Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
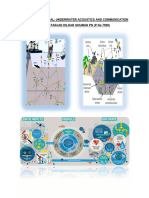
A Survey On Routing Protocols For Underwater Sensor Networks
Enviado por
plutopopTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
A Survey On Routing Protocols For Underwater Sensor Networks
Enviado por
plutopopDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
A Survey on Routing Protocols for Underwater Sensor
Networks
Aman Sharma Abdul Gaffar.H
School of Computer Science & Engineering School of computer science & Engineering
VIT University, VIT University, Vellore
Vellore India Vellore India
amansharma1015@gmail.com abdulgaffar@vit.ac.in
AbstractDifferent routing protocol perform different
role in the underwater sensor network. All routing
perform each and specific task into underwater sensor
network which responsible for networking problems
issue that is why this is the latest way of research.
Routing term derived from route that means a path a
way that perform different terms in underwater sensor
network problem related issue. The best part is today
many routing protocol are present in the underwater
wireless sensor network. Some different attributes
comes underwater wireless sensor network like likes
high bit error rates, limited band-width, 3D deployment
and high propagation delay. This paper is referring to
as helpful for giving brief overview about each and
every protocol and responsible for entire underwater
wireless sensor network.
Keyword: Underwater sensor network, routing protocol
I. INTRODUCTION
In our earth 25% covered by human being and
remaining space is covered by water that could be
river and oceans also. In underwater wireless sensor
network much small water living thing like fish,
crocodile and many more. Suppose a scientist work
on particular a particular thing so some special
devices should be in underwater wireless sensor
network that can work in underwater wireless sensor
network system which should be able to interact
within underwater. Today increasing the demand
some special routing protocol which can work into
underwater wireless sensor network. For the current
point of research scenario underwater sensor network
with some different routing protocol available that
play some specific role in the underwater wireless
sensor network that why some scientists are working
for developing algorithm. Underwater routing sensor
network not only helpful for giving high reliability
which should be able to control high reliability of
information sent to the SINK node but also its delay
relatively low. Underwater sensor network able to
perform operation into long terms non time critical
aquatic monitoring applications where GPS support
is not require. The architecture of routing protocols
easily adapt to changing topology. Reduce energy
consumption and the network nodes network
conflicts as much as possible. Some main challenges
are also including for routing protocol underwater
sensor network that challenges are High propagation
delays, Node mobility, Error prone acoustic
underwater channels, Error prone acoustic
underwater channels, Error prone acoustic
underwater channels. According to this paper its not
only useful for giving information about routing
protocol for underwater sensor networks but also
helpful for working scientist and those people who
are involving in research activities and is also useful
for giving correct way which one is correct routing
protocol underwater sensor network and which one is
perfect for project that can be easily identify by this
paper. [1]
II. DESIGN COMPONENT FOR UNDERWATER
SENSOR NETWORK
Some factors like transmission loss, multipath, noise,
propagation loss these are four major problems which
comes in underwater sensor network.[13]
A. Transmission loss [13]: Transmission loss is
combination of geometric spreading and attenuation.
It has independent of frequency. Geometric spreading
is expansion of wave fronts that increase the
Aman Sharma et al, International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks,Vol 2(1), 74-82
74
ISSN:2249-5789
propagation distance. Basically attenuation provoked
by increases with distance and frequency, absorption
due to conversion of acoustic energy into heat.
B. Noise [13]: It is divided into two ways as ambient
noise and manmade noise. This in mainly focus on
the shipping activity and machinery noise.
C. High delay [13]: The propagation speed in the
underwater sensor magnitude is less than compare to
the radio channel.
D. Multipath[13]: Basically this term is refer to as
more than one way for degradation of the acoustic
communication signal that generates that is refer to
as Inter Symbol Interference. The more than one
geometry based on the link configuration. There are
two channels like vertical channel and horizontal.
Horizontal channels may have long more than one
way spreads whereas Vertical channels may have
little time dispersion.
III ROLE OF UNDERWATER SENSOR NETWORK
Underwater sensor network able to perform
operations in wide range of applications that
application are perform different in underwater
sensor network some applications likes mine
reconnaissance, distributed tactical surveillance,
seismic monitoring, ocean sampling networks,
equipment monitoring, environmental monitoring,
assisted Navigation, Disaster prevention and
undersea explorations these all are the advantages of
the underwater sensor networks. Since no system is
perfect, therefore, even with all the above mentioned
advantages of the system, a few disadvantages still
exit like costly devices, more power requirement,
Intermitted memory, Spatial correlation.
A. Fastest way for finding underwater information
[1]: Underwater sensor is the latest and fastest way
of finding information which is available in
underwater sensor network. This information is not
only helpful for human being but also responsible for
researchers.
B. Monitor the environment & climate [13]: Most of
researchers want to know about what is happing
inside the water. It is depend on the situation suppose
if water is less so need for monitoring. But if water is
More like a ocean so monitoring is mandatory
because without monitoring we can never ever
analyze the problems. Underwater sensor network
system able to solve the problem those problems are
part of climate. Underwater sensor network play
major role in detect climate change, improve weather
forecast. Basically underwater sensor network not
only monitor the climate but also helpful in nuclear,
chemical and biological activates.
C. Underwater device monitor system [13]: For
monitoring the underwater sensor network where as
costly devices are there all these devices are more
costly that is play safety role in underwater sensor
network.
D. Undersea Explorations [13]: Underwater sensor
network perform operation into determine the paths
for laying undersea cables, remove underwater
reservoirs.
E. Ocean Sampling Networks [13]: Autonomous
underwater vehicles able for cooperative adaptive
sampling of the 3D coastal ocean environment.
F. Disaster Prevention [13]: Underwater sensor
network system able to perform seismic activity that
starts from remote locations which provide tsunami
warnings to coastal areas.
G. Assisted Navigation [13]: Underwater sensors are
able to perform bathymetry profiling, also able find
locate dangerous rock, submerged wrecks.
IV PROBLEM IN UNDERWATER SENSOR
NETWORK
A. More expensive Devices [13]: Underwater sensor
devices are more costly. And no more supplier are
provides these such kind of devices because these are
devices are part of research oriented activity.
Underwater sensor devices are not easily available in
the market.
B. High power require for communication [13]: In
underwater communication more power require
because for exchanging data inside in water need
more electricity require.
C. Hardware Protection requirement [13]: Inside the
water lot of underwater devices are available not
only for monitoring but also scientific work also
there that is why more security is require inside the
water for safety of the underwater components.
Aman Sharma et al, International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks,Vol 2(1), 74-82
75
ISSN:2249-5789
D. Intermitted data transfer [13]: Compare to
terrestrial sensor network system where very small
memory. But in underwater sensor network data
transferring could be create big interrupt at the time.
E. Reading problem in space sensors [13]: Generally
terrestrial sensors are related to each other. But In
underwater sensor network it may not be possible in
higher distance sensors but unlikely it could be co-
related in higher distance among sensors.
F. More sparse deployment [13]: In underwater
sensor network the deployment is often sparser but
compare to terrestrial sensor networks are densely
deployed.
G. Propagation delay [13]: This is also a major
problem which comes underwater sensor networks
time. Propagation delay is orders of magnitude higher
than in Radio Frequency variable and terrestrial
channels.
H. Impaired channel [13]: The underwater channel is
impaired because of multipath and fading.
J. Fouling and corrosion [13]: Underwater sensors
are prone to failures because of fouling and
corrosion.
K. Localization [11]: Localization is the challenging
factor that is require for data labeling while some
time critical applications require data without time
delay.
L. High Maintenance [11]: Underwater sensors
demands are increasing because for underwater
sensors are very costly which are not easily available
in the market and underwater sensor supplier and
consultants are not available everywhere that is why
cost is increasing. Underwater sensors are too costly
because for underwater sensor networks high
maintenance is required.
F. Temporary losses [13]: For the connectivity time
packet sending time it could be loss between the data
transmission.
M. High bit error rates [13]: In underwater sensor
network high bit error rates mostly come at the time
of duration.
N. Reliability [11]: This is one of the major design
issues for reliable delivery of sensed data to the
surface sink is a challenging task compare to
forwarding the collected data to the control center.
O. Limited battery power [13]: Battery power is the
major issues which mainly comes underwater sensor
network because many underwater devices working
throw the battery suppose if a underwater sensor
device is not working so underwater charging is not
possible or it may not be charged.
P. Limited bandwidth size [13]: In underwater sensor
another problem is issue is related to bandwidth
because bandwidth size is limited.
VI DESIGN ISSUE FOR ROUTING PROROCOL
UNDERWATER SENSOR NETWORK
The main issues for development for routing
protocols for underwater sensor network. [1]
A. Harsh deployment environment is the major
challenging factor which comes under routing
protocol for underwater sensor network.
B. Bandwidth capacity is low because routing
protocol for underwater sensor network comes from
high bit error rates.
C. Another problem related to low energy problem.
For each battery energy is require.
D. Node mobility is also another concern which
comes under routing protocol for underwater sensor
network because if they are not anchored at the
bottom of the sea. This situation conclusion in a
dynamic topology
E. Radio single are not efficient compare to routing
protocol for underwater sensor network. Because it
provides high propagation delays.
F. High propagation delays are the major factor of
routing protocol for underwater sensor network.
VII. DIFFERENT ROUTING PROTOCOL IN
UNDERWATER SENSOR NETWORK
There are ten different routing protocols available for
underwater sensor network.(a) Vector-Based
Forwarding Protocol or location-based routing
protocol, (b)Robustness Improved Location
Aman Sharma et al, International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks,Vol 2(1), 74-82
76
ISSN:2249-5789
protocol,(c) Depth-Based Routing protocol, (d) Hop-
by-Hop Dynamic Addressing Based protocol,(e)
Focused Beam Routing Protocol,(f) Path Unaware
Layered Routing Protocol,(g)Adaptive Routing
protocol,(h)GPS-free Routing Protocol, (i) A Low
Propagation Delay Multi-Path Routing Protocol,(j)
Pressure Routing Protocol. There is brief overview
about common routing protocol underwater sensor
network.
VIII. Routing Protocols for underwater sensor
network
A. Vector Based forwarding protocol: [2] [11]:
VBRP this protocol is known as location based
routing protocol. This is designed for underwater
sensor network. Basically it refer to as the problem
which helpful to improve the low delay and
successful rate. For the current point of research
scenario underwater sensor network with vector
routing forwarding protocol. Its architecture depend
upon underwater sensor network and it just a location
based protocol which play major role in the
underwater sensor network.VBF refer to as vector
based routing forwarding protocol. Sometimes VBF
also refer to as routing pipe which is perform a
specific task for built connection between source,
destination and packet delivery. The data packet is
collection of the aim, location of the sender,
forwarder and range field. VBF also refer to as
routing pipe which is perform a specific task for built
connection between source, destination and packet
delivery. Robustness, energy efficiency, High success
of data delivery and energy efficient these four
feather comes under location based protocol which
are not available in underwater sensor network that is
why a novel routing protocol known as VBF. This
protocol is helpful for packet carry routing related
information and no state information is require at
nodes as well as scalable in terms of network size. In
VBF only those nodes close to the routing vector are
involved in data forwarding. Therefore it is efficient.
Moreover our self adaption algorithm allows a node
to estimate its importance in its neighborhood and
thus adjust its forwarding policy to save more
energy.VBF utilities path redundancy (Controlled by
the routing pipe radius) to provide robustness agent
packet loss and node failure. The simulation results
have demonstrated the proving performance of VBF.
B. Robustness Improved Location protocol [3]:
RILP This protocol is also same as location based
routing protocol and also designed for underwater
sensor network as well as its behaving like VBF. This
is known hop to hop vector based forwarding
protocol But this protocol is much better than
location based routing protocol. One major problem
which comes in location based routing protocol that
is (i) low data delivery in sparse network, (ii) too
sensitive to routing pipe radius. Above these two
problems are removed in robustness improved
location protocol thats why some researcher mostly
prescribe this protocol. Another main comparison
between both of location based routing protocol and
vector based forwarding protocol hop to hop vector
based forwarding protocol is enhances data delivery
ratio in sparse networks compared with VBF that is
conduct simulations to evaluate Hop to Hop Vector
Based Forwarding protocol and the results show that
Hop to Hop Vector Based Forwarding yields much
better performance than VBF in sparse networks. In
addition, HH-VBF is less sensitive to the routing pipe
radius threshold. HH-VBF, an enhanced version of
the VBF routing protocol for Underwater Sensor
Networks. The new proposal introduces a hop-by-hop
approach, which is simple while novel and it can
significantly improve the robustness of packet
delivery in sparse networks: enhancing the data
delivery ratio while taxing less energy.
C. Depth-Based Routing protocol [8]:
DBRP refer to as depth based routing protocol. It is
behaving like greedy algorithm in which each sensor
separately. Each sensor depend on it is depth and the
depth of the previous sender, able to make the overall
result on whether to forward a packet. For example
suppose a node data sent its broadcasts. So here are
many neighboring nodes calculate their depths and
helpful to create a depth a difference with the sending
node upon receipt of the data packets. Nodes which
have lesser depths compare than the sender accept
these data packets, while other nodes simply discard
them. Aqua-Sim define terms to for simulations,
authors use NS2 include underwater sensor network
Aman Sharma et al, International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks,Vol 2(1), 74-82
77
ISSN:2249-5789
simulation packages extension. Its useful for
performance of the packet delivery ratio,
performance of average end-to-end delay,
performance of total energy consumption. Some
different comes here depth based routing protocol
where each node should have equipped with a
depth sensor, which one hand can increase the
cost while on the other hand can increase energy
consumption. Another drawback refers to as
broadcasting which helpful to step up the complexity
of the routing due to making more nodes candidate
for forwarding the data packets. Third drawback is
the dramatic change of performance as node density
varies. This protocol is combination of sent packet
and the route discovery. After all nodes deployed in
the water, they will start to detect their
underwater depth; and start the route discovery
process to choose their next hop nodes. Overall
Conclusion is packet from the source node through
the multi hop sends to sink node.
D. Hop to Hop Dynamic Addressing based Routing
protocol [6]:
Efficient communication is the major problem in
underwater sensor network. Radio signal cannot
spread well in deep water, and replace radio signal
with the acoustic channel. This replacement solution
in many effects like high error probability, low
bandwidths and high latency due to less propagation
speeds. A novel routing protocol called Hop by hop
dynamic addressing based for critical underwater
monitoring missions. This protocol applies on multi
sink architecture and also energy efficient, scalable
and robust. This protocol also helpful for design
monitoring underwater missions. The aim of hop by
hop dynamic addressing based routing protocol
helpful for maximize the delivery ratio, optimize
energy consumption and minimize the message
latency.
E. Focused Beam Routing Protocol for Underwater
Acoustic Networks [16]:
For the current point of research scenario underwater
sensor network with Focused Beam routing protocol.
The focused beam routing protocol works on Sparce
network. According to this routing protocol there are
one mobility static nodes. There are location
information require own location and sink location.
Basically Focused Beam routing protocol works on
geographic routing. This is known as scalable routing
technique that depends upon the location information.
Focused Beam routing protocol where static and
mobile underwater acoustic networks can work
without any clock synchronization. According to
performance if we are considering different node
densities and network loads so a discrete event
underwater acoustic network simulator should be
used. First of all we will observe the impact of node
density on the performance and results we can
compare with Dijkastras shortest path algorithm.
The technique should be able to dynamically discover
minimum energy routes with the minimum network
knowledge. According to performance wise con gets
bigger energy consumption is reduced. Routing
protocol helpful to verifying number of nodes
randomly positional within 200 km2 grid area, 4
sinks located at comers.
F. Path Unaware Layered Routing Protocol [5]:
This routing protocol just combination of two phases
one is called layering phase and second is called
communication phase. Communication phase helpful
to define on fly that come from source to sink node
across the concentric layers. Another layering phase
helpful to focus on layers of spheres is formed around
the sink node with each node belonging to only one
of the spherical layers. There are choosing radiuses of
spheres because that based on packet delivery latency
and probability of successful packet forwarding thats
why this knows as layering phase.
g. Adaptive Routing protocol [9]:
The aim of Adaptive Routing protocol helpful to
fulfill different application demand and also helpful
to accomplish a good trade-off among delivery ratio,
medium end-to-end delay and energy consumption
for all packets. There is a key idea resource
reallocation and exploit message redundancy means
multiple copy of same message. The outcomes of
Adaptive routing protocol achieve a good
performance trade-off among delivery ratio, medium
end-to-end delay and energy consumption and
different packet delivery according to application
requirements. According to performance wise
Aman Sharma et al, International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks,Vol 2(1), 74-82
78
ISSN:2249-5789
medium end to end delay is high and packet delivery
ratio should be good for important packages.
G. GPS-free Routing Protocol [7]:
This GPS-free Routing Protocol is created for
underwater sensor networks. This is known as
Distributed Underwater Clustering Scheme. It is also
helpful to compensate the high propagation delays of
the underwater medium and minimizes the proactive
routing exchange. According to performance wise
this protocol good packet delivery ratio for dense
network. This protocol is scalable and helpful to good
performance of proposed scheme. This protocol
helpful to achieves a very high packet delivery ratio
when it considerable to reduce the network overhead
and also increase the throughput. The GPS-free
Routing Protocol uniformly distributed n nodes like
N=100 volumes is 75X75X20000 cubic meter. The
mobility pattern randomly walks speed 0 to 5 m/s.
The rate of this protocol is 6.6 Kbit/s.
I. A Low Propagation Delay Multi-Path Routing
Protocol [15]:
This protocol is known as multi path touting protocol.
A Low Propagation Delay Multi-Path Routing
Protocol forms a route from source to the destination
which consists of n numbers of multi-sub paths
during the routing path structure. Multi sub paths are
helpful for sub paths form sender to its two-hop
neighbors thru a relay node in the neighborhood of
both sender and receiver nodes. Basically this
approach is useful to keep data collision at receivers
since they receive packets from different relay nodes.
J. Pressure Routing Protocol [14]:
This protocol works in underwater sensor network.
Pressure Routing Protocol is hydraulic pressure
depend on whatever cast routing protocol that applies
the pressure levels other way we can say that the
depth information to search paths for forwarding
packets from source to the surface buoys. The
Pressure Routing Protocol produced a novel
opportunistic routing approach that has an efficient
underwater dead end recovery mechanism along with
the clustering of the nodes and co-channel
interferences.
IX Table description
Routing protocol for underwater sensor
networks are of various kinds that cater to
various different needs of researchers and
scientists. Since each of these have a unique set
of advantages and disadvantages, it becomes
necessary for us to understand which of these
might suit a particular scenario best. Thus, in
order to solve these basic issues of being able to
find the correct protocol a combined study has
been presented in the table below. This simple
yet functional comparison would enable
everybody related to the domain to find the
exact set of protocols and solve a major issue
that arises at a basic level.
Aman Sharma et al, International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks,Vol 2(1), 74-82
79
ISSN:2249-5789
TABLE I Comparison table routing protocol for underwater sensor network
Routing
Protocols
for
Underwater
Sensor
Advantages Disadvantages
Vector
based
forwarding
Protocol
(1)Robustness.
(2)Energy Efficient.
(3)High success of data delivery.
(1)Low Bandwidth.
(2)High latency.
(3)Node floats mobility.
(4)High error Probability.
(5)Low data delivery in sparse network compare to robustness improved location protocol.
(6)Too sensitive to routing pipe radius.
(7)Delay efficiency, delivery ratio, performance and reliability are low.
Robustness
Improved
Location
based
routing
(1)High data delivery in sparse network.
(2) Less sensitive to the routing pipe
radius threshold.
(3)Much better performance and
reliability than VBF
in sparse networks.
(4)Transmission range should be
maximum pipe always every node
should have own pipe.
(1)Not able to explore an adaptive design for unevenly distributed networks.
(2)Not able to add a feedback mechanism to detect and Avoid voids in the network.
(3)Energy efficiency is low.
Depth based
Routing
(1) Multiple-sink underwater sensor
network architecture without
introducing extra cost.
(2) Not necessitate full dimensional
location information of sensor nodes.
(1)In case of acoustic channels, radio-frequency has o lot lower several orders of magnitudes longer
propagation delay and o lot lower bandwidths.
(2)Batteries are stranger to recharge. Underwater sensor nodes, Land based sensor nodes both are commonly
power supplied by batteries or interchange in hash underwater environments.
(3)Not energy efficient.
Dynamic
Hop-by-Hop
Dynamic
Addressing
Based (H2-
DAB)
Routing
Protocol
(1) In this protocol node movements
with water currents can be handled.
(2)no need to maintain complex routing
tables,
(3)No need to differentiated hardware or
new type of nodes.
(4)Multiple sink architecture is also
available.
(1) When choosing a forwarder node, the sender may not have a response from its neighbors especially in
sparse networks. To solve this problem, the protocol waits for a certain time that means time delay also and
then forwards the packet to a neighbor who is at the same depth. This will cause high end-to-end delay that
will also face.
(2)Critical underwater monitoring.
Focused
beam
routing
protocol
(1) This is a discrete event underwater
acoustic network simulator which is
useful for network loads.
(2)This protocol considering different
node densities.
(3)This is a scalable routing technique
which is based on positioning data.
(1)This protocol is not more reliable compare to HH-VBF.
(2)Bandwidths efficiency is not good.
Path
Unaware
Layered
routing
protocol
(1)Fixed routing table (Optional).
(2)Average delay, High delivery rate as
well as localization or synchronization.
(3) Successful packet transmission rate
is much better than Shortest path
algorithm.
(4) This protocol analyzes the packet
transmission success rate for various
success rate for various probability of
forwarding threshold values.
(1)The ring radius value affects the delivery rate to the extent that when delivery rate decreases.
(2)Success rate is not possible.
(3)Route length is also not possible.
(4)Statistical analysis of route duration is not possible.
Adaptive
Routing
Protocol
(1)The basic reason for using this
protocol is to achieve a different set of
services for different data packet types
based on priority and to provide an
optimal mix of services with respect to
(1)Not able to use water current movement models for more naturalistic environment.
(2)Not able to analyze the performance.
(3)Not able to dynamically adjust the weights in packet priority calculation according to network terms.
(4)Not good performance.
(5)Delivery efficiency is not good.
Aman Sharma et al, International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks,Vol 2(1), 74-82
80
ISSN:2249-5789
delivery ratio, energy consumption and
average delay.
(2)Its satisfy applications requirements,
end to end delay, energy consumption;
achieve a good trade off among delivery
ratio.
(3)Delivery ratio is high.
(4)This protocol is energy efficient,
bandwidth efficient and reliable.
GPS-free
Routing
Protocol
(1)Maintain Communication quality.
(2)Minimizes the proactive routing
message exchange.
(3) Guard time values to minimize data
loss
(4)Reduces the network overhead and
continue to growth throughput
consequently.
(4)This protocol compensates the high
propagation delays of the underwater
medium using a continually adjusted
timing advance merge with guard time
values to minimize data loss.
(5)Good performance and Scalable.
(6)High packet delivery ratio.
(1)Delivery efficiency is too less.
(2)Reliability is too less compare to other routing protocols.
(3)Performance is not much better than other protocols.
A Low
Propagation
Delay
Multi-Path
Routing
Protocol
(1)This protocol is much better than
HH-VBF and VBF because it has higher
throughput.
(2)It uses many matrix operations that
lead to high energy consumption.
(1)No seek for more effective RWA.
(2)Not able to optimize more aim which should be helpful for underwater sensor network.
Pressure
Routing
Protocol
(1)I n this protocol there is a mechanism
that choose the subset of forwarders
which maximizes greedy progress yet
limiting co-channel interferences thats
know as novel opportunistic routing
mechanism.
(2)One another method in this protocol
that out performs recently proposed
approaches that is known as efficient
underwater dead end recovery method.
(3)The outcomes of this protocol
confirmed the proposed protocols can
effectively handle the challenges.
(4)It has lower end to end to end delay
compare to DBR.
(5)Excellent performance, delivery
ratio, delay efficient.
(1)Much higher cost in packet transmission.
(2)Bandwidth efficiency and energy efficiency is not much good.
. CONCLUSION
This paper performs major task routing protocol for
underwater sensor network and play major role in
research. In this paper Routing protocol for
underwater sensor network is major research issue,
which is helpful to solving networking interrupts,
Aman Sharma et al, International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks,Vol 2(1), 74-82
81
ISSN:2249-5789
which generally comes into underwater sensor
network and also provide platform for finding
suitable routing protocol for specific purpose. The
best part is that, this paper is fully supported for
finding correct routing protocol for underwater
sensor network projects and some challenging
research projects which should be useful for entire
underwater sensor network system. A complete
comparison of various routing protocol has also been
done. All advantages as well as disadvantages has
also been shown that in turn would allow the readers
to find the requirement specific details about the
topic.
REFERENCES
[1] Yonca Bayrakdar, Nirvana Meratnia, Aylin Kantarci, A
comparative view of routing protocols for underwater wireless
sensor networks.978-1-61284-4577-0088-0/11/$26.00,2011IEEE
[2] Chang Su1, Xiaoming Liu1, P.R.China Vector-based low-delay
forwarding protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks, 2010
International Conference on Multimedia Information Networking
and Security,978-0-7695-4258-4/10 $26.00,2010 IEEE DOI
10.1109/MINES.2010.46.
[3] Nicolas Nicolaout, Jun-Hong Cui, KDario Maggiorini,
Improving the Robustness of Location-Based Routing for
Underwvater Sensor Networks,1-4244-0635-8/07/$20.00, 2007
IEEE.
[4] Paul Wang, Uichin Lee, Youngtae Noh, Luiz F. M. Vieira,
Mario Gerla, Jun-Hong Cui,Pressure Routing for Underwater
Sensor Networks, Bell Labs, 978-1-4244-5837-0/10/$26.00,2010
IEEE.
[5] Sarath Gopi, G. Kannan, Deepthi Chander, U. B. Desai and S.
N. Merchant, PULRP: Path Unaware Layered Routing Protocol for
Underwater Sensor Networks,978-1-4244-2075-9/08/$25.00 2008
,IEEE.
[6] Muhammad Ayaz, Azween Abdullah, Hop-by-Hop Dynamic
Addressing Based (H2 DAB) Routing Protocol for Underwater
Wireless Sensor Networks,978-0-7695-3922-5/09 $26.00,2009
IEEE,DOI 10.1109/ICIMT 2009.70
[7] Mari Carmen Domingo, Rui Prior, Design and Analysis of a
GPS-free Routing Protocol for Underwater Wireless Networks in
Deep Water, In 2007 International Conference on sensor
Technologies and applications,0-7695-2988-7/07 $25.00 2007.40.
[8] Liu Guangzong, , Li Zhibin, Depth-Based Multi-hop Routing
Protocol for Underwater Sensor Network, In 2010 2
nd
International
Conference on Industrial Mechatronics and Automation,978-1-
4244-7656-5/10/$26.00,2011 IEEE
[9]Zheng Guo, Gioele Colombit, Bing Wang, Jun-Hong Cui, Dario
Maggiorinit, Gian Paolo Rossit,Adaptive Routing in Underwater
Delay/Disruption Tolerant Sensor Networks, 979-1-4244-1959-
3/08/$25.00,2008 IEEE.
[10]John Heidemann,Yuan Li,Affan Syed,Jack Wills,Wei
YE,Underwater Sensor Networking: Research Challenges and
Potential Applications USC/ISI Technical Report ISI-TR-2005-
603.
[11] Muhammad Ayaz, Imran Baig, Azween Abdullah, Ibrahima
Faye, A survey on routing techniques in underwater wireless
sensor networks, 1084-8045/$ - see front matter & 2011 Elsevier
Ltd., doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2011.06.009
[12] Peng Xie, Jun-Hong Cui, Li Lao, VBF: Vector-Based
Forwarding Protocol for Underwater Sensor Networks, CSE
Technical Report: UbiNet-TR05-03.
[13] Ian F. Akyildiz, Dario Pompili, Tommaso Melodia, State of
the Art in Protocol Research for Underwater Acoustic Sensor
Networks, WUWNet06, September 25, 2006, Los Angeles,
California, USA, ACM 1-59593-484-7/06/0009 ...$5.00.
[14] Uichin Lee, Paul Wang, Youngtae Noh, Luiz F. M. Vieira,
Mario Gerla, Jun-Hong Cui, Pressure Routing for Underwater
Sensor Networks, 978-1-4244-5837-0/10/$26.00 2010 IEEE.
[15]Qiwu Wu, Xianwei Zhou, Jianping Wang, Zhizhong Yin,
Lingzhi Jiang, A low-cost delay-constrained routing and
wavelength assignment algorithm in WDM networks with sparse
wavelength conversions.
[16] Jonathan Schrauwen, Jeroen Van Lysebettens, Tom Claes,
Katrien De Vos, , Peter Bienstman, , Dries Van Thourhout, and
Roel Baets, Focused-Ion-Beam Fabrication of Slots in
SiliconWaveguides and Ring Resonators, IEEE PHOTONICS
TECHNOLOGY LETTERS, VOL. 20, NO. 23, DECEMBER 1,
2008.
Aman Sharma et al, International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks,Vol 2(1), 74-82
82
ISSN:2249-5789
Você também pode gostar
- Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks: Applications, Challenges and Design Issues of The Network LayerDocumento7 páginasUnderwater Wireless Sensor Networks: Applications, Challenges and Design Issues of The Network LayerWARSE JournalsAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges of Underwater Acoustic Sensor NetworksDocumento6 páginasChallenges of Underwater Acoustic Sensor NetworksMadhusudanan AshokAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges For Efficient Communication in UnderwatDocumento7 páginasChallenges For Efficient Communication in UnderwatDevanshu AnandAinda não há avaliações
- State of The Art in Protocol Research For Underwater Acoustic Sensor NetworksDocumento12 páginasState of The Art in Protocol Research For Underwater Acoustic Sensor NetworksAmmar AhsanAinda não há avaliações
- Undersea Wireless Sensor Network For Ocean Pollution PreventionDocumento8 páginasUndersea Wireless Sensor Network For Ocean Pollution PreventionAdekunle GbadeboAinda não há avaliações
- Mitrut Caraivan Et Al Multi-Purpose Underwater Data Collection SensorsDocumento5 páginasMitrut Caraivan Et Al Multi-Purpose Underwater Data Collection SensorsmccatysAinda não há avaliações
- Underwater Wireless Sensor Network: A Review: Shraddha S. Chafale, Prof. N.M. DhandeDocumento5 páginasUnderwater Wireless Sensor Network: A Review: Shraddha S. Chafale, Prof. N.M. DhandeAnonymous lPvvgiQjRAinda não há avaliações
- Aquatic ApplicationsDocumento8 páginasAquatic ApplicationsGautam DemattiAinda não há avaliações
- Developing Low Cost Intelligent Wireless Sensor Networks For Aquatic EnvironmentsDocumento6 páginasDeveloping Low Cost Intelligent Wireless Sensor Networks For Aquatic EnvironmentsRenz LorenzAinda não há avaliações
- Building Scalable Mobile Underwater Wireless Sensor NetworksDocumento8 páginasBuilding Scalable Mobile Underwater Wireless Sensor NetworksvineetpaladiAinda não há avaliações
- Survey of Underwater Wireless Technologies and Localization ProtocolsDocumento21 páginasSurvey of Underwater Wireless Technologies and Localization Protocolssuguna sugunaAinda não há avaliações
- Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks Research ChallengesDocumento23 páginasUnderwater Acoustic Sensor Networks Research ChallengesMoses TorkudzorAinda não há avaliações
- Realization of 3D Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks and Influence of Ocean Parameters On Node Location EstimationDocumento16 páginasRealization of 3D Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks and Influence of Ocean Parameters On Node Location EstimationJohn BergAinda não há avaliações
- Clam - Collaborative Embedded Networks For Submarine Surveillance: An OverviewDocumento4 páginasClam - Collaborative Embedded Networks For Submarine Surveillance: An OverviewamineAinda não há avaliações
- Prospects and Challenges of Underwater Acoustic Sensor NetworkingDocumento6 páginasProspects and Challenges of Underwater Acoustic Sensor NetworkingDeepak Singh YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Zigbee PDFDocumento4 páginasZigbee PDFdineshAinda não há avaliações
- Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks A Review of ReDocumento20 páginasUnderwater Wireless Sensor Networks A Review of ResekharraoAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Sensor Networks Track SoldiersDocumento10 páginasWireless Sensor Networks Track SoldiersLue niAinda não há avaliações
- Underwater Wireless CommunicationDocumento9 páginasUnderwater Wireless CommunicationsayaleeAinda não há avaliações
- Securing Underwater Wireless Communication Networks ReportDocumento22 páginasSecuring Underwater Wireless Communication Networks Reportvgbhat_02100% (4)
- Developing Low-Cost Intelligent Wireless Sensor Networks For Aquatic EnvironmentsDocumento6 páginasDeveloping Low-Cost Intelligent Wireless Sensor Networks For Aquatic EnvironmentsSathish KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Underwater Sensor NetworkDocumento73 páginasUnderwater Sensor NetworkRajAinda não há avaliações
- Shallow Water Acoustic Networks Full ReportDocumento26 páginasShallow Water Acoustic Networks Full ReportSimmi JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Sayoshni Seminar ReportDocumento18 páginasSayoshni Seminar ReportSayoshni Ghosh100% (1)
- 8 Research ProposalDocumento10 páginas8 Research ProposalMohammad ArifAinda não há avaliações
- Ijcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)Documento8 páginasIjcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)IAEME PublicationAinda não há avaliações
- A Survey of Techniques and Challenges in Underwater LocalizationDocumento61 páginasA Survey of Techniques and Challenges in Underwater LocalizationKhondoker Munim SalehinAinda não há avaliações
- Location Based Routing Protocols For Underwater Sensor NetworksDocumento5 páginasLocation Based Routing Protocols For Underwater Sensor NetworksInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementAinda não há avaliações
- Presented by Imtiaz Ahmed KhanDocumento37 páginasPresented by Imtiaz Ahmed KhanImtiaz Ahmed KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrophones Propagation Signal Attenuation Acoustic Waves Electromagnetic WavesDocumento8 páginasHydrophones Propagation Signal Attenuation Acoustic Waves Electromagnetic WavesPrakash VAinda não há avaliações
- An Energy Efficient Routing Algorithm For Underwater Acoustic Sensor NetworksDocumento5 páginasAn Energy Efficient Routing Algorithm For Underwater Acoustic Sensor NetworksMuthu Vijay DeepakAinda não há avaliações
- Underwater Wireless Communication NetworksDocumento12 páginasUnderwater Wireless Communication NetworksAmukta MalyadaAinda não há avaliações
- Seminar Report ON " ": Intelligent Sensor Based Monitoring System For Underwater PollutionDocumento12 páginasSeminar Report ON " ": Intelligent Sensor Based Monitoring System For Underwater PollutionTanmay TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Seminar On Underwater Wireless CommunicationDocumento21 páginasSeminar On Underwater Wireless CommunicationENG18EC0062-MD TANVEERAinda não há avaliações
- Underwater CommunicationDocumento11 páginasUnderwater Communicationsuman vvabAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of CoDBR and CEEDBR Protocols in Underwater Wireless Sensor NetworksDocumento8 páginasAnalysis of CoDBR and CEEDBR Protocols in Underwater Wireless Sensor NetworksbijcicnjounalAinda não há avaliações
- Underwater Sensor Networks ArchitectureDocumento8 páginasUnderwater Sensor Networks ArchitectureautorangersAinda não há avaliações
- Underwater Wireless CommunicationDocumento16 páginasUnderwater Wireless CommunicationAchyuth JanaAinda não há avaliações
- 04-3 SDRT A Reliable Data Transport Protocol For Underwater Sensor Networks (2010)Documento15 páginas04-3 SDRT A Reliable Data Transport Protocol For Underwater Sensor Networks (2010)piranhapressAinda não há avaliações
- AEA-QoS 深度学习 逐跳转发 小,密集Documento14 páginasAEA-QoS 深度学习 逐跳转发 小,密集张Ainda não há avaliações
- Jamming in Underwater Sensor Networks: Detection and MitigationDocumento11 páginasJamming in Underwater Sensor Networks: Detection and MitigationCarl FranksAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Challenges of Stationary Wireless Smart Ocean Observation SystemsDocumento14 páginasEngineering Challenges of Stationary Wireless Smart Ocean Observation Systemsal shayokhAinda não há avaliações
- Topic Name: Aqua Communication Using Modem: Seminar Examination Department of Mechanical Enginnering (AY-2021-22)Documento12 páginasTopic Name: Aqua Communication Using Modem: Seminar Examination Department of Mechanical Enginnering (AY-2021-22)Durgesh ShindeAinda não há avaliações
- Proposal ThesisDocumento15 páginasProposal ThesisYosef KirosAinda não há avaliações
- IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials: A Survey of Routing Protocols for Underwater Wireless Sensor NetworksDocumento24 páginasIEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials: A Survey of Routing Protocols for Underwater Wireless Sensor NetworksGJ GNANA VENKAT NAGAinda não há avaliações
- Securing Underwater WirelessDocumento7 páginasSecuring Underwater Wirelessiamumpidi100% (1)
- Case StudyDocumento9 páginasCase Studyrushi1990Ainda não há avaliações
- Fishermen Rescue System With LoRa ModuleDocumento5 páginasFishermen Rescue System With LoRa ModuleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- 163 SubmissionDocumento13 páginas163 SubmissionKeyur MahantAinda não há avaliações
- Research Paper On Underwater Wireless CommunicationDocumento6 páginasResearch Paper On Underwater Wireless CommunicationjhwmemrhfAinda não há avaliações
- A Survey of Techniques and Challenges in UnderwaterDocumento60 páginasA Survey of Techniques and Challenges in UnderwaterAjay SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Alemyene P1038-1046 PDFDocumento9 páginasAlemyene P1038-1046 PDFyemer AyanawAinda não há avaliações
- Sensors: Underwater Electromagnetic Sensor Networks-Part I: Link CharacterizationDocumento16 páginasSensors: Underwater Electromagnetic Sensor Networks-Part I: Link CharacterizationNeil OpenaAinda não há avaliações
- Zenia 2016Documento25 páginasZenia 2016M A DiptoAinda não há avaliações
- Shallow Water Acoustic NetworksDocumento7 páginasShallow Water Acoustic NetworkskmotiyaniAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Great Lakes Geo TechDocumento13 páginasWireless Great Lakes Geo Techsagar_srAinda não há avaliações
- Madhuri Springer PaperDocumento26 páginasMadhuri Springer PaperMadhuri RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Sensor Networks For Environmental Monitoring: The Sensorscope ExperienceDocumento5 páginasWireless Sensor Networks For Environmental Monitoring: The Sensorscope ExperienceAshna WaseemAinda não há avaliações
- Microwave and Millimeter Wave Circuits and Systems: Emerging Design, Technologies and ApplicationsNo EverandMicrowave and Millimeter Wave Circuits and Systems: Emerging Design, Technologies and ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- GRASP Design PatternsDocumento11 páginasGRASP Design Patternsplutopop50% (2)
- Logical ArchitectureDocumento23 páginasLogical ArchitectureplutopopAinda não há avaliações
- Ooad UNIT 5 NotesDocumento29 páginasOoad UNIT 5 NotesplutopopAinda não há avaliações
- Ooad Unit3 NotesDocumento15 páginasOoad Unit3 NotesplutopopAinda não há avaliações
- Ooad QB PDFDocumento14 páginasOoad QB PDFplutopopAinda não há avaliações
- Virtual SinkDocumento6 páginasVirtual SinkplutopopAinda não há avaliações
- Routing in UwsnDocumento9 páginasRouting in UwsnplutopopAinda não há avaliações
- Base Paper PDFDocumento8 páginasBase Paper PDFteddy1990Ainda não há avaliações
- Base Paper PDFDocumento8 páginasBase Paper PDFteddy1990Ainda não há avaliações
- Satellite Communication Fall 2011 Answer KeyDocumento7 páginasSatellite Communication Fall 2011 Answer KeyplutopopAinda não há avaliações
- Classifying and Extracting Data from the Deep WebDocumento12 páginasClassifying and Extracting Data from the Deep WebplutopopAinda não há avaliações
- Satellite Communication Fall 2011 Answer KeyDocumento7 páginasSatellite Communication Fall 2011 Answer KeyplutopopAinda não há avaliações
- Pro-Forma Proponent Compliance Monitoring Report (CMR) : Semi-Annual Module 5 of SMRDocumento5 páginasPro-Forma Proponent Compliance Monitoring Report (CMR) : Semi-Annual Module 5 of SMRJulius LabradorAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Environment Strategy Section 11-15 & AppendixDocumento52 páginas3 Environment Strategy Section 11-15 & AppendixDale WalkerAinda não há avaliações
- Environment MonitoringDocumento18 páginasEnvironment MonitoringLakshana BundhooAinda não há avaliações
- Hazelo Lab Pvt. LTD., Yadadri Bhuvanagiri District - Draft EIA Report (Part I) PDFDocumento263 páginasHazelo Lab Pvt. LTD., Yadadri Bhuvanagiri District - Draft EIA Report (Part I) PDFjyothiAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Monitoring Report-Oktober 2016Documento31 páginasEnvironmental Monitoring Report-Oktober 2016azuraidaAinda não há avaliações
- Non Food Manufacturing Plant ChecklistDocumento17 páginasNon Food Manufacturing Plant ChecklistJo YabotAinda não há avaliações
- Handbook On IWS For The Petrochemical and Refinery SectorDocumento50 páginasHandbook On IWS For The Petrochemical and Refinery SectorJesus MaestreAinda não há avaliações
- Usp 1116 em For Aseptic ProcessingDocumento11 páginasUsp 1116 em For Aseptic ProcessingKraken Ur100% (1)
- CMR and SMRDocumento19 páginasCMR and SMRBalot EspinaAinda não há avaliações
- Europsko Istraživanje o Kvaliteti Vode Za KupanjeDocumento28 páginasEuropsko Istraživanje o Kvaliteti Vode Za KupanjeIndex.hrAinda não há avaliações
- UK AP1000 Environment ReportDocumento403 páginasUK AP1000 Environment ReportCarl WilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- 49 - Bithoor - ESAMP - Draft Final PDFDocumento120 páginas49 - Bithoor - ESAMP - Draft Final PDFshaik irfanAinda não há avaliações
- Guidance 112 Overview of Trending of Environmental Monitoring SampleDocumento2 páginasGuidance 112 Overview of Trending of Environmental Monitoring SampleMina Maher MikhailAinda não há avaliações
- Libro Planificacion en Recursos Hidricoscompleto PDFDocumento690 páginasLibro Planificacion en Recursos Hidricoscompleto PDFSamuelson CAinda não há avaliações
- DPR MSWDocumento103 páginasDPR MSWवर्मा हेमन्तAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Audit Manual EDITED 29 Nov 2010Documento79 páginasEnvironmental Audit Manual EDITED 29 Nov 2010JocelynKongSingCheah100% (1)
- Content Weightages Environmental Protection Agency, Government of Khyber PakhtunkhwaDocumento3 páginasContent Weightages Environmental Protection Agency, Government of Khyber PakhtunkhwaZIA UR REHMANAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Maintenace Hse Manual May2017Documento194 páginasPlant Maintenace Hse Manual May2017Franki Hari MAinda não há avaliações
- Biocontamination ControlDocumento4 páginasBiocontamination ControlTim SandleAinda não há avaliações
- Tangedco Final Draft Eia ReportDocumento579 páginasTangedco Final Draft Eia ReportPradeep BalyanAinda não há avaliações
- Capstone Present FinalDocumento64 páginasCapstone Present Finalhysh89Ainda não há avaliações
- Baranagar ESIA ReportDocumento306 páginasBaranagar ESIA ReportbhaskarAinda não há avaliações
- NSCR EPRMP Vol 1 PDFDocumento233 páginasNSCR EPRMP Vol 1 PDFPeter Paul BucsitAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocumento24 páginasEnvironmental Impact AssessmentSeann Marquez100% (1)
- A New All-Season Passive Sampling System ForDocumento14 páginasA New All-Season Passive Sampling System ForMuhammed UlviAinda não há avaliações
- VALIDATION DICTIONARY DEFINITIONSDocumento57 páginasVALIDATION DICTIONARY DEFINITIONSPrince MoniAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Monitoring in Pharmaceutical FacilitiesDocumento40 páginasEnvironmental Monitoring in Pharmaceutical Facilitiesananth100% (3)
- Environmental Monitoring ProtocolDocumento3 páginasEnvironmental Monitoring Protocolfood tecknologistAinda não há avaliações
- PC-4 Environment Monitoring Device User ManualDocumento4 páginasPC-4 Environment Monitoring Device User ManualEisac Sagiman50% (2)
- Turnkey Dust MonitorsDocumento4 páginasTurnkey Dust MonitorsGiulliana Tiravanti BeoutisAinda não há avaliações