Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Matriculation Chemistry Polymers PDF
Enviado por
iki292Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Matriculation Chemistry Polymers PDF
Enviado por
iki292Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
FJ/Chemistry Unit, KMPk/Mac 2006 1
CHAPTER 21
POLYMERS
2
21.1 : Introduction
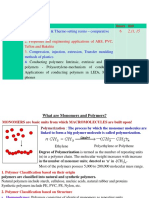
Polymer
- is a macro molecule that is made up of many small repeating units
called monomers linked together by covalent bond.
- polymer can be represented by their repeating unit in the long
chain.
Monomer
- is a basic molecular units that can joined to many others to form a
polymer.
n --
n
polymer monomer
polymer
!repeating unit"
n
n ---------
3
#omopolymer
- a polymer formed from only one types monomer units.
- $%ample :
n --
n
ethene
!ethylene"
polyethene
!polyethylene"
n&#
2
&#
2
-&#
2
&#
2
-
n
4
&opolymer
- a polymer formed from t'o or more different monomers.
- $%ample :
1(1-dichloroethene 1-chloroethene )aran*
n
n + n, --,-
n&#
2
&&l
2
+ n&#
2
&#&l -&#
2
-&&l
2
-&#
2
-&#&l-
n
5
21.2 : )tructures of Polymers
21.2.1 : -inear Polymers
-inear polymer is a polymer consist of monomers that are
linked in straight and long continuous chain.
-inear or straight-chain polymer can be folded back upon
themselves in a random fashion.
-inear polymer is recycleable because it is soft and can be
reformed 'hen heated.
n
---------
monomers link together
in a straight chain
folded linear polymer
in a random fashion
6
21.2.2 : &ross-linked Polymers
&ross-linked polymer contains branches that connect linear polymer chain( as sho'n
in the figures belo'.
&ross-linked polymer is harder !rigid" and more elastic polymer compared to linear
polymer.
It also cannot be remelted or remolded again.
.he e/uation belo' sho's the chemical reaction for the rubber vulcani0ation
process.
-ong polymer chain cross-linked by branched
-------------
-------------
1 1
7
In a vulcani0ation process( long chain of polyisoprene are cross-linked by sulphur
atoms.
fter vulcani0ation rubber becomes more stable over 'ide ranges of temperature
and far more durable than natural rubber.
-&#
2
& &#-&#
2
- +
&#
2
&#
2
-&#
2
& &#-&#
2
-
sulphur
&#
2
-&#& &#-&#
2
-&#& &#-&#
2
-
)
-&#& &#-&#
2
-&#& &#-&#
2
-
&#
2
&#
2
&#
2
)
8
21.2 : .ypes of Polymers
21.2.1 : 3atural Polymers
3atural polymers are polymers that synthesi0ed in nature
or naturally occurring polymers.
i. Proteins
Protein are the most abundant organic molecules in animals
such as en0ymes( hormones( hemoglobin and many other
things.
It is a natural polymer built from amino acids linked by
amide bonds.
#3-&-&
4
#
5 n
ii. &arbohydrates
&arbohydrates such as starch is also a polymer.
i. )tarch !amylose"
ii. )tarch !amylopectin"
- contains 6-!1(7"-glycosidic and 6-!1(8"-glycosidic linkages.
4
4
4
# #
4
4
4#
# #
#
#
#
&#
2
4#
&#
2
4#
4#
4#
4#
#
#
#
n
-!1(7"-glycosidic linkages
10
iii. 3atural 5ubber
3atural rubber is a polymer of 2-methyl-1(2-butadiena( also kno'n as
isoprene.
nother name for natural rubber is cis-1(7-polyisoprene.
ll the double bond in natural rubber are cis- configuration.
3atural rubber is soft( not strong or elastic and sticky( that makes it less
useful.
In order to make it more useful rubber has to undergo a vulcani0ation process.
n &#
2
9&-	&#
2
-&#
2
-&9&#&#
2
-
&#
2
&#
2
n
isoprene cis-polyisoprene
11
21.2.2 : )ynthetic Polymers
)ynthetic polymers are polymers that are prepared in industries from
monomers that have gone through polymeri0ation process.
Polymeri0ation is a process that combines monomers to form polymers.
)ynthetic polymers can be classified base on their method of preparation
! polymeri0ation process ".
21.2.2.1 : ddition Polymeri0ation
ddition polymeri0ation is the addition reaction in 'hich unsaturated
monomers are joined together by covalent bonds to form a polymer
'ithout elimination of a small molecule.
Polymers obtained by addition polymeri0ation are called addition polymers.
12
.herefore( addition polymer al'ays involves the
polymeri0ation of monomers 'hich have double bond 'ithin
the monomers.
Pero%ide is used as initiator in addition polymeri0ation.
i. :ormation of polyethene
ii. :ormation of polyvinyl chloride
n
&#
2
&#
2
-&#
2
-&#
2
-
5445
! "
n
n
#& &#
2
-#&-&#
2
-
5445
! "
n
&l &l
ethene polyethene
chloroethene
polychloroethene
!polyvinyl chloride or P;&"
13
iii. :ormation of polystyrene
iv. :ormation of polyisopropene
phenylethene
!styrene"
Polyphenylethene
!polystyrene"
isoprene
polyisoprene
n
#& &#
2
-#&-&#
2
-
5445
! "
n
n &#
2
9&-	&#
2
-&#
2
-&9&#&#
2
-
&#
2
&#
2
n
14
21.2.2.2 : &ondensation Polymeri0ation
&ondensation polymeri0ation is a process that combines the monomers
'ith elimination of a small molecule such as 'ater( methanol( hydrogen
chloride or ammonia to form a polymer.
.he polymers obtained from condensation polymeri0ation are called
condensation polymers.
.he monomers involves in this polymeri0ation must have at least t'o
identical or different functional group in the molecule.
<hen a carbo%ylic acid 'ith t'o =&44# group reacts 'ith an amine
'ith t'o =3#
2
groups( a polyamide is formed.
<hen a carbo%ylic acid 'ith t'o =&44# group reacts 'ith an alcohol
'ith t'o =4# groups( a polyester is formed.
15
!". Polyamides
i. :ormation of 3ylon 8(8
ii. :ormation of 3ylon 8
he%ane-1(8-diamine
3ylon 8(8
4 4
n #
2
3-!&#
2
"
8
-3#
2
+ n #4-&-!&#
2
"
7
-&-4#
-3-!&#
2
"
8
-3-&-!&#
2
"
7
-&- + n #
2
4
4 4
# #
! "
n
he%ane-1(8-dioic acid
!
"
n
n #
2
3-!&#
2
"
>
-&-4#
4 4
-3#-!&#
2
"
>
-&- + n #
2
4
3ylon 8
8-aminohe%anoic
acid
16
iii. :ormation of ?evlar
!,". Polyester
.he repeating functional groups in this polymer chain are ester.
.he most familiar polyester is polyethylene terephthalate kno'n as @acron and
.erylene.
1(7-diaminoben0ene
?evlar
terephthalic acid
n #-3- -3-# + n &l-&- -&-&l
4 4
#
#
3- -3-&- -&
#
# 4
4
n
+ n #&l
17
.he polymer is formed by the reaction of ethylene glycol
'ith methyl ester or terephtalic acid.
In this process( a molecule of methanol is split out for
each ne' ester group formed.
i. :ormation of @acron
@acron or poly!ethylene terephthalate" metanol
4 4
n &#
2
4-&- -&-4&#
2
+ n #4-&#
2
&#
2
-4#
-4-&#
2
&#
2
-4-&- -&- + n &#
2
4#
4 4
! "
n
1(2-ethanediol
!ethylene glycol"
dimethyl terephthalate
18
ii. :ormation of .erylene
.erylene
ethane-1(2-diol
ben0ene-1(7-dicarbo%ylic acid
'ater
4 4
n
#4-&#
2
&#
2
-4# + n
#4
-&- -&-4#
-4-&#
2
&#
2
-4-&- -&- + n
#
2
4
4 4
! "
n
1
21.7 : Ases of )ynthetic Polymers
3o. Polymer Ases
1 Polyethene plastics( drinking bottles( toys
2 Polyvinyl chloride piping( floor tiles( clothing( toys(
'ire covering
2 Polystyrene containers( thermal insulation-ice buckets
7 3ylon 8 .e%tile
> 3ylon 8(8 )'eater
8 ?evlar ,ullet proof vest
B @acron :abric
C .erylene :iber-optic material
Você também pode gostar
- SHIPPING TERMSDocumento1 páginaSHIPPING TERMSGung Mayura100% (1)
- Understanding Baking PDFDocumento289 páginasUnderstanding Baking PDFAlexandra Soares100% (1)
- The Iron Wall - Israel and The Arab WorldDocumento1.151 páginasThe Iron Wall - Israel and The Arab Worldsalie29296100% (11)
- 9781473615441 (1)Documento449 páginas9781473615441 (1)iki29275% (4)
- 9780299304300Documento255 páginas9780299304300iki292100% (1)
- Italian Cooking Recipes from Olean, NYDocumento150 páginasItalian Cooking Recipes from Olean, NYiki292100% (1)
- Sap Ewm - Erp Initial SetupDocumento3 páginasSap Ewm - Erp Initial SetupVAIBHAV PARAB80% (5)
- Unit:4, Engineering PolymersDocumento49 páginasUnit:4, Engineering PolymersDipesh PanditAinda não há avaliações
- PolymersDocumento22 páginasPolymersDr. Stan Wardel BA, MA, MChem, MBA, DPhil, DSc.Ainda não há avaliações
- Polymer Chemistry 16 17 I SemDocumento69 páginasPolymer Chemistry 16 17 I SemSam WhiteAinda não há avaliações
- polymer-151217133029Documento52 páginaspolymer-151217133029Sree Info TeluguAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 12 physics Important Questions Chapter 15 PolymersDocumento8 páginasCBSE Class 12 physics Important Questions Chapter 15 PolymersRahil ShamsiAinda não há avaliações
- Classification Based On Source: MacromoleculesDocumento7 páginasClassification Based On Source: MacromoleculesGauravAinda não há avaliações
- Polymers PDFDocumento6 páginasPolymers PDFvidushi1121Ainda não há avaliações
- PolymersDocumento17 páginasPolymersleaf5Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 1-Polymer Chemistry ACETR23Documento22 páginasUnit 1-Polymer Chemistry ACETR23scs150831100% (1)
- Unit 5-PolymerDocumento27 páginasUnit 5-PolymerN x10Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter - 15: Polymers: Expert Coaching ClassesDocumento10 páginasChapter - 15: Polymers: Expert Coaching ClassesTeju tejasAinda não há avaliações
- Chem 3Documento17 páginasChem 3Adi SoAinda não há avaliações
- Polymers: Daipayan Banerjee XII Science A 4Documento14 páginasPolymers: Daipayan Banerjee XII Science A 4Daipayan BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Polymers NotesDocumento55 páginasPolymers Notessamay gujratiAinda não há avaliações
- Module-3 ME NotesDocumento30 páginasModule-3 ME NotesdnalokeshAinda não há avaliações
- Polymer Technology-1Documento24 páginasPolymer Technology-1scs150831Ainda não há avaliações
- Subtopic 6.1: Polymers: MaterialsDocumento32 páginasSubtopic 6.1: Polymers: MaterialschiggsAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3Documento7 páginasUnit 3Shubham KhandelwalAinda não há avaliações
- SA Unit 5 POLYMER AND ORGANOMETALLIC COMPOUNDSDocumento34 páginasSA Unit 5 POLYMER AND ORGANOMETALLIC COMPOUNDSguptaneha8700003783Ainda não há avaliações
- Ch3 PolymersDocumento6 páginasCh3 Polymersباسمي العشقAinda não há avaliações
- Biological and Synthetic Polymers ComparedDocumento78 páginasBiological and Synthetic Polymers ComparedUmamaheswari GanesanAinda não há avaliações
- ST - Ann'S College of Engineering & Technology Engineering Chemistry Unit - I Polymer TechnologyDocumento18 páginasST - Ann'S College of Engineering & Technology Engineering Chemistry Unit - I Polymer TechnologyMaddu PavanAinda não há avaliações
- HND Polymer Note Part OneDocumento46 páginasHND Polymer Note Part OnemuhammadmaihadisiAinda não há avaliações
- Polymer Chemistry MKBDocumento54 páginasPolymer Chemistry MKBJHidgiwiwAinda não há avaliações
- Polymers Polymer (Or Macromolecule)Documento10 páginasPolymers Polymer (Or Macromolecule)John Nelson LorenzoAinda não há avaliações
- Polymer Chain Structure and PropertiesDocumento85 páginasPolymer Chain Structure and PropertiespraveenAinda não há avaliações
- Polymers: Classification: Natural and Synthetic Methods of The PolymerisationDocumento6 páginasPolymers: Classification: Natural and Synthetic Methods of The PolymerisationMahesh GandlaAinda não há avaliações
- Matriculation Chemistry (Polymers)Documento19 páginasMatriculation Chemistry (Polymers)ridwanAinda não há avaliações
- POLYMERS CLASSIFICATION GUIDEDocumento25 páginasPOLYMERS CLASSIFICATION GUIDEPrasad YarraAinda não há avaliações
- Polymersclass12 160109135318Documento33 páginasPolymersclass12 160109135318Dev Printing SolutionAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-1 Macromolecules With Problems - CompressedDocumento42 páginasUnit-1 Macromolecules With Problems - CompressedcoolinkenanatamAinda não há avaliações
- Man Made Fiber Processing TechnologyDocumento22 páginasMan Made Fiber Processing TechnologyGarmentLearnerAinda não há avaliações
- Materials and Instructions for Polymer ExperimentsDocumento30 páginasMaterials and Instructions for Polymer ExperimentsPaula Buján RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Polymers Lec-01 (Sarvesh Sir) - English NEET Crash Course Classnotes - Polymers - Sarvesh Sir FinalDocumento50 páginasPolymers Lec-01 (Sarvesh Sir) - English NEET Crash Course Classnotes - Polymers - Sarvesh Sir FinalVidhi BansalAinda não há avaliações
- 15 Polymers: Obtained From Natural Polymers by Subjecting Them To Some Chemical Processes. Eg: Vulcanised RubberDocumento6 páginas15 Polymers: Obtained From Natural Polymers by Subjecting Them To Some Chemical Processes. Eg: Vulcanised Rubbersreenivas1990Ainda não há avaliações
- macromoleculesDocumento35 páginasmacromoleculesAruna SriAinda não há avaliações
- PolymersDocumento40 páginasPolymersdevy rida100% (1)
- Lecture 23-25 Mechanism and Applications of Polymerization in Aromatic CompoundsDocumento35 páginasLecture 23-25 Mechanism and Applications of Polymerization in Aromatic CompoundsFalak SherAinda não há avaliações
- AFM Image Shows Real Polymer Chain 204 nm LongDocumento19 páginasAFM Image Shows Real Polymer Chain 204 nm LongDikshit TomerAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 24 - MacromoleculesDocumento6 páginasChapter 24 - MacromoleculesJERVINLIMAinda não há avaliações
- PolymersDocumento12 páginasPolymersNaman SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Recycling of Textile PolymersDocumento8 páginasChemical Recycling of Textile PolymersVaishali RaneAinda não há avaliações
- Properties and Applications of Common PolymersDocumento39 páginasProperties and Applications of Common PolymerskumarklAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2-Polymers & PolymerisationsDocumento24 páginasUnit 2-Polymers & PolymerisationsRafeulAinda não há avaliações
- PolymerDocumento95 páginasPolymerdefarsinke15Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit-25 - POLYMER: Important PointsDocumento11 páginasUnit-25 - POLYMER: Important PointsVijaychandar VijayAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of PolymersDocumento14 páginasClassification of PolymersFA Ay67% (6)
- PolymersDocumento106 páginasPolymersmambouhpriscaAinda não há avaliações
- PolymersDocumento6 páginasPolymersTr Mazhar PunjabiAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 5 Lesson 3Documento43 páginasIGCSE Chemistry Section 5 Lesson 3sanobarAinda não há avaliações
- CHE3172 Nanotechnology and Materials I: Introduction to Polymer MaterialsDocumento13 páginasCHE3172 Nanotechnology and Materials I: Introduction to Polymer MaterialsDivya KariaAinda não há avaliações
- Polymer Chemistry BasicsDocumento24 páginasPolymer Chemistry BasicsHarshal A ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Che 2Documento32 páginasChe 2dineshsilambam2305Ainda não há avaliações
- Polymer Monomers and Their UsesDocumento8 páginasPolymer Monomers and Their UsesChris McLeanAinda não há avaliações
- PE Assignment 19-NTU-TE-0117-1Documento16 páginasPE Assignment 19-NTU-TE-0117-1Ahmad ButtAinda não há avaliações
- Module-3 Additive Manufacturing 18 SchemeDocumento62 páginasModule-3 Additive Manufacturing 18 SchemeSANTOSHAinda não há avaliações
- NEET UG Chemistry PolymerDocumento11 páginasNEET UG Chemistry PolymerVeer SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Solid-Supported Combinatorial and Parallel Synthesis of Small-Molecular-Weight Compound LibrariesNo EverandSolid-Supported Combinatorial and Parallel Synthesis of Small-Molecular-Weight Compound LibrariesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Chelating Extractants: Equilibrium Constant of Liquid–Liquid Distribution ReactionsNo EverandChelating Extractants: Equilibrium Constant of Liquid–Liquid Distribution ReactionsAinda não há avaliações
- 49 PDFDocumento32 páginas49 PDFNicolas BaronAinda não há avaliações
- E Proceedings Ice2016Documento801 páginasE Proceedings Ice2016iki292Ainda não há avaliações
- Infused, Ted - Google Classroom - A 2020 - 2021 Comprehensive and Simple User Guide To Online Teaching and Learning With Step by Step Instructions, Tips and Tricks For Teachers (2020)Documento121 páginasInfused, Ted - Google Classroom - A 2020 - 2021 Comprehensive and Simple User Guide To Online Teaching and Learning With Step by Step Instructions, Tips and Tricks For Teachers (2020)iki292Ainda não há avaliações
- 9781472136480Documento319 páginas9781472136480iki292100% (1)
- Actio Research DR SatirahDocumento73 páginasActio Research DR Satirahiki292Ainda não há avaliações
- 100 Great Italian Recipes Delicious RecipesDocumento162 páginas100 Great Italian Recipes Delicious RecipesMr. Hofman100% (3)
- Karène Sanchez SummererSary Zananiri - European Cultural Diplomacy and Arab Christians in Palestine, 1918-1948 - Between Contention and ConnectionDocumento476 páginasKarène Sanchez SummererSary Zananiri - European Cultural Diplomacy and Arab Christians in Palestine, 1918-1948 - Between Contention and ConnectionSal LieAinda não há avaliações
- Designing A Mobile Game Application ForDocumento5 páginasDesigning A Mobile Game Application Foriki292Ainda não há avaliações
- Action ResearchDocumento16 páginasAction Researchiki292Ainda não há avaliações
- Nila Brook - Teaching in the Post Covid Classroom_ 2020-2021 Complete Beginners Guide to Organize Online Lessons. Everything You Need to Know About Zoom , Google Classroom and Distance Learning (2020) - Libgen.Documento131 páginasNila Brook - Teaching in the Post Covid Classroom_ 2020-2021 Complete Beginners Guide to Organize Online Lessons. Everything You Need to Know About Zoom , Google Classroom and Distance Learning (2020) - Libgen.iki292Ainda não há avaliações
- 1634858239Documento360 páginas1634858239iki292100% (1)
- Cuking Book For StudentsDocumento1.299 páginasCuking Book For StudentsSladjan Stojkovic94% (18)
- 100 Great Italian Recipes Delicious RecipesDocumento162 páginas100 Great Italian Recipes Delicious RecipesMr. Hofman100% (3)
- PDFDocumento360 páginasPDFiki292Ainda não há avaliações
- 200 Barbecue Recipes by Pickford LouiseDocumento490 páginas200 Barbecue Recipes by Pickford Louiseiki292Ainda não há avaliações
- Java 2 - The Complete ReferenceDocumento208 páginasJava 2 - The Complete Referenceiki292Ainda não há avaliações
- 20 Quick Cake Recipes On A Budget & For The Whole FamilyDocumento16 páginas20 Quick Cake Recipes On A Budget & For The Whole Familyiki292Ainda não há avaliações
- Java 2 - The Complete ReferenceDocumento208 páginasJava 2 - The Complete Referenceiki292Ainda não há avaliações
- 9783319395913Documento214 páginas9783319395913iki292100% (1)
- Visual Studio and C# IntroductionDocumento48 páginasVisual Studio and C# IntroductionnebanuitAinda não há avaliações
- Foundations of DatabasesDocumento702 páginasFoundations of DatabasesEva DuretAinda não há avaliações
- JDBC TutorialDocumento162 páginasJDBC TutorialPartho Bora100% (1)
- Java Collections FrameworkDocumento44 páginasJava Collections FrameworkAdarshAinda não há avaliações
- Java Collections FrameworkDocumento44 páginasJava Collections FrameworkAdarshAinda não há avaliações
- Visual Studio and C# IntroductionDocumento48 páginasVisual Studio and C# IntroductionnebanuitAinda não há avaliações
- PNW 0605Documento12 páginasPNW 0605sunf496Ainda não há avaliações
- 3 0 Visual Weld InspectorDocumento74 páginas3 0 Visual Weld InspectorVincent Sofia RaphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Proprietar Utilizator Nr. Crt. Numar Inmatriculare Functie Utilizator Categorie AutovehiculDocumento3 páginasProprietar Utilizator Nr. Crt. Numar Inmatriculare Functie Utilizator Categorie Autovehicultranspol2023Ainda não há avaliações
- Macdonald v. National City Bank of New YorkDocumento6 páginasMacdonald v. National City Bank of New YorkSecret SecretAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Human Resource Management Functions and Their ImportanceDocumento23 páginasIntroduction to Human Resource Management Functions and Their ImportancedhrupaAinda não há avaliações
- Eship 1Documento18 páginasEship 1Yash SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Nexus Undercarriage Cross Reference GuideDocumento185 páginasNexus Undercarriage Cross Reference GuideRomanAinda não há avaliações
- Automatizari Complexe - Laborator Nr. 4: Wind (M/S)Documento1 páginaAutomatizari Complexe - Laborator Nr. 4: Wind (M/S)Alexandru AichimoaieAinda não há avaliações
- 272 Concept Class Mansoura University DR Rev 2Documento8 páginas272 Concept Class Mansoura University DR Rev 2Gazzara WorldAinda não há avaliações
- E200P Operation ManualDocumento26 páginasE200P Operation ManualsharmasourabhAinda não há avaliações
- Jodi Ridgeway vs. Horry County Police DepartmentDocumento17 páginasJodi Ridgeway vs. Horry County Police DepartmentWMBF NewsAinda não há avaliações
- Numark MixTrack Pro II Traktor ProDocumento3 páginasNumark MixTrack Pro II Traktor ProSantiCai100% (1)
- Feb 22-Additional CasesDocumento27 páginasFeb 22-Additional CasesYodh Jamin OngAinda não há avaliações
- Request Letter To EDC Used PE PipesDocumento1 páginaRequest Letter To EDC Used PE PipesBLGU Lake DanaoAinda não há avaliações
- Request For AffidavitDocumento2 páginasRequest For AffidavitGhee MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- 34 Annual Report 2019 20Documento238 páginas34 Annual Report 2019 20Rahul N PatelAinda não há avaliações
- High Uric CidDocumento3 páginasHigh Uric Cidsarup007Ainda não há avaliações
- AssDocumento9 páginasAssJane SalvanAinda não há avaliações
- Amos Code SystemDocumento17 páginasAmos Code SystemViktor KarlashevychAinda não há avaliações
- A CASE STUDY OF AU SMALL FINANCE BANK'S SHRIRAMPUR BRANCHDocumento9 páginasA CASE STUDY OF AU SMALL FINANCE BANK'S SHRIRAMPUR BRANCHprajakta shindeAinda não há avaliações
- Acknowledgment: George & Also To Our Group Guide Asst. Prof. Simy M Baby, For Their Valuable Guidance and HelpDocumento50 páginasAcknowledgment: George & Also To Our Group Guide Asst. Prof. Simy M Baby, For Their Valuable Guidance and HelpKhurram ShahzadAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Lit 2014 ExamplarDocumento17 páginasMaths Lit 2014 ExamplarAnymore Ndlovu0% (1)
- Tutorial Manual Safi PDFDocumento53 páginasTutorial Manual Safi PDFrustamriyadiAinda não há avaliações
- Final Biomechanics of Edentulous StateDocumento114 páginasFinal Biomechanics of Edentulous StateSnigdha SahaAinda não há avaliações
- Discount & Percentage Word Problems SolutionsDocumento4 páginasDiscount & Percentage Word Problems SolutionsrheAinda não há avaliações
- Stage 1 Isolating Boiler Feed Pump 1. PurposeDocumento3 páginasStage 1 Isolating Boiler Feed Pump 1. Purposejoseph kamwendoAinda não há avaliações
- Personal InsuranceDocumento11 páginasPersonal InsuranceSumit Kumar SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Admission Checklist (Pre-) Master September 2021Documento7 páginasAdmission Checklist (Pre-) Master September 2021Máté HirschAinda não há avaliações