Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Kuliah Graphics Compatibility Mode
Enviado por
aqmar77Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Kuliah Graphics Compatibility Mode
Enviado por
aqmar77Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Graphics
Graphics p
The introduction of the Apple Macintosh computer and
the Microsoft Windows programchanged the way we the Microsoft Windows program changed the way we
worked with computers.
Using a mouse and a desktop metaphor, we click on
i d d d d f ld d i icons and drop-down menus, drag folders, and resize
windows.
We are accustomed to working with graphical images on g g p g
the screen and, in fact, expect to see them.
Graphics p
This document will provide you with a base
understanding and conceptual map of digital g p p g
image/graphics technology.
This document will not explain how to use any specific p y p
software application. Instead it will shine a guiding light
on the technicalities of digital imaging so that when you
approach a software application, you will have a approach a software application, you will have a
foundation of knowledge, and a sense of direction.
Type of Graphics
Type of Graphics yp p
Graphics may include a drawing/illustration,
photograph, diagrams, cartoons or graphs.
Photographs
Are one of the most "realistic" visuals. Color video
tape, color still pictures and even black and white tape, color still pictures and even black and white
photographs are very powerful communication tools.
Full-color photographs can also add impact to any
presentation when used as backgrounds for text and
hi graphics.
Drawings
Are usually less realistic than photographs but they Are usually less realistic than photographs, but they,
within themselves, have a wide range from realistic
to abstract.
Type of Graphics yp p
Cartoons
Are a separate class of drawings These cartoons may "humanize" Are a separate class of drawings. These cartoons may humanize
animals and objects or they may "stereotype". They may just be
"cute". For younger learners, these cartoons may capture and hold
attention. Often they can be used to establish a "guide" or "mentor"
that helps learners through the program that helps learners through the program.
Diagrams
Diagrams move toward the abstract end of the continuum. Although
they may in some cases look very realistic they usually go beyond they may, in some cases, look very realistic, they usually go beyond
realism to show things or relationships that the real object could not
show. J ust a few of the type of diagrams are shown to the right.
Type of Graphics yp p
Graphs
Often the information we are to transmit is a
mass of numerical data. If the data must be read
ith t t l d t t b t d with total accuracy, raw data must be presented.
However, more often than not a concern is to
display the data in an easily the data in an easily display the data in an easily the data in an easily
read format. This is the role of the graph.
Type of Graphics (Example) Type of Graphics (Example)
cartoon
diagram
photo
Type of Graphics (Example)
drawing
graph
Graphics Category
Graphics p
There are two categories of graphics :-
a) Vector
b) Bitmaps b) Bitmaps
Graphics p
What are the differences between two types of image above?
Bitmap Image p g
Bitmap graphics are also called raster graphics. A bitmap represents the
image as an array of dots, called pixels.
By zooming the image, you can see the number of pixels that build up the
total of image. Increasing the size of the bitmap image will reduce the
quality of image.
Bitmap Image p g
Bitmap graphics are resolution-dependent and generate large
file sizes. Scaling simply makes the viewed pixels larger or g py p g
smaller. This results in image quality problems, since software
must add or remove pixels to fit a select size.
Bitmap Image p g
1 matric dimention (1 bit) = monochrome
t (bl k & hit ) computers (black & white)
Hi h d th t 16 illi High depth represents = 16 million
colors.
color depth = 4 bit, 8 bit, 24 bit
Bitmap Image p g
Three methods to produce bitmap
iimages:
image capture directly from screen (screen image capture directly from screen (screen
capture).
graphics capture equipments : scanners, graphics capture equipments : scanners,
digital camera, video capture card or any
capture devices.
Vector Image g
The ability to resize and rotate a graphic without distortions a major
advantage of vector graphics.
Another advantage is their smaller file size. Because these graphics
are stored as sets of instructions, the file sizes can be significantly
smaller than bitmaps. smaller than bitmaps.
One of the drawbacks of vector graphics is that the more complex
they are, the larger the file size and the longer they take to appear
th A th di d t i th t th t di l on the screen. Another disadvantage is that they cannot display
photorealistic quality.
Vector Image g
S l f l t hi Sample of complex vector graphics
Vector Image g
Creating a circle with vector programs allows you to
specify only one color for the entire circle; but p y y ;
creating a bitmap circle allows you to change the
color of every pixel in the circle.
Thus the bitmap can be more photorealistic.
The trade-off is that bitmap graphic files are larger
than vector files.
File size is a function of the image size, color depth
d th l ti and the resolution.
Vector Image g
Vector graphics, also called draw-type
hi t i t i graphics, represent an image as a geometric
shape made up of straight lines, ovals,
curves and arcs When a line is drawn a set curves, and arcs. When a line is drawn, a set
of instructions is written to describe its size,
position, and shape. If more than one line is p , p
drawn, it has a precise relationship to the
other parts.
Vector Image g
Figure below shows a graphic, a pie chart, made up of a circle
and lines. The instructions that create the circle and lines
establish the relationship between them. If a change is made,
i th i f th i l th l ti hi b t th i l say, in the size of the circle, the relationship between the circle
and the lines stays the same.
Vector Image g
Next figure shows a graphic reduced in sized and
rotated. The reduced graphic keeps the same g p p
relationship as the original graphic.
Vector Image (example) g ( p )
Vector Image (example) g ( p )
Every vector object can be separated and
combined together and it gives advantage to combined together and it gives advantage to
graphic designer to present their ideas and
creativity.
Graphics Quality
Graphics Quality (Image Size) p y ( g )
Image size refers to the height and width of the
image measured in inches centimeters dots or image, measured in inches, centimeters, dots, or
any other unit of measure.
Image size is a little tricky to grasp due to the fact
that the resolution of an image can vary. For
example, it is not of much help to know that an
image is 3 by 5 inches if you do not knowhowmany image is 3 by 5 inches if you do not know how many
dots per inch make up the image.
Graphics Quality (Image Size) p y ( g )
And, an image of 3 by 5 inches at 100 dots per inch
contains the same amount of image data as does an g
image of 6 by 10 inches at 50 dots per inch.
Alternatively, if the image size is measured in dots y, g
or pixels, then you know exactly how much image
data exists because a 300 pixel by 500 pixel image
contains 15,000 pixels no matter how many pixels
you designate per inch you designate per inch.
How to increase dpi in graphics editing software?
Graphics Quality (Image Size) p y ( g )
Graphics Quality (Color Depth) p y ( p )
Color depth / bit depth is the range of
colors available for pixels colors available for pixels.
Now, when talking about color depth, Now, when talking about color depth,
we are essentially referring to how
many different colors can exist within a
ti l i particular image.
Graphics Quality (Color Depth) p y ( p )
An image with the shallowest (to use a
non technical term) color depth can non-technical term) color depth can
contain only two different colors.
The actual colors that are used within
an image make up the color palette for
th t i that image.
Graphics Quality (Color Depth) p y ( p )
For instance, an image of the
shallowest color depth could have a shallowest color depth could have a
palette of orange and blue. Therefore,
every dot in the image would either be y g
orange, or blue.
Graphics Quality (Color Depth)
Colour depth Bit for every pixels Formula Colour
1 bit 1 2
1
2
2 bit 2 2
2
4
3 bit 3 2
3
8
4 bit 4 2
4
16
5 bit 5 2
5
32
6 bit 6 2
6
64 6 bit 6 2
6
64
7 bit 7 2
7
128
8 bit 8 2
8
256
16 bit 16 2
16
65 536
24 bit 24 2
24
16 777 216
Graphics Quality (Color Depth) p y ( p )
Dithering is one process how to reduce colour depth from
high to low colour. g to o coou
For example, 8 bit colour depth can be reduced to 4 bit by
applying dithering process.
Imej 8 bit Imej 4 bit
Graphics Quality (Color Depth) p y ( p )
When one application/programm is doing
dith i it ill h th l t dithering process, it will change the colour to
patterns (two or more closer to the real image).
Graphics Quality (Resolution) p y ( )
You can think of a bitmapped image as a
piece of graph paper of any size that has piece of graph paper, of any size, that has
had each square filled in by a color.
I t j th ll d In computer jargon, the squares are called
dots or pixels. The term pixel was derived
from the term picture element. The resolution
f th i f t th b f d t of the image refers to the number of dots per
inch (dpi) there are in the image. For
example, the resolution of an image could be p g
100 dpi.
Graphics Quality (Resolution) p y ( )
Resolution can vary, and may initially be
determined by the hardware used to digitize y g
an image.
Resolution can be decreased, but not without ,
losing image detail. The resolution of an
image can also be increased, but to do so
the computer just guesses at what the added
l ti d t h ld l k lik Thi resolution data should look like. This
technique is called interpolation.
Graphics Quality (Resolution) p y ( )
Resolution can really only be increased by
redigitizing the image at a higher resolution redigitizing the image at a higher resolution.
Beware! Some digitizers, especially flatbed
scanners, claim high scanning resolutions
that are actually achieved through that are actually achieved through
interpolation.
Graphics Quality (Resolution) p y ( )
Resolution for bitmap image can be
determined by horizontal and vertical pixel determined by horizontal and vertical pixel
unit.
E l bit i ith 800 600 ik l Example, bitmap image with 800 x 600 piksel
resolution can be display in full screen SVGA
display.
Graphics Quality (Resolution) p y ( )
Resolution can also refer to total dot (dot per inch:
dpi) in every single inch in the image.
Example, one image can be 72dpi, 100dpi, 1200dpi or
more more.
Same size but different quality
Graphics Quality (Resolution) p y ( )
The Quality of Resolution y
depend on the equipments that use to
create and produce digital images such as
di it l t scanner,digital camera etc.
How about Graphics Card?
Graphics Quality (Example) p y ( p )
Resolution can really only be increased by
redigitizing the image at a higher resolution. Beware!
S di iti i ll fl tb d l i Some digitizers, especially flatbed scanners, claim
high scanning resolutions that are actually achieved
through interpolation.
36 dpi
72 dpi
42
Fail Format: Introduction
What are the differences for the formats above and how
t l t hi h f t t i d i ? to select which format to use in your design?
Graphics Format p
The most common image file types are :-
Windows bitmaps (.BMP)
Device independent bitmaps (.DIB)
PC Paintbrush (.PCX)
Truevision TGA (.TGA)
CompuServe GIF (.GIF)
Joint Experts Photography Group (.JPEG) g y ( )
Tagged Image File Format (.TIFF)
Apple Macintosh PICT (.PICT).
Working with Graphics
Followingare some considerations and guidelines to keep in mind when Following are some considerations and guidelines to keep in mind when
working with graphics :
- Select the right kind of graphics for the job
- Select the right graphics tool for the job
- Select the minimum color depth that is appropriate to your p pp p y
application
- Set up your delivery system correctly.
- Select bitmap file formats for quality and portability
- Use vector graphics formats that are understood by your authoring
system
Group Activity Group Activity
In group of 3, create ONE simple Main Menu (in any
topic) usingAdobe Photoshop with 640 x 480 topic) using Adobe Photoshop with 640 x 480
resolutions. Your Main Menu must meet the
specifications below:-
a) 3 images (Raster and Bitmap) - image can be
downloaded from the Internet
b) Text b) Text
c) JPEG format
d) Button
e) Effect - i e Feather Layer Style Filter e) Effect i.e. Feather, Layer Style, Filter
Your poster must comply the design principles (choose at
least 2 principles) as discussed in Week 4 least 2 principles) as discussed in Week 4.
Group Activity
P t M i M j t l t k t th l Present you Main Menu project last week to the class.
Things to be considered in the presentations are :-
a) How to improve the quality of graphics (Main Menu)
in relation to resolution, colour depth and image
size? size?
b) Explain the category of graphics used in your Main
Men Menu.
c) Share your knowledge/skills of developing the Main Menu
project with the class. Eg. Type of effect, editing tools etc.
Você também pode gostar
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Presented by Celia BandelierDocumento54 páginasPresented by Celia BandelierCharmee Jane Lozano PadillaAinda não há avaliações
- Top 50 Java Design Pattern Interview QuestionsDocumento67 páginasTop 50 Java Design Pattern Interview QuestionsАлекс ПолAinda não há avaliações
- Layout DesignDocumento19 páginasLayout Designaqmar77Ainda não há avaliações
- MarzanoDocumento6 páginasMarzanoaqmar77100% (1)
- Tshirt KebirusDocumento1 páginaTshirt Kebirusaqmar77Ainda não há avaliações
- Borang PEKADocumento1.441 páginasBorang PEKAaqmar77Ainda não há avaliações
- TH 3Documento1 páginaTH 3aqmar77Ainda não há avaliações
- SK Perumahan Tampoi 2 (1 Mac)Documento3 páginasSK Perumahan Tampoi 2 (1 Mac)aqmar77Ainda não há avaliações
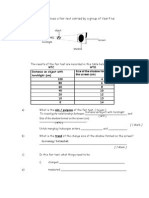
- Pupils.: Diagram Below Shows A Fair Test Carried by A Group of Year FiveDocumento2 páginasPupils.: Diagram Below Shows A Fair Test Carried by A Group of Year Fiveaqmar77Ainda não há avaliações
- Open University: M Alays IaDocumento7 páginasOpen University: M Alays Iaaqmar77Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Programming The NXP LPC4370 MCU Using The LPCxpresso Tools and Using Two LPC-Link2 BoardsDocumento28 páginasIntroduction To Programming The NXP LPC4370 MCU Using The LPCxpresso Tools and Using Two LPC-Link2 BoardsNarenAinda não há avaliações
- AIDocumento272 páginasAIRssb RssbAinda não há avaliações
- Control System Design of An Vtol Fixed-Wing AircraftDocumento4 páginasControl System Design of An Vtol Fixed-Wing AircraftkhoamaiAinda não há avaliações
- Cse Java Project On High Fi Infirmary PortalDocumento60 páginasCse Java Project On High Fi Infirmary PortalVijayendravarma DanduAinda não há avaliações
- Principle of Compiler Question and AnswerDocumento2 páginasPrinciple of Compiler Question and AnswerSyafiqa RoslanAinda não há avaliações
- Data CubeDocumento42 páginasData CubeGauravBhattAinda não há avaliações
- Sequence Alignment/Map Format SpecificationDocumento16 páginasSequence Alignment/Map Format SpecificationFilozófus ÖnjelöltAinda não há avaliações
- Data Mining Using R For Criminal DetectionDocumento7 páginasData Mining Using R For Criminal DetectionIJIRSTAinda não há avaliações
- Comparison of Data Usage Security Between Messenger and WhatsAppDocumento3 páginasComparison of Data Usage Security Between Messenger and WhatsAppAh SanAinda não há avaliações
- Mod6 4Documento10 páginasMod6 4mn3mAinda não há avaliações
- Sevecek Hyper V 2012 r2 VirtualizationDocumento56 páginasSevecek Hyper V 2012 r2 VirtualizationBala MuraliAinda não há avaliações
- TKLM 2.5 InstallationDocumento144 páginasTKLM 2.5 Installationrgarcp2348Ainda não há avaliações
- Configuring Windows Server 2008 As A Remote Access SSL VPN ServerDocumento24 páginasConfiguring Windows Server 2008 As A Remote Access SSL VPN Serverdark_moonx1Ainda não há avaliações
- List of Commands EIRDocumento17 páginasList of Commands EIRFranck BojorquezAinda não há avaliações
- Develop Applications Using Richfaces 4: Developer GuideDocumento98 páginasDevelop Applications Using Richfaces 4: Developer GuideAdam WashingtonAinda não há avaliações
- Nodeb LMT User Guide (v200r013 - 04) (PDF) - enDocumento205 páginasNodeb LMT User Guide (v200r013 - 04) (PDF) - enpr3m4n100% (5)
- MonitoringDocumento8 páginasMonitoringsid_srmsAinda não há avaliações
- RC4 Encryption Algorithm: Computer Network LaboratoryDocumento12 páginasRC4 Encryption Algorithm: Computer Network LaboratoryDivyakant MevaAinda não há avaliações
- MqttClient Publish Unsecure DOKU enDocumento32 páginasMqttClient Publish Unsecure DOKU enjuneAinda não há avaliações
- Normalised Least Mean-Square Adaptive Filtering: (Fast) Block LMS ELE 774 - Adaptive Signal Processing 1Documento28 páginasNormalised Least Mean-Square Adaptive Filtering: (Fast) Block LMS ELE 774 - Adaptive Signal Processing 1BabisIgglezosAinda não há avaliações
- Red Hat 6 Installation Guide - RHEL 6 Install ScreenshotsDocumento34 páginasRed Hat 6 Installation Guide - RHEL 6 Install ScreenshotsSabeer HusainAinda não há avaliações
- Math - Random in V8Documento18 páginasMath - Random in V8Barrel RollAinda não há avaliações
- SAP ERP Testing, SAP Automation Testing, HP QTP 11, HP ALMDocumento24 páginasSAP ERP Testing, SAP Automation Testing, HP QTP 11, HP ALMVGlobal GoviAinda não há avaliações
- Number System MCQ'sDocumento4 páginasNumber System MCQ'sGhanshyam Sharma0% (1)
- Toward Unified Control of Networks of Switches and Sensors Through A Network Operating SystemDocumento10 páginasToward Unified Control of Networks of Switches and Sensors Through A Network Operating Systemdan_intel6735Ainda não há avaliações
- CSCI 104 Inheritance: Mark Redekopp David KempeDocumento24 páginasCSCI 104 Inheritance: Mark Redekopp David KempeRahul KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Property ManagementDocumento16 páginasProperty ManagementhuyhanghaiAinda não há avaliações