office operations that might be payroll administration, customer help des-s/ call centres, tele.
mar-eting, accounting, billingJ the list is endless.
To put it in simple words a B(7 4business process outsourcing5 is a process in which a company
delegates some of its business processes mainly bac- office operations to a third party by giving
the third party total control over that process. Business process outsourcing otherwise -nown as
B(7 is the process of leveraging technology vendors in various third worlds or developing
40
nations for doing a job which was once the responsibility of the enterprise. 7r simply put, it is
the process of shifting an internal job process to an outside/e0ternal company which might have
a completely different geographical location.
,enerally the processes being outsourcing as part of B(7 are bac-end jobs li-e call/help
centres, call centre outsourcing services, medical transcription, billing, payroll processing, data
entry and the li-e. #ost of these jobs are outsourcing by first world nations li-e U"$ and U8 to
third world nations li-e India, (hilippines, hina, #alaysia and some eastern 6uropean
countries. These nations have a good pool of 6nglish spea-ing youth who receive accent and job
related training before they are inducted at a salary which is much lesser than what their
counterparts in first world nations would demand. This allows first world organiGations to get
higher profits and provide better services by lowering the prices and by recruiting more labour
than they could possibly do otherwise. In addition to benefiting the first world nations, business
process outsourcing has also benefited third world nations by generating much needed jobs.
$ B(7 or business process outsourcing company is different from a (67 in the sense that it
provides various facilities including 2*. $ B(7 can help improve the 2* process, provide 2*
data warehousing and self.access.
D2: THE *PO INDUSTRY
The B(7 industry has flourished at a frantic pace in the last few years and companies have
ended up with huge savings by being a part of the industry. By outsourcing their bac- office
business processes to cheaper nations li-e hina, India, (hilippines, #e0ico, "outh $frica etc.
companies can cut costs, better concentrate on their core businesses and strengths, ensure better
customer satisfaction and in a way get an edge over their competitors. $ report suggests that U"
firms have saved nearly OD billion through outsourcing to third world nations li-e India.
D2:24 SE+ECTING THE *PO COMPANIES
"electing on the right B(7 vendor is probably the ne0t most important tas- other than fi0ing up
on a B(7 destination. $lthough there are lots of organiGations and agencies dedicated to helping
buyers in ma-ing the right decision, there are some precautions that the buyer has to maintain.
D2:2: SE+ECTING THE *PO VENDORS
The -ey factor before finaliGing on a B(7 vendor is to scrutiniGe and analyses his strength and
e0pertise in terms of providing similar services to clients. 7ne good way to find this out would
be to follow up with the firmIs e0isting clients regarding the services. The B(7 vendor must
41
have proper 'uality certifications and should be in possession of s-illed manpower or must be in
a position to offer training facilities. $part from this the B(7 ompany should have a strong
financial bac-ground and should be willing to share ris- in the outsourcing contract. It is always
good to -now the -ind of services that the vendor offers and his relationship with other
outsourcing suppliers.
#ost companies decide to outsource their business processes to multiple B(7 companies rather
than a single one. This by all means is a good practice as the vendors will compete among
themselves to provide better service and the company will always be in a position to change
vendors in case one doesnIt live up to the mar-.
D2:2D *PO COMPANIES IN INDIA
$s the B(7 boom grows relatively unheard offshore outsourcing destinations li-e (une and
8ol-ata in subcontinent India are rising to fame with the state governments starting to spend
money in developing the infrastructures and formulating friendlier ta0es and other legal norms.
#ost B(7 companies in the Indian "ubcontinent are 'uality certified from leading 'uality firms
li-e I"7 EFFF, ## etc. and have access to high tech technologies and infrastructure.
"ure enough companies li-e IB#, #icrosoft, 7racle, isco, (rudential, 2ewlett (ac-ard, $TT
Aireless, Dell and many more consider India to be their first choice as an offshore contact centre
outsourcing destination.
D2:21 GETTING STARTED
If you are planning to ta-e a plunge into the B(7 wave, you got to formulate an effective plan by
understanding your vision along with your long term goals. Deciding on the right B(7
destination and more importantly the right B(7 vendor can go a long way in ensuring smooth
operations with good returns. $s of now, India with its easily available 6nglish spea-ing,
computer literate, low cost manpower, better infrastructure and 'uality certified software and
B(7 venders seems to be a great destination for outsourcing. "o ta-e your pic-R
D2:27 *PO INDIA 6 PRESENT AND FUTURE
The B(7 boom has helped developing countries li-e India in a major way by creating 'uality job
opportunities in turn benefiting the Indian economy. "o what is it that ma-es B(7 India stand
out in the crowdN
D2:28 THE INDIAN EDGE
42
India in the recent years has shown huge developments in the areas of communication, power
and software developments. India e0ports software to E@ different countries and stands second in
the world as far as software e0ports are concerned. In addition India has I"7 EFFF, ## 'uality
certified software firms that have a reputation of providing 'uality services. India stands out of
the rest in terms of better IT and technological infrastructure, low cost, s-illed manpower that is
readily available, friendly ta0ation and other laws, a stable government, a fast paced economy
and 'uality certified software firms.
D2:2F HRO IN INDIA
IT city Bangalore seems to be a hot destination for B(7s swiftly followed by similar
technologically advanced cities li-e hennai, 2yderabad, #umbai, Delhi, 8ol-ata and (une. $ll
these cities in India are technologically advanced and have a good infrastructure with almost <BD
'uality certified B(7 vendors.
D2:29 HR *USINESS PROCESS OUTSOURCING
2* business process outsourcing is pic-ing up pace as more and more companies feel that bac-
offer 2* operations ta-e up lots of their resources. $s for IT, India seems to be a major hub for
2* outsourcing too. ities having a good infrastructure li-e Bangalore, Delhi, (une, Bombay
and hennai are being seen as a major offshore outsourcing destinations as of now. The Bombay
offshore outsourcing industry seems to be pic-ing up really well at present as compared to
hennai and Bangalore, who seem to be calling the shots right now.
D2:2/ ASP <APP+ICATION SERVICE PROVIDER=
$n $"( or application service provider company will host the 2* service on the web and rent it
to users. 6,K (eople"oft
D2:24. E6SERVICES <E+ECTRONIC SERVICES=
6 services are those human resource service companies that are web based. Both B(7 and $"(Is
can be referred as e.service companies. $ company which has decided to outsource its human
resources has to decide as to which type of vendor to go for and which offshore destination to
choose for outsourcing its human resource functions. The major destination for outsourcing
human resources is seen as India. India has many companies that offer 2* services and best of
allJ most of these companies are 'uality certified. This ma-es outsourcing to them a relatively
safer option. $part from this India also have good communications infrastructure, cheaper labour
and a stable government. In addition to India some other good sales force outsourcing, research it
43
outsourcing and 2* outsourcing services destinations are hina and (hilippines. In addition the
*omania outsourcing industry is also on the bloom and is a good option for U8 firms who want
to play it safe outsourcing 2* function.
D2D24 INDUSTRY PROFI+E OF SOFTWARE 3 IT INDUSTRY
D2D2: IT SERVICES OUTSOURCING
The IT services outsourcing sector is the fastest growing sector in the outsourcing mar-et and
has been growing at a frantic pace with more and more companies planning to ta-e the plunge.
$ccording to various estimates the IT services outsourcing mar-et will reach U" O <FF billion by
<FF! and will grow even further. $s for the IT service outsourcing destinations are concerned,
India stands out way ahead of the rest. This is because India has many 'uality certified software
firms, computer savvy wor-force and relatively cheaper rates of operation. India also e0ports
software to 9E different countries and has a great infrastructure in terms of communication.
D2D2D IT OUTSOURCING TO INDIA
Ahen it comes to singling out the most popular destination for IT outsourcing, one name very
well stands out of the rest IndiaR In all its glory India in the past three years has become the most
popular destination for IT outsourcing with more than <=F fortune 9FFF companies using its
outsourcing services. Cou can do IT outsourcing and wor- at home directory from home. "o
what is it that gives India its popularityN 3etIs loo- at some major factors.
In India, the software boom started somewhere in the late 9EEFs. #ost of the Indian software
companies at that moment offered only limited software services such as the ban-ing and the
engineering software. The business software boom started with the emergence of C<8 problem,
when a large number of s-illed personnel were re'uired to fulfill the mammoth database.
correction demand in order to cope up with the advent of the new millennium.
The profile of the Indian IT "ervices has been undergoing a change in the last few years, partly
as it moves up the value chain and partly as a response to the mar-et dynamics. Ten years ago,
most U" companies would not even consider outsourcing some of their IT projects to outside
vendors. :ow, ten years later, a vast majority of U" companies use the professional services of
Indian "oftware engineers in some manner, through large, medium or small companies or
through individuals recruited directly.
44
The mar-et competition is forcing organiGations to cut down on costs of products. The
professional IT services on the other hand are becoming increasingly e0pensive. The offshore
software development model is today where onsite professional services were ten years ago.
There is a high chance 4almost a mathematical certainty5, that in less than ten years, the vast
majority of IT services 4software development being just one of them5 from developed countries,
will be, one, outsourced and two, outsourced to an offshore vendor.
Despite the global economic slowdown, the Indian IT software and services industry is
maintaining a steady pace of growth. "oftware development activity is not confined to a few
cities in India. "oftware development centers, such as Bangalore, 2yderabad, #umbai, (une,
hennai, alcutta, Delhi.:oida.,urgaon, /adodara, Bhubaneswar, $hmedabad, ,oa,
handigarh, and Trivandrum are all developing 'uic-ly. $ll of these places have state.of.the.art
software facilities and the presence of a large number of overseas vendors. India1s most priGed
resource is its readily available technical wor- force. India has the second largest 6nglish.
spea-ing scientific professionals in the world, second only to the U.". It is estimated that India
has over ! million technical wor-ers, over 9,D=< educational institutions and polytechnics, which
train more than >B,BD@ computer software professionals every year. The enormous base of
s-illed manpower is a major draw for global customers. India provides IT services at one.tenth
the price. :o wonder more and more companies are basing their operations in India.
The industry is in an e0pansion mode right now, with doGens of new offshore IT services vendors
emerging everyday, the industry has a high probability of being subjected to the DFK<F rule in not
too distant a future. In perhaps another ten years, DF percent of all outsourced offshore
development wor- will be done by <F percent of all vendors, a small number of high 'ualities,
trusted vendors. 7nly a few selected countries and only the most professional companies in those
countries will emerge as winners. India is the country of choice for offshore software
development. It has the potential to become and remain the country of choice for all software
developments and IT enabled services, second only to the U"$. The third choice could be far
distant.
India is among the three countries that have built supercomputers on their own. The other two
are U"$ and ?apan. India is among si0 countries that launch satellites and do so even for
,ermany and Belgium. IndiaIs I:"$T is among the worldIs largest domestic satellite
communication systems. India has the third largest telecommunications networ- among the
emerging economies, and it is among the top ten networ-s of the world .To become a global
leader in the IT industry and retain that position, India needs to constantly -eep moving up the
45
value chain, focusing on finished products and solutions, rather than purely on s-ill sets and
resumes. It also needs to be able to pac-age its services as products, rather than offering them as
raw material. It needs to be able to recogniGe and build up on its strengths and wor- on
wea-nesses. $nother e0tension of the IT industry is the IT6" 4Information Technology 6nabled
"ervices5 which is a sector dependent on IT sector.
Information technology consulting 4IT consulting or business and technology services5 is a field
that focuses on advising businesses on how best to use information technology to meet their
business objectives. In addition to providing advice, IT consultancies often implement, deploy,
and administer IT systems on businessesI behalf.
D2D21 DE++ OUTSOURCING 6 +ATEST NEWS
Dell outsourced its computer support operations to India and had set up major call center
operations in cities li-e Bangalore and hennai. But the company has received many complaints
in terms of bad customer service along with rude comments and bad accents.
This has lead the Dell outsourcing unit to rethin- its strategies regarding utility outsourcing call
center. $ccording to a report in the local newspaper $ustin.$merican "tatesman, Dell has
decided to move bac- its technical support jobs from India to U". But Dell outsourcing in terms
of support for home users is still being outsourced to India in large numbers. Dell outsourcing is
a live e0ample of how things can go wrong in an outsourcing contract if things are not planned
out properly. Though outsourcing can be beneficial to organiGations there are many myths
offshore outsourcing IT that needs to be clearedN )irstly outsourcing is in no way the ultimate
answer. #any business white papers outsourcing IT have clearly stated that outsourcing can only
be beneficial to those who do so analyGing the short as well as long term goals of an
organiGation. Therefore first and foremost organiGations should research outsourcing what is it
and in which way will it be beneficial to them. IT outsourcing advantages are many, but same is
the case with operations failing and organiGations bac-ing up.
D2D27 I*M OUTSOURCING 6 +ATEST DEVE+OPMENTS
IB# outsourcing jobs to offshore destinations li-e India and hina has met up with large scale
opposition by its own employees. IB# in the recent times has outsourced nearly 9FFF low end as
well as high end jobs to offshore destinations resulting in huge layoffs and has plans to move
another !FFF jobs to India, hina and other nations. (ools of IB# employees in the U"$ have
formed a union to fight the IB# outsourcing of jobs.
46
The labour union represents a small portion of IB# employees who have plans to ta-e action
against the company in case of any more jobs outsourced. They have even decided not to train
any replacement wor-ers from third world countries. Through business process outsourcing IB#
on the other hand has promised the generation of more and better paying jobs in U" as compared
to <FF= is a comment seen with much speculation by the IB# employees. I: the recent times
many companies are facing similar situations li-e outsourcing it IB#. The organiGation1s come
into two fold pressure in such situations. They have to decide between growth and social
implications of their actions.
D2D28 ATTRITION IN ITS SECTOR 3 HRO
The Aord %$& 4$ttrition5 Is Bac- In 7utsourcing ompanies Aith uncertainty easing attrition,
the biggest nightmare for 2* managers in IT services and outsourcing companies, is on the
horiGon while for some firms, it is already here. "o just how are the big = IT services firms faring
on the attrition and hiring frontN onsider the following attrition rates.
D2D2F INFOSYS
$ttrition at Infosys rose from 9F.EL the last 'uarter to 99.>L. 2owever, a #arch Aall "treet
?ournal article 'uoted a 3"$ $sia.(acific report as saying that there are unconfirmed rumors
that !,FFF.!,<FF employees have resigned at Infosys for the month of )ebruary alone ; well
beyond the 9,<FF employees who should be resigning each month 4as of December =9, Infosys
had about 9FE,DD< employees5. :evertheless, it was also noted that Infosys had the largest bench
strength in the industry at almost <F,FFF free resources.
D2D29 TATA CONSU+TANCY SERVICES <TCS=
$ttrition at T" has been stable at around 99.@L ; although company officials e0pect this rate to
rise. 2owever, the Aall "treet ?ournal noted in )ebruary that T" will go on a hiring spree and
hire up to =F,FFF new employees after the ne0t fiscal year begins on $pril 9. This is on top of the
99,@FF planned hires for the first 'uarter of <F9F. It was also noted that BFL of new hires for the
new fiscal year will be fresh graduates and more than <,FFF employees will be recruited from
outside India.
D2D2/ WIPRO
Aipro had an attrition rate of about 9=.!L ; up from an average of D.EL over the past three
'uarters. 2ence, the 2indu Business 3ine noted that they were planning a salary hi-e for
)ebruary along with promotions to help prevent attrition from rising further while recruitment
47
initiatives would happen on a demand basis and include a mi0 of campus hires and science
graduates along with e0perienced talent. #eanwhile, the 2indu Business 3ine 'uoted ,irish
(aranjpe, the ?oint.67 of Aipro1s IT "ervices group, as saying that the company1s bench
strength was around B,@FF to D,FFF on an employee base of about 9F=,FFF while the industry
bench strength standard is usually twice that.
2owever, another 2indu Business 3ine article noted that the brunt of any rise in attrition rates
will li-ely be borne by mid.siGe software outsourcers who could see attrition rates reach the 9@L
level. #oreover and since the big players have mostly not been hiring for some time, employees
with midsiGe firms are more li-ely to consider jumping to larger companies if they are offered
the right opportunity.
#eanwhile, utiliGation rates 4that is, the number of employees billed per hundred verses those
who are on the bench5 are also increasing at the big = IT services firms. $ccording to the 2indu
Business 3ine, utiliGation rates rose from >B.=L to >D.DL at Infosys, B=.>L to BB.<L at Tata
onsultancy "ervices 4T"5 and BF.DL to B=.<L at Aipro.
:evertheless, as utiliGation and attrition rates rise, it1s time for companies to once again thin-
about long.term strategies for retaining employees. $s *aman *oy, the chairman and managing
director of B(7 firm Suattro, noted in the )inancial 60press, meddling with salary and benefits
is a short.term strategy 4he chooses to focus on in.house training to create an efficient group of
high achievers5 while attrition is merely a symptom and not a disease. In other words, it1s the
symptom of an increasingly healthier job mar-et and economy for outsourcing.
CHAPTER-4
48
ata Analysis
And
Inter!retation
CHAPTER61
DATA ANA+YSIS 3 INTERPRETATION
DATA CO++ECTION INSTRUMENT
Based on the data collected through a well.structured 'uestionnaire, the opinion of the
respondents is analysed. The 'uestionnaire method of data collection is 'uite popular, so the
49
'uestions related to the objectives of the study were as-ed from the respondents. The
'uestionnaire was formulated on the basis of ideas related to the subject after a detailed
discussion with the guide.
ANA+YSIS OF DATA 3 ITS INTERPRETATION
RESPONDENT PROFI+E and ORGANIIATION DETAI+S
Tab!e 124 De@atment and De'i)nati#n P#"i!e #" t$e e'@#ndent'
S2 N# De'i)nati#n
N#2 #"
Re'@#ndent'
Pe%enta)e
9 60ecutive 9@ 9@L
< #anager <> <>L
= (ractioner =! =!L
! $ssistant #anager <@ <@L
@ T7T$3 9FF 9FFL
50
Ga@$ 124 De@atment and De'i)nati#n P#"i!e #" t$e e'@#ndent'
Ana!,'i'K
It is evident from table and graph no.!.9 that out of 9FF respondents, 9@ were 2* 60ecutives,<>
were 2* #anagers Ahile =! were wor-ing as 2* (ractioner and other <@L respondents were
wor-ing on the post of $ssistant #anagers.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that respondents from various categories too- active participation to answer the
'uestionnaire but the ma0imum no. of participants belonged to the 2* (ractioner ,roup who
was the youngest among all which is a point of significance as the majority of youngsters were
interested in answering the 'uestionnaire. $s far as the department is concerned, all the
respondents were from the 2* Department of different organiGations.
51
Tab!e 12: Yea' #" W#B EH@eien%e #" t$e e'@#ndent'
"r. :o
Yea' O" W#B
EH@eien%e
N#2 #"
Re'@#ndent'
Pe%enta)e
9 = ; @ years !@ !@L
< > ; 9F years << <<L
= 99 ; 9@ years 9D 9DL
! 9> and above years 9@ 9@L
@ T7T$3 9FF 9FFL
Ga@$ 12: Yea' #" W#B EH@eien%e #" t$e e'@#ndent'
Ana!,'i'-
)rom table and graph no.!.<, it is evident that the ma0imum no. of respondents were having =.@
years of wor- e0perience 4!@L5 and minimum no. of respondents 49@L5 were having wor-
e0perience of 9> years and above. 4<<L5 respondents were having wor-.e0perience of > to 9F
years and the rest 49D5 L of respondents were having a wor- e0perience of 99 . 9@ years.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that the respondents belong to almost all the managerial levels but young
managers too- a -een interest in responding the 'uestionnaire.
NAME OF ORGANIIATION J COMPANY
52
The present study titled %T26 I#($T 7) 2* 7UT"7U*I:, 7: /$*I7U" 2*
)U:TI7:" AIT2 *6)6*6:6 T7 IT I:DU"T*C& was planned for purely academic
research purpose and the data collected for this study is being analysed and interpreted. )or this
purpose, a 'uestionnaire was evolved on the basis of which different information was collected
from various organiGations and companies.
The companies which participated in this research project are as followsK
9. IB# India (vt. 3td
<. D633 India (vt. 3td
=. :78I$ India
!. :78I$ "I6#6:" :6TA7*8"
@. :/IDI$ India (vt. 3td
>. #I*7"7)T India (vt. 3td
B. AI(*7 India (vt. 3td
D. $D/$:6D #I*7 D6/I6" India
E. 26A36TT.($8$*D India (vt. 3td
9F. I:)7"C" India (vt. 3td
)rom the above list, it is evident that most of the #:s now.a.days practice 2*7 for various
2* functions and concentrate more on the core competencies.
Tab!e 12D A@@#Himate HR 'ten)t$ in t$e #)aniEati#n
53
"r.
:o
$ppro0imate :o. 7f
6mployees
(ercentage of
employees
9 9FF to @FF @L
< @F9 to 9FFF EL
= 9FF9 to @FFF 9<L
! @FF9 to 9FFFF 9!L
@ 9FFF9 and $bove >FL
> T7T$3 9FFL
Ga@$ 12D A@@#Himate HR 'ten)t$ in t$e #)aniEati#n
Ana!,'i'-
)rom the table and graph no.!.= it is evident that >FL of the organiGations have more than 9FFFF
employees whereas 9!L organiGations have an employee range of @FF9 to 9FFFF. The =
rd
common ranges of employees are in between 9FF9 to @FFF49<L5. The ne0t < categories fall
within the range of @F9 to 9FFF4EL5 and 9FF to @FF4@L5 respectively.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that most of the respondents belong to large organiGations but small and medium
siGed enterprises 4"#6s5 also have a significant representation.
54
Tab!e 121 Re'@#n'e #" t$e #)aniEati#n' t#(ad' HR #ut'#u%in)
"r. :o. *esponse *egarding 2* 7utsourcing (ercentage
9 Ces B!L
< :o <>L
= T7T$3 9FFL
Ga@$ 121 Re'@#n'e #" t$e #)aniEati#n' t#(ad' HR #ut'#u%in)
Ana!,'i'-
)rom the table and graph no.!.! it is evident that B>L organiGations practices 2*7 on a
regular basis while the rest <>L do not outsource 2* functions.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that majority of 2* managers feel that 2* functions should be outsourced for
various important reasonsJ e.g. to reduce cost, to focus and improve the core competencies of the
business, still there is a significant no. of 2* managers who don1t agree with 2* outsourcing
because it wea-ens the in.house 2* department.
55
Tab!e 127 A@@#Himate n#2 #" @e#@!e #ut'#u%ed b, >ai#u' #)aniEati#n'
"r. :o.
$ppro0imate :o. 7f (eople 7utsourced By Different
7rganiGations
(ercentage
9 9FF to @FF 9!L
< @F9 to 9FFF 9>L
= 9FF9 to @FFF !FL
! @FF9 and $bove =FL
@ T7T$3 9FFL
Ga@$ 127 A@@#Himate n#2 #" @e#@!e #ut'#u%ed b, >ai#u' #)aniEati#n'
Ana!,'i'-
)rom the table and graph no!.@ it is evident that the ma0imum no. of people outsourced by
different organiGations fall between the range of 9FF9 to @FFF, i.e. !FL. The ne0t common
range of human resource outsourced by different organiGations is @FF9 and above 4=FL5.
2owever some organiGations outsource smaller no. of people which come under the range of
@F9 to 9FF9. The minimum no. of people outsourced by various organiGations range from
9FF to @FF 49!L5.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus is clear that major #:s are now practicing heavy 2* outsourcing and are focusing
more on their core businesses. #ost of the organiGations are outsourcing a significant no. of
56
manpower which is up to @FFF 4!FL5 and more than @FFF 4=FL5. Thus it is clear that BFL
organiGations are outsourcing their 2* re'uirements. 6ven many small and medium siGe
enterprises 4"#6s5 are also outsourcing a considerable amount of human resource which
comes under the range of 9FF to 9FFF 4=FL5.
Tab!e 128 MaA# HR "un%ti#n' #ut'#u%ed b, >ai#u' #)aniEati#n'
57
58
S2 N#2
HR Fun%ti#n'
Out'#u%ed
E''entia!!,
Out'#u%ed
K
Fe&uent!,
Out'#u%ed K
S#metime'
Out'#u%ed
K
Rae!,
Out'#u%ed
K
Ne>e
Out'#u%e
dK
TOTA+
9
Pa,#!!
@#%e''in)
>@L <@L 9FL FL FL 9FFL
<
Tainin) and
De>e!#@ment
@BL <=L <FL FL FL 9FFL
= Re%uitment >BL <FL 9=L FL FL 9FFL
!
Man@#(e
@!annin)
@FL =FL 9@L @L FL 9FFL
@
Em@!#,ment +a(
and Re)u!at#,
C#m@!ian%e
@9L <FL 9EL 9FL FL 9FFL
> TaH Mana)ement ><L 9BL 9DL =L FL 9FFL
B
Pe"#man%e
Mana)ement
@9L <>L 9EL !L FL 9FFL
D
C#ndu%tin)
Em@!#,ee Su>e,
!@L ==L 9@L BL FL 9FFL
E
Maintenan%e #"
Pe'#na! Re%#d'
@<L <!L 9DL >L FL 9FFL
9F
Out'#u%in)
Entie HR
Fun%ti#n'
9@L 9@L <FL <FL =FL 9FFL
59
Ana!,'i'-
)rom the table and graph no.!.> it is evident that most of the organiGations outsource various 2*
functions on a regular basis. The most important 2* functions outsourced by them are (ayroll
processing, Training and Development, *ecruitment, #anpower planning, 6mployment 3aw and
*egulatory ompliance, Ta0 #anagement, (erformance #anagement, onducting 6mployee "urvey,
#aintenance of (ersonal *ecords, etc. The ma0imum percentage of E''entia!!, Out'#u%ed HR
Fun%ti#n' was *ecruitment 4>BL5, (ayroll (rocessing 4>@L5 and Ta0 #anagement 4><L5. The
minimum incidence of essentially outsourced 2* functions was outsourcing entire 2* functions 49@L5
and conducting employee survey 4!@L5. 2owever the other 2* functions which were essentially
outsourced are #aintenance of (ersonal *ecords 4@<L5, (erformance #anagement 4@9L5, 6mployment
3aw and *egulatory ompliance 4@9L5 and #anpower (lanning 4@FL5 respectively. $s far as the
percentage of Fe&uent!, Out'#u%ed HR Fun%ti#n' is considered, the ma0imum incidence was of
conducting employee survey 4==L5, #anpower planning 4=FL5, (erformance #anagement 4<>L5,
(ayroll processing 4<@L5, #aintenance of (ersonal *ecords 4<!L5 and training and Development 4<=L5
respectively. 2owever the minimum percentages of 2* functions outsourced in this category were of
outsourcing entire 2* functions 49@L5, Ta0 #anagement 49BL5, *ecruitment 4<FL5 and 6mployment
3aw and *egulatory ompliance 4<FL5 respectively.
$s far as the percentage of S#metime' Out'#u%ed HR "un%ti#n' is concerned, the ma0imum no. of
incidences were of training and development, 7utsourcing 6ntire 2* functions 4<FL each5, followed by
performance management and 6mployment 3aw and *egulatory ompliance 49EL each5 along with Ta0
#anagement and #aintenance of (ersonal *ecords 49DL each5 followed by #anpower (lanning and
onducting 6mployee "urvey 49@L each5 respectively. 2owever the minimum percentage of 2*
)unctions outsourced in this category were of (ayroll (rocessing 49FL5 and *ecruitment 49=L5. $s far as
the percentage of Rae!, Out'#u%ed HR "un%ti#n' is concerned, the ma0imum no. of incidences were
of outsourcing entire 2* functions 4<FL5, 6mployment 3aw and *egulatory ompliance 49FL5 followed
by conducting employee survey 4BL5 and #aintenance of (ersonal *ecords 4>L5 respectively. 2owever
the minimum percentage of 2* )unctions outsourced in this category were of Ta0 #anagement 4=L5,
(erformance #anagement 4!L5 and #anpower (lanning 4@L5 respectively. $s far as the percentage of
Ne>e Out'#u%ed HR "un%ti#n' is concerned, the ma0imum no. of incidence was of 7utsourcing 6ntire
2* functions 4=FL5 and the rest of the outsourced 2* functions were nil 4FL5.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that the most commonly outsourced 2* functions by most of the organiGations +
companies are *ecruitment 4>BL5, (ayroll (rocessing 4>@L5 and Ta0 #anagement 4><L5. The
ne0t most common category of outsourced 2* functions is Training + Development 4@BL5,
60
#aintenance of (ersonal *ecords 4@<L5 and (erformance #anagement 4@9L5, 6mployment
3aw + *egulatory ompliance 4@9eachL5. Thus it is clear that most of the 2* functions are
outsourced regularly. Thus it is evident that 2* 7utsourcing is an evolving industry and 2*7
functions as a strategic tool aimed primarily to assist organisations on their core businesses.
Tab!e 12F Im@#tant ea'#n' "# #ut'#u%in) HR "un%ti#n' b, >ai#u' #)aniEati#n'
61
S2
N#2
Im@#tant ea'#n' "#
#ut'#u%in) HR "un%ti#n'
M#'t
Im@#tant
Rea'#n
Mu%$
Im@#tant
Rea'#n
Im@#tant
Rea'#n
+e''
Im@#tant
Rea'#n
+ea't
Im@#tant
Rea'#n
TOTA+
9 T# Sa>e C#'t BB 9= 9F F F 9FFL
< T# Sa>e Time B@ 9B D F F 9FFL
=
T# In%ea'e T$e Ca@a%it,
#" T$e O)aniEati#n
@B =9 9E = F 9FFL
! T# Gain TaH *ene"it >F 9! <> F F 9FFL
@
T# Im@#>e +e>e!' O"
Lua!it, 3 Pe"#man%e
!@ =@ 9@ @ F 9FFL
> T# Im@#>e E""i%ien%, =D !< 9D < F 9FFL
B T# In%ea'e P#du%ti>it, >! 9! 99 E < 9FFL
D
T# Im@#>e Lua!it, #"
Se>i%e
@! <B 9= > F 9FFL
E T# A%$ie>e *ette ROI @D 9E 99 9< F 9FFL
9F
T# Gain EH@eti'e
Su@@#t
@> <! 9< D F 9FFL
62
Ana!,'i'-
)rom the table and graph no.!.B it is evident that various organiGations are outsourcing different
2* functions on a regular basis on account of different reasons out of which t$e m#'t
im@#tant ea'#n' are to M'a>e %#'tM or to reduce costs 4BBL5, to 'a>e time 4B@L5, to gain
ta0 benefit 4>FL5, to increase the capacity of organiGation 4@BL5, to achieve better *7I 4*eturn
7n Investment5 4@DL5, t# in%ea'e @#du%ti>it, <81K=5 to gain e0pert support 4@>L5, to
improve 'uality of service 4@!L5, to improve level of 'uality + performance 4!@L5 and to
improve efficiency 4=DL5. Thus it is clear that the most important causes of 2*7 areK
To save cost 4BBL5
To save time 4B@L5
To increase productivity 4>!L5
The least important cause is to increase efficiency 4=DL5. 2owever among much important
reasons of 2*7, %to improve efficiency& is on the top 4!<L5 followed by %to improve level of
'uality + performance 4=@L5, %to improve Suality of service& 4<BL5, to increase the capacity of
organiGation 4=9L5 and to gain e0pertise support 4<!L5 respectively whereas the least important
cause in this group is to save cost 49=L5, followed by ta0 benefit + increase in
productivity49!Leach5 followed by %to save time 49BL5 and to achieve better *7I 49EL5. In the
im@#tant ea'#n' category, the ma0imum incident is of %to gain ta0 benefit 4<>L5 and
minimum is of %to save time 4DL5. In !e'' im@#tant ea'#n' )#u@, the ma0imum incident co.
relates %to achieve better *7I 49<L5 and the minimum incidence co.relates to %improve
efficiency 4<L5&. 2owever in !ea't im@#tant %ate)#,, only one factor is identified which co.
relates with improved productivity. Thus it is clear that increase productivity is a consistent
reason for 2*7 in all the categories.
Inte@etati#n-
Thus it is clear thatK
$5 The most important reasons for 2*7 areK 4B5 the other important reasons for 2*7
areK
To save cost .BBL NTo achieve better *7I .@DL
To save time .B@L NTo increase capacity of organiGation.@BL
To increase productivity.>!L NTo gain e0pertise support.@>L
63
To gain ta0 benefit.>FL NTo improve the 'uality of service.@!L
Tab!e 129 Im@#tant "a%t#' "# %$##'in) a t$id @at, 'u@@!ie "# HR #ut'#u%in)
Ana!,'i'-
)rom the table and graph no.!.D, it is evident that t$e m#'t im@#tant "a%t#' "# %$##'in) a
>end# # t$id @at, 'u@@!ie "# HRO are service 'uality 4B@L5, e0isting relationship 4>>L5
64
S2
N#
Im@#tant Fa%t#' F# C$##'in)
A T$id Pat, Su@@!ie F# HR
Out'#u%in)
M#'t
Im@#tant
Fa%t#'
Mu%$
Im@#tant
Fa%t#'
Im@#tant
Fa%t#'
+e''
Im@#tant
Fa%t#'
TOTA+
9 +#(e't C#'t >@ <@ 9! > 9FFL
< Se>i%e Lua!it, B@ 9E @ 9 9FFL
= EHi'tin) Re!ati#n'$i@ >> <! 9B = 9FFL
! St#n) HR P#%e'' EH@eti'e >@ 9E 9@ 99 9FFL
@ Sten)t$ In Cu't#miEed S#!uti#n =< <B == D 9FFL
+ strong 2* process e0pertise 4>@L5. The ne0t common causes in this category are lowest cost
4>@L5 and strength in customiGed solutions 4=<L5.
In t$e %ate)#, #" mu%$ im@#tant "a%t#' for choosing a vendor to provide 2*7 services, the
reasons which have been identified are customiGed solutions 4<BL5, lowest cost 4<@L5 +
e0isting relationship 4<!L5. 2owever the service 'uality + strong 2* process e0pertise are also
e0pressed as important reasons.
In im@#tant "a%t# )#u@ strength in customiGed solutions is on the top 4==L5 + service
'uality is at the bottom level 4@L5. The other factors in this category are e0isting relationship
49BL5, strong 2* (rocess 60pertise 49@L5 + lowest cost 49!L5.
$s far as the !e'' im@#tant 3 !ea't im@#tant reasons are concerned, the ma0imum incidences
are of strong 2* process e0pertise 499L5 and strength in customiGed solutions 4DL5 followed by
lowest cost 4>L5 + service 'uality 49L5. In least important group, no factor was identified.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that in the opinion of most of the 2* managers, the most important reasons to
select a vendor or third party supplier areK
"ervice Suality 4B@L5
60isting *elationship 4>>L5
3owest ost 4>@L5
"trong 2* (rocess 60pertise 4>@L5
2owever strength in customiGed solutions 4=<L5 is also seen as an important factor to select the
vendor for different services which are being outsourced by the various organiGations. In this
conte0t, it is very relevant to e0plain that the factor of lowest cost is not so significant as the
'uality of service + e0isting relationship between the two parties. "o it is conclude that though
the lowest cost is an important factor in choosing the vendor or third party supplier for
7utsourcing different 2* )unctions but the 'uality of service + e0isting relationship with the
vendor are of great significance.
65
Tab!e 12/ O@ini#n' #n di""eent a'@e%t' #" HR #ut'#u%in) in e!ati#n t# >ai#u' HR
"un%ti#n'2
Ga@$ 12/ O@ini#n' #n di""eent a'@e%t' #" HR #ut'#u%in) in e!ati#n t# >ai#u' HR
"un%ti#n'
Ana!,'i'-
)rom the table and graph no.!.E, it is evident that DFL of the 2* #anagers have completely
agreed with the fact that HR Out'#u%in) i' an an'(e t# a>#id $i)$ !ab# %#'t 3 eH@en'i>e
66
S2
N#
Di""eent a'@e%t' #" HR #ut'#u%in) O@ini#n
ompletely
agree
#ostly
agree
$gree
(artially
agree
Disagree T7T$3
9.
Is 2* outsourcing is the answer to avoiding
high labour cost + e0pensive technologyN
DF 9> ! F F 9FFL
<.
Is 2* outsourcing is a viable choice for small
to mid.siGed businesses to limit staffing
burdens while maintaining high 'uality 2*
functionsN
>F <= 9F B F 9FFL
=.
Is 2* outsourcing can provide services +
highly trained professionals that businesses
need often with significant cost savings over
hiring full time 2* staffN
!@ <B <= @ F 9FFL
te%$n#!#),2 9>L 2* #anagers M#'t!, a)eed with the above factJ however !L did agree that
the above fact is true in relation with 2* 7utsourcing.
$s far as the statement I' HR #ut'#u%in) i' a >iab!e %$#i%e "# 'ma!! t# mid6'iEed bu'ine''e' t#
!imit 'ta""in) buden' ($i!e maintainin) $i)$ &ua!it, HR "un%ti#n'O is concerned, >FL of the 2*
#anagers completely agreed, <=L mostly agreed, 9FL just agreed + BL partially agreed but none of
them was against the above fact.
A' "a a' t$e 'tatement I' HR #ut'#u%in) %an @#>ide 'e>i%e' 3 $i)$!, tained @#"e''i#na!' t$at
bu'ine''e' need #"ten (it$ 'i)ni"i%ant %#'t 'a>in)' #>e $iin) "u!! time HR 'ta""O& is concerned, !@L
of the 2* #anagers completely agreed, <BL mostly agreed, <=L just agreed + @L partially agreed but
none of them was against the above fact.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that all the three facts about 2* outsourcing are very relevant + are of great
significance because DFL, >FL and !@L 2* managers support the above opinions related to 2*
7utsourcing. Thus it is evident thatK
2* 7utsourcing is the answer to avoid high labour cost
2* outsourcing is a viable choice for small to mid.siGed businesses
2* outsourcing can provide better services + highly trained professionals at
comparatively lower cost
Tab!e 124. T,@e #" t$e !e)a! 'e>i%e a)eement 'tandad in%!uded in HR Out'#u%in)
C#nta%t
S2 N#2 +e)a! Se>i%e A)eement Standad In%!uded In HRO
C#nta%t
Pe%enta)e
9 6mployee "atisfaction =FL
< Issue *esolution =>L
= Delivery of Data <<L
! "ystem $vailability 9<L
@ T7T$3 9FFL
67
Ga@$ 124. T,@e #" t$e !e)a! 'e>i%e a)eement 'tandad in%!uded in HR Out'#u%in) C#nta%t
Ana!,'i'-
)rom the table and graph no.!.9F, it is evident that issue resolution 4=>L5, had been the most
important legal service agreement standard of 2*7 contract, while system availability 49<L5,
was least important reason for this fact. 2owever employee satisfaction 4=FL5 + delivery of data
4=<L5 had also been the important factors of this issue of 2* outsourcing.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that issue resolution 4=>L5 must be -ept in mind and should be essentially
fulfilled in the matter of legal service agreement standard of 2* outsourcing, but rest of the
factors, i.e., 6mployee "atisfaction 4=FL5, Delivery of Data 4<<L5 and "ystem $vailability
49<L5 can1t be ignored in this respect.
68
Tab!e 1244 HR Fun%ti#n' W$i%$ Ae N#t Out'#u%ed O *ein) Out'#u%ed Eit$e
Patia!!, # C#m@!ete!,2
S2
N#
MaA# HR Fun%ti#n'
N#t
Out'#u%ed
K
Patia!!,
Out'#u%ed
K
C#m@!ete!,
Out'#u%ed
K
TOTA+
4 Pa,#!! @#%e''in) 4.K ::K 89K 4..K
: Tainin) 3 De>e!#@ment 9K 4/K FDK 4..K
D Re%uitment 44K 4:K FFK 4..K
1 Man@#(e @!annin) :.K 17K D7K 4..K
7
Em@!#,ment +a( 3 Re)u!at#,
C#m@!ian%e
D.K 77K 47K 4..K
8 TaH Mana)ement :7K D/K D8K 4..K
F Pe"#man%e Mana)ement 4FK 7:K D4K 4..K
9 C#ndu%tin) Em@!#,ee Su>e, 74K D1K 47K 4..K
/
Maintenan%e #" Pe'#na!
Re%#d'
:.K 17K D7K 4..K
69
70
Ana!,'i'-
)rom the table and graph no. !.99, it is evident that the maA# HR "un%ti#n' which are
%#m@!ete!, #ut'#u%ed by different organiGations are e%uitment 4BBL5, tainin) 3
de>e!#@ment 4B=L5, @a,#!! @#%e''in) 4>DL5.Ta0 management 4=>L5, #aintenance of
(ersonnel *ecords 4=@L5, #anpower (lanning 4=@L5 and (erformance #anagement 4=9L5. The
other 2* )unctions which are completely outsourced are 6mployment 3aw + *egulatory
ompliance as well as onducting 6mployee "urvey 49@L each5.
The HR Fun%ti#n' which are Patia!!, Out'#u%ed are 6mployment 3aw + *egulatory
ompliance 4@@L5, (erformance #anagement 4@<L5, #aintenance of (ersonal *ecords 4!@L5,
and #anpower (lanning 4!@L5. The other partially outsourced 2* )unctions are onducting
6mployee "urvey 4=!L5, training + development 49EL5 and *ecruitment 49<L5.
There are some organiGations which do not outsource some of their 2* )unctions li-e
onducting 6mployee "urvey 4@9L5, 6mployment 3aw + *egulatory ompliance 4=FL5, Ta0
#anagement 4<@L5, #anpower (lanning and #aintenance of (ersonal *ecords 4<FL each5.
2owever minimum incidences of 2* )unctions which are not outsourced by certain
organiGation are (ayroll (rocessing 49FL5, Training + Development 4DL5 and *ecruitment
499L5.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that the *ecruitment is the most important 2* function which is completely
outsourced by BBL of organiGations, partially outsourced by 9<L and not outsourced by 99L of
organiGations. Training + Development is the ne0t most important 2* )unction which is
completely outsourced by B=L of organiGations while 9EL of organiGations outsourced it
partially but DL organiGations handle it in.house. (ayroll processing is another important 2*
)unction which is completely outsourced by >DL organiGations, partially outsourced by <<L and
not outsourced by 9FL of organiGations.
The ne0t important 2* functions which are completely outsourced by =>L, =@L, =9L and 9@L
of organiGations are Ta0 #anagement, #aintenance of (ersonnel records, (erformance
#anagement, onducting 6mployee "urvey and 6mployment 3aw + *egulatory ompliance
respectively. The other important 2* )unctions which are partially outsourced by @@L, @<L,
!@L, =EL and =!L of the organiGations are 6mployment 3aw + *egulatory ompliance,
(erformance #anagement, #anpower planning , #aintenance of (ersonnel *ecords, Ta0
#anagement and onducting 6mployee "urvey.
71
The 2* )unctions which are not outsourced by @9L, =FL, <@L, <FL and 9BL of the
organiGations are onducting 6mployee "urvey, 6mployment 3aw + *egulatory ompliance
Ta0 #anagement, #anpower planning, #aintenance of (ersonnel records and (erformance
#anagement respectively.
Tab!e 124: O@ini#n ab#ut t$e im@a%t #" HR Out'#u%in) #n >ai#u' HR attibute'2
"r. :o HR Attibute' EH%e!!ent Ve,
G##d
G##d A>ea)e P## TOTA+
9 *u'ine'' @e"#man%e >F <F 9= B F 9FFL
< Em@!#,ee 3 O)aniEati#n C#6
#dinati#n
@= 9E <! ! F 9FFL
= Em@!#,ee G#b6Fit !E <= 9@ 9= F 9FFL
! Em@!#,ee Pe"#man%e @D 9> << ! F 9FFL
@ Em@!#,ee De>e!#@ment >@ 9@ E 99 F 9FFL
> Em@!#,ee M#a! 3 M#ti>ati#n !@ <! 9= 9D F 9FFL
B Em@!#,ee Sati'"a%ti#n @< 9E 9> 9= F 9FFL
D E""e%ti>ene'' #" tainin) >B 9D 9< = F 9FFL
Ga@$ 124: O@ini#n' ab#ut t$e im@a%t #" HR Out'#u%in) #n >ai#u' HR
Ana!,'i'K
72
It is evident from the table and graph no.!.9< that 2* 7utsourcing has an EH%e!!ent @#'iti>e
im@a%t& on various 2* attributes and )unctions such as 6ffectiveness of training 4>BL5,
6mployee Development 4>@L5, Business (erformance 4>FL5, 6mployee (erformance 4@DL5,
6mployee + 7rganiGation o.7rdination 4@=L5, 6mployee ?ob fit 4!EL5 and 6mployee #oral
+ #otivation 4!@L5.
$s far as the %Ve, G##d P#'iti>e Im@a%t of 2* outsourcing on different 2* )unctions +
$ttributes is concerned it was found to be <!L, <=L, <FL. 9EL, 9DL, 9> L + 9@L for
6mployee #oral + #otivation, 6mployee ?ob fit, , 6mployee "atisfaction, 6mployee +
7rganiGation o.7rdination, 6mployee (erformance and 6mployee Development respectively.
$s far as the %G##d P#'iti>e Im@a%t of 2* outsourcing on different 2* )unctions +
$ttributes is concerned it was found to be <!L, <<L, 9>L, 9@L, 9=L, 9<L + EL for 6mployee
+ 7rganiGation o.7rdination, 6mployee (erformance, 6mployee "atisfaction, 6mployee ?ob
fit, 6mployee #oral + #otivation, 6ffectiveness of Training and 6mployee Development
respectively.
$s far as the %A>ea)e P#'iti>e Im@a%t of 2* outsourcing on different 2* )unctions +
$ttributes is concerned it was found to be 9DL, 9=L, 99L, BL, !L + =L for 6mployee #oral
+ #otivation, 6mployee ?ob fit + 6mployee "atisfaction, 6mployee Development, Business
(erformance, 6mployee (erformance, 6mployee + 7rganiGation o.7rdination and
6ffectiveness of Training respectively.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that 2* 7utsourcing has an EH%e!!ent P#'iti>e Im@a%t on 6ffectiveness of
Training 4>BL5, 6mployee Development 4>@L5 and Business (erformance 4>FL5. 2*
7utsourcing has a Ve, )##d P#'iti>e Im@a%t on 6mployee #oral + #otivation 4<!L5,
6mployee ?ob fit 4<=L5, 6mployee "atisfaction 49EL5, 6mployee (erformance 49>L5 and
6mployee + 7rganiGation o.7rdination 49EL5.
Thus it clear that 2* 7utsourcing is a boon for enhancing various organiGational capacities and
for overall improvement of different 2* functions of different organiGations according to their
various needs + re'uirements.
73
Tab!e 124D O@ini#n ab#ut Out'#u%in) O@ti#n' (it$ Re"een%e T# #)aniEati#na! HR
P#!i%ie'5 Pa%ti%e' 3 Ta!ent Need' #" IT Indu't,
S2 N#2 Re'@#n'e Re)adin) HR Out'#u%in) Pe%enta)e
4 Ye' F8K
: N# 47K
D CanPt Sa, /K
1 TOTA+ 4..K
Ga@$ 124D O@ini#n ab#ut Out'#u%in) O@ti#n' (it$ Re"een%e T# #)aniEati#na! HR
P#!i%ie'5 Pa%ti%e' 3 Ta!ent Need' #" IT Indu't,
74
Ana!,'i'
It is evident from the Table and ,raph no. !.9= that most of the 2* #anagers 4B>L5 are of the
opinion that 2* 7utsourcing can boost the performance of IT industriesJ however 9@L were of
the opinion that it may impact negatively. 2owever EL 2* #anagers were indifferent.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear majority of 2* #anagers 4B>L5 are of the opinion that to improve the condition
of the IT industries, 2* 7utsourcing is essential, but while doing so proper care + precaution
should be applied so as to ensure the proper implementation of organiGational policies +
practices.
Tab!e 1241 O@ini#n #" HR Mana)e' #n ($et$e HR Out'#u%in) ma, $e!@ t# edu%e t$e
Rate #" Attiti#n in IT O)aniEati#n'O
S2
N#2
O@ini#n #" HR Mana)e' #n M($et$e HR Out'#u%in) ma,
$e!@ t# edu%e t$e Rate #" Attiti#n in IT O)aniEati#n'OM
Pe%enta)e
4 Ye' 98K
: N# .9K
D CanPt Sa, .8K
1 TOTA+ 4..K
Ga@$ 1241 O@ini#n #" HR Mana)e' #n ($et$e HR Out'#u%in) ma, $e!@ t# edu%e t$e
Rate #" Attiti#n in IT O)aniEati#n'O
75
Ana!,'i'
It is evident from the above Table and ,raph that 2* 7utsourcing is very effective in controlling
the rate of attrition in the IT sector. D>L 2* managers supported the above viewJ however DL
were against it, while >L were having an indifferent opinion.
Inte@etati#nK
Thus it is clear that 2* 7utsourcing can effectively control the P#b!em Attiti#n in IT "ector.
Attiti#n is the biggest nightmare for 2* #anagers in IT services and outsourcing companies.
Thus it is clear that both 2* outsourcing + IT Industries may be benefitted by mutual co.
operation + co.ordination because they are inter.dependent and inter.related as D>L 2*
#anagers agreed with the above fact.
Tab!e 1247 O@ini#n #" HR Mana)e' #n $#( (e!! $a>e ,#u HR #ut'#u%ed "un%ti#n'
"u!"i!!ed t$ei #bAe%ti>e'O
76
S2
N#2
O@ini#n #" HR Mana)e' #n H#( (e!! $a>e ,#u HR
#ut'#u%ed "un%ti#n' "u!"i!!ed t$ei #bAe%ti>e'
Pe%enta)e
4 EH%e!!ent F9K
: Ve, G##d 44K
D G##d FK
1 A>ea)e 1K
7 Detei#ated .K
8 TOTA+ 4..K
Tab!e 1247 O@ini#n #" HR Mana)e' #n $#( (e!! $a>e ,#u HR #ut'#u%ed "un%ti#n'
"u!"i!!ed t$ei #bAe%ti>e'O
Ana!,'i'
77
)rom the table and graph no. !.9@ it is clear that outsourced 2* )unctions were eH%e!!ent in
fulfilling the different objectives and needs of the organiGations for which they were underta-en.
BDL of 2* #anagers agreed with this fact. 2owever 99L, Band !L were of the opinion that the
outsourced 2* functions were >e, )##d5 )##d 3 a>ea)e in fulfilling the given objectives.
Inte@etati#n
Thus it is clear that the concept of 2* 7utsourcing has proved to be a boon in completing the
different tas-s, objectives and needs for which they have been assigned. BDL 2* #anagers have
rated its efficiency as 60cellent, 99L have rated it as /ery ,ood, BL have rated it to be good
and the rest !L have rated it as $verage in performance. In no case Deterioration was observed.
Thus it has been proved that 2* outsourcing can provide services + highly trained professionals
that businesses need often with significant cost savings over hiring full time employees.
78
CHAPTER-"
#$MMAR%
&'
'I(I()#
CHAPTER67
79
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
The present study titled THE IMPACT OF HR OUTSOURCING ON VARIOUS HR
FUNCTIONS WITH REFERENCE TO IT INDUSTRY is an attempt to understand the pros
and cons of 2* 7utsourcing on various 2* functions. Based on the data collected an in.depth
analysis has been made and the results are interpreted. The following findings are given based on
the analysis of the data obtained through survey.
724 T# 'tud, t$e di""eent a'@e%t' #" HR #ut'#u%in)
To study the different aspects of 2* 7utsourcing, the 'uestions 9 to = + B to DJ from the
'uestionnaire have been used to collect the re'uired data and information on the basis of
which the following facts have been observed about the different aspects of 2* 7utsourcing.
#ost of the respondents belong to large organiGations but small + medium enterprises
4"#6s5 also have a significant representation and the majority of 2* #anagers feel that 2*
)unctions should be outsourced.
#ost of the organiGations are outsourcing a significant no. of manpower which is up to @FFF
and even more than @FFF. "mall and medium siGe enterprises 4"#6s5 are also outsourcing a
considerable amount of 2*, which comes under the range of 9FF to 9FFF.
2* 7utsourcing is an answer to avoid high labour cost + e0pensive technology.
2* outsourcing is a viable choice for small to mid.siGed businesses to limit staffing burdens
while maintaining high 'uality 2* functions.
2* outsourcing can provide services + highly trained professionals that businesses need
often with significant cost savings over hiring full time 2* staff.
$s far as the legal service agreement standard included in 2* 7utsourcing contract is
concerned, the Issue resolution, had been the most important legal service agreement
standard of 2*7 contract. 2owever employee satisfaction + delivery of data had also been
the important factors of this issue of 2* outsourcing.
72: T# 'tud, t$e im@#tant ea'#n' "# HR Out'#u%in)
80
To -now the important reasons for 2* 7utsourcing, the 'uestion no.@ from the 'uestionnaire
has been used to collect the re'uired data and information on the basis of which the
following facts have been observed about the important reasons for 2* 7utsourcing in the
order of rating, merit and significance.
$5 The most important reasons for 2*7 areK 4B5 the other important reasons for 2*7
areK
To save cost NTo achieve better *7I
To save time NTo increase capacity of organiGation
To increase productivity NTo gain e0pertise support
To gain ta0 benefit NTo improve the 'uality of service
To improve levels of performance N To improve efficiency
72D T# 'tud, t$e im@#tant "a%t#' e'@#n'ib!e t#(ad' %$##'in) a t$id @at, 'u@@!ie "#
HR Out'#u%in)2
)or this purpose 'uestion no.> has been used from the 'uestionnaire to collect the re'uired data
and information on the basis of which the following facts have been observed in relation to the
important reasons for choosing a third party supplier for 2* 7utsourcing in the order of rating,
merit and significance.
"ervice Suality
60isting *elationship
3owest ost
"trong 2* (rocess 60pertise
"trength In ustomiGed "olution
In this reference, a relevant factor was noted that though the lowest cost was considered as an
important factor in choosing the vendor or third party supplier for outsourcing different 2*
)unctions but most of the managers gave top priority to the 'uality of service and their e0isting
relationship with the vendor.
81
721 T# 'tud, t$e maA# HR "un%ti#n' bein) #ut'#u%ed in t$e Indian indu't, eit$e
%#m@!ete!, # @atia!!,
)or this purpose 'uestions ! + E from the 'uestionnaire have been used to collect the re'uired
data and information on the basis of which the following facts have been observed in relation to
the major 2* functions being outsourced in the Indian industry either completely or partially in
the order of rating, merit and significance.
The most commonly outsourced 2* functions by most of the organiGations + companies were
*ecruitment, (ayroll (rocessing and Ta0 #anagement. The ne0t most common category of
outsourced 2* functions was Training + Development, #aintenance of (ersonal *ecords,
(erformance #anagement and 6mployment 3aw + *egulatory ompliance.
The major 2* functions which are completely outsourced by different organiGations are
recruitment, training + development, payroll processing +Ta0 management
The 2* )unctions which are (artially 7utsourced are 6mployment 3aw + *egulatory
ompliance, (erformance #anagement, #aintenance of (ersonal *ecords, and #anpower
(lanning and onducting 6mployee "urvey.
727 T# 'tud, t$e im@a%t #" HR #ut'#u%in) #n >ai#u' HR "un%ti#n' 3 #n t$e e""e%ti>ene''
#" t$e HR de@atment2
)or this purpose 'uestion 9F from the 'uestionnaire have been used to collect the re'uired data
and information on the basis of which the following facts have been observed in relation to the
impact of 2* outsourcing on the various 2* functions + on the effectiveness of the 2*
department in the order of rating, merit and significance.
2* 7utsourcing is a boon for enhancing various organiGational capacities and for overall
improvement of different 2* functions of different organiGations according to their various
needs + re'uirements
2* 7utsourcing has an 60cellent (ositive Impact onK
6ffectiveness of Training
6mployee Development
Business (erformance
82
2* 7utsourcing has a /ery good (ositive Impact onK
6mployee #oral + #otivation
6mployee ?ob fit
6mployee "atisfaction
6mployee (erformance
6mployee + 7rganiGation o.7rdination
728 T# 'tud, t$e %#6e!ati#n bet(een HR Out'#u%in) 3 IT indu't,
)or this purpose 'uestions 99 and 9< from the 'uestionnaire have been used to collect the
re'uired data and information on the basis of which the following facts have been observed with
reference to the co.relation between 2* 7utsourcing + IT industry.
#ajority of 2* #anagers are of the opinion that to improve the condition of the IT
industries, 2* 7utsourcing is essential.
#ajority of 2* #anagers agreed with the fact that both 2* outsourcing + IT Industries
may be benefitted by mutual co.operation + co.ordination because they are inter.
dependent and inter.related.
that 2* 7utsourcing is very effective in controlling the rate of attrition in the IT sector
72F T# 'tud, t$e e""e%ti>ene'' #" HR "un%ti#n t$at i' bein) #ut'#u%ed2
)or this purpose 'uestion 9= from the 'uestionnaire has been used to collect the re'uired data and
information on the basis of which the following facts have been observed with reference to the
effectiveness of 2* function that is being outsourced in the order of rating, merit and
significance.
2* 7utsourcing has proved to be a boon in completing the different tas-s, objectives and
needs for which they have been assigned. BDL 2* #anagers have rated its efficiency as
60cellent, 99L have rated it as /ery ,ood, BL have rated it to be good and the rest !L
have rated it as $verage in performance. In no case Deterioration was observed.
83
CHAPTER-*
#$))E#TI&(
# A(
C&(C+$#I&(
#
84
SUGGESTIONS
7n the basis of the present study, the following recommendations are suggested for a successful
2* outsourcingK
The outloo- of the Indian industry is gradually shifting from anti to pro towards 2*
outsourcing, but there is still a long way to go as far as trusting an outside organiGation
4vendor5. The companies need to build a relation of trust and understanding with total
communication as the base. This would help to serve the interest of both the parties better
and to a greater e0tent.
In terms of effectiveness, it is important for the company to be engaged continuously with
the vendors in order to succeed. Unless one engages with the vendor upfront to e0plain the
re'uirements and e0pectations in detail, it is difficult to get efficient results from outsourced
operations. $ccountability is the -ey success factor.
)ortnightly or monthly meetings should be held with the vendors in order to understand the
level of progress as well as to assess the needs of the vendors. Understanding the business
from the vendor1s point of view is essential for the success of any outsourcing contract.
ompensation of the employees is a major factor which should be -ept in mind before
outsourcing. The amount of compensation has a significant impact on the effectiveness of the
2* functions. )or e0ample as the avg. #onthly salary increases the effectiveness of the
outsourced recruitment with respect to the level of psychological contract proportionately
increases. "o in such cases companies paying higher compensation can outsource their
recruitment function to a vendor for greater effectiveness.
The outsourcer should e0ercise great care while engaging a vendor. This tas- will largely
determine the success of the partnership. The tas- may be entrusted to a consulting company
or be done in.house. In the latter, the outsourcer can form a team to select the vendor
85
Based on the analysis it is important to device a proper reporting relationship with the vendor
for an on.going and transparent communication process to ma-e 2* outsourcing more
effective. )or this purpose, first shortlist probable candidates and brief them clearly about the
job e0pectations. These e0pectations have to be realistic and achievable. This will in turn
help the service provider to assess whether it can measure up to those e0pectations.
(rovide enough information to the prospective service provider with regard to the scope of
the relationship, the time. frame, and the price that is being offered in return for the services.
/ague issues should be clarified and prospective vendors should be as-ed to provide
references of clients whom they have served so as to get in touch with them and see- their
opinion about their services + performance.
)or effective 2* 7utsourcing, the client company should -eep in the mind the technical
-now. how and e0pertise available with the vendor. 60perience is also a factor that should be
considered. (ricing or the cost factor largely determines the success of outsourcing.
2owever, a low cost factor alone should not be the criterion for selection because the 'uality
of service has a great impact on the success of client.
The 2* vendor performs specialiGed operations to -eep up its mar-et competitivenessJ so the
employees of the vendor may need training to spruce up their s-ill. It will be in the client
companyIs interest to ensure and provide training to the outsourced employees. 3egal issues,
labor laws and ta0ation policies all have a major role in determining the success of
outsourcing so the terms and condition of the relationship should be mutually agreed and
written down in order to avoid confusion or vagueness.
It would be better for the client to entrust a small project to the service provider initially. This
will reduce the e0tent of ris- and give a fair idea of how well the service provider is going to
perform.
ultural differences are li-ely especially when it comes to offshore outsourcing. The
relationship between the outsourcer and the service provider is best served when these
differences are identified, understood and respected. (rograms to bridge the gap should be
held where both sides can come closer.
86
CONC+USION
This research helps to gain an insight to the contemporary developments in the field of 2*
outsourcing in the Indian industry. It helps to clarify many myths about 2* outsourcing and also
brings up interesting facts about the same. #ost of the respondents belong to large organiGations
but small and medium siGed enterprises 4"#6s5 also have a significant representation. #ost of
the organiGations are outsourcing a significant no. of manpower which is up to @FFF and even
more than @FFF. "mall and medium siGe enterprises 4"#6s5 are also outsourcing a considerable
amount of 2*, which comes under the range of 9FF to 9FFF.
The most important reasons for 2* outsourcing are to Hsave costH or to reduce costs, to %save
time&, to gain ta0 benefit, to increase the capacity of organiGation, to achieve better *7I 4*eturn
7n Investment5, to increase productivity, to gain e0pert support, to improve 'uality of service, to
improve level of 'uality + performance and to improve efficiency. The important reasons for
choosing a third party supplier for 2* 7utsourcing in the order of rating, merit and significance
are "ervice Suality, 60isting *elationship, 3owest ost, "trong 2* (rocess 60pertise and
"trength in ustomiGed "olution.2* 7utsourcing is essential to improve the condition of the IT
industries. 2* outsourcing + IT Industries both are benefitted by mutual co.operation + co.
ordination because they are inter.dependent and inter.related. It is very effective in controlling
the rate of attrition in the IT sector.
2* 7utsourcing is a very effective tool for enhancing various organiGational capacities and for
overall improvement of different 2* functions of different organiGations according to their
various needs and re'uirements and also in completing the different tas-s, objectives and goals
for which they have been assigned. It has an 60cellent (ositive Impact on 6ffectiveness of
Training, 6mployee Development and Business (erformance and it also has a very good positive
impact on 6mployee #oral + #otivation, 6mployee ?ob fit, 6mployee "atisfaction, 6mployee
(erformance and 6mployee + 7rganiGation o.7rdination.
87
The present study has been conducted on a smaller sample siGe due to time constraint and the
respondents were from specific areas and did not cover whole of India and the primary data is
based on the responses to the 'uestions which can be influenced by personal bias and subjective
perception of the individuals and the present study is limited only to IT Industry.
SUGGESTIONS FOR FURTHER RESEARCH
$lthough a lot of wor- has been done in similar areas before, this research is an effort to loo- at
the things from a fresh and a different angle. Thus this research wor- can be used as a source of
secondary data by other researchers as it contains significant amount of analysis in areas which
have not been e0plored much till now. It can also be used as a tool for comparative analysis of
the past and present 2* outsourcing scenario and to understand the changes that have ta-en
place. It is also suggested that further research studies should be conducted on this topic, on a
larger scale with a bigger sample siGe, including more industrial sectors which outsource
different 2* )unctions li-e IT6", 3ogistics, 2ealthcare, financial "ervices and #anufacturing
"ector in India.
88
,I,+I&)RAPH
%
89
*I*+IOGRAPHY
*##B'-
$rmstrong, # %$ 2andboo- of 2* management practices&, D
th
edition <FF<
G#una!'-
Bondarou-, T./. and *uel, 2.?.# 4<FFE5 %6lectronic 2uman *esource #anagement, the
International ?ournal of 2uman *esource #anagement.&
8ern, T and Blois, 8. 4<FF<5 %:orm development in outsourcing relationship, ?ournal of
Information Technology&
3ogan, #.". 4<FFF5 %Using $gency Theory to design successful outsourcing relationships,
International ?ournal of 3ogistics #anagement&
Re@#t' 3 Re>ie('-
2es-eth, $nthoy, $ report on %7utsourcing the 2* )unction. (ossibilities + (itfalls&
8lementive, $le0ey %"ociety 7) 2* #anagement. 7utsourcing "urvey *eport about 2*
7utsourcing&
#c)arlan, ).A. and :olan, *.3 49EE@5 %2ow to manage an IT outsourcing alliance, "loan
#anagement *eview&
:ahapiet, ?. and ,hoshal, ". 49EED5 %"ocial capital, intellectual capital, and the organiGational
advantage, $cademy of #anagement *eview&
Aillcoc-s, 3., 2indle, ?., )eeny, D., and 3acity, #. 4<FF!5. %IT and Business (rocess
7utsourcingK The 8nowledge (otential, Information "ystems #anagement&
Aillcoc-s, 3.(., and 8ern T. 49EEB5. $ report on %IT 7utsourcing as "trategic (artnering.&
Web'ite'-
www.google.com
www.hrmgt.com
www.shm.org 4"ociety for 2uman *esource #anagement5
www.younghrmanager.com
www.hr.com
www.hrmgt.com
90
A((E-$RE
91
ANNE?URE
Suestionnaire
7n
THE IMPACT OF HR OUTSOURCING ON VARIOUS HR FUNCTIONS
WITH REFERENCE TO IT INDUSTRY
4This Suestionnaire is being prepared purely for academic research purpose by #r.:irvanJ a #B$
)inal "emester "tudent of $charya Institute of #anagement $nd "ciences 4$I#"5, (eenya
Bangalore. This research wor- is done to complete my dissertation titled %T26 I#($T 7) 2*
7UT"7U*I:, 7: /$*I7U" 2* )U:TI7:" AIT2 *6)6*6:6 T7 IT I:DU"T*C& for
the degree of #B$ from Bangalore University. *espected "ir/ #a1am I need your valuable time +
support to complete my project, so please answer the following 'uestions by your e0perienced +
learned responses. The Data collected through this 'uestionnaire will be -ept completely
confidential.5
Designation. Department.
:o. of years of e0perience.
:ame of organiGation/company.
95 Ahat is the total manpower strength in your organiGationN
T(lease mention the appro0imate :o..
<5 2as your organiGation outsourced manpowerN
Ces
:o
=5 (lease specify the appro0imate no. of people outsourced by your organiGationN
9FF.@FF
@F9.9FFF
9FF9.@FFF
@FF9 + $bove
7thers, please specify.
92
!5 Ahat are the major 2* functions outsourced in your organiGationN
4(lease tic- in the given bo0es + also rate the outsourced 2* functions from 9 to @5
@.essentially outsourced, !.fre'uently outsourced, =.sometimes outsourced, <.rarely
outsourced,
9.never outsourced
(ayroll processing 9 < = ! @
Training + Development 9 < = ! @
*ecruitment 9 < = ! @
#anpower planning 9 < = ! @
6mployment 3aw + *egulatory ompliance 9 < = ! @
Ta0 #anagement 9 < = ! @
(erformance #anagement 9 < = ! @
onducting 6mployee "urvey 9 < = ! @
#aintenance of (ersonal *ecords 9 < = ! @
7utsourcing 6ntire 2* )unctions 9 < = ! @
@5 (lease rate the following reasons for outsourcing 2* functions by your organiGation from
9 to @N
@.most important, !.much important, =. important, <.less important, 9. least important
To save cost 9 < = ! @
To save time 9 < = ! @
To increase the capacity of the organiGation 9 < = ! @
To gain ta0 benefit 9 < = ! @
To improve levels of 'uality + performance 9 < = ! @
93
To improve efficiency 9 < = ! @
To increase productivity 9 < = ! @
To improve 'uality of service 9 < = ! @
To achieve better *7I 9 < = ! @
To gain e0pertise support 9 < = ! @
>5 Ahen choosing a third party supplier for 2* outsourcingJ what factors are most
important to youN
(lease rate them in order of their importance from 9 to @.
@.most important, !.much important, =. important, <.less important, 9. least important
3owest ost 9 < = ! @
"ervice Suality 9 < = ! @
60isting *elationship 9 < = ! @
"trong 2* (rocess 60pertise 9 < = ! @
"trength in ustomiGed "olutions 9 < = ! @
7ther factor if any please specify. 9 < = ! @
B5 Ahat is your opinion about different aspects of 2* outsourcing in relation to various 2*
functionsN
(lease rate them from 9 to @.
94
@.ompletely agree !. #ostly agree =. $gree <.(artially agree 9. Disagree
D5 Ahat is the legal service agreement standard included in your 2* outsourcing contractN
6mployee "atisfaction
Issue *esolution
Delivery of Data
"ystem $vailability
E5 (lease specify the different 2* functions which are being completely outsourced or
partially outsourced or not outsourced in your organiGationK
ompletely (artially :ot 7utsourced (ayroll processing
ompletely (artially :ot 7utsourced Training + Development
ompletely (artially :ot 7utsourced *ecruitment
ompletely (artially :ot 7utsourced #anpower planning
ompletely (artially :ot 7utsourced 6mp. 3aw + ompliance
ompletely (artially :ot 7utsourced Ta0 #anagement
ompletely (artially :ot 7utsourced (erformance #anagement
ompletely (artially :ot 7utsourced onducting 6mp. "urvey
ompletely (artially :ot 7utsourced #aintenance of (.*ecords
9F5 Ahat is your opinion about the Im@a%t of 2* outsourcing on various 2* $ttributesN
95
A'@e%t' 7pinion Aith *ating @ ; 9
a5 Is 2* outsourcing is the answer to avoiding high labour
cost + e0pensive technologyN
9 < = ! @
b5 Is 2* outsourcing is a viable choice for small to mid.siGed
businesses to limit staffing burdens while maintaining high
'uality 2* functionsN
9 < = ! @
c5 Is 2* outsourcing can provide services + highly trained
professionals that businesses need often with significant
cost savings over hiring full time 2* staffN
9 < = ! @
4(lease rate them from 9 to @5
@.60cellent !. /ery ,ood =. ,ood <.$verage 9. (oor
HR Attibute' Im@a%t (it$ atin) 7 t# 4
EH%e!!ent
Ve, G##d G##d A>ea)e P##
*u'ine'' @e"#man%e @ ! = < 9
Em@!#,ee 3 O)aniEati#n C#6#dinati#n @ ! = < 9
Em@!#,ee G#b6Fit @ ! = < 9
Em@!#,ee Pe"#man%e @ ! = < 9
Em@!#,ee De>e!#@ment @ ! = < 9
Em@!#,ee M#a! 3 M#ti>ati#n @ ! = < 9
Em@!#,ee Sati'"a%ti#n @ ! = < 9
E""e%ti>ene'' #" tainin) @ ! = < 9
995 Do you agree that 2* needs to help IT 7rganiGations to evaluate their outsourcing
options with reference to their 2* policies, practices + organiGational talent needsN
Ces
:o
an1t "ay
9<5 Do you thin- that 2* outsourcing can help to reduce the rate of attrition in IT
organiGationsN
Ces
:o
an1t "ay
9=5 2ow well have your 2* outsourced functions fulfilled their objectivesN
60cellent
/ery ,ood
,ood
$verage
Deteriorated
96
T$anB Y#uC
97
Você também pode gostar
- CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL - A Study On Indian Stock MarketsDocumento78 páginasCAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL - A Study On Indian Stock Marketsnikhincc100% (1)
- Internal and External Business EnvironmentDocumento7 páginasInternal and External Business EnvironmentMohammad RIzwan88% (34)
- Crompton Greaves - PPT Teachers NotesDocumento5 páginasCrompton Greaves - PPT Teachers NotesnikhinccAinda não há avaliações
- Project Report On Recriutment and SelectionDocumento62 páginasProject Report On Recriutment and SelectionnikhinccAinda não há avaliações
- Project FlipkartDocumento91 páginasProject Flipkartnikhincc77% (98)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- How To "Revert-Back" To "Previous-Version"???: Build 1 Testing DeploymentDocumento19 páginasHow To "Revert-Back" To "Previous-Version"???: Build 1 Testing DeploymentClaudiu Stefan HaiduAinda não há avaliações
- A Study On Pushover Analysis Using Capacity Spectrum Method Based On Eurocode 8Documento13 páginasA Study On Pushover Analysis Using Capacity Spectrum Method Based On Eurocode 8ephAinda não há avaliações
- ARIMI Et Al-2010-Journal of Texture Studies PDFDocumento21 páginasARIMI Et Al-2010-Journal of Texture Studies PDFRomaric OuetchehouAinda não há avaliações
- Have A One Track Mind: Lorna WingDocumento4 páginasHave A One Track Mind: Lorna WingsophilauAinda não há avaliações
- GED 7 Life and Works of Jose RizalDocumento104 páginasGED 7 Life and Works of Jose RizalRheamie Fuyonan100% (1)
- Design MatrixDocumento1 páginaDesign MatrixThakur Kali DassAinda não há avaliações
- Visual Programming NotesDocumento0 páginaVisual Programming NotesSamuel VictorAinda não há avaliações
- Linux Lab-1Documento32 páginasLinux Lab-1Naveen KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Gep Primary Water Resource Aug12 NSWDocumento50 páginasGep Primary Water Resource Aug12 NSWNitin AroraAinda não há avaliações
- PhotoshopCC KBSCDocumento4 páginasPhotoshopCC KBSCHusk EisbornAinda não há avaliações
- Eaton Industrial Special Process List (SPL)Documento5 páginasEaton Industrial Special Process List (SPL)amirkhakzad498Ainda não há avaliações
- 6-Boundary and Initial ConditionsDocumento8 páginas6-Boundary and Initial ConditionsqazwsxAinda não há avaliações
- G-10 Biology, 3rd Work Sheet On Nervous SystemDocumento3 páginasG-10 Biology, 3rd Work Sheet On Nervous SystemhannahAinda não há avaliações
- Toplotna Pumpa Hidria Clint - Eu - Cha K - 182 P 604 P - cls61.7 EngDocumento2 páginasToplotna Pumpa Hidria Clint - Eu - Cha K - 182 P 604 P - cls61.7 EngMuhidin KozicaAinda não há avaliações
- Competitiveness Huawei Casestudy WebDocumento40 páginasCompetitiveness Huawei Casestudy Webjameslee27Ainda não há avaliações
- Kinematics of A Novel Nine Degree of Freedom Configurable Gough-Stewart PlatformDocumento19 páginasKinematics of A Novel Nine Degree of Freedom Configurable Gough-Stewart PlatformNeider NadidAinda não há avaliações
- Recap For Inset 03-16-2021Documento1 páginaRecap For Inset 03-16-2021Melicia LimboAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Reservoir Heterogeneity in Laminated ReservoirsDocumento3 páginasEffects of Reservoir Heterogeneity in Laminated ReservoirsErik Andres Garcia VillarroelAinda não há avaliações
- The Roleof Social Media MarketingDocumento13 páginasThe Roleof Social Media Marketingpreschool academyAinda não há avaliações
- Is - 2026-4Documento27 páginasIs - 2026-4jm.mankavil6230Ainda não há avaliações
- 2ND Quarter MTB - Mle Lesson Plan December 2, 2022Documento4 páginas2ND Quarter MTB - Mle Lesson Plan December 2, 2022sherry ann corderoAinda não há avaliações
- Earth Air Heat Exchanger in Parallel ConnectionDocumento5 páginasEarth Air Heat Exchanger in Parallel Connectionseventhsensegroup100% (1)
- GP125 - 200s Maintenance Manual-A520180913Documento170 páginasGP125 - 200s Maintenance Manual-A520180913paulatclayxAinda não há avaliações
- SPHE8281DDocumento35 páginasSPHE8281Ddiego-tAinda não há avaliações
- DLP #7 Eng 7Documento2 páginasDLP #7 Eng 7Lenn Don50% (2)
- GasLink - Development of GLIADocumento24 páginasGasLink - Development of GLIAOribuyaku DamiAinda não há avaliações
- 193-Cable Tray QtyDocumento4 páginas193-Cable Tray QtyprkshshrAinda não há avaliações
- Nexys 2Documento12 páginasNexys 2sacramusAinda não há avaliações
- Image Processing (Rry025)Documento22 páginasImage Processing (Rry025)Babasrinivas GuduruAinda não há avaliações
- Sternberg TheoryDocumento20 páginasSternberg TheoryKhadijah ElamoreAinda não há avaliações