Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CCNA - Exploration Network Fundamentals - ENetwork Practice Final Exam
Enviado por
brone8Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CCNA - Exploration Network Fundamentals - ENetwork Practice Final Exam
Enviado por
brone8Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1
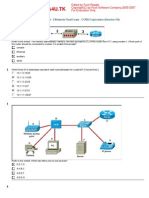
Refer to the exhibit. A user wants to access the Internet from the PC. A part of the running configuration of the router is shown. Which
default gateway IP address should be configured at the PC to enable this access?
10.1.192.1
10.1.192.2
10.1.192.54
192.31.7.1
2 What are three characteristics of CSMA/CD? (Choose three.)
It monitors the media for presence of a data signal.
After detecting a collision, hosts can resume transmission after a random timer has expired.
A jam signal is used to ensure that all hosts are aware that a collision has occurred.
Devices can be configured with a higher transmission priority.
Data is transmitted only when the data signal is present.
It uses a token system to avoid collisions.
3
Refer to the exhibit. What is required on host A for a network technician to create the initial configuration on Router1?
an FTP client
a Telnet client
a terminal emulation program
a web browser
4 The Layer 4 header contains which type of information to aid in the delivery of data?
service port number
host logical address
device physical address
virtual connection identifier
5
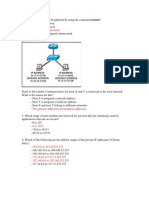
Refer to the exhibit. Which set of devices contains only intermediary devices?
A, B, D, G
A, B, E, F
C, D, G, I
G, H, I, J
6 Which three statements are true about network layer addressing? (Choose three.)
It uniquely identifies each host.
It assists in forwarding packets across internetworks.
It uses a logical 32-bit IPv4 address.
It is not a configurable address.
It is a physical address.
It identifies the host from the first part of the address.
7 Which physical connector type is used for a serial V.35 connection to the CSU/DSU?
8 A network administrator is asked to design a new addressing scheme for a corporate network. There are 60 users in the main office, 40
users in the branch office, 28 users in manufacturing, 12 in the sales office, and 4 users in the research office. Which VLSM addressing
scheme that uses the 192.168.88.0/24 network will fulfill the requirements while wasting the fewest addresses?
192.168.88.0/26 main
192.168.88.32/26 branch
192.168.88.64/26 manufacturing
192.168.88.96/27 sales
192.168.88.128/28 research
192.168.88.0/26 main
192.168.88.64/26 branch
192.168.88.128/27 manufacturing
192.168.88.160/28 sales
192.168.88.176/29 research
192.168.88.0/27 main
192.168.88.32/27 branch
192.168.88.64/28 manufacturing
192.168.88.80/29 sales
192.168.88.88/30 research
192.168.88.0/27 main
192.168.88.64/28 branch
192.168.88.80/28 manufacturing
192.168.88.96/29 sales
192.168.88.104/30 research
9
Refer to the exhibit. The PC, the routing table of which is displayed, is configured correctly. To which network device or interface does
the IP address 192.168.1.254 belong?
PC
switch
router interface fa0/0
router interface fa0/1
10 What is the result of using the clock rate 56000 command at the serial interface of the router?
The interface is configured as a DCE device.
The interface timers are cleared.
The FastEthernet interface is made to emulate a serial interface by assigning it a timing signal.
The IP address for the serial interface is configured.
11
Refer to the exhibit. A network technician has made several changes to R1 since the configuration has last been saved. The modified
configuration did not produce the desired changes. The technician wants to store a backup copy of the saved configuration on a TFTP
server before reloading. Which action will cause the unmodified data to be saved on the TFTP server?
12 By using the ipconfig command, a network administrator determines that a workstation has the address 192.168.3.38 with 29 bits set in
the subnet mask. To what network does the workstation belong?
192.168.3.8
192.168.3.16
192.168.3.24
192.168.3.32
13
Refer to the exhibit. Host X is unable to communicate with host Y. Which command can be run at host X to determine which
intermediary device is responsible for this failure?
telnet 192.168.1.1
ping 192.168.1.1
ftp 192.168.1.1
tracert 192.168.1.1
14 Which fiber connector supports full-duplex Ethernet?
15
Refer to the exhibit. Host A wants to access the Internet. Which combination of a Layer 2 address and a Layer 3 address will enable this
access from host A?
Destination MAC: 0030.8596.DE83 Default gateway: 209.165.202.130
Destination MAC: 0030.8596.DE82 Default gateway: 172.16.9.2
Destination MAC: 0030.8517.44C4 Default gateway: 172.16.1.1
Destination MAC: 0030.8517.44C4 Default gateway: 209.165.202.130
16
Refer to the exhibit. The diagram represents the process of sending email between clients. Select the list below that correctly identifies
the component or protocol used at each numbered stage of the diagram.
1.MUA 2.MDA 3.MTA 4.SMTP 5.MTA 6.POP 7.MDA 8.MUA
1.MUA 2.POP 3.MDA 4.SMTP 5.MTA 6.MDA 7.SMTP 8.MUA
1.MUA 2.POP 3.SMTP 4.MDA 5.MTA 6.SMTP 7.POP 8.MUA
1.MDA 2.SMTP 3.MTA 4.SMTP 5.MTA 6.MUA 7.POP 8.MDA
1.MUA 2.SMTP 3.MTA 4.SMTP 5.MTA 6.MDA 7.POP 8.MUA
17 What are two characteristics of the data link layer? (Choose two.)
It segments and reorders the data.
It exchanges the frames between nodes.
It defines the method by which network devices place data onto the media.
It manages the transfer of data between the processes that run on each host.
It retrieves signals from the media and restores them to their bit representations.
18
Refer to the exhibit. Which two facts can be determined about the topology? (Choose two.)
Four collision domains are present.
One logical network is represented.
Two broadcast domains are present.
Three networks are needed.
Three logical address ranges are required.
19 Which memory contents will change as a result of using the Router# erase startup-config command on a router?
RAM
ROM
flash
NVRAM
20
Refer to the exhibit. The serial interface of the router was configured with the use of the commands that are shown. The router cannot
ping the router that is directly connected to interface serial 0/0/0. What should the network technician do to solve this problem?
Configure the description at interface serial 0/0/0.
Configure an IP address on interface serial 0/0/0.
Remove the no shutdown command at interface serial 0/0/0
Reboot the router.
21 Which OSI layer uses the header information to reassemble the data segments into streams?
application layer
network layer
presentation layer
session layer
transport layer
22 What information is contained in the header of Layer 3 to help data delivery?
port number
device physical address
destination host logical address
virtual connection identifier
23
Refer to the exhibit. A PC is connected to a network. Which action will verify that the PC can communicate with its default gateway?
Use the ping 127.0.0.1 command.
Use the ipconfig command.
Use the ipconfig/all command.
Use the ping 10.0.0.254 command.
24
Refer to the exhibit. Which Layer 2 protocol could be used inside nework A and network C?
IP
TCP
UDP
Ethernet
25 While configuring a router, a network technician wants to name the router. Which prompt should the technician see when enteri ng the
hostname command?
Router>
Router#
Router(config)#
Router(config-line)#
26 A network technician is tasked with setting up a network for six users, but the users should be able to use their accounts to log on from
any of the six computers. What type of network should be used?
workgroup
P2P applications
peer-to-peer network
client-server network
27
Refer to the exhibit. Host A sends a frame to host C with a destination MAC address CC. The MAC address for host C is not in the MAC
table of switch SW1. How will SW1 handle the frame?
Switch SW1 will drop the frame.
Switch SW1 will forward the frame to host C.
Switch SW1 will flood the frame out all ports.
Switch SW1 will flood the frame out all ports except port Fa0/1.
28 Which statement is true about the ICMP protocol?
It is an application layer protocol.
It is designed to make IP a reliable protocol.
It is often filtered out of networks for security purposes.
If a host does not respond to an ICMP echo request, the host is not functioning.
29
Refer to the exhibit. Host B was powered off. What change will occur in the MAC table of the switch?
The table will remain unaffected.
The switch will remove the MAC address at Fa0/19.
The switch will retain the MAC address until host B is powered on again.
The switch will rebuild the MAC table by assigning the FFFF.FFFF.FFFF address to port Fa0/19.
30 As network administrator, what is the subnet mask that allows 510 hosts given the IP address 172.30.0.0?
255.255.0.0
255.255.248.0
255.255.252.0
255.255.254.0
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.128
31
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a link that is down between Router1 and Router2. To correct the problem,
which wire pairs need to be switched on one of the Ethernet cable ends?
pair 1 and pair 2
pair 1 and pair 3
pair 2 and pair 3
pair 2 and pair 4
32
Refer to the exhibit. A web browser is running on host PC1 with an IP address 10.10.2.2/24. A dynamic port number of 49152 is
assigned to the browser. The browser sends a request for a web page to the web server with an IP address 192.168.1.254/24. Which
statement is true?
The session is established using TCP, and the socket number for the web server is 192.168.1.254: 80.
The session is established using TCP, and the socket number for the web server is 192.168.1.254: 49152.
The session is established using UDP, and the socket number for the web server is 192.168.1.254: 80.
The session is established using UDP, and the socket number for the web server is 192.168.1.254: 49152.
33 A network administrator wants to restrict access to the router privileged EXEC mode. Which password should the administrator use?
enable
aux
console
VTY
34 Which three IPv4 addresses represent a broadcast for a subnet? (Choose three.)
172.16.4.63 /26
172.16.4.129 /26
172.16.4.191 /26
172.16.4.51 /27
172.16.4.95 /27
172.16.4.221 /27
35
Examine the graphic with current configurations. Host A in the Clerical office failed and was replaced. Although a ping to 127.0.0.1 was
successful, the replacement computer cannot access the company network. With proxy ARP disabled on the Fa0/0 interface of the New
York router, what is the likely cause of the problem?
network card failure
network cables unplugged
IP address incorrectly entered
subnet mask incorrectly entered
36
Refer to the exhibit. A technician uses the nslookup command on the PC and views the output that is displayed in the exhibit. What is
the IP address of the primary domain name server used by the host?
10.10.10.32
192.168.1.5
192.168.1.99
192.168.2.100
37
Refer to the exhibit. The NAT functionality of the router is enabled to provide Internet access to the PC. However, the PC is still unable
to access the Internet. Which IP address should be changed to 209.165.201.1 to enable the PC to access the Internet?
192.168.1.191
192.168.1.101
192.168.1.1
192.168.1.254
38 A user types the enable command. What task can be performed at the privileged EXEC mode?
Configure the device.
Configure individual interfaces.
Configure individual terminal lines.
Issue show and debug commands.
39
Refer to the exhibit. Which option shows the correct topology given the configuration of Router1?
40 If an administrator wished to return a router to the default state, what additional step must be taken after issuing the command erase
start-up config?
Reload the device.
Issue the command copy running-config start-up config.
Perform a show running-config to verify that the file was removed.
Enter the interface commands to allow the device to connect to the network.
41
Refer to the exhibit. The host was disconnected from switch 2 and connected to switch 1. Which combination of IP address, subnet
mask, and default gateway should be assigned to this host to allow it to function in the network?
IP address: 10.10.9.37 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.240 Default gateway: 10.10.9.35
IP address: 10.10.9.37 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.224 Default gateway: 10.10.9.35
IP address: 10.10.9.29 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.248 Default gateway: 10.10.9.35
IP address: 10.10.9.32 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.224 Default gateway: 10.10.9.35
IP address: 10.10.9.37 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.224 Default gateway: 196.1.105.6
IP address: 10.10.9.63 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.224 Default gateway: 10.10.9.35
42 Which statement is true about router hostnames?
A hostname should be unique on each router.
A router hostname cannot contain capital letters.
A router hostname is configured in privileged executive mode.
A router hostname must be created before any other configurations can be added to the device.
43 Which device should be used for routing a packet to a remote network?
access switch
DHCP server
hub
router
44
Refer to the exhibit. The headers added at each layer are shown. Which layer adds the destination and source process numbers to
ensure that data is delivered to the correct application?
physical layer
data link layer
network layer
transport layer
46
Refer to the exhibit. Which logical topology describes the exhibited network?
star
ring
point-to-point
multi-access
47
Refer to the exhibit. At which OSI layer is serial interface 0/0/1 experiencing problems?
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
48 A network has grown too large for technicians to configure network addresses and hosts files for name resolution. Which two application
layer services should be added to the server to allow these needs to be satisfied dynamically? (Choose two.)
DNS
FTP
DHCP
HTTP
SMTP
49 What is the Cisco IOS?
system software for Cisco devices
Read Only Memory in Cisco devices
non-volatile storage for device configurations
an initial operating system that is used for boot functions
50
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator on PC1 wants to view some HTML code from a web page housed on the web server. Which cl ient
application will allow this request to be started?
Personalized Feedback For: brone8
Network Fundamentals
Chapter 1: Living in a Network-Centric World
Chapter 2: Communicating over the Network
2.1 The Platform for Communications
2.1.1 The Elements of Communication
2.1.2 Communicating the Messages
2.1.3 Components of the Network
2.1.4 End Devices and their Role on the Network
2.1.5 Intermediary Devices and their Role on the Network
2.1.6 Network Media
2.2 LANs, WANs, and Internetworks
2.3 Protocols
2.4 Using Layered Models
2.5 Network Addressing
2.5.1 Addressing in the Network
2.5.2 Getting the Data to the End Device
2.5.3 Getting the Data through the Internetwork
2.5.4 Getting the Data to the Right Application
2.5.5 Warriors of the Net
2.6 Chapter Labs
2.7 Chapter Summary
2.8 Chapter Quiz
Chapter 3: Application Layer Functionality and Protocols
3.1 Applications - The Interface Between the Networks
3.2 Making Provisions for Applications and Services
3.2.1 The Client-Server Model
3.2.2 Servers
3.2.3 Application Layer Services and Protocols
3.2.4 Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications (P2P)
3.3 Application Layer Protocols and Services Examples
3.4 Chapter Labs and Activities
3.5 Chapter Summary
3.6 Chapter Quiz
Chapter 4: OSI Transport Layer
4.1 Roles of the Transport Layer
4.1.1 Purpose of the Transport Layer
4.1.2 Controlling the Conversations
4.1.3 Supporting Reliable Communication
4.1.4 TCP and UDP
4.1.5 Port Addressing
4.1.6 Segmentation and Reassembly - Divide and Conquer
4.2 The TCP Protocol - Communicating with Reliability
4.3 Managing TCP Sessions
4.4 The UDP Protocol - Communicating with Low Overhead
4.5 Lab Activities
4.6 Chapter Summary
4.7 Chapter Quiz
Chapter 5: OSI Network Layer
Chapter 6: Addressing the Network - IPv4
6.1 IPv4 Addresses
6.2 Addresses for Different Purposes
6.2.1 Types of Addresses in an IPv4 Network
6.2.2 Calculating Network, Hosts and Broadcast Addresses
6.2.3 Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast - Types of Communication
6.2.4 Reserved IPv4 Address Ranges
6.2.5 Public and Private Addresses
6.2.6 Special IPv4 Addresses
6.2.7 Legacy IPv4 Addressing
6.3 Assigning Addresses
6.4 Is It On My Network?
6.4.1 The Subnet Mask - Defining the Network and Host Portions
6.4.2 ANDing - What Is In Our Network?
6.4.3 The ANDing Process
6.5 Calculating Addresses
6.5.1 Basic subnetting
6.5.2 Subnetting - Dividing Networks into Right Sizes
6.5.3 Subnetting - Subnetting a Subnet
6.5.4 Determining the Network Address
6.5.5 Calculating the Number of Hosts
6.5.6 Determining Valid Addresses for Hosts
6.5.7 Assigning Addresses
6.5.8 Addressing in a Tiered Internetwork
6.6 Testing the Network Layer
6.6.1 Ping 127.0.0.1 - Testing the Local Stack
6.6.2 Ping Gateway - Testing Connectivity to the Local LAN
6.6.3 Ping Remote Host - Testing Connectivity to Remote LAN
6.6.4 Traceroute (tracert) - Testing the Path
6.6.5 ICMPv4 - The Protocol Supporting Testing and Messaging
6.7 Labs and Activities
6.8 Chapter Summaries
6.9 Chapter Quiz
Chapter 7: Data Link Layer
7.1 Data Link Layer - Accessing the Media
7.2 Media Access Control Techniques
7.2.1 Placing Data on the Media
7.2.2 Media Access Control for Shared Media
7.2.3 Media Access Control for Non-Shared Media
7.2.4 Logical Topology vs Physical Topology
7.2.5 Point-to-Point Topology
7.2.6 Multi-Access Topology
7.2.7 Ring Topology
7.3 Media Access Control Addressing and Framing Data
7.4 Putting it All Together
7.4.1 Follow Data Through an Internetwork
7.5 Labs and Activities
7.6 Chapter Summary
7.7 Chapter Quiz
Chapter 8: OSI Physical Layer
8.1 The Physical Layer - Communication Signals
8.2 Physical Signaling and Encoding: Representing Bits
8.3 Physical Media - Connecting Communication
8.3.1 Types of Physical Media
8.3.2 Copper Media
8.3.3 Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
8.3.4 Other Copper Cable
8.3.5 Copper Media Safety
8.3.6 Fiber Media
8.3.7 Wireless Media
8.3.8 Media Connectors
8.4 Lab - Media Connectors
8.5 Chapter Summaries
8.6 Chapter Quiz
Chapter 9: Ethernet
9.1 Overview of Ethernet
9.2 Ethernet - Communication through the LAN
9.3 The Ethernet Frame
9.4 Ethernet Media Access Control
9.5 Ethernet Physical Layer
9.6 Hubs and Switches
9.6.1 Legacy Ethernet - Using Hubs
9.6.2 Ethernet - Using Switches
9.6.3 Switches - Selective Forwarding
9.6.4 Ethernet - Comparing Hubs and Switches
9.7 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
9.8 Chapter Labs
9.9 Chapter Summary
9.10 Chapter Quiz
Chapter 10: Planning and Cabling Networks
10.1 LANs - Making the Physical Connection
10.1.1 Choosing the Appropriate LAN Device
10.1.2 Device Selection Factors
10.2 Device Interconnections
10.2.1 LAN and WAN - Getting Connected
10.2.2 Making LAN Connections
10.2.3 Making WAN Connections
10.3 Developing an Addressing Scheme
10.4 Calculating the Subnets
10.5 Device Interconnections
10.6 Chapter Labs
10.7 Chapter Summary
10.8 Chapter Quiz
Chapter 11: Configuring and Testing Your Network
11.1 Configuring Cisco devices - IOS basics
11.2 Applying a Basic Configuration Using Cisco IOS
11.2.1 Devices Need Names
11.2.2 Limiting Device Access - Configuring Passwords and Using Banners
11.2.3 Managing Configuration Files
11.2.4 Configuring Interfaces
11.3 Verifying Connectivity
11.3.1 Test the Stack
11.3.2 Testing the Interface Assignment
11.3.3 Testing Local Network
11.3.4 Testing Gateway and Remote Connectivity
11.3.5 Tracing and Interpreting Trace Results
11.4 Monitoring and Documenting of Networks
11.5 Lab Activity
11.6 Summary
11.7 Chapter Quiz
Você também pode gostar
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102No EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Serial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsNo EverandSerial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (9)
- CompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101No EverandCompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101Ainda não há avaliações
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1No EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- C Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemNo EverandC Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA Cheat Sheet: OSI Model vs. TCP/IP Model OSI Reference Model TCP/IP Model Protocol SuiteDocumento18 páginasCCNA Cheat Sheet: OSI Model vs. TCP/IP Model OSI Reference Model TCP/IP Model Protocol SuiteGhazwan Salih33% (3)
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedAinda não há avaliações
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationAinda não há avaliações
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamNo EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamAinda não há avaliações
- ARM Microcontrollers Programming for Embedded SystemsNo EverandARM Microcontrollers Programming for Embedded SystemsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- NSX 62 InstallDocumento132 páginasNSX 62 InstallMuhammad RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- IP Addressing and Subnetting Workbook - Instructors Version 1.5Documento85 páginasIP Addressing and Subnetting Workbook - Instructors Version 1.5Earl Davis Florant80% (10)
- Network ProjectDocumento6 páginasNetwork ProjectMohammed MustafaAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Manual TELLIN-USAU Universal Signaling Access UnitDocumento86 páginasTechnical Manual TELLIN-USAU Universal Signaling Access Unitrobins rajAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna 1 FinalDocumento61 páginasCcna 1 FinalTamer Abu-ShraikhAinda não há avaliações
- Saes T 555Documento21 páginasSaes T 555Jayvee Baradas ValdezAinda não há avaliações
- ESwitching Lab 7 5 2Documento23 páginasESwitching Lab 7 5 2Ninja NuggetAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna1 Practice Final ExamDocumento15 páginasCcna1 Practice Final ExamMyra KuykendallAinda não há avaliações
- Prctice Final Exam Ccna1Documento24 páginasPrctice Final Exam Ccna1Kristo RadionAinda não há avaliações
- Diorey Practice ExamDocumento22 páginasDiorey Practice ExamYeroid Diorey PotestasAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna1 Final Exam1 2011 MaxDocumento17 páginasCcna1 Final Exam1 2011 MaxAtu Tubagus Ali, STAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna1-Final 2 v4.0Documento18 páginasCcna1-Final 2 v4.0rajnox100% (6)
- Final Thang1.Documento21 páginasFinal Thang1.Hùng QuáchAinda não há avaliações
- Which Three Addresses Belong To The Category of Private IP AddressesDocumento20 páginasWhich Three Addresses Belong To The Category of Private IP AddressesablacadablaAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna 1 Final - WWW - MediafireDocumento20 páginasCcna 1 Final - WWW - MediafireAntónio MarquesAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2011Documento24 páginasCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2011funnwburbsAinda não há avaliações
- Take Assessment - Enetwork Practice Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)Documento18 páginasTake Assessment - Enetwork Practice Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)Korisne SlikeAinda não há avaliações
- Set 1Documento14 páginasSet 1Engr ZynaAinda não há avaliações
- Soal CcnaDocumento22 páginasSoal CcnaArifuddin AmalikAinda não há avaliações
- Click To Download PDFDocumento53 páginasClick To Download PDFlacusclyne87Ainda não há avaliações
- Practice 100Documento19 páginasPractice 100ask_gabyAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco Final Exam LösungenDocumento23 páginasCisco Final Exam LösungenSascha WegenastAinda não há avaliações
- C. Due To A Security Violation, The: The Entries Specify Four Telnet Lines For Remote AccessDocumento29 páginasC. Due To A Security Violation, The: The Entries Specify Four Telnet Lines For Remote AccessdouglasfmoraisAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA1 Feb 2011Documento24 páginasCCNA1 Feb 2011Um MahmoudAinda não há avaliações
- NeffDocumento16 páginasNeffAliAbdulKarimAinda não há avaliações
- Enetwork Practice Final Exam - Ccna Exploration Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)Documento24 páginasEnetwork Practice Final Exam - Ccna Exploration Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)soso1990fgAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna Answers by AbhishekkunalDocumento23 páginasCcna Answers by AbhishekkunalAbhishek KunalAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2011Documento28 páginasCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2011Yawe Kizito Brian PaulAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers - UPDATE 2012 - Eg.1Documento16 páginasCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers - UPDATE 2012 - Eg.1Dobre DanielAinda não há avaliações
- Top of FormDocumento28 páginasTop of Formsybell8Ainda não há avaliações
- Final Answers Ccna Exploration 1Documento20 páginasFinal Answers Ccna Exploration 1Abhishek KunalAinda não há avaliações
- Final Exam PutraDocumento20 páginasFinal Exam PutracrabmoetAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam Answers 2014Documento22 páginasCCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam Answers 2014jonmicAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA Cisco Network Fundamentals Final Exam-Practice (Ver 4.0)Documento23 páginasCCNA Cisco Network Fundamentals Final Exam-Practice (Ver 4.0)sabriel69100% (1)
- CCNA 2 Discovery Final V4.1Documento50 páginasCCNA 2 Discovery Final V4.1Sandra100% (5)
- CCNA1var.2 100p 12Documento7 páginasCCNA1var.2 100p 12tibimaAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA 1 Exploration 2013 Practice Final Answers PDFDocumento10 páginasCCNA 1 Exploration 2013 Practice Final Answers PDFyukina_snowangel100% (2)
- Ccna 1 Exploration 2013 Final Exam Answers 98%Documento12 páginasCcna 1 Exploration 2013 Final Exam Answers 98%yukina_snowangel100% (3)
- Ccna-4-Final Exam-Full 100% PassDocumento15 páginasCcna-4-Final Exam-Full 100% PassChristan CalvaridoAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam V4Documento30 páginasCCNA 1 Practice Final Exam V4miljkoyuAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA 1 Final Exam AnswersDocumento80 páginasCCNA 1 Final Exam AnswersTatenda BizureAinda não há avaliações
- Examen Final Ccna1 v5.0Documento23 páginasExamen Final Ccna1 v5.0Kristian Marlon PrietoAinda não há avaliações
- Inside GlobalDocumento13 páginasInside GlobalKleinhaus GyörgyAinda não há avaliações
- Inside GlobalDocumento13 páginasInside GlobalKleinhaus GyörgyAinda não há avaliações
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkAinda não há avaliações
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksAinda não há avaliações
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingAinda não há avaliações
- Ch2 and Ch3 AssignmentDocumento7 páginasCh2 and Ch3 Assignmentbrone8Ainda não há avaliações
- Cisco 2960 SwitcDocumento1 páginaCisco 2960 Switcbrone8Ainda não há avaliações
- FDocumento25 páginasFbrone8Ainda não há avaliações
- CIS 460 Week 4 Homework 4 - Feb2012Documento3 páginasCIS 460 Week 4 Homework 4 - Feb2012brone8Ainda não há avaliações
- Ch2 and Ch3 AssignmentDocumento7 páginasCh2 and Ch3 Assignmentbrone8Ainda não há avaliações
- Switching & Transmission MediaDocumento43 páginasSwitching & Transmission MediaVicky VigneshAinda não há avaliações
- Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0)Documento12 páginasImplementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0)alizamaxAinda não há avaliações
- KS3 Presentation - 24 Introduction To NetworksDocumento48 páginasKS3 Presentation - 24 Introduction To Networkshunia abbass100% (1)
- JN0-102 2Documento31 páginasJN0-102 2KarthikAinda não há avaliações
- CBT Nuggets SadrzajDocumento7 páginasCBT Nuggets SadrzajSavic SrdjanAinda não há avaliações
- HP TruCluster Server V5.1ADocumento21 páginasHP TruCluster Server V5.1AAlexandru BotnariAinda não há avaliações
- Windows Server 2012 R2 NIC Teaming User GuideDocumento53 páginasWindows Server 2012 R2 NIC Teaming User GuideUncarachaAinda não há avaliações
- Osa Express - Implemantation Guide - RedBook IBMDocumento318 páginasOsa Express - Implemantation Guide - RedBook IBMJorge Carvalho0% (1)
- 1.3 Computer Networks Connections and Protocols End of Topic QuizDocumento30 páginas1.3 Computer Networks Connections and Protocols End of Topic QuizSara737Ainda não há avaliações
- Wan ProposalDocumento7 páginasWan Proposalcmy5073Ainda não há avaliações
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDocumento3 páginas1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsJozeph Abod67% (3)
- 2 - Introduction To Huawei Quidway LAN Switches ISSUE1.01Documento48 páginas2 - Introduction To Huawei Quidway LAN Switches ISSUE1.01Jose Luis ArmandoAinda não há avaliações
- Data Center Applications Standards Reference Guide: White PaperDocumento10 páginasData Center Applications Standards Reference Guide: White PaperzhraniAinda não há avaliações
- MTA OD 366 ExternalDocumento2 páginasMTA OD 366 ExternalSlime ManAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Outcomes: Computer Science Class - Xi Code No. 083 2021-22Documento10 páginasLearning Outcomes: Computer Science Class - Xi Code No. 083 2021-22shivam namdevAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Networks MCQSDocumento3 páginasComputer Networks MCQSKashaf AmreenAinda não há avaliações
- When A Party Makes A Local Telephone Call To Another PartyDocumento5 páginasWhen A Party Makes A Local Telephone Call To Another PartyAniqa AfzalAinda não há avaliações
- Ws c3560x 24t S DatasheetDocumento4 páginasWs c3560x 24t S DatasheetMasterB.E.RAinda não há avaliações
- SignalingDocumento96 páginasSignalingJeansel KahelAinda não há avaliações
- Modul 07b Inter-Vlan (Latihan 2)Documento5 páginasModul 07b Inter-Vlan (Latihan 2)Niken LarasatiAinda não há avaliações
- 640 911Documento96 páginas640 911ivailo770% (1)
- Computer 2018 5th6thDocumento20 páginasComputer 2018 5th6thAnmol JandyalAinda não há avaliações
- 02-VLAN Configuration Guide HP ComwareDocumento8 páginas02-VLAN Configuration Guide HP ComwareElvis de León100% (1)
- PDNE With PDLNE PDFDocumento46 páginasPDNE With PDLNE PDFJamshihas ApAinda não há avaliações