Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Diabetes
Enviado por
Yannah Mae EspineliDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Diabetes
Enviado por
Yannah Mae EspineliDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
DIABETES
DIABETES
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic derangement that arises from lack of insulin and inability of
cells to recognize it.
Is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by increased levels of glucose in the blood
resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both.
What is insulin?
Insulin stimulates the liver to form glycogen into glucose and inhibits conversion of
noncarbohydrates into glucose.
Insulin transports glucose into the cell for use as energy and storage of glycogen.
What is a glucagon?
Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen and convert certain noncarbohydrates
such as amino acids, into glucose, raising blood sugar concentration. Glucagon much more
effectively elevates the blood glucose than epinephrine.
Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus:
Family history of diabetes
Obesity ! "# kg$m%& ' Obesity causes resistance to endogenous insulin
(ace$ethnicity
)ge ! *+ y&
,reviously identified impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance
-ypertension ! .*/$0/ mm -g&
-D1 cholesterol level 2 3+ mg$d1& and or triglyceride level !"+/ mg$d1&
-istory of gestational diabetes or delivery of babies over 0 lbs
,hysiological$emotional stress4 causes prolonged elevation of stress hormones which revises
glucagon
,regnancy4 increases levels of estrogen which antagonizes insulin
CASSIFICATI!"
Insulin #e$en#ent%&u'enile%T($e I Diabetes
)usually appears before age of twenty and is an autoimmune disease: the immune system destroys the
beta cells of the pancreas. This type is treated with insulin and diet.
"on)insulin #e$en#ent%*aturit()onset%T($e II Diabetes
)in these type, beta cells produces insulin, but body cells lose the ability to recognize it. The condition
usually develops gradually after age forty. Most affected individuals are overweight or obese when
symptoms begin. Treatment includes controlling of diet, exercising, and maintaining a desirable body
weight.
+estational Diabetes
)is high blood sugar that starts or is first diagnosed during pregnancy.
Page .
DIABETES
,AT-!,-.SI!!+.
(According to patient .!"s condition#
Page "
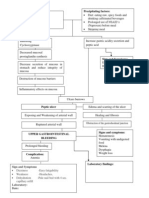
Predisposing Factors:
4age above */ years old
4gender
4family history mother
and sister&
Precipitating Factors:
4obesity
4physiologic and
emotional stress
4diet
Impaired insulin secretion by
pancreatic beta cells
Insulin resistance
Decreased glucose
transport into muscle
cells
5levated hepatic
glucose production
Increased
breakdown of fat
6uild4up of glucose in the blood
Increased amounts of insulin are secreted to maintain
glucose level at a normal or slightly elevated level.
7etabolic syndrome&
6eta cells cannot keep up with the increased demand
for insulin
Glucose level rises and type II diabetes develops
DIABETES
Page 3
-yperglycemia
8apillary basement membrane thickening
Diffuse glomerular sclerosis
95,-(O,):-;
5nd4stage renal disease
DIABETES
CI"ICA MA"IFESTATI!"S
T$ %&'('%A& MA(')*TAT'+(* ,!(, +( T$ !AT'(T-* &.& +) $/!01&/%M'A/
%lassic clinical manifestations of all types include the three 2!-s3
,)olyuria increased urination&
,)olydipsiaincreased thirst&
,)olyphagia increased appetite&
,atients e<perience polyuria and polydipsia as a result of the e<cess loss of fluid associated with
osmotic diuresis. ,atients also e<perience polyphagia that results from the catabolic state induced by
insulin deficiency and the breakdown of proteins and fats.
OTHER SYMPTOMS:
fatigue and weakness
sudden vision changes
tingling or numbness in hands or feet
dry skin
skin lesions or wounds that are slow to heal
recurrent infections
weight loss, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain :ype .&
ASSESSME"T A"D DIA+"!STICS
Fasting plasma glucose F,G& greater than or e=ual to ."> mg$d1&
Glucose level " hours after receiving glucose e=ual or greater than "// mg$d1&
5valuation for complications
:est for microalbuminuria
?erum creatinine level
@rinalysis
5lectrocardiogram
MEDICA MA"A+EME"T
7ain goal of diabetes treatment is to normalize insulin activity and blood glucose levels to reduce the
development of vascular and neuropathic complications.
"0TRITI!"A T-ERA,.
9utrition and 7eal planning4 control caloric intake to attain or maintain a reasonable body
weight, control blood glucose levels, and normalization of lipids and blood pressure to prevent
heart disease.
Aeight control
,-ARMAC!!+IC T-ERA,.
'nsulin therapy
4:ype .B e<ogenous insulin must be administered for life because the body loses ability to produce
Page *
DIABETES
insulin
4:ype "B insulin may be necessary on a long4term basis to control glucose levels if meal planning and
oral agents are ineffective.
CATE+!RIES !F I"S0I"
Ti*e course Agent In#ications
(apid acting 1ispro -umalog&
)spart 9ovolog&
Glulisine )pidra&
@sed for rapid reduction of glucose level, to treat
postprandial hyperglycemia, and$or to prevent
nocturnal hypoglycemia
?hort )cting (egular -umalog (,
9ovolin (, Iletin II
(egular&
@sually administered "/43/ minutes before a
mealC may be taken alone or in combination with
longer acting insulin
Intermediate4acting 9,- neutral protamine
-agedorn&
@sually taken after food
Dery long acting Glargine 1antus&
Detemir 1evemir&
@sed for basal dose
Oral )ntidiabetic agents biguanides, alpha4glucosidase inhibitors, first and second generations
of sulfonylurase&
,ramlintide ?ymlin&4 used to treat hyperglycemia to adults who have not achieved acceptable
levels of glucose control despite the use of insulin at mealtimes. For :ype . and :ype "
Diabetes.
5<enatide 6yetta& treatment for :ype " diabetes in combination with formin or sulfonylureas.
5nhances insulin secretion.
AC0TE C!M,ICATI!"S
hypoglycemia
diabetic ketoacidosis
hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketonic syndrome
!"+)TERM C!M,ICATI!"S
7acrovascular complications
7icrovascular 8omplication
4 Diabetic retinopathy
4 9ephropathy
4 Foot and 1eg problems
"0RSI"+ MA"A+EME"T
,roviding patient education
:he disease itself
InEection of insulin
diet
medications
,RE1E"TI!"
Page +
DIABETES
8hange in lifestyle. Do e<ercises and avoid sedentary lifestyle.
7aintain weight and 67I at normal level.
Do not smoke$ ?top smoking because it increases the risk for stroke.
-ave a proper and balance diet.
RES!0RCES:
Internet:
httpB$$www.medicinenet.com$diabetesFmellitus$page".htm 23ritten: 4une 567 8598:
httpB$$www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov$pubmedhealth$,7-///.G0G$ 2ast re'ie3e# August ;7 8598:
httpB$$emedicine.medscape.com$article$..#G+34overviewHaw"aab>b"b3 2u$#ate#: 4ul( 8<7 859<:
Books:
-ole=s Essentials of -u*an Anato*( an# ,h(siolog( 95
th
E#ition 2co$(right > 855?:
Brunner an# Su##arth=s Te@tbook of Me#ical)Surgical "ursing 98
th
E#ition 2co$(right > 8595:
Page >
Você também pode gostar
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Pathophysiology of DiseaseDocumento7 páginasPathophysiology of DiseaseYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of DiseaseDocumento7 páginasPathophysiology of DiseaseYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of DiseaseDocumento7 páginasPathophysiology of DiseaseYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Burnout Syndrome - Stress in Health Care Professionals Working To Fight Covid-19 in Public HospitalsDocumento14 páginasBurnout Syndrome - Stress in Health Care Professionals Working To Fight Covid-19 in Public HospitalsIJAERS JOURNALAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Uses For Medical MarijuanaDocumento4 páginas7 Uses For Medical MarijuanaYhojan Surco ZavalaAinda não há avaliações
- (Pittsburgh Pocket Psychiatry Series) Michael J Marcsisin, Jason B Rosenstock, Jessica M Gannon-Schizophrenia and Related Disorders-Oxford University Press (2017) PDFDocumento313 páginas(Pittsburgh Pocket Psychiatry Series) Michael J Marcsisin, Jason B Rosenstock, Jessica M Gannon-Schizophrenia and Related Disorders-Oxford University Press (2017) PDFToader AndreiAinda não há avaliações
- Paliative CareDocumento402 páginasPaliative CarewardahAinda não há avaliações
- Videbeck Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing Chapter Work SheetDocumento46 páginasVidebeck Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing Chapter Work SheetYannah Mae Espineli100% (1)
- Pathophysiology - HypokalemiaDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology - HypokalemiaYannah Mae Espineli33% (3)
- Ventricular Septal DefectDocumento6 páginasVentricular Septal DefectYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Management 1. Approach ConsiderationsDocumento10 páginasMedical Management 1. Approach ConsiderationsYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Breast MastitisDocumento2 páginasBreast MastitisYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Pearson's Correlation TestDocumento27 páginasPearson's Correlation TestYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlansDocumento5 páginasNursing Care PlansYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Brogada SyndromeDocumento19 páginasBrogada SyndromeYannah Mae Espineli100% (1)
- Some Definitions in Psychiatric NursingDocumento9 páginasSome Definitions in Psychiatric NursingYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Detection of Ulcer Disease: Peptic Ulcers Gastric Ulcers Gastric CarcinomasDocumento3 páginasDetection of Ulcer Disease: Peptic Ulcers Gastric Ulcers Gastric CarcinomasYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Discharge Plan For CADDocumento2 páginasDischarge Plan For CADYannah Mae EspineliAinda não há avaliações
- Indoor Air PollutionDocumento24 páginasIndoor Air PollutionMohamed SalemAinda não há avaliações
- Renee IOWL - Workbook - 1 - 18Documento182 páginasRenee IOWL - Workbook - 1 - 18Mirna Velazquez100% (1)
- Briefing Practical Literature Searching and Critical Appraisal (Diagnosis and Therapy) - Dr. Lukman Ade Chandra, M.med., M. Phil (2022)Documento16 páginasBriefing Practical Literature Searching and Critical Appraisal (Diagnosis and Therapy) - Dr. Lukman Ade Chandra, M.med., M. Phil (2022)Sheila Tirta AyumurtiAinda não há avaliações
- Preventative Care Assignment 3 (1) ADocumento9 páginasPreventative Care Assignment 3 (1) AOdia OaikhenaAinda não há avaliações
- Causes of Pain in The Right Side of The HeadDocumento3 páginasCauses of Pain in The Right Side of The HeadUtpal KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 4 MHPPDocumento11 páginasAssignment 4 MHPPBabar AliAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. D.N. Prastowo, SP - PD: Bagian Penyakit Dalam Rs. Hana Charitas - Arga Makmur Bengkulu 2017Documento45 páginasDr. D.N. Prastowo, SP - PD: Bagian Penyakit Dalam Rs. Hana Charitas - Arga Makmur Bengkulu 2017nanikAinda não há avaliações
- Lung Sounds 7Documento1 páginaLung Sounds 7Kyle LatayanAinda não há avaliações
- Lyceum of the Philippines University College of Nursing Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasLyceum of the Philippines University College of Nursing Drug Studykaye barrionAinda não há avaliações
- Journal of Anatomy - 2017 - Kirkpatrick - The Plantar Calcaneal Spur A Review of Anatomy Histology Etiology and KeyDocumento9 páginasJournal of Anatomy - 2017 - Kirkpatrick - The Plantar Calcaneal Spur A Review of Anatomy Histology Etiology and KeyUlla NasAinda não há avaliações
- Obesity in UK, Alexandra VelescuDocumento15 páginasObesity in UK, Alexandra VelescuGabriela AlexandraAinda não há avaliações
- Mental Illness Annotated BibliographyDocumento8 páginasMental Illness Annotated Bibliographyapi-386396722Ainda não há avaliações
- Animal Health and Welfare Module 1Documento127 páginasAnimal Health and Welfare Module 1prevosterfuturemwampweAinda não há avaliações
- Students With Mental RetardationDocumento3 páginasStudents With Mental RetardationNorain KasanAinda não há avaliações
- Interview QuestionsDocumento7 páginasInterview QuestionsMuhammad SaadAinda não há avaliações
- Health FairDocumento11 páginasHealth FairThe Lima NewsAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Essentials of Pediatric Nursing 2nd Edition Theresa KyleDocumento13 páginasTest Bank For Essentials of Pediatric Nursing 2nd Edition Theresa KyleJamesJacksonjbpof100% (76)
- Growing in Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) Market To Set New Business Opportunities For Start Up CompanyDocumento2 páginasGrowing in Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) Market To Set New Business Opportunities For Start Up CompanyPR.comAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Nutritional Problems of Adolescents 2Documento30 páginas11 Nutritional Problems of Adolescents 2Danilo Sare IIIAinda não há avaliações
- CPE 103 Lecture on Developmental DisabilitiesDocumento29 páginasCPE 103 Lecture on Developmental DisabilitiesMay Flor T. BelandoAinda não há avaliações
- Adult Health (Integration)Documento26 páginasAdult Health (Integration)L1NEDS DAinda não há avaliações
- Psychiatric Medication BasicsDocumento16 páginasPsychiatric Medication BasicsCarmen HollidayAinda não há avaliações
- PAFP Consensus Guidelines On Preparation and Resumption of Clinic Services - FINALDocumento17 páginasPAFP Consensus Guidelines On Preparation and Resumption of Clinic Services - FINALPatricia Franco-VillaAinda não há avaliações
- UpToDate 2021 Overview of Cerebellar Ataxia in AdultsDocumento55 páginasUpToDate 2021 Overview of Cerebellar Ataxia in AdultsPaloma GBAinda não há avaliações
- History of Polio-1Documento21 páginasHistory of Polio-1world photocopyAinda não há avaliações
- Kripps Newsletter 5Documento135 páginasKripps Newsletter 5suckerxAinda não há avaliações