Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Anatomy and Physiology of The Heart
Enviado por
Ruki HartawanTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Anatomy and Physiology of The Heart
Enviado por
Ruki HartawanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
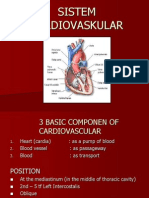
CARDIOVASCULAR
SYSTEM
Anatomy & Physiology
dr. Jeffrey Wirianta
March 8
th
2004
THE HEART
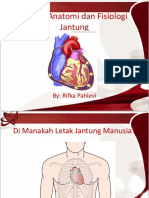
Lokasi Jantung
Di dalam Pericardium di rongga mediastinum
dalam rongga Thorak
Tepat di belakang tulang dada ( sternum )
Kurang lebih 2/3 bagian terletak di sebelah kiri
dari garis tengah
Fungsi dan Ukuran
Fungsi : sebagai pompa ganda agar terjadi
aliran dalam pembuluh darah yang
disebabkan adanya pergantian antara
kontraksi ( sistolik ) dan relaksasi
( diastolik )
Ukuran : 250 350 gram
( kira-kira sebesar kepalan tangan )
Fibrous Skeleton
Kerangka jantung yang
terdiri dari jaringan
kolagen yang tebal dan
kuat
Penunjang fisik jantung
Pegangan katup
Mencegah kelebihan
regangan otot jantung
Electrical insulation
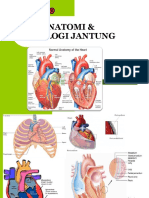
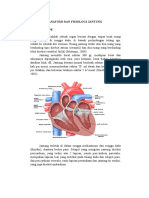
Anatomy of the Heart
Pericardium :
Outer fibrous sack
Myocardium :
Thick muscle walls
Endocardium :
Innermost surface
Endothelium
Simple squamous
epithelium
Interventriculer Septum
Papillary muscle
Semilunar Valve
Perikardium
Perikardium Fibrosa
Lapisan paling luar rongga Pericardium
Menjaga kedudukan jantung di rongga mediastinum
Perikardium Serosa
Lapisan parietalis
Lapisan bagian dalam dari rongga pericardial
Lapisan visceralis / epicardium
Rongga Perikardium
Cairan pericardium
Mengurangi gesekan saat jantung bergerak
Anatomy of the Heart
Heart chambers :
Left & right atria
Left & right ventricles
Heart valves :
Atrioventricular valves :
Right : Tricuspid
Left : Bicuspid/Mitral
Semilunar valves
Right : Pulmonary valve
Left : Aortic valve
Anatomy of the Heart
Aorta
Coronary arteries
Arterioles
Capillaries
Venules
Coronary sinus
Right atrium
Coronary circulation
Tipe-tipe sel Otot Jantung
Autoritmik
autoritmik mampu berdepolarisasi spontan
produce pacemaker potentials
menyalurkan aksi potensial ( impulses ) melewati
myocardium
tidak berkontraksi
Kontraktil
Potensial aksi menimbulkan kontraksi
Aliran darah ditimbulkan oleh pergantian dari
kontraksi ( SISTOLIK ) dan Relaksasi ( DIASTOLIK )
Intrinsic Conducting System
Sinoatrial node
Electrical pace maker
Atrioventricular node
Receives impulses
originating from SA node
Bundle of His
Electrical link between
atria and ventricles
Purkinje fibres
Distribute impulses to
ventricles
Sel Autoritmik
Fase Depolarisasi
Fase Repolarisasi
Fase Istirahat
Sel Kontraktil
Fase Depolarisasi
Fase Plateu
Fase Repolarisasi
Fase Istirahat
Conduction System
SA Node
Internodal branch
AV Node
Hiss Bundle
Purkinje Fiber
Contraction
Cardiac Action Potentials
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
The Electrocardiogram ( ECG )
P wave : atrial
depolarisation
QRS complex :
ventricular
depolarisation
T wave : ventricular
repolarisation
Atrial repolarisation
hidden by QRS
P
Q
R
S
T
The Electrocardiogram
(ECG)
Leads can be placed on
wrists and left ankle
( right ankle is earthed )
Voltages are measured
across each point as
shown
I = L wrist to R wrist
II = R wrist to L ankle
III = L ankle and L wrist
The heart sits in the
centre of the triangle
I
II
III
+/-
+
-
The Electrocardiogram
The three standard
measurements can
be used to
electronically
calculate the
currents flowing
towards each limb
aVR
aVL
aVF
+
The Cardiac Cycle
Systole :
Period of ventricular contraction
Blood ejected from heart
Diastole :
Period of ventricular relaxation
Blood filling
Stroke Volume
The amount of blood ejected from the
heart in one beat
Average is 60 - 100 ml
Depends on preload, contractile force and
afterload
Cardiac Output
The amount of blood ejected from the
heart in one minute
Cardiac output = heart rate x stroke
volume
Starlings Law
The more the myocardium is stretched, the
greater the stroke volume
Has limits
Dependent upon venous return
Blood Pressure
BP = cardiac output x systemic vascular
resistance
Definitions
Chronotropy Change in heart rate
Inotropy Change in contractile
force
Dromotropy Change in conduction
velocity
Can be positive or negative
Você também pode gostar
- Sistem Kardiovaskular NewDocumento25 páginasSistem Kardiovaskular NewDina Rasmita100% (3)
- Fisiologi KardiovaskularDocumento35 páginasFisiologi KardiovaskularAdrianusAinda não há avaliações
- Bedah DigestiDocumento143 páginasBedah DigestiSince Ivanna RumbiakAinda não há avaliações
- Sirs Sepsis Mods Mof DanDocumento19 páginasSirs Sepsis Mods Mof DanRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah Anfis CardiovasculerDocumento29 páginasKuliah Anfis CardiovasculerErvhina Agni TrianiAinda não há avaliações
- Slide Makalah Anatomi Sistem KardiovaskulerDocumento58 páginasSlide Makalah Anatomi Sistem KardiovaskulerDjoefrei100% (1)
- Fisiologi KardiovaskulerDocumento41 páginasFisiologi Kardiovaskuleryo2_laxana100% (2)
- Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem KardiovaskulerDocumento24 páginasAnatomi Fisiologi Sistem KardiovaskulerRizky SamalAinda não há avaliações
- Sistem Sirkulasi FiksDocumento50 páginasSistem Sirkulasi FiksAfrinda MukaromahAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Fisiologi Kardiovaskuler PDFDocumento70 páginasAnatomi Fisiologi Kardiovaskuler PDFThufeil AddausyAinda não há avaliações
- Sistem JantungDocumento34 páginasSistem JantungNalamaran ThanarasaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Sistem Kardiovaskuler-aKBID-MRADocumento46 páginasAnatomi Sistem Kardiovaskuler-aKBID-MRAsekprodi profesifkyarsiAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi FisiologiDocumento4 páginasAnatomi FisiologiSamAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Kardiovaskular by RicaDocumento149 páginasAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Kardiovaskular by Ricanono wartonoAinda não há avaliações
- Ekg 12 Lead Dan InterpretasiDocumento84 páginasEkg 12 Lead Dan InterpretasiDea NainggolanAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi JantungDocumento24 páginasAnatomi Dan Fisiologi JantungEndah Novianti SoenarsinAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem KardiovaskularDocumento143 páginasAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Kardiovaskularnono wartonoAinda não há avaliações
- Fisiologi KardiovaskulerDocumento52 páginasFisiologi KardiovaskulerMaria Belladonna100% (1)
- Sistem KardiovaskulerDocumento36 páginasSistem KardiovaskulerTesia YosepaAinda não há avaliações
- Anfis-Sistem KardiovaskulerDocumento35 páginasAnfis-Sistem KardiovaskulerKhofifah KhusnulAinda não há avaliações
- 4.fis Vasc & Sirkulasi 2019 MHSWDocumento56 páginas4.fis Vasc & Sirkulasi 2019 MHSWdina aulia lestariAinda não há avaliações
- Resume KMB I (Fisiologi Jantung)Documento8 páginasResume KMB I (Fisiologi Jantung)AnittaAinda não há avaliações
- SP Anfis JantungDocumento23 páginasSP Anfis JantungIna IsnasaumiAinda não há avaliações
- AirinDocumento20 páginasAirinxxxdfghtAinda não há avaliações
- Patologi Kardiovaskuler Pulmonal Pertemuan 2Documento55 páginasPatologi Kardiovaskuler Pulmonal Pertemuan 2Weddy MartinAinda não há avaliações
- Fisiologi Pembuluh DarahDocumento76 páginasFisiologi Pembuluh DarahRoselin Megasari MendrofaAinda não há avaliações
- Anfis Sistem KARDIOVASKULARDocumento43 páginasAnfis Sistem KARDIOVASKULARAnisa GustianaAinda não há avaliações
- Sistem Kardiovaskuler TLMDocumento39 páginasSistem Kardiovaskuler TLMbonbabon13Ainda não há avaliações
- Ringkasan Jantung Dan Pembuluh DarahDocumento8 páginasRingkasan Jantung Dan Pembuluh DarahRisnaAinda não há avaliações
- Anfis KardiovaskulerDocumento30 páginasAnfis KardiovaskulerArdhy Mac Abram0% (1)
- 5.FISIOLOGI JANTUNG (Mekanisme Kontraksi Jantung)Documento18 páginas5.FISIOLOGI JANTUNG (Mekanisme Kontraksi Jantung)Cut Nabila AmaniAinda não há avaliações
- Slide Kardio HP.2019Documento78 páginasSlide Kardio HP.2019Indah frysay marbunAinda não há avaliações
- Asuhan Keperawatan Gagal Jantung KongestifDocumento9 páginasAsuhan Keperawatan Gagal Jantung KongestifMochamad Maf Tu'inAinda não há avaliações
- Anfis CardiovaskulerDocumento27 páginasAnfis CardiovaskulerarinaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Fisiologi Kardio HayyuDocumento10 páginasAnatomi Fisiologi Kardio HayyuayucitoAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem Kardiovaskuler-MrDocumento59 páginasAnatomi Fisiologi Sistem Kardiovaskuler-MrAnggun SabatyAinda não há avaliações
- Fisiologi Jantung - Pengantar EkgDocumento56 páginasFisiologi Jantung - Pengantar EkgAyu SafitriAinda não há avaliações
- Penyakit Jantung BawaanDocumento23 páginasPenyakit Jantung BawaanRick RomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi JantungDocumento46 páginasAnatomi Jantungsepta rezitaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Fisiologi Jantung 1Documento46 páginasAnatomi Fisiologi Jantung 1Ferdiansyah PutraAinda não há avaliações
- Patofisiologi Penyakit JantungDocumento86 páginasPatofisiologi Penyakit JantungjeinpratpongAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Fisiologi CardiovaskulerDocumento96 páginasAnatomi Fisiologi CardiovaskulerkikiAinda não há avaliações
- Sistem Pumbuluh DarahDocumento24 páginasSistem Pumbuluh DarahSel VanyAinda não há avaliações
- LP ADHF Niluh Nita AsriyaniDocumento34 páginasLP ADHF Niluh Nita AsriyaniI Wayan Adi SuciptaAinda não há avaliações
- C15 - Riska Nurlaila - BAB 1 Dan 2 Jilid 2Documento21 páginasC15 - Riska Nurlaila - BAB 1 Dan 2 Jilid 2riskaAinda não há avaliações
- Fisiologi CardiovascularDocumento6 páginasFisiologi CardiovascularZaenul Arfian NaserAinda não há avaliações
- Matrikulasi KedokteranDocumento43 páginasMatrikulasi Kedokterankresna0108DOCAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Kardiologi Jantung RobbyDocumento13 páginasTugas Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Kardiologi Jantung Robbyrobby andriadiAinda não há avaliações
- ANFIS Sistem KardiovaskulerDocumento17 páginasANFIS Sistem KardiovaskulerMila AmaliahAinda não há avaliações
- Let's Recall KardiologiDocumento28 páginasLet's Recall KardiologiYumiSapta KanaAinda não há avaliações
- Pert. 2 KardiovaskularDocumento59 páginasPert. 2 KardiovaskularElkana florentina pardosiAinda não há avaliações
- 2 FisiologikardiovaskularDocumento27 páginas2 FisiologikardiovaskularCinta MeilikaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi & Fisiologi Kardiovascular 2016Documento69 páginasAnatomi & Fisiologi Kardiovascular 2016Oncix PermanaAinda não há avaliações
- Catatan Biomedik KARDIOVASKULER 1Documento12 páginasCatatan Biomedik KARDIOVASKULER 1nabella novacAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi JantungDocumento10 páginasAnatomi Dan Fisiologi JantungalifAinda não há avaliações
- 1 AF - Sistem Kardiovaskular - JantungDocumento135 páginas1 AF - Sistem Kardiovaskular - JantungGIZI RSUD TAMANSARIAinda não há avaliações
- LP HHD WhanaDocumento17 páginasLP HHD WhanasaalimAinda não há avaliações
- Efek Covid 19 Pada Organ Jantung Dan Pembuluh Darah Dr. MiaDocumento24 páginasEfek Covid 19 Pada Organ Jantung Dan Pembuluh Darah Dr. MiaJaqueline EffendyAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology of Analgesic Drugs (20 Okt 2017)Documento44 páginasPharmacology of Analgesic Drugs (20 Okt 2017)Ruki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- SepsisDocumento49 páginasSepsisWidi Nur Wicaksana100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Analgesic Drugs (20 Okt 2017)Documento44 páginasPharmacology of Analgesic Drugs (20 Okt 2017)Ruki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- Iskemik Dan Infark InterpretationDocumento25 páginasIskemik Dan Infark InterpretationRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Aru - Kemoterapi MRCCCDocumento37 páginasDr. Aru - Kemoterapi MRCCCRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- Intrepretasi AGD BOGOR UpdateDocumento71 páginasIntrepretasi AGD BOGOR UpdateRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- ANCCS Hemorhagic Stroke MinDocumento37 páginasANCCS Hemorhagic Stroke MinBuat Apa ProductionAinda não há avaliações
- KimiaDocumento34 páginasKimiamega paramitha100% (1)
- Deteksi Dini Kanker Serviks PDFDocumento55 páginasDeteksi Dini Kanker Serviks PDFRuki Hartawan100% (1)
- Hipertensi & HipotensiDocumento30 páginasHipertensi & HipotensiAbi FaizAinda não há avaliações
- Efusi Pleura Ganas Fkuwks 2017Documento17 páginasEfusi Pleura Ganas Fkuwks 2017Nas IndrajanuAinda não há avaliações
- Prof Barmawi Kuliah 3 Hepatitis CitoDocumento30 páginasProf Barmawi Kuliah 3 Hepatitis CitoRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- Protokol Sepsis Amp Syok SepsisDocumento6 páginasProtokol Sepsis Amp Syok SepsisRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- CBD NefroDocumento33 páginasCBD NefroRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- Prof Barmawi Kuliah 3 Hepatitis CitoDocumento30 páginasProf Barmawi Kuliah 3 Hepatitis CitoRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrisi Parenteral Pada Neonatus (Clinical PractiDocumento11 páginasNutrisi Parenteral Pada Neonatus (Clinical PractiRahardi FebryantoAinda não há avaliações
- Hepatologi KlinikDocumento69 páginasHepatologi KlinikRuki Hartawan100% (1)
- Infeksi Saluran KemihDocumento5 páginasInfeksi Saluran KemihRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- KolestasisDocumento24 páginasKolestasisRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- Tb. ParuDocumento27 páginasTb. ParuRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- Penanganan Kasus Flu Burung EditingDocumento20 páginasPenanganan Kasus Flu Burung EditingRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- AP PPGD Introduction FKDocumento35 páginasAP PPGD Introduction FKRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- Sindroma Kesukaran Pernafasan NeonatusDocumento27 páginasSindroma Kesukaran Pernafasan NeonatusMarfain AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Ilmu Kedokteran TropisDocumento22 páginasIlmu Kedokteran TropisDwi Septa MulyadiAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah 01 Kejang DemamDocumento33 páginasKuliah 01 Kejang DemamRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- ProstatDocumento7 páginasProstatRuki HartawanAinda não há avaliações
- 8.infection Control of TB in Hospital SettingDocumento22 páginas8.infection Control of TB in Hospital SettingVera NersAinda não há avaliações