Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CheckPoint Security Administration Module - PartI - 09nov2009
Enviado por
Luu TuongDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CheckPoint Security Administration Module - PartI - 09nov2009
Enviado por
Luu TuongDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Check Point Security
Administration Training
Phan Thanh Long
Cng ty Misoft
Email: longpt@misoft.com.vn
Check Point Security Administration
Course Map
Module 1: Check Point Firewall Architecture &
Installation
Module 2: Security Policy
Module 3: Network Address Translation
Module 4: Log/Monitoring
Module 5: SmartDefense
Module 6: Encryption and VPNs
Module 7: Disaster Recovery
Check Point Security Administration
Course Map
Module 1: Check Point Firewall Architecture &
Installation
Module 2: Security Policy
Module 3: Network Address Translation
Module 4: Log/Monitoring
Module 5: SmartDefense
Module 6: Encryption and VPNs
Module 7: Disaster Recovery
Check Point Security
Administration
Module 1: Check Point Firewall
Architecture & Installation
Module 1: Check Point Firewall
Architecture & Installation
Introduction
Objectives
Describe the purpose of a firewall.
Describe and compare firewall architectures
Identify the different components of
Check Point firewall
Check Point firewall Deployments Models
SIC (Secure Internal Communication )
SmartConsole components
Lab 1: Firewall Stand-alone Installation
Lab 2: Firewall Distributed Installation
Describe the purpose of a firewall
Firewall Technologies
A firewall is a system designed to
prevent unauthorised access to or from a
secured network
act as a locked security door between internal
and external networks
data meeting certain criteria will be allowed
through
However, note that a firewall can only
protect a network from traffic filtered
through it
Internet
SSL
DMZ
IPSec
Trusted Networks
Trusted Users
Firewall
What is a Firewall?
Describe and compare firewall
architectures
Firewall Technologies
Packet Filters
Application-Layer Gateway
Stateful Inspection
Packet Filters
Packet Filtering Path in the OSI Model
Packet Filters
The Advantages of Packet Filtering:
Inexpensive
Application transparency
Faster than application layer gateways
The Disadvantages of Packet Filtering:
Access to a limited part of a packet header
only
Limited screening above the network layer
Very limited ability to manipulate information
Application-Layer Gateway (Proxy)
Application-Layer Gateway Path
Application-Layer Gateway
The advantages of application layer gateways are:
Good security
Full application-layer awareness
The disadvantages of Application Layer Gateways (Proxy) are:
Each service requires its own process, so the number of available
services and their scalability is poor
Implementation at the application level is detrimental to performance
Most proxies are not transparent
Vulnerable to operating system and application level bugs
Overlooks information contained in lower layers
Stateful Inspection
Stateful Inspection Technology
invented by CheckPoint Software Technologies
Stateful Inspection
It is not sufcient to examine packets in isolation.
State informationderived from past communications and other
applicationsis an essential factor in making the control decision
for new communication attempts.
The ability to perform Information manipulation on data in any part
of the packet
Check Point Firewall Architecture
SmartConsole (Client)
SmartCenter (Management Server)
Security Gateway (Enforcement)
SmartCenter
SmartConsole
Security Gateway
SmartConsole
SmartDashboard
SmartConsole
SmartCenter (Management)
Security policy is defined using the
SmartDashboard
It is then saved to the SmartCenter
SmartCenter maintains policy
databases including
network object definitions
user definitions
security policy
log files
SmartCenter
Security Gateway (Firewall Enforcement)
Deployed on the gateway
An Inspection script written in
INSPECT is generated from the
security policy
Inspection code is compiled from the
script and downloaded to the Security
Gateway
Security Gateway Security Gateway
How Security Gateway Works
INSPECT engine allowing Packets
if a packet passes inspection, the Firewall
Module passes packets through the TCP/IP
stack to their destination
if packets are destined for the OS local
processes, are inspected then passed through
the TCP/IP stack
if packets do not pass inspection, they are
blocked.
How Security Gateway Works
INSPECT engine
INSPECT Engine analyzes packet and extracts all relevant
information (communication and application level)
The INSPECT Engine resides in an operating systems
kernel, loaded between the second and third levels, which are
the network interface card (NIC) driver
By inspecting communications at the kernel level, the
INSPECT Engine intercepts and analyzes all packets before
they reach the operating system
No packet is processed by any of the higher protocol layers,
unless FireWall verifies that it complies with the enterprise
security policy
How Security Gateway Works
Security features
IPS
subscription
Anti-Spam
subscription
Web Application Firewall
expansion
SSL VPN / QoS
expansion
URL Filtering
subscription
VPN (site-to-site, remote access)
standard
Anti-virus / Anti-spyware
subscription
The best Firewall in the market
HTTP FTP
Instant Msg E-mail P2P
VoIP SQL
standard
Stand-alone Deployments Models
Distributed Deployments Models
Secure Internal Communication (SIC)
SIC secures communication between
Check Point components such as
SmartCenter
SmartConsole
Security Gateway
Customer log modules
OPSEC applications
...
Security Benefits of SIC
Confirms a SmartConsole connecting
to a SmartCenter is authorised
Verifies that a security policy loaded
on a Security Gateway came from an
authorised SmartCenter
SIC ensures that data privacy and
integrity is maintained
SIC Certificates
SIC Certificates
enables each CheckPoint enabled
machine to be uniquely identified
a unique certificate is generated for each
physical machine
certificates are generated by the Internal
Certificate of Authority (ICA) on the
Management module
SIC Certificates
the ICA automatically creates a certificate
for the Management module during
installation
certificates for other modules are created
via a simple initialisation from the
Management Client
upon initialisation, the ICA creates, signs
and delivers a certificate to the
communication component
Distributed VPN-1 NGX configuration
with certificates
SmartConsole components
SmartDashboard
SmartView Tracker
SmartView Monitor
SmartUpdate
Policy Editor
SmartDashboard
SmartView Tracker
Log viewer/management
SmartView Monitor
SmartUpdate
SmartUpdate
Module 1:
Review
Summary
Review Questions
Review and discussion
Review Question
What is Stateful Inspection Firewall?
What process does Check Point FireWall
use to accept, drop, or reject packets?
What three components making up Check
Point Firewall?
What are key SmartConsole Components?
What are deployments Models
Lab 1: NGX Stand-alone Installation
Installing VPN-1 NGX (SmartCenter
and Security Gateway) on
SecurePlatform
Installing SmartConsole on Windows
Lab 1: NGX Stand-alone Installation
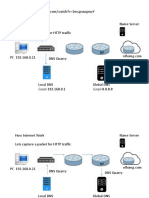
Lab Topology
Security Administration
Lab IP Addresses
PC IP PC
(Web Server)
IP FW Internal
(Int 0)
IP FW DMZ
(Int 1)
IP FW External (Int 2) FW Default Gateway
1 172.16.1.5/24 172.16.1.1/24 172.17.1.1/24 192.168.50.1/24 192.168.50.254/24
2 172.16.2.5/24 172.16.2.1/24 172.17.2.1/24 192.168.50.2/24 192.168.50.254/24
3 172.16.3.5/24 172.16.3.1/24 172.17.3.1/24 192.168.50.3/24 192.168.50.254/24
4 172.16.4.5/24 172.16.4.1/24 172.17.4.1/24 192.168.50.4/24 192.168.50.254/24
5 172.16.5.5/24 172.16.5.1/24 172.17.5.1/24 192.168.50.5/24 192.168.50.254/24
6 172.16.6.5/24 172.16.6.1/24 172.17.6.1/24 192.168.50.6/24 192.168.50.254/24
7 172.16.7.5/24 172.16.7.1/24 172.17.7.1/24 192.168.50.7/24 192.168.50.254/24
8 172.16.8.5/24 172.16.8.1/24 172.17.8.1/24 192.168.50.8/24 192.168.50.254/24
9 172.16.9.5/24 172.16.9.1/24 172.17.9.1/24 192.168.50.9/24 192.168.50.254/24
10 172.16.10.5/24 172.16.10.1/24 172.17.10.1/24 192.168.50.10/24 192.168.50.254/24
11 172.16.11.5/24 172.16.11.1/24 172.17.11.1/24 192.168.50.11/24 192.168.50.254/24
12 172.16.12.5/24 172.16.12.1/24 172.17.12.1/24 192.168.50.12/24 192.168.50.254/24
13 172.16.13.5/24 172.16.13.1/24 172.17.13.1/24 192.168.50.11/24 192.168.50.254/24
14 172.16.14.5/24 172.16.14.1/24 172.17.14.1/24 192.168.50.14/24 192.168.50.254/24
15 172.16.15.5/24 172.16.15.1/24 172.17.15.1/24 192.168.50.15/24 192.168.50.254/24
16 172.16.16.5/24 172.16.16.1/24 172.17.16.1/24 192.168.50.16/24 192.168.50.254/24
17 172.16.17.5/24 172.16.17.1/24 172.17.17.1/24 192.168.50.17/24 192.168.50.254/24
18 172.16.18.5/24 172.16.18.1/24 172.17.18.1/24 192.168.50.18/24 192.168.50.254/24
19 172.16.19.5/24 172.16.19.1/24 172.17.19.1/24 192.168.50.19/24 192.168.50.254/24
20 172.16.20.5/24 172.16.20.1/24 172.17.20.1/24 192.168.50.20/24 192.168.50.254/24
SecurePlatform Installation
H iu hnh da trn Linux (Linux based,
kernel 2.4 & 2.6)
C th ci t trn my ch (Open Servers),
thit b ca Check Point (UTM-1, Power-1), hay
thit b ca third-party (Crossbeam)
Ci bng cch boot a CD, qua cng USB
(usb CD hoc usb device)
S dng giao din dng lnh, hoc qua giao
din Web (ch thit b Check Point yu cu
ci qua giao din Web trc) khi ci t
SecurePlatform Installation
Mt s ch
t hostname chun, tn ny s dng t cho
object
t thi gian, ngy thng chnh xc, vi mi
gi Vietnam GMT + 7
Management IP s l IP dng Object. S dng
a ch Interface hng v SmartCenter, hoc
mng ni b (stand-alone deployment)
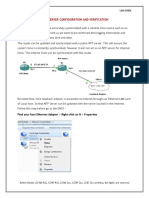
SecurePlatform Configuration
Cu hnh qua dng lnh (Console, SSH)
Cu hnh qua giao din Web
webui enable [https port]
webui disable
SecurePlatform Configuration
Mt s lnh, tin ch thng dng
sysconfig : thit lp hu ht cu hnh c bn
os
cpconfig: cu hnh sn phm Check Point
expert : vo Expert Mode dng cc lnh
linux
fw ver, fwm ver
cpstop, cpstart, cprestart
fw stat: xem policy ang ci trn firewall
SecurePlatform Configuration
Mt s lnh, tin ch thng dng
fwunloadlocal: g b Policy trn firewall
Khi ci t xong Check Point, chnh sch mc
nh cm tt c ci t. S dng lnh khi
cn m cho cc kt ni qun tr ban u, test,
hoc khi b firewall block chnh mnh
SecurePlatform Routing
Routing
ip route add x.x.x.x /xx via x.x.x.x
ip route add x.x.x.x /xx dev ethx
ip route add default via x.x.x.x
ip route add default dev ethx
Ip route show
route --save
Lab 2: Distributed Deployments
Installation
Installing SmartCenter Windows
Server 2003
Installing Security Gateway on
SecurePlatform
Installing SmartConsole on Windows
Lab2: Distributed Deployments
Installation
Lab Topology
Security Administration
Lab IP Addresses
PC IP PC
(Web Server)
IP SmartCenter IP FW Internal
(Int 0)
IP FW Server
(Int 1)
IP FW External (Int
2)
FW Default
Gateway
1 172.16.1.5/24 172.17.1.2/24 172.16.1.1/24 172.17.1.1/24 192.168.50.1/24 192.168.50.254/24
2 172.16.2.5/24 172.17.2.2/24 172.16.2.1/24 172.17.2.1/24 192.168.50.2/24 192.168.50.254/24
3 172.16.3.5/24 172.17.3.2/24 172.16.3.1/24 172.17.3.1/24 192.168.50.3/24 192.168.50.254/24
4 172.16.4.5/24 172.17.4.2/24 172.16.4.1/24 172.17.4.1/24 192.168.50.4/24 192.168.50.254/24
5 172.16.5.5/24 172.17.5.2/24 172.16.5.1/24 172.17.5.1/24 192.168.50.5/24 192.168.50.254/24
6 172.16.6.5/24 172.17.6.2/24 172.16.6.1/24 172.17.6.1/24 192.168.50.6/24 192.168.50.254/24
7 172.16.7.5/24 172.17.7.2/24 172.16.7.1/24 172.17.7.1/24 192.168.50.7/24 192.168.50.254/24
8 172.16.8.5/24 172.17.8.2/24 172.16.8.1/24 172.17.8.1/24 192.168.50.8/24 192.168.50.254/24
9 172.16.9.5/24 172.17.9.2/24 172.16.9.1/24 172.17.9.1/24 192.168.50.9/24 192.168.50.254/24
10 172.16.10.5/24 172.17.10.2/24 172.16.10.1/24 172.17.10.1/24 192.168.50.10/24 192.168.50.254/24
11 172.16.11.5/24 172.17.11.2/24 172.16.11.1/24 172.17.11.1/24 192.168.50.11/24 192.168.50.254/24
12 172.16.12.5/24 172.17.12.2/24 172.16.12.1/24 172.17.12.1/24 192.168.50.12/24 192.168.50.254/24
13 172.16.13.5/24 172.17.13.2/24 172.16.13.1/24 172.17.13.1/24 192.168.50.11/24 192.168.50.254/24
14 172.16.14.5/24 172.17.14.2/24 172.16.14.1/24 172.17.14.1/24 192.168.50.14/24 192.168.50.254/24
15 172.16.15.5/24 172.17.15.2/24 172.16.15.1/24 172.17.15.1/24 192.168.50.15/24 192.168.50.254/24
16 172.16.16.5/24 172.17.16.2/24 172.16.16.1/24 172.17.16.1/24 192.168.50.16/24 192.168.50.254/24
17 172.16.17.5/24 172.17.17.2/24 172.16.17.1/24 172.17.17.1/24 192.168.50.17/24 192.168.50.254/24
18 172.16.18.5/24 172.17.18.2/24 172.16.18.1/24 172.17.18.1/24 192.168.50.18/24 192.168.50.254/24
19 172.16.19.5/24 172.17.19.2/24 172.16.19.1/24 172.17.19.1/24 192.168.50.19/24 192.168.50.254/24
20 172.16.20.5/24 172.17.20.2/24 172.16.20.1/24 172.17.20.1/24 192.168.50.20/24 192.168.50.254/24
Check Point Security
Administration
Module 2: Security Policy
Security Administration
Course Map
Module 1: Check Point Firewall Architecture
& Installation
Module 2: Security Policy
Module 3: Network Address Translation
Module 4: Log/Monitoring
Module 5: SmartDefense
Module 6: Encryption and VPNs
Module 7: Disaster Recovery
Module 2: Security Policy
Introduction
Objectives
Explain the function and operation of a Security
Policy
Create and modify policy, rules, objects
Modify Global Properties
Configure anti-spoofing on the firewall
Use Policy Package Management
Use Database Revision Control
Security Policy Defined
What is a Security Policy?
a set of rules that defines network security
Considerations
Which services, including customized
services and sessions, are allowed across
the network?
Which user permissions and authentication
schemes are needed?
Which objects are in the network? Examples
include gateways, hosts, networks, routers,
and domains.
56
2006 Check Point Software
Rule Base
2
Launching the SmartDashboard
Check Point SmartDashboard
enables administrators to define security policy
only one administrator with read/write
permissions can be logged in at any one time
Start \ Programs \ Check Point SmartConsole R65 \ SmartDashboard
Defining Basic Objects
Defining Node Object
Defining Network Object
Defining Address range Object
Defining Group Object
Launching the SmartDashboard and
define basic objects
Anti-Spoofing
Scenario
Anti-spoofing
Spoofing is a technique used by
intruders attempting to gain
unauthorised access
a packets source IP address is altered to
appear to come from a part of the network
with higher privileges
Anti-spoofing verifies that packets are
coming from, and going to, the correct
interfaces on the gateway
i.e. packets claiming to originate in the
internal network, actually DO come from
that network
Configuring Anti-Spoofing
Networks reachable from an interface
need to be defined appropriately
Should be configured on all interfaces
Spoof tracking is recommended
Anti-spoofing rules are enforced
before any rule in the Security Policy
rule base
Configuring Anti-Spoofing
Configuring Anti-Spoofing
Rule Base Defined
Rule Base Elements
- No.
-Name
-Source
- Destination
- VPN
- Services
- Action
- Track
- Install on
- Time
- Comment
Creating the Rule Base
The default rule
added when you add a rule to the Rule
Base
The Basic Rules
Cleanup Rule
CP follows the principle that which is not
expressly permitted, is prohibited
all communication attempts not matching a
rule will be dropped
the cleanup rule drops all the communication
but allows specific logging
The Basic Rules
The Stealth Rule
prevents users from connecting directly to
the firewall
Implicit, Explicit Rules and
NGX creates implicit rules from
Global Properties
Explicit rule created by Administrator
in the SmartDashboard
Control Conections
VPN-1 NGX creates a group of implicit
rules that it places first, last or before
last
Implicit rules, Global Properties
Rule Base Order
VPN-1 NGX enforces the rule base in
following order:
IP spoofing
NAT
Security Policy First rule
Administrator defined rule base
Security Policy before last rule
Cleanup rule or Security Policy last rule
Create a new policy package
Add new rule into policy
Add object into rule
Basic Policy
Verify / Install and Uninstall a
Security Policy
Verify a Security Policy
Select Policy \ Verify from the SmartDashboard
Click OK
Install/Uninstall a Security Policy
Select Policy \ Install (or Uninstall) from the
SmartDashboard
Click Select All to select all items on the
screen (specific items may be deselected)
Click OK
Install Policy
Defining and install a basic policy
Defining and install a basic policy
Stealth Rule
Allow Ping to firewall gateway
Allow Ping from Internal network to
outside
Allow Internet access (HTTP)
Cleanup Rule
Defining and install a basic policy
Modify Routing Table for ping test
-sysconfig
-add route:
Dest 172.16.x.0/24 gateway 192.168.50.x
85
Advanced Security Policy
Hide/Unhide rule
Enable/Disable rule
Add section title
Object Cloning
Masking Rules
Rules in a rule base can be hidden to allow
easier reading of a complex rulebase
(masking rules)
All other rules will be visible however their
numbers wont change
Hidden rules are still enforced on the
gateway
Viewing Hidden Rules
if View Hidden in the Rules>Hide menu is
checked, all rules set as hidden are displayed
Unhiding Hidden Rules
select Unhide All from the Rules>hide menu
Hide/Unhide rule
Disabling Rules
Disabling Rules
a disabled rule will only take effect after
the security policy is reinstalled
the rule will still be displayed in the
rulebase
Enabling a Disabled Rule
select the disabled rule and right click
select Disable Rule to deselect
remember to reinstall the policy
Enable/Disable rule
Add section title
Add section title (continue)
Object Cloning
Policy editing
Clone Object
Add Section Title
Hide rule
Disable Rule
Command Line Options for the
Security Policy
Basic Options
cpstart/cpstop starts and stops all CP
applications running on the machine
cprestart issues a cpstop and a cpstart
cplic print displays the details of the NGX
licenses
fw ver, fwm ver: displays version
fw unloadlocal: uninstalls current policy of
local Gateway
Improving Performance
SmartCenter
listing machine names and IP addresses
in a hosts file will decrease installation
time for created network objects
/etc/hosts (Solaris)
\winnt\system32\drivers\hosts (Windows)
Improving Performance
Security Gateway
Keep the rulebase simple
Position the most frequently used rules at
the top of the rulebase
Dont log unnecessary connections
Limit the use Reject action in rules
Use a network object in place of many
node objects
Use IP address ranges in rules instead of
a set of nodes
Database revision control and Policy
package management
Database revision control
DRC gives the admin to create fallback
configurations when implementing new
objects or rules
Policy package management
PPM gives the admin to create multiple
versions of a Security Policy but the
objects needs to stay the same
Using Database Revision Control
Using Database Revision Control
and Policy Package management
Review
1. If a rule is masked or hidden, is it disabled and no
longer part of the Rule Base?
2. When you select a rule, and then select Disable
Rule(s) from the menu, what must you also do
before the rule is actually disabled?
3. How does masking help you maintain a Rule Base?
4. Define some guidelines for improving VPN-
1/FireWall-1 NGs performance via a Security Policy
5. Which of following options used to back up entire
Policy database?
Database revision control
Policy package management
Check Point Security
Administration
Module 3: Network Address Translation
Security Administration
Course Map
Module 1: Check Point Firewall Architecture
& Installation
Module 2: Security Policy
Module 3: Network Address Translation
Module 4: Log/Monitoring
Module 5: SmartDefense
Module 6: Encryption and VPNs
Module 7: Disaster Recovery
Introduction
Objectives
List the reasons and methods for Network
Address Translation
Demonstrate how to set up Static NAT
Demonstrate how to set up Dynamic (Hide)
NAT
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation
What is NAT?
as a component of Check Point Firewall it
is used for three things :
to make use of private IP addresses on the
internal network
to conceal internal networks from out side
networks for security reasons
to give ease and flexibility to network
administration
For example, an internal Web server with IP
address 192.168.1.1 could be assigned a NAT
address of 172.10.101.111
Module 3:
NAT
IP Addressing
RFC 1918 details the reserved address groups
Class A network numbers
10.0.0.0 10.255.255.255
Class B network numbers
172.16.0.0 172.31.255.255
Class C network numbers
192.168.0.0 192.168.255.255
Module 3
Network Administration
VPN-1/Firewall-1 supports two types of NAT
Static NAT
Dynamic (Hide) NAT
Understanding Dynamic (Hide) NAT
Module 3:
Dynamic NAT
Module 3
Dynamic (Hide) NAT Ctd.
hide mode packets source port numbers are
modified
destination of a packet is determined by the port
number
port numbers are dynamically assigned from two
pools of numbers :
from 600 to 1023
from 10,000 to 60,000
hide mode cannot be used for protocols where
the port number cannot be changed or where the
destination IP address is required
Module 3:
Hide Mode Address Translation
Module 3:
Hiding Behind Gateway
all clients will be hidden behind the
firewalls server side interface
Understanding Static NAT
Module 3
Static Source NAT
translates private internal source IP addresses
to a public external source IP address
initiated by internal clients with private IP
address
Module 3:
Static Source NAT
Module 3:
Address Translation Using Static Source
Mode
Module 3
Static Destination NAT
translates public addresses to private
addresses
initiated by external clients
Module 3:
Address Translation Using Static
Destination Mode
Module 3:
Address Translation Using Static
Destination Mode
204.32.38.112
Module 3:
Automatic and Manual NAT Rules
NAT Rules
NAT rules consist of two elements
the conditions that specify when the rule is
to be applied
the action to be taken when the rule is
applied
each section in the NAT Rule Base Editor is
divided into Source, Destination and Service
Module 3
Edit Objects properties to enable Automatic NAT
Module 3
Configure manual NAT
Automatic NAT rules are generated by Gateway
Module 3:
Static NAT
Hide NAT
Lab
Hide NAT allows LAB to connect the Internet
Static NAT allows Webserver to be public so users
outside can access it
Check Point Security
Administration
Module 4: Log/Monitoring
Security Administration
Course Map
Module 1: VPN-1 NGX Architecture
Module 2: Security Policy
Module 3: Network Address Translation
Module 4: Log/Monitoring
Module 5: SmartDefense
Module 6: Encryption and VPNs
Module 7: Disaster Recovery
Module 3: Log/Monitoring
Introduction
Objectives
Use SmartViewTracker to display information
about traffic controlled by NGX
Use SmartViewTracker to block an intruder
connection
Use SmartViewMonitor to display information
about firewalls and connections status in real
time, and to block Suspicious Activity
SmartView Tracker
Provides visual tracking, monitoring
and accounting information
Provides control over the log files
display
Allows quick access to information
Any event which causes an alert is
logged, including some system
events such as an install of a policy
130
2006 Check Point Software
SmartConsole: SmartView Tracker
1
SmartView Tracker
Log File Management
the File menu allows the administrator to
perform the following tasks:
Open
Save as
Export
Switch active file
Purge active file
View events using filters
Logs management
View administrators activities
Block intruders
SmartUpdate
Made up of two components
Packages Manager and License
Manager
allows tracking of currently installed
versions of CP and OPSEC products
updating of installed CP and OPSEC
software remotely from a centralised
location
centrally managing licenses
SmartUpdate Architecture
Distributed Configuration
NGX Licensing
License Types
central the license is linked to the IP
number of the management server
local tied to the IP number to which the
license will be applied
Obtaining Licenses
locate certificate key on the CD cover of
the CP CD
contact www.checkpoint.com- selecting
User Center to obtain eval or permanent
license
Check Point User Center
136
2006 Check Point Software
SmartConsole: SmartView Monitor
1
Checking status in SmartView
Monitor
Gateway - Network Activity
Suspicious Activity
Setting up Suspicious Activity rule
Block Suspicious Activity
n tp
1. Thnh phn SmartConsole no cho bit Policy no ang ci
trn mt Firewall gateway?
2. Ngi qun tr nghi ng mt firewall y cng, thnh phn
SmartConsole no gip ngi qun tr kim tra thng tin ny?
3. SmartConsole no c s dng trc tin gip ngi
qun tr g ri mt li kt ni xy ra
4. File log hin hnh (active log) dung lng qu ln, v save
ni dung file log hin hnh sang mt file log khc lu, cn
dng thao tc g?
5. Lm th no kch hot license cho mt filewall?
Check Point Security
Administration NGX I
Authorized Check Point Distributor
Module 5: SmartDefense - Chng
tn cng , qut virus, lc URL
Check Point Security Administration
Course Map
Module 1: Check Point Firewall Architecture
& Installation
Module 2: Security Policy
Module 3: Network Address Translation
Module 4: Log/Monitoring
Module 5: SmartDefense
Module 6: Encryption and VPNs
Module 7: Disaster Recovery
Module 4: SmartDefense - Chng tn
cng, qut virus, lc URL
Gii thiu
Mc tiu
To cc profile chng tn cng v p dng
cho cc tng la khc nhau
Cu hnh chng cc tn cng mc mng v
ng dng
Cp nht cc tn cng mi nht
Xem xt c tn cng no xy ra
Cu hnh qut virus, lc URL
Module 4:
Chng tn cng - IPS
Nguyn tc kim sot truy cp da trn s hiu
cng, a ch ngun, ch, Tuy nhin iu ny
cha , cc tn cng ng dng vn c th din ra
qua cc truy cp dch v c m.
SmartDefense l kh nng pht hin v ngn chn
xm nhp IPS ti mc ng dng
Cc mu pht hin tn cng c cp nht lin tc
trong thi gian thc
Module 4:
To cc profiles cho cc tng la
Module 4:
To cc profiles cho cc tng la
Mi profile l mt tp cc cu hnh chng tn
cng. Ngi qun tr c th to nhiu profile khc
nhau p dng cho cc tng la khc nhau.
Profile default (mc nh) bao gm cc cu hnh
chng tn cng (c kch hot) c bn nht.
Module 4:
Cu hnh chng tn cng cho cc profile
Xem thng tin, m t, s nh hng ca tn cng
Module 4:
Kch hot cu hnh chng tn cng
Module 4:
Cu hnh chng tn cng cho cc profile
Chn profile v kch hot chng tn cng, iu chnh cc thng s
ph hp
Module 4:
p dng cc profiles cho cc tng la
Module 4:
Dch v SmartDefense: Cp nht chng tn
cng
Module 4:
Dch v SmartDefense
S dng ti khon UserCenter c cp login
Download bn cp nht chng tn cng mi nht (khi
dch v cn hiu lc)
Hin th cc tn cng mi c cp nht mi nht,
xem cc li khuyn v hng dn cu hnh chng tn
cng
Module 4:
Dch v SmartDefense
Module 4:
Nhn bit c tn cng xy ra?
Cu hnh track cc tn cng
S dng SmartView Tracker, SmartView Monitor v
xem cc hng dn trong SmartDefense Services
Module 4:
Qut Virus ti Gateway
Turn on Anti-virus
Component
162
Module 4:
Antivirus
Integrated Antivirus
Policy & Updates
Qut virus ngay ti cng truy cp, ngn chn trc khi
chng vo h thng
Qut cho cc giao thc SMTP, POP3, FTP, HTTP, qut
theo lung hoc theo IP
C th qut, bypass hoc cm khi truy cp cc loi file
163
Turn on URL
filtering component
Module 4:
Lc URL
164
URL Filtering
165
URL Filtering Advanced option
d/s URLs/IPs
cho php
d/s URLs/IPs
cm
Cc truy cp
ngoi l
Thng bo ngn
chn
166
URL Filtering Database
Updates are part of the SDAV Subscription
167
URL Filtering
URL database hng u
(Websense)
Hn 15 million sites
Cp nht nhanh v
chnh xc cao
Tch hp cht ch vi
SmartCenter
Module 4:
SmartDefense
Check Point Security
Administration
Module 7: Disaster Recovery
Check Point Security Administration
Course Map
Module 1: Check Point Firewall Architecture
& Installation
Module 2: Security Policy
Module 3: Network Address Translation
Module 4: Log/Monitoring
Module 5: SmartDefense
Module 6: Encryption and VPNs
Module 7: Disaster Recovery
Disaster Recovery
Introduction
Objectives
Backups are used to restore configurations
and keep downtime to a minimum
Backup and Restore system
configurations
Backup
backup f filename
backup e on 17:00 m 25 --file filename
backup e : to view the schedule setting
/var/CPbackup/backups
Restore
restore
[L] Restore local backup package
[T] Restore backup package from TFTP server
[S] Restore backup package from SCP server
[R] Remove local backup package
[Q] Quit
Backup and Restore Policy database
$FWDIR (/opt/CPsuite-R65/fw1)
conf: rules, objects, policy, user database
lib:
log:
objects.C and objects_5_0.C
($FWDIR/conf)
rulebase_5_0.fws ($FWDIR/conf)
fwauth.NDB ($FWDIR/conf and
$FWDIR/database)
Backup and Restore Policy database
Export
/opt/CPsuite-R65/fw1/bin/upgrade_tools/
Copy windows\Actions on CD2 to C:\
upgrade_export filename
Import
upgrade_import filename
Backup and Restore System
Configuration, Policy database and
Log files
snapshot command
Image management via Web console
Backup and Restore
Você também pode gostar
- 8.checkpoint Firewall Interview QuestionsDocumento7 páginas8.checkpoint Firewall Interview Questionsnagendra_badam100% (1)
- Securing Communication of Legacy Applications with IPSec: Step-by-Step Guide to Protecting “Data in Transit” without Changes in Your Existing SoftwareNo EverandSecuring Communication of Legacy Applications with IPSec: Step-by-Step Guide to Protecting “Data in Transit” without Changes in Your Existing SoftwareAinda não há avaliações
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNo EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityAinda não há avaliações
- Checkpoint TroubleshootingDocumento33 páginasCheckpoint TroubleshootingKrasimir Kotsev100% (1)
- Edu-201 - Lab Manual Pan-Os 5.0Documento39 páginasEdu-201 - Lab Manual Pan-Os 5.0fortinet12350% (2)
- Palo+Alto+Interview+Questions + (Compliance) +Documento11 páginasPalo+Alto+Interview+Questions + (Compliance) +GangaAinda não há avaliações
- PaloAltoNetworks Designs Guide RevB PDFDocumento110 páginasPaloAltoNetworks Designs Guide RevB PDFsatya28100% (2)
- Pcnsa Study Guide Latest PDFDocumento187 páginasPcnsa Study Guide Latest PDFmandar kulkarni100% (3)
- PCNSE 8.1 - Study - Guide - 2018.07Documento196 páginasPCNSE 8.1 - Study - Guide - 2018.07martin10090% (1)
- Aruba Partner Workshop PDFDocumento138 páginasAruba Partner Workshop PDFjannnu_sbAinda não há avaliações
- R80 Student Manual + OCRDocumento256 páginasR80 Student Manual + OCRVinee PahujaAinda não há avaliações
- Checkpoint Firewall Administration Training Part1Documento48 páginasCheckpoint Firewall Administration Training Part1Raja Athi100% (1)
- Palo AltoTroubleshooting Decision Tree Guide PDFDocumento22 páginasPalo AltoTroubleshooting Decision Tree Guide PDFAponteTrujillo100% (1)
- SD-Access Deployment GuideDocumento95 páginasSD-Access Deployment GuideAriAinda não há avaliações
- EDU 110 80a Lab GuideDocumento153 páginasEDU 110 80a Lab Guidemanish kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Troubleshooting Palo Alto Docs GuideDocumento502 páginasTroubleshooting Palo Alto Docs GuideIti70100% (2)
- Troubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsNo EverandTroubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Palo Alto LabDocumento87 páginasPalo Alto LabWilinton Cuevas Poma100% (1)
- Checkpoint CCSA by Keith Barker Site To Site VPNDocumento41 páginasCheckpoint CCSA by Keith Barker Site To Site VPNshikhaxohebkhanAinda não há avaliações
- Training CheckpointDocumento63 páginasTraining Checkpointrajivmukherjee07Ainda não há avaliações
- Sdwan Practice Lab 1 v1.1Documento261 páginasSdwan Practice Lab 1 v1.1Lam Van BuiAinda não há avaliações
- SD Wan Architecture Guide PDFDocumento65 páginasSD Wan Architecture Guide PDFTawakalAinda não há avaliações
- Paloalto - Packet FlowDocumento11 páginasPaloalto - Packet FlowOrang E Dan100% (1)
- Lab - Ccna SecurityDocumento36 páginasLab - Ccna SecurityMohanMishraAinda não há avaliações
- EDU 110 9.0 Labguide PDFDocumento265 páginasEDU 110 9.0 Labguide PDFElbarni MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- CCNP RouteDocumento65 páginasCCNP RouteMashud Ashraf BarbhuiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Guide ISE 1 2 ProfilingDocumento39 páginasLab Guide ISE 1 2 Profilingjuliushasan2Ainda não há avaliações
- Palo Alto Interview QuestionsDocumento5 páginasPalo Alto Interview QuestionsRamesh S0% (1)
- CCNP SecDocumento210 páginasCCNP SecThien Nhan Vo Nguyen100% (2)
- Iser Lab For BYODDocumento25 páginasIser Lab For BYODzohebsarwar82Ainda não há avaliações
- Pcnse Study GuideDocumento226 páginasPcnse Study Guidedebjyoti GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- PCNSA Study Guide 2020 PDFDocumento192 páginasPCNSA Study Guide 2020 PDFScrcum100% (4)
- CCSA Class SlidesDocumento285 páginasCCSA Class SlidesphamvanhaAinda não há avaliações
- Checkpoint FirewallDocumento14 páginasCheckpoint FirewallJonnalagadda Harshavardhan100% (2)
- Palo Alto Firewall VirtualizationDocumento394 páginasPalo Alto Firewall VirtualizationRyanb378Ainda não há avaliações
- Cisco MerakiDocumento27 páginasCisco MerakiShiv Bhattarai100% (2)
- PCNSE Study Guide Aug 2020 PDFDocumento346 páginasPCNSE Study Guide Aug 2020 PDFPiyush Chavda100% (1)
- PaloAlto Firewall Interview Questions Net Tech LatestDocumento12 páginasPaloAlto Firewall Interview Questions Net Tech LatestADITYA KAUSHIKAinda não há avaliações
- Palo Alto Networks - Testking.pcnse7.v2016!09!07.by - Pierre.51qDocumento37 páginasPalo Alto Networks - Testking.pcnse7.v2016!09!07.by - Pierre.51qSaurabh Gupta100% (1)
- F5 BIG-IP Local Traffic Manager Service Insertion With Cisco Application Centric InfrastructureDocumento56 páginasF5 BIG-IP Local Traffic Manager Service Insertion With Cisco Application Centric InfrastructureSurath KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Orion Administrator GuideDocumento352 páginasOrion Administrator GuideJulio Cesar EMAinda não há avaliações
- BIG-IP Application Security Manager ImplementationsDocumento396 páginasBIG-IP Application Security Manager Implementationsfortinet123Ainda não há avaliações
- Fortinet CliDocumento20 páginasFortinet CliRasakiRraskiAinda não há avaliações
- Check Point Firewall Interview QuestionsDocumento5 páginasCheck Point Firewall Interview QuestionsHemant Sharma100% (2)
- Implement MP-BGP EVPN VxLAN Control Plane v1 Demo GuideDocumento24 páginasImplement MP-BGP EVPN VxLAN Control Plane v1 Demo Guideberwal1916Ainda não há avaliações
- EDU 311 80a Student Lab Guide - 08Documento39 páginasEDU 311 80a Student Lab Guide - 08Ajeet Singh100% (1)
- VPN Top 100 Interview Questions and Answers: Ques 1. What Is VPN?Documento27 páginasVPN Top 100 Interview Questions and Answers: Ques 1. What Is VPN?Arvind Kumar100% (1)
- Paloalto Lab Part 1 2019Documento39 páginasPaloalto Lab Part 1 2019Quang Anh100% (1)
- EDU-210-8.1-Lab Guide PDFDocumento167 páginasEDU-210-8.1-Lab Guide PDFMilošKovačević0% (1)
- Check Point VPN Debugging GuideDocumento6 páginasCheck Point VPN Debugging Guidesgopal7Ainda não há avaliações
- ASA Firewall Interview Questions and Answers (CCIE) - Networker InterviewDocumento10 páginasASA Firewall Interview Questions and Answers (CCIE) - Networker InterviewRaj KaranAinda não há avaliações
- BIG-IP LTM Architecture and High AvailabilityDocumento19 páginasBIG-IP LTM Architecture and High Availabilityanh0050% (2)
- Ccna SecurityDocumento81 páginasCcna SecurityBrahim El-Asri100% (1)
- Pcnse Study Guide PDFDocumento344 páginasPcnse Study Guide PDFMahmud AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- VXLAN Deployment - Use Cases and Best PracticesDocumento76 páginasVXLAN Deployment - Use Cases and Best PracticesMalesPulangAinda não há avaliações
- Palo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNo EverandPalo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsAinda não há avaliações
- SYSDESKDocumento4 páginasSYSDESKapi-72678201Ainda não há avaliações
- Advance Java Module TestDocumento13 páginasAdvance Java Module TestAnkitaAryaAinda não há avaliações
- Information Sheet 1.2-1 Operating System: Install and Configure Computer Systems Developed byDocumento19 páginasInformation Sheet 1.2-1 Operating System: Install and Configure Computer Systems Developed byAre Em Gee100% (1)
- 03 - ePDG AAA & Nodes PDFDocumento30 páginas03 - ePDG AAA & Nodes PDFAshish NokiaAinda não há avaliações
- Catalog Anytone 2023 ENGDocumento32 páginasCatalog Anytone 2023 ENGnenadbjelicAinda não há avaliações
- Intelli SnapDocumento44 páginasIntelli SnapVenkat ChowdaryAinda não há avaliações
- RnqfficeDocumento212 páginasRnqfficeFichDich InDemArschAinda não há avaliações
- Errata At90s2313Documento2 páginasErrata At90s2313carlos augusto do carmo braiaAinda não há avaliações
- AsasasasasaDocumento27 páginasAsasasasasaSivaReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Control Builder Components Theory: Experion PKSDocumento1.398 páginasControl Builder Components Theory: Experion PKSAnkoosh MandanAinda não há avaliações
- 13-Inventory of Training ResourcesDocumento3 páginas13-Inventory of Training ResourcesMichaella De Jesus Failon100% (1)
- Qualys Was API User GuideDocumento544 páginasQualys Was API User Guidemadhan21Ainda não há avaliações
- Primavera UnifierDocumento37 páginasPrimavera UnifierkadamvinayaksAinda não há avaliações
- Ubuntu 12.04 - Install Sun JDK 6-7: Search..Documento20 páginasUbuntu 12.04 - Install Sun JDK 6-7: Search..kumar9030Ainda não há avaliações
- CM52 at Command Manual Rev R1DDocumento158 páginasCM52 at Command Manual Rev R1Dzuhri2goAinda não há avaliações
- Modicon Quantum - SOE SystemDocumento4 páginasModicon Quantum - SOE SystemAgis Rijal AtmawijayaAinda não há avaliações
- Merging NADAC ASIO and CoreAudio GuideDocumento36 páginasMerging NADAC ASIO and CoreAudio GuideDavid JacquesAinda não há avaliações
- Practica IT Essentials V5.0Documento2 páginasPractica IT Essentials V5.0Manuel Huertas HonoresAinda não há avaliações
- CH 1Documento62 páginasCH 1waqarsyedwaqar76Ainda não há avaliações
- Cisco SD-WAN Extranet VPN LabDocumento24 páginasCisco SD-WAN Extranet VPN LabShashank TripathiAinda não há avaliações
- Sequential Logic CircuitsDocumento18 páginasSequential Logic CircuitsMona SayedAinda não há avaliações
- Operation Guide For UMaker ToolDocumento25 páginasOperation Guide For UMaker ToolhamidAinda não há avaliações
- Java QuizDocumento18 páginasJava Quizssa_joeAinda não há avaliações
- VB Tutorial-Connect VB Application With MS Access Through CodingDocumento19 páginasVB Tutorial-Connect VB Application With MS Access Through CodingBeschiAntonyD79% (19)
- AT42QT1010 Breakout HookupGuideDocumento7 páginasAT42QT1010 Breakout HookupGuidescrubberAinda não há avaliações
- The Bcs Professional Examinations BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT April 2008 Examiners' Report Object Oriented ProgrammingDocumento11 páginasThe Bcs Professional Examinations BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT April 2008 Examiners' Report Object Oriented ProgrammingOzioma IhekwoabaAinda não há avaliações
- Infineon Infineon TLE8080EM DS v01 02 enDocumento38 páginasInfineon Infineon TLE8080EM DS v01 02 enYael AlcaAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Guide: Block DiagramDocumento60 páginasReference Guide: Block DiagrambestalfiraAinda não há avaliações
- CrowdforGeeks - CTM QaDocumento9 páginasCrowdforGeeks - CTM QaVirat VasuAinda não há avaliações
- Catalog Optocuploare Temic 1996Documento77 páginasCatalog Optocuploare Temic 1996misternoAinda não há avaliações