Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Y10 Plant Transport Lesson 1
Enviado por
Sherry Lee0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
85 visualizações27 páginasDistribution of Xylem and Phloem in plants, an introduction to plant transport.
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDistribution of Xylem and Phloem in plants, an introduction to plant transport.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
85 visualizações27 páginasY10 Plant Transport Lesson 1
Enviado por
Sherry LeeDistribution of Xylem and Phloem in plants, an introduction to plant transport.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 27
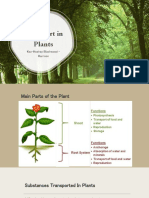
Transportation in Plants
8.1: Transport System
LO:
State the functions of xylem and phloem
Identify the position of xylem and phloem in
transverse sections of root, stems and leaves.
Transport in Plants
Plants have two different types of 'transport'
tissue.
Xylem transports water and solutes from the
roots to the leaves, phloem transports food
from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
A group of xylem vessels and phloem tubes is
called a vascular bundle.
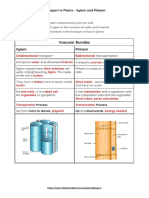
Xylem
Xylem cells have extra reinforcement in
their cell walls, and this helps to support
the weight of the plant.
Stem the xylem and phloem are arranged in bundles near the edge of the
stem to resist compression and bending forces.
Comparison of Xylem and Phloem
Tissue Process Functions Structure
Xylem Transpiration
Transport water
and mineral ions
up to the leaves
Columns of hollow, dead
reinforced cells.
Their walls are made of
cellulose and lignin.
Phloem Translocation
Transport
sucrose and
amino acids
down to the
roots and up to
the flowers and
fruits.
Columns of living cells
joined end to end.
Each sieve tube element
has a companion cell next
to it.
Companion cell have
nucleus.
Xylem Vessel and Phloem Sieve Tube
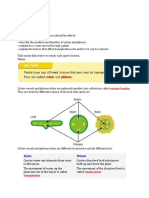
Distribution of Xylem and Phloem
Distribution of xylem and phloem tissue in
roots of dicotyledonous plants
ALBIO9700/2006JK
ALBIO9700/2006JK
Distribution of xylem and phloem tissue
in stems of dicotyledonous plants
ALBIO9700/2006JK
Distribution of xylem and phloem tissue
in leaves of dicotyledonous plants
Comparison between monocots and dicots
Learning Check!
Plenary
1. Xylem vessels transport water and mineral
ions from the roots up the stem to the
leaves.
2. Phloem vessels transport sucrose, made in
the leaves during photosynthesis and in
storage organs, to other parts of the plant.
3. Xylem and phloem are distributed in a central
core inside a root. Inside a stem they are
organised into vascular bundles.
8.2: Water Uptake
LO:
Identify root hairs as seen under microscope
and relate their structures to water uptake.
State the pathway taken by water through
root, stem and leaf
The Internal Structure of a root
Root Hairs
Adaptations:
- many root hairs
- long extension, thin
- permeable cell walls
To provide large surface
area which water and
mineral ions are
absorbed.
water potential gradient
Root hair
Xylem
vessels
Leaves
air
How water is absorbed by a plant?
Roots
Plants absorb water from the soil by osmosis.
Root hair cells are adapted for this by having a
large surface area to speed up osmosis.
The absorbed water is transported through the
roots to the rest of the plant where it's used
for different purposes:
1. It's a reactant used in photosynthesis
2. It supports leaves and shoots by keeping the cells
rigid
3. It cools the leaves by evaporation
4. It transports dissolved minerals around the plant
Soil water is a dilute solutions
which contains mineral ions
such as nitrate and potassium.
The cell sap in the root hair
cells is more concentrated
solution than soil water. This is
because root hair cells absorb
mineral ions and contains
sugar.
Therefore, water diffuses from
soil into the root hair cells by
osmosis.
How water is absorbed by a plant?
How water is absorbed by a plant?
Water then pass across the cortex
of the root. Most of the water
moves through the cell walls and in
the spaces between the cells. Some
moves from cells to cells. Water
eventually reaches the xylem in the
centre of the root.
From here water moves up the
xylem through the stem and to the
leaves where it enters the spongy
mesophyll cells.
Much of the water enters the cell
walls, evaporates to form water
vapour and then diffuses through
stomata to the atmosphere.
Extension:
Transpiration Pull:
Transpiration is the evaporation of water from
the leaves and the loss of water vapour to the
atmosphere through the stomata.
Water is pulled up the xylem in the stem from
the roots to the leaves by transpiration pull.
Transpiration Pull
The mass flow of water up the xylem relies on
two properties of water:
Cohesion- the water molecules tend to attract
each other, sticking together.
Adhesion the water molecules tend to stick
to the inside of the xylem vessel.
The movement of water up the xylem is called
the transpiration stream.
Transpiration Stream
Learning Check!
Learning Check 2
Plenary
1 Water enters a root hair cell by osmosis. It then
passes across the cells of the root cortex by
osmosis before passing into the xylem and then
up the stem to the leaves.
2 Root hairs are well adapted for the absorption of
water since they have thin cell walls and have a
large surface area.
3 Loss of water from the leaves 'pulls' more water
up the stem from the roots in the transpiration
stream.
Você também pode gostar
- Transport in PlantsDocumento28 páginasTransport in PlantsGautam Dayal100% (1)
- Transport in PlantsDocumento46 páginasTransport in PlantsNoorSabaAinda não há avaliações
- BOQ Approach RoadDocumento4 páginasBOQ Approach RoadApollo RajkumarAinda não há avaliações
- 06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Documento24 páginas06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Saurabh ShivakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8-Transport in PlantsDocumento33 páginasChapter 8-Transport in PlantsrinaahwAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in Plants HandoutDocumento5 páginasTransport in Plants HandoutAsawni McDowellAinda não há avaliações
- Dean Martin Mambo ItalianoDocumento2 páginasDean Martin Mambo ItalianoMofan LaiAinda não há avaliações
- Science KitchenDocumento46 páginasScience KitchenSherry LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento65 páginasTransport in Plantswienna1987Ainda não há avaliações
- Bill of Materials and Cost Estimates (Sample)Documento1 páginaBill of Materials and Cost Estimates (Sample)Sharazil Mabanag69% (16)
- Ch-8 Transport in PlantsDocumento18 páginasCh-8 Transport in PlantsHaziq KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Quotation For Soil TestDocumento1 páginaQuotation For Soil TestBikas Jha100% (1)
- Lesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. Objectives: at The End of The Session, Students Are Expected ToDocumento2 páginasLesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. Objectives: at The End of The Session, Students Are Expected ToJT SaguinAinda não há avaliações
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento57 páginasTransport in PlantsIbrahim NOORZADAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsDocumento49 páginasBiology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsAbdiwahab IssackAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE Biology Topic 8 Transport in Plants PresentationDocumento28 páginasIGCSE Biology Topic 8 Transport in Plants PresentationhannahhishamAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 Transport in Plants 8.1 & 8.2Documento52 páginasChapter 8 Transport in Plants 8.1 & 8.2Ali OpAinda não há avaliações
- Plant TransportDocumento41 páginasPlant Transportyohoho 87Ainda não há avaliações
- Transport in Plant - Class NotesDocumento32 páginasTransport in Plant - Class Noteszaijah taylor4AAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 (2) - RemovedDocumento249 páginasBiology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 (2) - RemovedMathableAinda não há avaliações
- Ch-8 Transport in PlantsDocumento12 páginasCh-8 Transport in Plantsdaveymilan36Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 Transport in PlantDocumento40 páginasChapter 8 Transport in Plantjzdf2d9nnvAinda não há avaliações
- Absorption of WaterDocumento43 páginasAbsorption of WaterOGAANSHO TUBEAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento24 páginasTransport in PlantsAreebAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Transport SystemsDocumento20 páginasPlant Transport Systemscale suarezAinda não há avaliações
- 8-Transport in PlantsDocumento24 páginas8-Transport in PlantsᎡѦc̸ɛ 2834Ainda não há avaliações
- Transport in Plants - Chapter 8Documento2 páginasTransport in Plants - Chapter 8Viviana PlacentinoAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsDocumento49 páginasBiology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsPeter Osundwa Kiteki100% (2)
- Lecture 12 - Transport in PlantsDocumento8 páginasLecture 12 - Transport in PlantsAmmar RizwanAinda não há avaliações
- Support and Transport in PlantsDocumento37 páginasSupport and Transport in PlantsGuruKPO100% (1)
- Plant Transport-Grade 11-EditedDocumento37 páginasPlant Transport-Grade 11-EditedAsawni McDowellAinda não há avaliações
- 5090 - Topic6 - Bio - Transport in Flowering PlantsDocumento32 páginas5090 - Topic6 - Bio - Transport in Flowering PlantsMaryam ShahidAinda não há avaliações
- Hortbot Lesson Plan6Documento9 páginasHortbot Lesson Plan6BarbyannAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento14 páginasTransport in PlantsMuhammad Faizan KaleemAinda não há avaliações
- Transport and Transpiration in Plants NOTESDocumento10 páginasTransport and Transpiration in Plants NOTESYasmin YehiaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology PosterDocumento5 páginasBiology PosterMenara RathnayakeAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento35 páginasTransport in PlantsChantae JulienAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento20 páginasTransport in PlantsForthtAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 8 Transport in Plants: 8.1 Vascular Tissue Functions of Xylem & PhloemDocumento10 páginasTopic 8 Transport in Plants: 8.1 Vascular Tissue Functions of Xylem & PhloemMuhammad Hassan TariqAinda não há avaliações
- Independent Notes Plant TransportDocumento3 páginasIndependent Notes Plant TransportIqbal WahyuAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Transport 1Documento25 páginasPlant Transport 1Tosis MajidAinda não há avaliações
- 3.1.2 Transport in PlantsDocumento9 páginas3.1.2 Transport in PlantssjAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Form 2 NotesDocumento80 páginasBiology Form 2 NotesLutern RayAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 - Transport Systems in Dicotyledonous PlantsDocumento4 páginasUnit 2 - Transport Systems in Dicotyledonous PlantsSherif Borhamy AzmyAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento56 páginasTransport in PlantsTrynosAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in Plants: Plant RootsDocumento6 páginasTransport in Plants: Plant RootsShantejah MitchellAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 6: Plant Structure & FunctionDocumento36 páginasTopic 6: Plant Structure & FunctionChiangshiuan SooAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Transport - TranspirationDocumento50 páginasPlant Transport - TranspirationJoel RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- TRANSPORT in PLANTSDocumento27 páginasTRANSPORT in PLANTSRish HeeAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in Plants: By:-Mr - Deepak Upreti Biology Teacher Gmis, JakartaDocumento26 páginasTransport in Plants: By:-Mr - Deepak Upreti Biology Teacher Gmis, Jakartakiera angAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento3 páginasTransport in Plantsoten.temotika02Ainda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento6 páginasTransport in PlantsAbhyudaya SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Topic:: Submitted To: Prof. Hina TariqDocumento6 páginasTopic:: Submitted To: Prof. Hina TariqZubair BalouchAinda não há avaliações
- GCSE Biology Physiology Part 2 (Transport in Plants)Documento3 páginasGCSE Biology Physiology Part 2 (Transport in Plants)Fasih AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Part 1 Plant TransportDocumento28 páginasPart 1 Plant Transportrawan SaketAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento5 páginasTransport in Plantsbaone segaetshoAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in Flowering Plants Final VersionDocumento9 páginasTransport in Flowering Plants Final VersionJohn MoyoAinda não há avaliações
- Transportation in PlantsDocumento31 páginasTransportation in PlantssamskruthamanabroluAinda não há avaliações
- Plant TransportDocumento2 páginasPlant TransportWafiyah AwaisAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in Plants - PhloemDocumento4 páginasTransport in Plants - Phloemlwandlemkhonza96Ainda não há avaliações
- TRANSPORT IN VASCULAR PLANTS-ekmDocumento18 páginasTRANSPORT IN VASCULAR PLANTS-ekmHesbone AneneAinda não há avaliações
- Plant TransportDocumento23 páginasPlant TransportBalakrishnan MarappanAinda não há avaliações
- A, Level Transport by MR Li - 1Documento107 páginasA, Level Transport by MR Li - 1asadukimbugwe20Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 TranspirationDocumento20 páginas1 TranspirationSuriez DoAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in PlantsDocumento12 páginasTransport in PlantsRahil BhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Think Global and British Council The Global Skills GapDocumento12 páginasThink Global and British Council The Global Skills GapSherry LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4: Variation and ClassificationDocumento16 páginasUnit 4: Variation and ClassificationSherry LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Results: Raw Data: Solution Width (MM) Before & After Length (MM) Before & After Mass (G) Before & AfterDocumento2 páginasResults: Raw Data: Solution Width (MM) Before & After Length (MM) Before & After Mass (G) Before & AfterSherry LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Azalea Begonia Alcatraz Camellia Clavel: Noun Noun Noun Noun NounDocumento6 páginasAzalea Begonia Alcatraz Camellia Clavel: Noun Noun Noun Noun Nounshabin sAinda não há avaliações
- Tree Nursery How To PDFDocumento6 páginasTree Nursery How To PDFpankaj suryaAinda não há avaliações
- Cement - Quality Types & UsesDocumento13 páginasCement - Quality Types & UsesRundhuAinda não há avaliações
- Cultivation 161022015221Documento96 páginasCultivation 161022015221Harish KakraniAinda não há avaliações
- How To Mix MortarDocumento3 páginasHow To Mix MortarRi Sovannaphumi100% (1)
- Tomato Factsheet 2013Documento4 páginasTomato Factsheet 2013Crystal Redhead-GouldAinda não há avaliações
- Constituent Materials of Concrete: by Nick Gromicko, CMI® and Kenton ShepardDocumento9 páginasConstituent Materials of Concrete: by Nick Gromicko, CMI® and Kenton ShepardWalterAinda não há avaliações
- Stela Menduga Produktivitas TanamanDocumento92 páginasStela Menduga Produktivitas TanamanRezaIndriadiAinda não há avaliações
- ACT-question Bank Unit-3 PDFDocumento2 páginasACT-question Bank Unit-3 PDFmeena y rAinda não há avaliações
- Experimental Investigation On Coir Geotextile Reinforced SubgradeDocumento5 páginasExperimental Investigation On Coir Geotextile Reinforced SubgradeDipendra AwasthiAinda não há avaliações
- Production Technology of Spices, Aromatic, Plantation CropsDocumento115 páginasProduction Technology of Spices, Aromatic, Plantation CropsRadhey Shyam KumawatAinda não há avaliações
- Mangosteen IndustryDocumento3 páginasMangosteen IndustryChristopherOropelAinda não há avaliações
- 3M Protocol Rc222Documento1 página3M Protocol Rc222Rommel SacramentoAinda não há avaliações
- GRDC Plant Back Guide Manual LRDocumento48 páginasGRDC Plant Back Guide Manual LRElla SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Jatropha Curcas LDocumento3 páginasJatropha Curcas LChin Suk MeiAinda não há avaliações
- 13a. Road Construction MethodsDocumento18 páginas13a. Road Construction MethodsSheeraz AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Common Gardening ToolsDocumento10 páginasCommon Gardening ToolsjudithdacutanAinda não há avaliações
- Diseases of SoybeanDocumento3 páginasDiseases of SoybeanManuel VegasAinda não há avaliações
- What To Expect From This Lecture: CE 310 - Transportation Engineering - IDocumento12 páginasWhat To Expect From This Lecture: CE 310 - Transportation Engineering - IHarshvardhan SiddharthAinda não há avaliações
- AAB Ahmednagar 22-12-2015 PDFDocumento1 páginaAAB Ahmednagar 22-12-2015 PDFbharatAinda não há avaliações
- Soil MechDocumento21 páginasSoil MechAhsan AbbasAinda não há avaliações
- nrcs142p2 053291Documento8 páginasnrcs142p2 053291Yhuli ZwitterzzajawchAinda não há avaliações
- Noting Significant Details in A Selection ReadDocumento2 páginasNoting Significant Details in A Selection ReadMichaela Tandoc Muyano - Bernardo100% (2)
- Types of Fruits Quiz: Grade 8Documento1 páginaTypes of Fruits Quiz: Grade 8tyas mouriAinda não há avaliações
- Boq Cme: 1 Pole Foundation Soil WorkDocumento1 páginaBoq Cme: 1 Pole Foundation Soil WorkyuwonoAinda não há avaliações
- Echeveria - WikipediaDocumento5 páginasEcheveria - WikipediaMh HarisAinda não há avaliações