Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test: Multiple Choice
Enviado por
dipankar65Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test: Multiple Choice
Enviado por
dipankar65Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test
Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
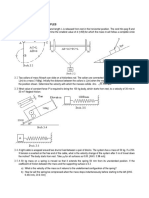
____ 1. A single conservative force F
x
= (6.0x 12) N (x is in m) acts on a particle moving along the x axis. The
potential energy associated with this force is assigned a value of +20 J at x = 0. What is the potential energy at
x = 3.0 m?
a. +11 J
b. +29 J
c. +9.0 J
d. 9.0 J
e. +20 J
____ 2. A 12-kg block on a horizontal frictionless surface is attached to a light spring (force constant = 0.80 kN/m).
The block is initially at rest at its equilibrium position when a force (magnitude P = 80 N) acting parallel to
the surface is applied to the block, as shown. What is the speed of the block when it is 13 cm from its
equilibrium position?
a. 0.78 m/s
b. 0.81 m/s
c. 0.71 m/s
d. 0.58 m/s
e. 0.64 m/s
____ 3. A 0.60-kg object is suspended from the ceiling at the end of a 2.0-m string. When pulled to the side and
released, it has a speed of 4.0 m/s at the lowest point of its path. What maximum angle does the string make
with the vertical as the object swings up?
a. 61
b. 54
c. 69
d. 77
e. 47
____ 4. A 2.5-kg object suspended from the ceiling by a string that has a length of 2.5 m is released from rest with the
string 40 below the horizontal position. What is the tension in the string at the instant when the object passes
through its lowest position?
a. 11 N
b. 25 N
c. 42 N
d. 18 N
e. 32 N
____ 5. A 0.04-kg ball is thrown from the top of a 30-m tall building (point A) at an unknown angle above the
horizontal. As shown in the figure, the ball attains a maximum height of 10 m above the top of the building
before striking the ground at point B. If air resistance is negligible, what is the value of the kinetic energy of
the ball at B minus the kinetic energy of the ball at A (K
B
K
A
)?
a. 12 J
b. 12 J
c. 20 J
d. 20 J
e. 32 J
____ 6. A skier weighing 0.70 kN goes over a frictionless circular hill as shown. If the skier's speed at point A is 9.2
m/s, what is his speed at the top of the hill (point B)?
a. 3.1 m/s
b. 6.2 m/s
c. 5.2 m/s
d. 4.1 m/s
e. 6.5 m/s
____ 7. A spring (k = 200 N/m) is suspended with its upper end supported from a ceiling. With the spring hanging in
its equilibrium configuration, an object (mass = 2.0 kg) is attached to the lower end and released from rest.
What is the speed of the object after it has fallen 4.0 cm?
a. 90 cm/s
b. 79 cm/s
c. 96 cm/s
d. 83 cm/s
e. 57 cm/s
____ 8. A 2.0-kg block sliding on a horizontal frictionless surface is attached to one end of a horizontal spring (k =
200 N/m) which has its other end fixed. If the block has a speed of 4.0 m/s as it passes through the
equilibrium position, what is its speed when it is 20 cm from the equilibrium position?
a. 2.6 m/s
b. 3.1 m/s
c. 3.5 m/s
d. 1.9 m/s
e. 2.3 m/s
____ 9. A 20-kg mass is fastened to a light spring (k = 380 N/m) that passes over a pulley as shown. The pulley is
frictionless, and the mass is released from rest when the spring is unstretched. After the mass has dropped
0.40 m, what is its speed?
a. 2.2 m/s
b. 2.5 m/s
c. 1.9 m/s
d. 1.5 m/s
e. 3.6 m/s
____ 10. A spring (k = 600 N/m) is placed in a vertical position with its lower end supported by a horizontal surface. A
2.0-kg block that is initially 0.40 m above the upper end of the spring is dropped from rest onto the spring.
What is the kinetic energy of the block at the instant it has fallen 0.50 m (compressing the spring 0.10 m)?
a. 5.3 J
b. 6.8 J
c. 6.3 J
d. 5.8 J
e. 6.5 J
____ 11. A 3.0-kg mass is dropped from the edge of a 50-m tall building with an initial speed of zero. The mass strikes
the ground with a downward velocity of 25 m/s. How much work is done on the mass by air resistance
between the point where it is dropped and the point where it strikes the ground?
a. 0.46 kJ
b. 0.53 kJ
c. 0.61 kJ
d. 0.38 kJ
e. 0.81 kJ
____ 12. A large spring is used to stop the cars after they come down the last hill of a roller coaster. The cars start at
rest at the top of the hill and are caught by a mechanism at the instant their velocities at the bottom are zero.
Compare the compression of the spring, x
A
, for a fully loaded car with that, x
B
, for a lightly loaded car when
m
A
= 2m
B
.
a.
x
A
= x
B
.
b. x
A
= x
B
.
c.
x
A
= x
B
.
d. x
A
= 2 x
B
.
e. x
A
= 4 x
B
.
____ 13. Cubical blocks of mass m and side l are piled up in a vertical column. The total gravitational potential energy
of a column of three blocks is
a.
mgl.
b. 3mgl.
c.
mgl.
d. 6mgl.
e. 9mgl.
____ 14. A spring with spring constant k = 800 N/m is extended 12 cm from its equilibrium position. A spring with 6.0
cm extension from equilibrium will have the same potential energy as the first spring if its spring constant is
a. 200 N/m.
b. 400 N/m.
c. 800 N/m.
d. 1600 N/m.
e. 3200 N/m.
____ 15. The block shown is released from rest when the spring is stretched a distance d. If k = 50 N/m, m = 0.50 kg, d
= 10 cm, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is equal to 0.25,
determine the speed of the block when it first passes through the position for which the spring is unstretched.
a. 92 cm/s
b. 61 cm/s
c. 71 cm/s
d. 82 cm/s
e. 53 cm/s
____ 16. A 1.2-kg mass is projected down a rough circular track (radius = 2.0 m) as shown. The speed of the mass at
point A is 3.2 m/s, and at point B, it is 6.0 m/s. How much work is done on the mass between A and B by the
force of friction?
a. 8.9 J
b. 7.3 J
c. 8.1 J
d. 6.6 J
e. 24 J
____ 17. The two masses in the figure are released from rest. After the 3.0-kg mass has fallen 1.5 m, it is moving with
a speed of 3.8 m/s. How much work is done during this time interval by the frictional force on the 2.0 kg
mass?
a. 12 J
b. 17 J
c. 20 J
d. 8.0 J
e. 28 J
____ 18. A pendulum bob has potential energy U
0
when held taut in a horizontal position. The bob falls until it is 30
away from the horizontal position, when it has potential energy U
A
. It continues to fall until the string is
vertical, when it has potential energy U
B
. Compare its potential energies at O, A, and B.
a. U
0
= U
A
= U
B
.
b. U
A
U
B
= 2U
0
.
c. U
A
U
B
= U
0
U
A
.
d. U
0
= U
B
= 2U
A
.
e. U
0
U
A
= 2(U
A
U
B
).
____ 19. Which of the following is a conservative force? (All refer to a car on a slope.)
a. The force you exert on the car pushing it uphill.
b. The force exerted by rain drops falling on the car.
c. The frictional force of the road on the car.
d. The gravitational force acting on the car.
e. The force you exert on the car (pushing it uphill) after it starts to slide downhill.
Problem
20. A simple pendulum, 2.0 m in length, is released from rest when the support string is at an angle of 25 from
the vertical. What is the speed of the suspended mass at the bottom of the swing?
AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test
Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. ANS: B PTS: 1
2. ANS: A PTS: 1
3. ANS: B PTS: 1
4. ANS: C PTS: 1
5. ANS: A PTS: 1
6. ANS: C PTS: 1
7. ANS: B PTS: 1
8. ANS: C PTS: 1
9. ANS: A PTS: 1
10. ANS: B PTS: 1
11. ANS: B PTS: 1
12. ANS: C PTS: 1
13. ANS: C PTS: 1
14. ANS: E PTS: 1
15. ANS: C PTS: 1
16. ANS: C PTS: 1
17. ANS: D PTS: 1
18. ANS: C PTS: 1
19. ANS: D PTS: 1
PROBLEM
20. ANS:
1.9 m/s
PTS: 1
Você também pode gostar
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 9Th Edition Serway Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento44 páginasPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 9Th Edition Serway Test Bank Full Chapter PDFwadeperlid9d98k100% (8)
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 9th Edition Serway Test BankDocumento23 páginasPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 9th Edition Serway Test Bankninhletitiaqt3100% (27)
- Practice Test FinalDocumento23 páginasPractice Test FinalAllison TielkingAinda não há avaliações
- TB Chapter5Documento18 páginasTB Chapter5Jerry HuntAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocumento14 páginasRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBá Phong LêAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocumento17 páginasRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBaoduy NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Physics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsDocumento9 páginasPhysics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsNathaly SosaAinda não há avaliações
- Gravity and Energy Multiple Choice PracticeDocumento11 páginasGravity and Energy Multiple Choice PracticeJohnAinda não há avaliações
- Work and EnergyDocumento2 páginasWork and EnergyMauricioCuellar100% (1)
- Quiz02: Top of FormDocumento4 páginasQuiz02: Top of FormJay WongAinda não há avaliações
- AP Physics Work Energy Chapter 7 Multiple ChoiceDocumento4 páginasAP Physics Work Energy Chapter 7 Multiple ChoiceDSaulBAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Work and Energy ProblemsDocumento12 páginasPhysics Work and Energy ProblemsAlyssa Fermin0% (1)
- Ch8 Review Problems NewDocumento6 páginasCh8 Review Problems NewVic VanceAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Exit Exam ReviewDocumento13 páginasPhysics Exit Exam ReviewJohn Mark Osias100% (1)
- AP Phys C Fall Final Web RevDocumento12 páginasAP Phys C Fall Final Web RevNadhya FadlillahAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICS EXAM REVIEWDocumento18 páginasPHYSICS EXAM REVIEWCha Castillo100% (1)
- 102 Physics Answers-EK EditionDocumento15 páginas102 Physics Answers-EK Editionadom09Ainda não há avaliações
- Phys 204 Final Exam MechanicsDocumento5 páginasPhys 204 Final Exam MechanicsMalik AAinda não há avaliações
- The Laws of Motion: Multiple ChoiceDocumento8 páginasThe Laws of Motion: Multiple Choicealiya mAinda não há avaliações
- PhysDocumento10 páginasPhysahmedAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 2. Exam 2 AnswersDocumento7 páginasPhysics 2. Exam 2 AnswersWino PazAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7—Energy of a System Multiple ChoiceDocumento25 páginasChapter 7—Energy of a System Multiple ChoiceLeo Fuentes100% (1)
- Practice Exam 2 PDFDocumento8 páginasPractice Exam 2 PDFDavid WeitzelAinda não há avaliações
- Final Exam Sample Physics 71Documento11 páginasFinal Exam Sample Physics 71Jay VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 71 2nd LE Reviewer IDocumento2 páginasPhysics 71 2nd LE Reviewer IChristian GalopeAinda não há avaliações
- Force ProblemsDocumento2 páginasForce ProblemsAnthropophobe NyctophileAinda não há avaliações
- Testbank Chapter09Documento20 páginasTestbank Chapter09AldrianYanesa100% (1)
- TB Chapter13 PDFDocumento16 páginasTB Chapter13 PDFsuryapmohantyAinda não há avaliações
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocumento19 páginasHapter: Conceptual Problemsadel0% (1)
- AP Physics Free Response Practice – Work Power EnergyDocumento31 páginasAP Physics Free Response Practice – Work Power EnergyutheinsweAinda não há avaliações
- DynamicsDocumento3 páginasDynamicsjj012586Ainda não há avaliações
- (Physics) AnswersDocumento15 páginas(Physics) AnswersLoraine Rose EstivaAinda não há avaliações
- Ce2 Sample2Documento5 páginasCe2 Sample2ParZiValAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5, EnergyDocumento8 páginasChapter 5, Energynaru_chan1003Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 & 4Documento13 páginasUnit 3 & 4Ram Chandra0% (1)
- Work Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsDocumento6 páginasWork Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsAnusha HussainAinda não há avaliações
- PHYCS101 - Test2 RevisionDocumento8 páginasPHYCS101 - Test2 RevisionAli MaarajAinda não há avaliações
- USTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 SolutionDocumento10 páginasUSTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 Solutionabcvn67Ainda não há avaliações
- Extra Problems Chap. 5Documento11 páginasExtra Problems Chap. 5Roaa HamadaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Foundations and Connections 1St Edition Katz Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento41 páginasPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Foundations and Connections 1St Edition Katz Test Bank Full Chapter PDFBrendaTaylorwzab100% (7)
- 2010 Physics Model YekaDocumento9 páginas2010 Physics Model YekaTizita EmanaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 1 Sample Multiple Choice ProblemsDocumento4 páginasPhysics 1 Sample Multiple Choice ProblemsXinhua WangAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsDocumento57 páginasUnit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsLissa Hannah100% (1)
- UP College of Science Physics 71 Second Long Exam ReviewDocumento11 páginasUP College of Science Physics 71 Second Long Exam ReviewYamiyoAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Practice Problems: Work and EnergyDocumento5 páginasPhysics Practice Problems: Work and EnergysaparullahAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank 7Documento20 páginasTest Bank 7LukeLi100% (1)
- UP Physics Exam TitleB. 6.28 rad/sD. 1.57 rad/sDocumento12 páginasUP Physics Exam TitleB. 6.28 rad/sD. 1.57 rad/sCharmaine ColetaAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Sheet WPEDocumento9 páginasPractice Sheet WPENaveen JaferAinda não há avaliações
- AP Physics C Web Review Chapter 5 Work and EnergyDocumento4 páginasAP Physics C Web Review Chapter 5 Work and EnergyFares HeshamAinda não há avaliações
- Student's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Documento2 páginasStudent's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Nam Anh Nguyễn HữuAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 2007 EUEEDocumento8 páginasPhysics 2007 EUEElikinaw demisieAinda não há avaliações
- Forces on masses connected by rope over pulleyDocumento28 páginasForces on masses connected by rope over pulleydebasijAinda não há avaliações
- 2b-Dynamics FR Practice ProblemsDocumento24 páginas2b-Dynamics FR Practice ProblemsTiff VoAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Laws and Momentum Reading QuizDocumento58 páginasNewton's Laws and Momentum Reading QuizAltammar13Ainda não há avaliações
- National University Physics Midterm ExamDocumento4 páginasNational University Physics Midterm ExamBá Phong LêAinda não há avaliações
- Work Power and Energy Test WPDocumento6 páginasWork Power and Energy Test WPtabilinAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Exam Review 2Documento11 páginasDiagnostic Exam Review 2France Mico SobrevegaAinda não há avaliações
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Bg1806 PDF EngDocumento32 páginasBg1806 PDF Engdipankar65Ainda não há avaliações
- PUB InnovationinWater Issue9Documento40 páginasPUB InnovationinWater Issue9dipankar65Ainda não há avaliações
- 6 Sequence & Series Part 1 of 2Documento20 páginas6 Sequence & Series Part 1 of 2Ayush PateriaAinda não há avaliações
- SAT II Physics Formula SheetDocumento10 páginasSAT II Physics Formula Sheetalex100% (1)
- Trigonometric GraphsDocumento12 páginasTrigonometric GraphsjorenAinda não há avaliações
- Basic CalculusDocumento292 páginasBasic Calculuslouis_kwan_10% (1)
- VMC JEE Entrance Exam-2015/Paper-2Documento14 páginasVMC JEE Entrance Exam-2015/Paper-2RahulDhamaniaAinda não há avaliações
- 2015jeeadvp 1Documento18 páginas2015jeeadvp 1dipankar65Ainda não há avaliações
- SUBJECTIVE FIITJEE Question Papers From Rankers Study Material For IIT JEEDocumento354 páginasSUBJECTIVE FIITJEE Question Papers From Rankers Study Material For IIT JEEPritish JaiswalAinda não há avaliações
- Quote Price: Type of Trip: Duration: Places Highlight: InclusionsDocumento3 páginasQuote Price: Type of Trip: Duration: Places Highlight: Inclusionsdipankar65Ainda não há avaliações
- A Short Life of Sri RamakrishnaDocumento122 páginasA Short Life of Sri Ramakrishnaapi-3695801100% (1)
- L No 10Documento40 páginasL No 10surya_bwAinda não há avaliações
- Disaster Management Class 10Documento69 páginasDisaster Management Class 10YashVanjani60% (15)
- Limits and Continuity2Documento12 páginasLimits and Continuity2Oghenerukevwe EzewuAinda não há avaliações
- Physic Xi 2011Documento230 páginasPhysic Xi 2011Ashok PradhanAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Boyle's and Charles's Laws Practice ProblemsDocumento2 páginasChemistry Boyle's and Charles's Laws Practice Problemsdipankar65Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics Grade 12Documento222 páginasPhysics Grade 12Jan100% (12)
- Mth/Yr England Australia India Pakistan South Africa Sri Lanka West IndiesDocumento5 páginasMth/Yr England Australia India Pakistan South Africa Sri Lanka West IndiesPrem KrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- SAT II Physics Formula SheetDocumento10 páginasSAT II Physics Formula Sheetalex100% (1)
- Filtration and Fouling Problems in A Swro Plant On The GulfDocumento15 páginasFiltration and Fouling Problems in A Swro Plant On The Gulfdipankar65Ainda não há avaliações
- SAT II Physics Formula SheetDocumento10 páginasSAT II Physics Formula Sheetalex100% (1)
- The Case For Corporate Governance: Standing Out in An Uncertain WorldDocumento60 páginasThe Case For Corporate Governance: Standing Out in An Uncertain WorldendlessmaxAinda não há avaliações
- Cooling Tower FundamentalsDocumento117 páginasCooling Tower Fundamentalsapi-375105488% (16)
- Condensate PolisherDocumento20 páginasCondensate Polisherdipankar65Ainda não há avaliações
- Cooling Tower FundamentalsDocumento117 páginasCooling Tower Fundamentalsapi-375105488% (16)
- What Causes the Aurora BorealisDocumento12 páginasWhat Causes the Aurora Borealisakhil gharuAinda não há avaliações
- McKenney's, Inc. Wins "Beyond LEED" Category at First-Ever LEED Showcase AwardsDocumento2 páginasMcKenney's, Inc. Wins "Beyond LEED" Category at First-Ever LEED Showcase AwardsMcKenney's IncAinda não há avaliações
- WEP Narayana SheetsDocumento6 páginasWEP Narayana Sheetsrahuljain1100% (1)
- Wind Energy For Water Pumping in Rural Areas: Abdeen Mustafa OmerDocumento10 páginasWind Energy For Water Pumping in Rural Areas: Abdeen Mustafa OmerKetan VadorAinda não há avaliações
- PV Theory PDFDocumento18 páginasPV Theory PDFSara OsmanAinda não há avaliações
- Energy and Fuel Data SheetDocumento11 páginasEnergy and Fuel Data SheetkreutzAinda não há avaliações
- Zero Energy BuildingsDocumento17 páginasZero Energy BuildingsKashyap Sid100% (1)
- Modern Physics: Teaching Modern Physics in a Bilingual Spanish-English ContextDocumento282 páginasModern Physics: Teaching Modern Physics in a Bilingual Spanish-English ContextevaprofebioAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrogenics (Use For Catalog) HystatDocumento28 páginasHydrogenics (Use For Catalog) Hystatc108Ainda não há avaliações
- Phonon VibrationsDocumento12 páginasPhonon Vibrationspricil99Ainda não há avaliações
- List of Clearances, Approvals Required For Power Projects in IndiaDocumento3 páginasList of Clearances, Approvals Required For Power Projects in Indiapandetarun100% (1)
- Nagarjuna Sagar WPP UnitsDocumento3 páginasNagarjuna Sagar WPP UnitsN. Sasidhar0% (1)
- Ravi Presentation1Documento18 páginasRavi Presentation1ravi kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Power PlantsDocumento6 páginasPower PlantsyogusmiluAinda não há avaliações
- Advances and Trends of Energy Storage Technology in Microgrid 2013 PDFDocumento13 páginasAdvances and Trends of Energy Storage Technology in Microgrid 2013 PDFbdsrlAinda não há avaliações
- Exp. 7 Gas DiffusionDocumento2 páginasExp. 7 Gas DiffusionElaine PuiAinda não há avaliações
- Solar Power Project: MVS Ravi KumarDocumento16 páginasSolar Power Project: MVS Ravi KumarRavi Kumar MvsAinda não há avaliações
- K Ekkkjfffffffffffffnergy and WorkDocumento33 páginasK Ekkkjfffffffffffffnergy and WorkRavi YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Estimation of Electrolytic Hydrogen Production Potential in Venezuela From Renewable EnergiesDocumento8 páginasEstimation of Electrolytic Hydrogen Production Potential in Venezuela From Renewable EnergiesMeita Pratiwi100% (1)
- Gbu PJB Plta Brantas1Documento13 páginasGbu PJB Plta Brantas1syafrizkaAinda não há avaliações
- For Candidates Applying For Physics, and Physics and PhilosophyDocumento8 páginasFor Candidates Applying For Physics, and Physics and PhilosophyAhmad HaikalAinda não há avaliações
- Answers Chapter 13 and 14 Physics MCDocumento7 páginasAnswers Chapter 13 and 14 Physics MCmike100% (1)
- Kinetic Theory & Thermal Properties Notes IGCSE AVGDocumento12 páginasKinetic Theory & Thermal Properties Notes IGCSE AVGWeteach100% (3)
- 5.3 Thermal PhysicsDocumento28 páginas5.3 Thermal PhysicsMuhammad DanialAinda não há avaliações
- CH 27 Answers PDFDocumento13 páginasCH 27 Answers PDFMuhammad SalmanAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of Wind Energy On Power System Operation: Joris SoensDocumento55 páginasImpact of Wind Energy On Power System Operation: Joris SoensBrzata PticaAinda não há avaliações
- Contribution of Unu-Gtp Training To Geothermal Development in Pertamina Geothermal Energy, IndonesiaDocumento6 páginasContribution of Unu-Gtp Training To Geothermal Development in Pertamina Geothermal Energy, IndonesiaMuhammad Noble HidayatullahAinda não há avaliações
- Homer Lab 04Documento9 páginasHomer Lab 04DiegoFernandoRojasTorresAinda não há avaliações
- Solar Energy Fact SheetDocumento4 páginasSolar Energy Fact SheetHossam Al-Dein Mostafa HelmyAinda não há avaliações