Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Config and Faults Rectification
Enviado por
Mahamadou Ousseini Barkiré0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
21 visualizações36 páginasBTS Logical Model describes a logical representation of the BTS as viewed from the BSC for the purposes of O&M communication. The model comprises a structured hierarchy of instances of Managed Object (MO) of a given Managed Object class. The Transceiver Group is a special case as it does not have any hardware or software of its own. Instead, it consists of a set of Managed Objects from other Managed Object classes.
Descrição original:
Título original
100007156 Config and Faults Rectification
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoBTS Logical Model describes a logical representation of the BTS as viewed from the BSC for the purposes of O&M communication. The model comprises a structured hierarchy of instances of Managed Object (MO) of a given Managed Object class. The Transceiver Group is a special case as it does not have any hardware or software of its own. Instead, it consists of a set of Managed Objects from other Managed Object classes.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
21 visualizações36 páginasConfig and Faults Rectification
Enviado por
Mahamadou Ousseini BarkiréBTS Logical Model describes a logical representation of the BTS as viewed from the BSC for the purposes of O&M communication. The model comprises a structured hierarchy of instances of Managed Object (MO) of a given Managed Object class. The Transceiver Group is a special case as it does not have any hardware or software of its own. Instead, it consists of a set of Managed Objects from other Managed Object classes.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 36
RBS configuration and Faults Rectification
-Site Configuration Overview
-Fault management of RBS
-Taking BTS health checkup
-Queries Session
Site Configuration Overview
Understanding the CDD
Update in OSS
Integration and DIP provided from field
Logical configuration and New Site loading.
Remove Call bar and Site activation
Taking Site health check up
Basic components of GSM system.
GSM system is divided into Two parts.
1) BSS
2) SS
BSS Includes your BTS and BSC ,where as SS includes your
MSC/VLR,GMSC,HLR.
======================================
=
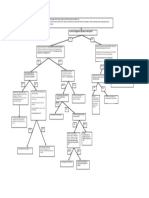
BTS Logical Model:
BTS Logical Model describes a logical representation of
the BTS as viewed from the BSC for the purposes of
O&M communication. The model comprises a structured
hierarchy of instances of Managed Object (MO) of a
given Managed Object Class.
Managed Object:
The class of all objects within the BTS Logical Model with
which the BSC can communicate. A Managed Object
(MO) is a logical representation of hardware units and
software at the BTS site. Note that hardware can be
shared between Managed Objects of different classes.
The Transceiver Group is a special case as it does not
have any hardware or software of its own. Instead, it
consists of a set of Managed Objects from other
managed object classes.
Logical Managed Object (MO)
TG
Transceiver Group
TX
TS
CON
RX
TF
TRX
DP BSC/TRC MSC
TX
TS
RX
TRX
TX
TS
RX
TRX
IS
CF
Transceiver Group (TG), Central Functions (CF), Transceiver Controller (TRXC), Interface
Switch (IS), LAPD Concentrator (CON), Timing Function (TF), Digital Path (DP), Transmitter
(TX), Receiver (RX) and Timeslot (TS). BTS Logical Model G01 comprises one or more
instances of MO of class: TG, TF, TRXC, TX, RX and TS.
BTS Logical Model:
BTS Logical Model describes a logical representation of the BTS as viewed
from the BSC for the purposes of O&M communication. The model
comprises a structured hierarchy of instances of Managed Object
(MO) of a given Managed Object Class. BTS Logical Model G12
comprises one or more instances of MO of class: Transceiver Group
(TG), Central Functions (CF), Transceiver Controller (TRXC), Interface
Switch (IS), LAPD Concentrator (CON), Timing Function (TF), Digital
Path (DP), Transmitter (TX), Receiver (RX) and Timeslot (TS). BTS
Logical Model G01 comprises one or more instances of MO of class:
TG, TF, TRXC, TX, RX and TS.
Cell Design Data steps:
The parameters provided by RF Planning
->Find the Undefined TG RXMOP:MO=RXOTG-1&&-511;
->Find unused CBCH Code for the Cell RXMBP:ID=ALL,NOTEXT;
->Defined the Cell and parameter using DT to the BSC
->Defined the Neighbor Of the Cell
RLNRP:CELL=ZUNBT1,CELLR=ALL,NODATA;
->Defined Site Details in MSC :(connect MSC )
MGCEP:CELL=KHUDE13;
MGCEI:CELL=ZUNBT13,CGI= 404-16-26-26263,BSC=NEBDIM1;
Update In OSS by Adjustment Procedure
New Site Loading:
rxtcp:moty=rxotg,cell=jonai01;
rxcdp:mo=rxotg-59;
dtstp:dip=jonai01;
dtdip:dip=jonai01;
ntcop:snt=etm2-0;
exdai:dev=RBLT2-576&&-607;
blode:dev=RBLT2-576&&-607;
rxapi:mo=rxotg-59,dcp=1&&31,dev=RBLT2-577&&-607;
rxesi:mo=rxotg-59,subord;
rxble:mo=rxotg-59,subord;
rxesi:mo=rxocf-59;
rxble:mo=rxocf-59;
rxmsp:mo=rxocf-59;
Active/Halt the Cell site
RLSBP:CELL=PIS0023;
RLNRP:CELL=PIS0023,CELLR=ALL,NODATA;
RLSTC:CELL=PIS0023,STATE=ACTIVE;
RLSTC:CELL=PIS0023,STATE=HALTED;
RBS FAULTS Rectification
Understand Various faults
How to follow the OPI
Apply the proper resolution
Coordinate with field Engineer
BTS Interfaces
Various device Defined
RBS faults
LOOP TEST FAILED,
TS SYNC FAULT
PERMANENT FAULT
ABIS PATH UNAVAILABLE
BTS INT AFFECTED(FC+TT)
RBS faults
CF Loading failed (Site/cell is not coming up)
TRX is/are not coming up
RXOIS not coming up
RXOTF not coming up/Not config.
Site showing in Local Mode
Site is down
General Commands Used for Faults Rectification
1)To view External Alarm of particular site:-
a) Allip:acl =a1;
b) Allip:acl =a2;
c) Allip:acl =a3;
2) To find out the TG Mo for particular site:-
Run RXTCP:MOTY=RXOTG,CELL=<CELL NAME>
3) To check Internal Alarm at site:-
RXASP:MO=RXOTG-< TG NO>;
Run RXMFP:MO=RXOCF-<TG NO.>;
It will give printout having Fault codes as :-
2A:8 - VSWR
2A:33 - RX DIVERSITY
2A:41 - LOST COMM. TO TRU
2A:42 - LOST COMM. TO CDU
2B:10 - SITE ON BATTERY
2B:4 - TX SATURATION
What is Power Fail alarm?
Mains supply fail is called power fail.In Delhi at many sites 3phase power supply is available
and so many sites running on 1phase power supply.
What happens when Power Fail occurs in a site?
When power fail occurs then site (BTS) at first goes into battery then after a short while DG set
on.A BTS (or RBS in Ericsson terminology) is running on +24 volts power supply.Actually here
battery placed as battery bank ( i.e combination of many batteries).
Battery bank voltage is about 23.5volts.Generally there are two battery banks are placed in the
shelter.Total battery bank capacity is 800amph ( each have a capacity of 400amph).Depends
on the condition of batteries this combined battery can serve supply to BTS for maximum
4hours.
How a site can get its power and what are the power related faults?
The detailed procedure is given below:
The mains power supply at first enters into the PSU (Power Supply Unit).The RBS2000 series
is based on standardized hardware units called Replaceable Unit (RU).
The major RU are:
(1) Power Supply Unit (PSU) or Power Interface Unit (PIU),
(2) Combining and Distribution Unit (CDU),
Alarms:
4) To check no. of sites down in Particular BSC:-
Run RLCRP:CELL=ALL;
Check if BCCH=0,site is down
5) To check the running configuration of a site:-
Run RLSLP:CELL=<CELL NAME>;
Check for NCH where BCCH,SDCCH & TCH values are displayed.
Run RXCDP:MO=RXOTG-<TG No>;
Check for the MOs which are in CONFIG & UNUSED,SELECT mode.
This command also tells the frequencies alloted TRX wise.
6) To check the state of a cell:-
Run RLSTP:CELL=<CELL NAME>;
It will shown wheather site is in active or halted state
7) To check the software of BTS:-
Run RXMOP:MO=RXOTG-<TG NO>;
Check SWVERACT
General Commands Used for Faults Rectification
8) To check the BTS type:-
Run RXMFP:MO=RXOCF-<TG. NO>;
Check for RULOGICALID type ,for 2206,2106,2204 it is mentioned in
that parameter.
9) To check the DIP (digital Interface path) status:
Run DTSTP:DIP=<DIP NAME>;
It will print the status of dip as WO,ABL,LOS etc
10) To check the devices atttched to the TG:-
Run RXAPP:MO=RXOTG-<TG NO>;
11) To check the status of TG,CF,TRX:-
RXMSP:MO=RXOTG-<TG NO>; same for CF
RXMSP:MO=rxotrx-<tg no>-<tei value>,subord;
General Commands Used for Faults Rectification
To change the Port A to C
Block and Out of service of TG
rxape: mo=rxotg-36,dcp=all;
RXAPI:MO=RXOTG-36,DCP=1&&31,DEV=RBLT2-4961&&-4991;(Port A)
RXAPI:MO=RXOTG-36,DCP=287&&317,DEV=RBLT2-4961&&-4991; (Port C)
To change the DIP
RXAPP:MO=RXOTG-36; (DCP=1&&31,DEV=RBLT2-4961&&-4991)
rxape: mo=rxotg-36,dcp=all;
(Block/De-block the Dev Keep 0 no DCP MBL, Reset the DIP and then Attached)
RXAPI:MO=RXOTG-36,DCP=1&&31,DEV=RBLT2-1537&&-1567;
General Commands Used for Faults Rectification
General Commands Used for Faults Rectification
Give the loading to CF
RXBLI:MO=RXOTG-<tg no>,SUBORD,FORCE;
RXESE:MO=RXOTG-<tg no>,SUBORD;
RXESI:MO=RXOTG-<tg no>,SUBORD;
RXBLE:MO=RXOTG-<tg no>,SUBORD;
When a Site is down:-DO RCA
1. Find TG no.
2. Check rxmsp if CF is in noop state.
3. Check the status of dip
4. Find dip connected to TG :-
1. RXMDP:MO=RXOCF-<TG NO>;(check device connected to CF)
2. RXAPP:MO=RXOTG-<TG NO>;(Check the Dev connected to TG)
3. RADEP:DEV=RBLT2-<DEVICE NO>;(check the SNT of device)
4. NTCOP:SNT=ETM2-3;(check the dip name verifying that device in that
SNT)
5. DTSTP:DIP=<dip name>;
If dip is break escalate to FM engineer.
If Dip is working check the external alarm at site
If no alarm is there and CF is still in noop state, Try to reload the CF
How to remove Abis path unavailable
<rxasp:mo=rxotg-222;
RADIO X-CEIVER ADMINISTRATION
MANAGED OBJECT ALARM SITUATIONS
MO SCGR SC RSITE ALARM SITUATION
RXOTG-222 JHKR11_C
RXOTS-222-0-3 JHKR11_C ABIS PATH UNAVAIL
RXOTS-222-1-7 JHKR11_C ABIS PATH UNAVAIL
RXOTS-222-2-7 JHKR11_C ABIS PATH UNAVAIL
RXOTS-222-3-6 JHKR11_C ABIS PATH UNAVAIL
RXOTS-222-3-7 JHKR11_C ABIS PATH UNAVAIL
TAKE Log of RXAPP:MO=RXOTG-222;
rxapp:mo=rxotg-222;
RADIO X-CEIVER ADMINISTRATION
ABIS PATH STATUS
MO
RXOTG-222
DEV DCP APUSAGE APSTATE 64K TEI
RBLT2-3395 3 MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
RBLT2-3396 4 MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
RBLT2-3399 7 MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
RBLT2-3400 8 MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
RBLT2-3402 10 MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
RBLT2-3403 11 CONC CF/TRXC SIGNAL NO 59 2 3
RBLT2-3404 12 CONC TRXC SIGNAL NO 0 1
RBLT2-3405 13 MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
<
Find the missing RBLT2 devices by
Rxmdp:moty=rxots,dev=rblt2-3406;
rxmdp:moty=rxots,dev=rblt2-3406;
RADIO X-CEIVER ADMINISTRATION
MANAGED OBJECT DEVICE INFORMATION
MO DEVS DEVT SDEV
RXOTS-88-9-3 RBLT2-3406 0010
RXOTS-88-9-4 RBLT2-3406 0001
Find rxapp for TG 88.
RXAPP:MO=RXOTG-88;
RXOTG-88
DEV DCP APUSAGE APSTATE 64K TEI
RBLT2-3393 1 MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
RBLT2-3406 14 MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX16 SPEECH/DATA NO
MPLEX32 IDLE NO
RBLT2-3407 15 UNDEF IDLE NO
RBLT2-3408 16 UNDEF IDLE NO
How to remove Abis path unavailable
Remove the undef idle devices from Tg and attach it to TG 222
Rxape:mo=rxotg-88,dcp=15&16;
Rxapi:mo=rxotg-222,dcp=15&16,dev=rblt2-3407&-3408;
Check again rxasp:mo=rxotg-222;
<rxasp:mo=rxotg-222;
RADIO X-CEIVER ADMINISTRATION
MANAGED OBJECT ALARM SITUATIONS
MO SCGR SC RSITE ALARM SITUATION
RXOTG-222 JHKR11_C
END
Alarm removed
How to remove Abis path unavailable
TS SYNC FAULT
WHY..??
Synchronization has been lost on the uplink or downlink Transcoder and Rate
Adaptation Unit (TRAU) channels.
How to resolve the Problem..
Check Abis path DCP mapping.
Devices should be defined on correct DCPs w.r.t the Port A,B,C or D at RBS side.
If 2-DIPs are given & 1-DIP needs to be cascaded between two cabinets, then always
define both DIPs to Master cabinet & then cascade one of them with another cabinet.
In case of MBC site there should not be mismatch in devices and DCPs i.e., fault will
occur if 900 Mhz band devices attach on 1800 Mhz band devices.
Commands used to resolve TS SYNC fault..
RXAPP:MO=RXOTG-<TG>; // Check ABIS print & find
wrong device
RXMDP:MO=RXOTS-<TG>-<TRX>-<TS>; // Find wrong Device
associated with TS
RXBLI:MO=RXOTS-<TG>-<TRX>-<TS>; // Block the TS
RXESE:MO=RXOTS-<TG>-<TRX>-<TS>; // Out of Service TS
RXAPE:MO=RXOTG-<TG>,DCP=<dcp>; // Remove the device
RXAPP:MO=RXOTG-<TG>; // Check ABIS print
RXASP:MO=RXOTG-<TG>; // Check Alarm Status
LOOP TEST FAILED
WHY..??
An automatic loop test of the traffic carrying capabilities has failed.
Commands used to resolve LOOP TEST FAILED..
RXBLI:MO=RXOTS-<TG>-<TRX>-<TS>; // Block TS
RXLTI:MO=RXOTS-<TG>-<TRX>-<TS>; // Loop Test on TS
RXBLE:MO=RXOTS-<TG>-<TRX>-<TS>; // Deblock TS
PERMANENT FAULT
WHY..??
A MO is classified as being permanently faulty when fault situations have
occurred, and have been cleared, a certain number of times within a certain
period of time. Manual intervention is required to bring such equipment back into
operation.
How to resolve the Problem..
Give soft reset (Block/Deblock)
Give hard reset
If alarm not disappear, Change the Hardware (H/W Faulty)
Commands used to resolve PERMANENT FAULT..
RXBLI:MO=RXOTRX-<TG>-<TRX>,SUBORD,FORCE; // Block MO
RXESE:MO=RXOTRX-<TG>-<TRX>,SUBORD; // Out of Service MO
RXESI:MO=RXOTRX-<TG>-<TRX>,SUBORD; // In Service MO
RXBLE:MO=RXOTRX-<TG>-<TRX>,SUBORD; // Deblock MO
RXASP:MO=RXOTG-<TG>; // Check alarm again
RXMFP:MO=RXOTRX-<TG>-<TRX>; // Check Fault code
RXMSP:MO=RXOTG-<TG>,SUBORD; // Check MO state
LOCAL MODE
WHY..??
The MO is in Local Mode or the MO has subsequently changed from Local to Remote Mode
and a fault exists in the communication link between the BSC and the BTS.
How to resolve the Problem..
Escalate to field engineer & get local mode changed to remote mode.
Hard Reset at BTS site & Reload IDB & then Soft Reset.
If from NOC end TRU is showing in local mode and Field engg. says at his end TRU is
blinking (already in remote mode), then check..
RXMSP:MO=RXOCON-<TG>;
RXMSP:MO=RXOIS-<TG>;
Check DCP1 & DCP2 defined on TRUs are correct using command
RXMOP:MO=RXOTRX-<TG>-<TRX>;
If every parameter is properly defined then escalate to field engineer to recheck
TRUs/DXU & related connection & load IDB again.
Change the Hardware
TF not Synchronized
WHY..??
DIP not working or bad quality
DXU E1 Port Faulty
DXU Faulty
How to Resolve the Problem..
Give soft & hard reset to DXU or CF
RXBLI, RXESE, RXESI, RXBLE
Check DIP status & DIP Quality
DTSTP:DIP=<DIP>;
DTQUP:DIP=<DIP>;
Reset DIP if error on DIP & Give soft Reset
DTQSR:DIP=<DIP>,ES,SES,SF;
DTQSR:DIP=<DIP>,DEGR,UNACC;
Ask FM engg. to check E1 port & connector at DXU & Reload IDB
If problem does not resolve change the E1 port A to Port B or C or D & Reload IDB
Lastly change DXU.
Managed Objects States
Replacement of Faulty DRU
DRU may gets faulty by TX
saturation alarm, RF loop test fault,
TX/RX min gain max gain violated,
TX max power restricted, If dTRU
has any hardware faulty then RED
LED will start to glow. Following
steps must be taken while replacing
dTRU.
Identify the faulty DRU by reading
IDB Radio or Maintenanc MO
faults.
Loose all the screws of the
DRU.
Put DRU in local mode.
Disconnect TX/RX cables
from it.
Power off DRU.
Replace the faulty DRU by
new one.
Insert back DRU in its slot
and connect all the cables back
their position.
Power up the DRU. Put DRU
in remote mode.
Replacement of Faulty DXU-31
DXU-31 or its flash card may
become faulty. BSC will no
longer communicate with DXU.
BSC will get DIP ABL and OML
Fault. No external alarms will
communicate to BSC. If DXU
gets faulty RED LED on it will
start to glow. Following steps
must be taken while replacing
DXU or flash card.
Ensure whether OMT can be
connected to DXU or not.
IDB can be read or not.
Loose all the screws of the DXU.
Put DXU in local mode.
Disconnect ESB cable, Y link
cables and Port (A, B, C, D) cables from
it.
Power off DXU.
Replace the faulty DXU by new
one.
Insert the flash card according to its
orientation.
Insert back DXU in its slot and
connect all the cables back their position.
Power up the DXU.
BST Health checkup
RXTCP:MOTY=RXOTG,CELL=cell id;
RXCDP:MO=RXOTG-tg no;
RXASP:MO=RXOTG-tg no;
RXMSP:MO=RXOTG-tg no,SUBORD;
RXMFP:MO=RXOTG-tg no;
RXAPP:MO=RXORG-tg no;
RXCAP:MO=RXOTG-tg no,SUBORD;
RXMOP:MO=RXOTG/CF/TRX/TX;
Cell Health Checkup
rlncp:cell=xxx (to get neighbors)
rlnrp:cell=xxx, cellr=xxx; (to get neighbors relation)
rldgp:cell=xxx (to get GSM type and CHGR)
rlmfp:cell=xxx (to get MBCCHNO, active and idle)
rlcxp:cell=xxx (to get DTXD state)
rlcpp:cell=xxx (to get power of cell)
rlchp:cell=xxx (to get Configuration Frequency Hopping Data)
rlcfp:cell=xxx (to get the DCHNO of cell)
rlslp:cell=xxx (to get Supervision of Logical Channels Availability)
rlbdp:cell=xxx (to get GPRS state).
rldep:cell=xxx (to get Description Data).
rlgap:cell=xxx (to get channel group allocation data)
rllop:cell=xxx (to get all power)
rlhpp:cell=xxx (to get channel allocation profile)
rllpp:cell=xxx (to get cell locating penalty).
rllfp:cell=xxx (to get cell locating filter).
rlldp:cell=xxx (to get cell locating disconnect)
rlihp:cell=xxx (to get system information Intracell handover)
rlssp:cell=xxx (to get system information)
rlsbp:cell=xxx (to get system info BCCH)
rlbcp:cell=xxx (to get dynamic BTS power)
rlprp:cell=xxx (to get differential channel allocation)
rllcp:cell=xxx (to get cell load sharing)
rlbdp:cell=xxx (to get radio control cell config BPC)
Você também pode gostar
- Mop - Anr Mobility - Faj 121 2551Documento11 páginasMop - Anr Mobility - Faj 121 2551Mahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- Workshop Load Balance Parameters - ListDocumento6 páginasWorkshop Load Balance Parameters - ListMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- OMF000405 Case Study - Congestion: ISSUE1.4Documento79 páginasOMF000405 Case Study - Congestion: ISSUE1.4Mahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- UMTS Coverage DiscussionDocumento57 páginasUMTS Coverage DiscussionMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- Anr Mobility Pre PostDocumento4 páginasAnr Mobility Pre PostMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- Telkomsel Call Flow CSDocumento13 páginasTelkomsel Call Flow CSMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- Umts Ho EventsDocumento51 páginasUmts Ho EventsMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- UMTS LOG File Analysis & Optimization 1 PDFDocumento63 páginasUMTS LOG File Analysis & Optimization 1 PDFMahamadou Ousseini Barkiré100% (1)
- 3G ImpDocumento60 páginas3G ImpMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - KPI Presentation Ver 1-8 Serv LevDocumento88 páginas2 - KPI Presentation Ver 1-8 Serv LevMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- IFHO FlowchartDocumento1 páginaIFHO FlowchartMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- Optimization ParametersDocumento16 páginasOptimization ParametersMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- Events in TEMS ProductsDocumento60 páginasEvents in TEMS ProductsMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- Automatic Start of TEMS DiscoveryDocumento5 páginasAutomatic Start of TEMS DiscoveryMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- 3G Alarm Impact To PerformanceDocumento8 páginas3G Alarm Impact To PerformanceMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- Rwafi StatsDocumento8 páginasRwafi StatsMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- F5 Big-Ip Dns (Or GTM) : RakeshDocumento26 páginasF5 Big-Ip Dns (Or GTM) : RakeshudithapriyangaAinda não há avaliações
- 520-0013-06 TECH NOTE Theory of The Session-AgentDocumento8 páginas520-0013-06 TECH NOTE Theory of The Session-AgentJuanitoAinda não há avaliações
- Netconfig Tool Oper ManualDocumento68 páginasNetconfig Tool Oper ManualMiguel Angel Cara Rios100% (1)
- Aegon Case StudyDocumento6 páginasAegon Case Studyshyam_mohan_6Ainda não há avaliações
- Host Driver Logs CurrentDocumento5 páginasHost Driver Logs Currentvenosyah devanAinda não há avaliações
- GLP1000 - Brochure v1.1 SEPT2014 PDFDocumento2 páginasGLP1000 - Brochure v1.1 SEPT2014 PDFRavi KudalAinda não há avaliações
- Pexip Infinity VMR Scheduling Exchange Deployment Guide V33.aDocumento93 páginasPexip Infinity VMR Scheduling Exchange Deployment Guide V33.asetelin677Ainda não há avaliações
- Aws Reference ArchitectureDocumento75 páginasAws Reference Architecturepisanij123100% (4)
- 304TX DataSheetDocumento2 páginas304TX DataSheetcarlosorizabaAinda não há avaliações
- Yamrajgaming V3Documento194 páginasYamrajgaming V3sniper GamingAinda não há avaliações
- Performance Testing With JMeter PDFDocumento134 páginasPerformance Testing With JMeter PDFMayur BaghlaAinda não há avaliações
- Network Engineer Interview Questions-2Documento14 páginasNetwork Engineer Interview Questions-2mushahidAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco ThesisDocumento9 páginasCisco ThesisDavid VardanyanAinda não há avaliações
- 05-System Maintenance Command Reference-BookDocumento143 páginas05-System Maintenance Command Reference-BookreoguanAinda não há avaliações
- Dual Band Wireless Ac 3168 BriefDocumento2 páginasDual Band Wireless Ac 3168 BriefGabriel DimaAinda não há avaliações
- 36211-E40 CoverDocumento7 páginas36211-E40 CoverevolvingsatAinda não há avaliações
- Form ValidationDocumento4 páginasForm ValidationJASPER WESSLYAinda não há avaliações
- Installing Wordpress Blog Using Apache On EC2 LinuxDocumento17 páginasInstalling Wordpress Blog Using Apache On EC2 LinuxUbaid SaadAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna 2 Module 11 v4.0Documento3 páginasCcna 2 Module 11 v4.0ccnaexploration4Ainda não há avaliações
- Test Plan Guru99Documento9 páginasTest Plan Guru99saswataAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Manual v1.0: CL3000 Series Asynchronous Control SystemDocumento6 páginasEngineering Manual v1.0: CL3000 Series Asynchronous Control SystemJaime VillamizarAinda não há avaliações
- IBM Spectrum Protect: Trusted Backup and Recovery Software SolutionsDocumento8 páginasIBM Spectrum Protect: Trusted Backup and Recovery Software Solutionsaldozp1Ainda não há avaliações
- IFHO FlowchartDocumento1 páginaIFHO FlowchartMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréAinda não há avaliações
- By Prof. Santos Kumar Das: Data Communication Networks (Ec 6501) Chapter 3: Data CommunicationsDocumento21 páginasBy Prof. Santos Kumar Das: Data Communication Networks (Ec 6501) Chapter 3: Data CommunicationsDeepak SutharAinda não há avaliações
- Ruckus SCG Config Wlan MibDocumento6 páginasRuckus SCG Config Wlan MibEddy EspinozaAinda não há avaliações
- CKAN Installation & ConfigurationDocumento23 páginasCKAN Installation & ConfigurationKamel MallehAinda não há avaliações
- VMTC01: Installation OverviewDocumento3 páginasVMTC01: Installation Overviewcad cadAinda não há avaliações
- Cyber Law and Cyber Security PDFDocumento34 páginasCyber Law and Cyber Security PDFarjun sabuAinda não há avaliações
- NetScaler Fundamentals Lab GuideDocumento74 páginasNetScaler Fundamentals Lab Guidekayudo80Ainda não há avaliações
- Application ID ListDocumento9 páginasApplication ID Listelhadniz0% (1)