Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
5 C O N I C S: Parabola
Enviado por
Dattatray NerkarTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
5 C O N I C S: Parabola
Enviado por
Dattatray NerkarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Tutorials '9892603993 MH-CET/XII Mathematics
5 C O N I C S
A conic is the locus of a point such that the ratio of its distance from a fixed point to its distance
from a fixed straight line is constant.
The fixed point is called focus of the conic and is denoted by S. the fixed straight line is called
directrix of the conics and is denoted by d . The constant ratio is called the eccentricity of the
conic and is denoted by e
If S is the focus , d is the directrix P ( x1, y1) is any point on the conic and P d , the e!uation
of the conic is gi"en by PS = e PM .
This property of the conics is called focus-directrix property .
If e # 1 , the conic is called a Parabola
If e $ 1 , the conic is called a Ellipse
If e % 1 , the conic is called a Hyperbola
The general e!uation of a conic is gi"en by a
general second degree e!uation in x and y.
Important Term in Conics
!"is A line about &hich a conic is symmetrical is called an axis of the conic
#erte" The point in &hich an axis of a conic meets the cur"e is called a "ertex of the conics.
$ocal point ' The distance of a point on a conic from its focus is called focal distance
$ocal Chor% ' A chord of a conic passing through its focus is called a focal chord .
&atus 'ectum ' The focal chord of a conic perpendicular to its axis is called is called its latus
rectum.
PARABOLA
(roperties o) (ara*ola
+, The tangent at any point on the parabola bisects the angle bet&een the focal chord through that
point and a line perpendicular to the directrix
2, The intercept on the tangent of the parabola bet&een its point of contact and the directrix
subtends a right angle at the focus.
3, The sub(tangent is bisected at "ertex
-, The circle on a focal radius of a parabola as diameter touches tangent at "ertex .
., The locus of the perpendiculars to the tangent of the parabola from the focus is tangent at
"ertex .
6, If the tangent at the point P and ) of parabola meet at * , then S*
+
# SP. S)
/, Through the "ertex , of the parabola y
2
= 4ax , a line is dra&n perpendicular to any tangent ,
meeting it in P and the parabola in ) , then ,P.,) is constant.
Conics - : 15
Tutorials '9892603993 MH-CET/XII Mathematics
PARABOLA
Definition A parabola is the locus of a point such that its distance from a fixed point is e!ual to
its distance from a fixed straight line.
The e!uation y
2
= 4ax is called standard e!uation of parabola.
The e!uations x = at
2
and y = 2at &here -t. the parameter , are called parametric e!uations
(ara*ola y
2
0 -a" y
2
0 - -a" "
2
0 -ay "
2
0 --ay
/ocus
(a, 0) ((a, 0) (0, a) (0, (a)
1irectrix
x 2 a # 0 x ( a # 0 y 2 a # 0 y ( a # 0
Axis
3!uation of axis
4(axis
y # 0
4(axis
y # 0
5 6axis
x # 0
5 6axis
x # 0
7ertex
(0, 0) origin (0, 0) origin (0, 0) origin (0, 0) origin
8ength 8atus 9ectum
:a :a :a :a
3nds of 8atus 9ectum
(a, +a) (a, (+a) ((a, +a) ((a, (+a) (+a, a) ((+a, a) (+a, (a) ((+a, (a)
3!uation of 8. 9.
x ( a # 0 x 2 a # 0 y ( a # 0 y 2 a # 0
Tangent at "ertex
x # 0, 5 6axis x # 0, 5 6axis y # 0, 4(axis y # 0, 4(axis
3xtent of Parabola
I ; I7 !uadrant II ; III !uadrant I ; II !uadrant III ; I7 !uadrant
Standard 3!uation
(ara*ola In general t&o tangents can
be dra&n to parabola from a
point P( x
1
, y
1
) in its plane
If m
1
and m
+
are the slopes of
the t&o tangents , then
1
+ 1
1
1
+ 1
. ;
x
a
m m
x
y
m m = = +
If the tangents dra&n at P(t)
and )(t) on the parabola
intersect at 9 then
( ) ) (
+ 1 + 1
t t a t t a R + =
y
+
# :ax
Parametric 3!uation x # at
+
, y # +at
3!uation of tangent at
P(x
1
, y
1
)
) ( +
1 1
x x a y y + =
3!uation of tangent at
P ( )
yt = x + at
2
3!uation of tangent in
terms of slope ;
Point of contact
m
a
mx y + =
m
a
m
a +
,
+
E L L I P S E
Ellipse 1
+
+
+
+
= +
b
y
a
x
1 a 2 * , 1
+
+
+
+
= +
b
y
a
x
1 * 2 a ,
Conics - : 16
Tutorials '9892603993 MH-CET/XII Mathematics
/ocus S( ae , 0 ) S ((ae, 0) S( 0 , be ) S (0, (be)
1irectrix d
e
a
x = , d
e
a
x = d
e
b
x = , d
e
b
x =
Axis ( length )
a<or Axis (x(axis ) # +a
inor Axis (y(axis ) # +b
a<or Axis (x(axis ) # +b
inor Axis (y(axis ) # +a
=entre ( 0, 0 ) ( 0, 0 )
8ength 8atus 9ectum
a
b
+
+
b
a
+
+
3nds of 8atus 9ectum 8 ) , (
+
a
b
ae 8 ) , (
+
a
b
ae
8 ) , (
+
be
b
a
8
) , (
+
be
b
a
3!uation of 8. 9. x # ae , x # ( ae y # be , y # ( be
9elation bet&een a ; b b
+
# a
+
( 1 6e
+
) a
+
# b
+
( 1 6e
+
)
7ertices
A ( a, 0 ) , A.( (a, 0 )
>( 0, b ) , >.( 0, (b )
A ( a, 0 ) , A.( (a, 0 )
>( 0, b ) , >.( 0, (b )
3ccentricity
a
b a
e
+ +
=
b
a b
e
+ +
=
1istance bet&een foci 2ae 2be
1istance bet&een
directrices e
a +
e
b +
Standard 3!uation
Ellipse
1
+
+
+
+
= +
b
y
a
x
Parametric
3!uation
x = a cos , y = b
sin
3!uation of tangent
at
P(x1, y1)
1
+
1
+
1
= +
b
yy
a
xx
3!uation of tangent
at
P ( )
1
sin cos
= +
b
y
a
x
3!uation of tangent
in
terms of slope ;
Point of contact
+ + +
b m a mx y + =
c
b
c
m a
+ +
,
3!uation of 1irector
=ircle
x
2
+ y
2
= a
2
+ b
2
H Y P E R B O L A
Hyper*ola 1
+
+
+
+
=
b
y
a
x
1
+
+
+
+
=
a
x
b
y
/ocus S( ae , 0 ) S ((ae, 0) S( 0 , be ) S (0, (be)
Conics - : 17
Tutorials '9892603993 MH-CET/XII Mathematics
1irectrix 1
e
a
x = , d
e
a
x = d
e
b
x = , d
e
b
x =
Axis ( length )
Trans"erse Axis (x(axis ) # +a
=on<ugate Axis (y(axis ) # +b
Trans"erse Axis (x(axis ) # +b
=on<ugate Axis (y(axis ) # +a
=entre ( 0, 0 ) ( 0, 0 )
8ength 8atus 9ectum
a
b
+
+
b
a
+
+
3nds of 8atus 9ectum 8 ) , (
+
a
b
ae 8 ) , (
+
a
b
ae
8 ) , (
+
be
b
a
8
) , (
+
be
b
a
3!uation of 8. 9. x # ae , x # ( ae y # be , y # ( be
9elation bet&een a ; b b
+
# a
+
(e
+
61) a
+
# b
+
(e
+
61)
7ertices
A ( a, 0 ) , A.( (a, 0 )
>( 0, b ) , >.( 0, (b )
A ( a, 0 ) , A.( (a, 0 )
>( 0, b ) , >.( 0, (b )
3ccentricity
a
b a
e
+ +
+
=
b
b a
e
+ +
+
=
1istance bet&een foci 2ae 2be
1istance bet&een
directrices e
a +
e
b +
Standard 3!uation
Hyper*ola
1
+
+
+
+
=
b
y
a
x
Parametric 3!uation x = a sec , y = b tan
3!uation of tangent at
P(x1, y1)
1
+
1
+
1
=
b
yy
a
xx
3!uation of tangent at
P ( )
1
tan sec
=
b
y
a
x
3!uation of tangent in
terms of slope ;
Point of contact
+ + +
b m a mx y =
c
b
c
m a
+ +
,
3!uation of 1irector
=ircle
x
2
+ y
2
= a
2
b
2
Ellipse :
Definition : A ellipse is the locs of a point in a plane sch that ratio of its !istance from a fixe!
point an! fixe! strai"ht line is a constant less than one#
The e!uation 1
+
+
+
+
= +
b
y
a
x
is called standard e!uation of ellipse
Conics - : 18
Tutorials '9892603993 MH-CET/XII Mathematics
The e!uations x = a cos
and y = b sin &here - . the parameter, are called parametric
e!uations
In general t&o tangents can be dra&n from a point P ( x1 , y1) to the ellipse 1
+
+
+
+
= +
b
y
a
x
If m1 and m+ are slopes of these tangents then
+
1
+
1
+ 1
+ 1
+
a x
y x
m m
= +
and
+ +
1
+ +
1
+ 1
.
a x
b y
m m
=
(roperties o) ellipse
+, The sum of the focal distance of a point on the ellipse is e!ual to the length of the ma<or axis.
3' The sum of the focal distance of a point on the ellipse 1
+
+
+
+
= +
b
y
a
x
is +a
+) If p1 , p+ are the length of the perpendicular segments from the foci of the ellipse 1
+
+
+
+
= +
b
y
a
x
to any tangent, then p1 . p+ # b
+
3'
The product of the lengths of perpendicular segments from the foci on any tangent to the ellipse
1
+
+
+
+
= +
b
y
a
x
is b
+
?) The intercept on any tangent to an ellipse bet&een its point of contact and the directrix
subtends right angle at the corresponding focus. 3'
If the tangent at a point P on an ellipse meets a directrix in ) , then the segment P) subtends
right angle at the corresponding focus
:) The focus of the foot of the perpendicular from a focus of the ellipse, 1
+
+
+
+
= +
b
y
a
x
on any
tangent is its auxiliary circle.
Hyperbola :
Definition ' A hyperbola is the locus of a point in a plane such that ratio of its distance from a
fixed point and fixed straight line is a constant greater than one.
The e!uation 1
+
+
+
+
=
b
y
a
x
is called standard e!uation of hyperbola
Conics - : 19
Tutorials '9892603993 MH-CET/XII Mathematics
The e!uations x = a sec
and y = b tan &here -. the parameter , are called parametric
e!uations
In general t&o tangents can be dra&n from a point P ( x1 , y1) to the hyperbola 1
+
+
+
+
=
b
y
a
x
If m1 and m+ are slopes of these tangents then
+
1
+
1
+ 1
+ 1
+
a x
y x
m m
= +
and
+ +
1
+ +
1
+ 1
.
a x
b y
m m
=
(roperties o) Hyper*ola
1) The difference bet&een the focal distance of a point on the hyperbola is e!ual to the length of
its trans"erse axis. 3'
If P is any point on the hyperbola 1
+
+
+
+
=
b
y
a
x
, and S , S are the foci , then @ SP 6 S P @ # +a .
+) The product of the lengths of the perpendicular from the foci and any tangent to the hyperbola
1
+
+
+
+
=
b
y
a
x
is e!ual to b
+
.
?) The tangent at a point P on a hyperbola bisects the angle bet&een the focal radii to the point
P.
:) The locus of the foot of the perpendicular from the focus on the hyperbola 1
+
+
+
+
=
b
y
a
x
on
any tangent is its auxiliary circle.
Conics - : 20
Você também pode gostar
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Parabola 123Documento9 páginasParabola 1231553Ainda não há avaliações
- Parabola Notes For IIT JEE - pdf-56 PDFDocumento9 páginasParabola Notes For IIT JEE - pdf-56 PDFSubbu SarabuAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Optics For Charged Particles: Ying K. WuDocumento24 páginasMagnetic Optics For Charged Particles: Ying K. WussuresuAinda não há avaliações
- ParabolaDocumento9 páginasParabolaMohd Sofian MustaffaAinda não há avaliações
- Conic Section Free DPPDocumento24 páginasConic Section Free DPPprem19999Ainda não há avaliações
- Conic Section Part 4 of 8Documento24 páginasConic Section Part 4 of 8majji satishAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperbola ProblemsDocumento16 páginasHyperbola Problemskishangopi123Ainda não há avaliações
- Sample Booklet (Study Material + Model Paper) For SA-2 Class 10Documento32 páginasSample Booklet (Study Material + Model Paper) For SA-2 Class 10Apex Institute88% (8)
- Best Approach: Conic Section (Sheet)Documento79 páginasBest Approach: Conic Section (Sheet)Shivam RoyAinda não há avaliações
- AodDocumento41 páginasAodAditya BansalAinda não há avaliações
- Integral Calculus Analytic GeometryDocumento8 páginasIntegral Calculus Analytic GeometryPerrie H.Ainda não há avaliações
- IIT Mathematics 2005Documento7 páginasIIT Mathematics 2005Robin SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Conic Section Part 2 Hyperbola Download in PDFDocumento9 páginasClass 11 Maths Chapter 11 Conic Section Part 2 Hyperbola Download in PDFMohsin Manzoor Bhat100% (1)
- Conics ArjunaDocumento6 páginasConics Arjunaajgangster3Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit1 Lesson3-ParabolaDocumento45 páginasUnit1 Lesson3-Parabolachristine faith seducoAinda não há avaliações
- Parabola Theory EDocumento16 páginasParabola Theory Ethinkiit100% (1)
- Math 1432 Notes - Week 8Documento13 páginasMath 1432 Notes - Week 8Kyle BroflovskiAinda não há avaliações
- Straight LinesDocumento127 páginasStraight LinesVIDYA SRI GANESHAinda não há avaliações
- Conic Section Muti Choice Questions: P and P and O IsDocumento4 páginasConic Section Muti Choice Questions: P and P and O IsThunderswordAinda não há avaliações
- Ellipse Theory eDocumento18 páginasEllipse Theory ethinkiit100% (1)
- Applications 2Documento39 páginasApplications 2Riddhima MukherjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Nota 2010Documento78 páginasNota 2010Muhammad NuruddinAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus With Analytic Geometry: Rolando S. Merle, MaedDocumento59 páginasCalculus With Analytic Geometry: Rolando S. Merle, MaedRolando MerleAinda não há avaliações
- Parametric CurvesDocumento8 páginasParametric Curvessiva_ksrAinda não há avaliações
- l5 Further Geometry2Documento47 páginasl5 Further Geometry2Corrine ChanAinda não há avaliações
- Application of Derivatives Theory - eDocumento41 páginasApplication of Derivatives Theory - ethinkiitAinda não há avaliações
- Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces 1. Curves in The PlaneDocumento20 páginasDifferential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces 1. Curves in The PlaneRobert KemperAinda não há avaliações
- Conic Sections: S (P, Q) R P (X, Y) SP RDocumento16 páginasConic Sections: S (P, Q) R P (X, Y) SP RChristian M. MortelAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics FormulaDocumento5 páginasMathematics FormuladeenawantsAinda não há avaliações
- ANALYTIC GEOMETRY For DEMODocumento16 páginasANALYTIC GEOMETRY For DEMOnikkoAinda não há avaliações
- Conic Section PDFDocumento17 páginasConic Section PDFAjinkya Patil0% (1)
- CIRCLEA Theory Solved Example IitjeeDocumento11 páginasCIRCLEA Theory Solved Example IitjeeShashank ShekharAinda não há avaliações
- Straigt LinesDocumento50 páginasStraigt LinesAvnish BhasinAinda não há avaliações
- 1720 Chapter 10 Notes - StewartDocumento19 páginas1720 Chapter 10 Notes - StewartChristian YerkesAinda não há avaliações
- Conics: Abdul Hamed A. Adiong Stem 11-St - LawrenceDocumento18 páginasConics: Abdul Hamed A. Adiong Stem 11-St - LawrenceAbdul AdiongAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1.3Documento16 páginasLesson 1.3Baroxx DiazAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 - 2014 (1B)Documento5 páginas2013 - 2014 (1B)Syed SalmanAinda não há avaliações
- Anna's AssignmentDocumento16 páginasAnna's Assignmenttumaini murrayAinda não há avaliações
- ConicsDocumento9 páginasConicsWael MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Straight LinesDocumento4 páginasStraight Linesblue_l1Ainda não há avaliações
- Selected Theory Is Found at The Final Part of The Set All Answers Are To Be ExplainedDocumento5 páginasSelected Theory Is Found at The Final Part of The Set All Answers Are To Be Explaineddevkc25Ainda não há avaliações
- Conic Sections: ParabolaDocumento92 páginasConic Sections: ParabolaJR DevienteAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 Introduction To Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento12 páginasModule 1 Introduction To Trigonometric FunctionsAleph Continuum100% (1)
- 1.plane Coordinate GeometryDocumento10 páginas1.plane Coordinate GeometryPoh Koon Seng100% (1)
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form5Documento28 páginasSPM Add Maths Formula List Form5Sayantani GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3Documento39 páginasApplied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3bigbangmelvanAinda não há avaliações
- "Just The Maths" Unit Number 8.6 Vectors 6 (Vector Equations of Planes) by A.J.HobsonDocumento10 páginas"Just The Maths" Unit Number 8.6 Vectors 6 (Vector Equations of Planes) by A.J.HobsonDaniel BoenfieAinda não há avaliações
- Marko Radovanovic Complex Numbers in GeometryDocumento53 páginasMarko Radovanovic Complex Numbers in Geometrymaraujo68Ainda não há avaliações
- 06gm CurvesDocumento11 páginas06gm CurvesRajesh MahapatraAinda não há avaliações
- ConicsDocumento9 páginasConicsniranjankumar79Ainda não há avaliações
- Problem Set 1: 1 Questions On Understanding The LectureDocumento6 páginasProblem Set 1: 1 Questions On Understanding The LectureShweta SridharAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Area For Irregular ShapeDocumento8 páginasChapter 2 Area For Irregular ShapeMaisah Bha100% (1)
- Formula Sheet: PS+QR QsDocumento4 páginasFormula Sheet: PS+QR QsTsehayMegersaAinda não há avaliações
- University of Dhaka Basic of GraphDocumento36 páginasUniversity of Dhaka Basic of GraphRedowan Mahmud RatulAinda não há avaliações
- MATH39001 - Combinatorics and Graph Theory - Exam - Jan-2011Documento8 páginasMATH39001 - Combinatorics and Graph Theory - Exam - Jan-2011scribd6289Ainda não há avaliações
- 2 - Conic SectionsDocumento66 páginas2 - Conic SectionsBaui KojiAinda não há avaliações
- CalculusII Baitap BXDDocumento19 páginasCalculusII Baitap BXDSâm Mai HuyềnAinda não há avaliações
- 3 - Complex NumbersDocumento10 páginas3 - Complex NumbersDattatray NerkarAinda não há avaliações
- Neet 13 Question PaperDocumento19 páginasNeet 13 Question PaperDattatray NerkarAinda não há avaliações
- B y A X B y A X: Circle Parabola Ellipse HyperbolaDocumento1 páginaB y A X B y A X: Circle Parabola Ellipse HyperbolaDattatray NerkarAinda não há avaliações
- Books List PDFDocumento4 páginasBooks List PDFRohit Kumar100% (2)
- Trigonometric RatioDocumento11 páginasTrigonometric RatioDattatray NerkarAinda não há avaliações
- MT Cet InformationDocumento48 páginasMT Cet InformationDattatray NerkarAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Mathematical Logic: Statement: A Declarative Sentence Which Is Either True or False But Not Both Is Called ADocumento4 páginas1 Mathematical Logic: Statement: A Declarative Sentence Which Is Either True or False But Not Both Is Called ADattatray NerkarAinda não há avaliações
- Limits TheoryDocumento2 páginasLimits TheoryDattatray NerkarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Objectives: Planar Rigid-Body MotionDocumento15 páginasChapter Objectives: Planar Rigid-Body MotionvenkatAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 2.1 Motion: Mr. AhnDocumento223 páginasTopic 2.1 Motion: Mr. AhnBrady LiamAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 10 Math - CircleDocumento19 páginasGrade 10 Math - CircleRobengie MoneraAinda não há avaliações
- 1-5 Angle Pairs Reteaching Wks PDFDocumento2 páginas1-5 Angle Pairs Reteaching Wks PDFBosRajAinda não há avaliações
- Special Triangle Grade 9Documento10 páginasSpecial Triangle Grade 9Niño Lemuel Lazatin ConcinaAinda não há avaliações
- Let Review: MathematicsDocumento102 páginasLet Review: MathematicsFghhAinda não há avaliações
- Slicing of 3-d ObjectsDocumento2 páginasSlicing of 3-d Objectsapi-365838707Ainda não há avaliações
- LM Pre Calculus Q1 M7 V2-LaconsayDocumento19 páginasLM Pre Calculus Q1 M7 V2-LaconsayLynette Licsi0% (1)
- 9X MORD - M - Surface Areas and Volumes (Sol)Documento16 páginas9X MORD - M - Surface Areas and Volumes (Sol)Dhanalakshmi DhanalakshmiAinda não há avaliações
- Math Resources Geometry FormulasDocumento2 páginasMath Resources Geometry FormulasMoslem GrimaldiAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 7 Division Finals QuestionsDocumento2 páginasGrade 7 Division Finals QuestionsJasmin And - Angie97% (35)
- Berkeley Math CircleDocumento2 páginasBerkeley Math Circlehuymai54c0% (1)
- Taxicab CircumcirclesDocumento3 páginasTaxicab Circumcirclesapi-255059274Ainda não há avaliações
- Crystal Lattice DiffractionDocumento5 páginasCrystal Lattice DiffractionthynameisraymondAinda não há avaliações
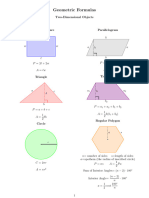
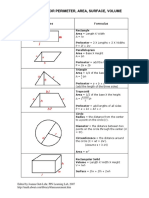
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocumento2 páginasGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFLucky MalhotraAinda não há avaliações
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocumento7 páginasRepublic of The PhilippinesDonna Sheena SaberdoAinda não há avaliações
- Math Note For DuetDocumento4 páginasMath Note For DuetRedoy HossainAinda não há avaliações
- Class: VIII Sub: Mathematics Chapter: 1 Rational Numbers Worksheet 1Documento36 páginasClass: VIII Sub: Mathematics Chapter: 1 Rational Numbers Worksheet 1Sumeet KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Geometry For Maths OlympiadDocumento8 páginasGeometry For Maths OlympiadCambridgeSchool NoidaAinda não há avaliações
- Trigonometric Identities and FormulasDocumento6 páginasTrigonometric Identities and FormulasRajesh MauryaAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Rhombuses, Rectangles, and SquaresDocumento2 páginasProperties of Rhombuses, Rectangles, and SquaresmadalinaCM50% (2)
- Projection of PlanesDocumento23 páginasProjection of PlanesPrakash KatdareAinda não há avaliações
- MathDocumento4 páginasMathJadesola AwosikaAinda não há avaliações
- 200 Important Quantitative Aptitude Questions For AAI JE ATC 2023 ExamDocumento18 páginas200 Important Quantitative Aptitude Questions For AAI JE ATC 2023 ExamOwaisAinda não há avaliações
- Topper 110 2 3 Maths Solution Up202308291227 1693292242 2785Documento19 páginasTopper 110 2 3 Maths Solution Up202308291227 1693292242 2785abhimanyou076Ainda não há avaliações
- Sample Paper 10 MathsDocumento11 páginasSample Paper 10 Mathsaneeshkilli2008100% (1)
- A Cylindrical Tank Measures 12ft Long and 3ft in DiameterDocumento3 páginasA Cylindrical Tank Measures 12ft Long and 3ft in DiameterJohn Miko JavierAinda não há avaliações
- Great CircleDocumento8 páginasGreat Circlearik yumnaAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 3, Chapter 1-2Documento2 páginasQuiz 3, Chapter 1-2Mansoor Aslam33% (3)
- Geometry Eoc Practice Test 1Documento26 páginasGeometry Eoc Practice Test 1api-279522974100% (1)