Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Directing and Leadership Concepts Explained
Enviado por
deepashajiTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Directing and Leadership Concepts Explained
Enviado por
deepashajiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
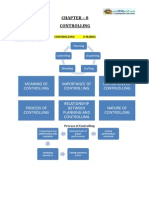
CHAPTER -7
DIRECTING
CONCEPT MAPPING:
Concept and importance
Elements of Directing
- Supervision-concept, functions of a supervisor.
- Motivation-concept, Maslows hierarchy of need: inancial and non-financial
incentives.
- !eadership-concept, styles-authoritative, democratic and laisse" faire.
- Communication- concept, formal and informal communication# $arriers to
effective communication, how to overcome the $arriers.
Key Concepts in Nutshell
Meanin o! Di"ectin: %t refers to instructing, guiding, communicating and inspiring
people in the organisation .
I#po"tance o! Di"ectin: &'(. %t initiates action. &)(.%t integrates employees efforts.
&*(%t is the means of motivation. &+(%t facilitates implementing changes.
&,(%t creates $alance in the organi"ation.
Ele#ents o! Di"ectin: &'(Supervision &)(Communication &*(!eadership
&+(Motivation
Concept of Supervision: Supervision refers to monitoring the progress of wor- of ones
su$ordinates and guiding them properly.
$unctions o! a %upe"&iso":&'(acilitates control &)(.ptimum utili"ation of
resources&*(Maintenance of discipline &+(eed$ac- &,(%mproves communication
&/(%mproves motivation
Motivation- Moti&ation process of stimulating people to accomplish desired goals. %t
depends up on satisfying the needs of people.
Maslo'(s Hie"a"chy o! Nee)s: - 0ccording to Maslow, man does every wor- to satisfy
his need. 0 man has various needs and their order can $e determined. 1he needs of a
human $eing serve as a motivation for him. .n the $asis of priority human needs can
$e divided into five parts &i( 2hysiological needs, &ii( Safety needs, &iii(.0ffiliation or
social needs, &iv( Esteem needs and &v( Self-actuali"ation needs.
$inancial o" Moneta"y Incenti&es: inancial incentives are those incentives which
are evaluated in terms of money. 1hese are helpful to satisfy 2hysiological and Safety
3eeds. %t includes the following &i( 2ay and allowances, &ii( 2roductivity-lin-ed wage
%ncentives, &iii( 4onus, &iv( 2rofit sharing, &v( Co-partnership &iv( Suggestions, &vi(
5etirement $enefits, &vii( 2er6uisites.
Non-!inancial o" Non-#oneta"y Incenti&es: 3on-financial incentives are not directly
related with money. 1hese incentives help in the satisfaction of top hierarchy needs
li-e social, esteem and self-actuali"ation. %t includes the following &i(.Status &ii(
.rgani"ational climate &iii( Career advancement opportunity &iv( 7o$ enrichment &v(
Employee recognition programmes &vi( 7o$ security &vii( Employee participation &viii(
Employee empowerment.
Meanin o! *ea)e"ship : %t refers to influence others in a manner to do what the
leaders wants them to do.
*ea)e"ship %tyles:
I+ Autoc"atic *ea)e"ship %tyle:-
&a(.Meaning: %t refers to that leadership style in which the leader tends to run the show all $y
him-self.
&$(.Characteristics: &i( Centrali"ed 0uthority, &ii( Single 8man Decision, &iii( 9rong 4elief
5egarding Employee, &iv( .nly Downward Communications.
&c(. 0dvantages: &i( :uic- and Clear Decisions, &ii( Satisfactory 9or-, &iii( 3ecessary for !ess
Educated Employees.
&d(.Disadvantages: &i( !ac- of Motivation, &ii( 0gitation $y Employees, &iii( 2ossi$ility of
2artiality.
II+ De#oc"atic *ea)e"ship %tyle :-
&a(. Meaning: %t refers to that leadership style in which the leader consult with his su$
ordinates $efore ma-ing any final decisions.
&$(.Characteristics: -&i(Cooperative 5elations,&ii(4elief in Employees, &iii( .pen
Communication.
&c (.0dvantages : &i( ;igh Morale, &ii(Creations of More Efficiency and 2roductivity, &iii(
0vaila$ility of Sufficient 1ime for Constructive 9or-.
&d(.Disadvantages: &i( 5e6uirement of Educated Su$ordinates, &ii( Delay in Decisions, &iii(!ac-
of 5esponsi$ility in Managers.
III+ *aisse,-!ai"e o" $"ee-"ein *ea)e"ship %tyle: -
&a(. Meaning : %t refers to that leadership style in which the leader gives his su$ ordinates
complete freedom to ma-e decisions.
&$(Characteristics &i(ull faith in su$ordinates, &ii( %ndependent Decision-ma-ing system,&iii(
Decentralisation of 0uthority &iv(Self-Directed Supervisory and Controlled.
&c(. 0dvantages.&i(Development of Self-confidence in Su$ ordinates, &ii( ;igh-level
Motivation,&iii(;elpful in Development and E<tension of the Enterprise.
&d(. Disadvantages.&i(.Difficulty in Cooperation, &ii(!ac- of %mportance of Managerial 2ost, &iii(
Suita$le only for ;ighly Educated Employees.
Co##unication: Communication refers to process of e<change of ideas $etween or among
persons and creates understanding. Communication process involves the elements of source,
encoding, channel, receiver, decoding and feed$ac-.
$o"#al Co##unications refers to all official communications in the form of orders, memos,
appeal, notes , circular, agenda, minutes etc.
In!o"#al Co##unications are usually in the form of rumours, whispers etc. 1hey are
unofficial, spontaneous, unrecorded, spread very fast and usually distorted.
-a""ie"s may e<ist for effective communications. Some of these $arriers include-semantic
$arriers, organi"ational $arriers, language $arriers, transmission $arriers, psychological
$arriers and personal $arriers.
Manae" should ta-e appropriate measures to overcome these $arriers and promote
effective communication in the organi"ation such as
I#p"o&in co##unication e!!ecti&eness:
i. Clarify the ideas $efore communication ii. Communicate according to the needs of receiver.
iii. Consult others $efore communicating iv. 4e aware of language v. Convey things of help
and value to listeners vi. Ensure proper feed$ac- vii. Communicate for present as well as
future viii. ollow up communications and i<. 4e a good listener.
KE. CONCEPT /0E%TION% 1ITH AN%1ER%
/23 1hat is #eant 4y Di"ectin5 E6plain the i#po"tance o! )i"ectin5 7M
0ns: Directing is telling people what to do and seeing that they do it to the $est of their a$ility.
%t includes ma-ing assignment, e<plaining procedures, seeing their mista-es are corrected,
providing on the =o$ instructions and issuing orders.
I#po"tance o! Di"ectin: -
'. %t initiates action
) %t integrates employees efforts
*. %t is the means of motivation
+. %t facilitates implementing changes.
,. %t creates $alance in the organi"ation
/83 Mention the ele#ents o! )i"ectin5 2M
0ns: '( supervision )( motivation *( leadership +( communication
/93 E6plain ho' )i"ectin is a pe"&asi&e !unction o! #anae#ent 2M
0ns: Directing is a pervasive function as every manager from top e<ecutive to superior
performs it.
/:3+;Di"ectin is the least i#po"tant !unction o! #anae#ent+( Do you a"ee 'ith this
state#ent5 Gi&e any t'o "easons in suppo"t o! you" ans'e"+ : M
0: 3o, % dont agree with this statement.
%mportance of direction: Direction may $e regarded as the heart of the management process.
%t is e<plained under the following parts:
a(.%nitiates action: 0ll organi"ational activates are initiated through direction.
$(.%ntegrates employees efforts: 0t all levels of management the su$ordinates under the
managers.
Managers integrate the wor- of su$ordinates.
c(.Means of motivation : Directing helps in motivating employees towards organi"ational
goals
/<3+=The post o! supe"&iso" shoul) 4e a4olishe) in the hie"a"chy o! #anae"s>+ Do you
a"ee5 Gi&e any th"ee "easons in suppo"t o! you" ans'e"+ 7M
0(.3o, % dont agree, $ecause a supervisor performs the following functions to achieve
organi"ation goals.
unctions of the supervisor:
a(.2lanning the wor-. 1he supervisor has to determine wor- schedule for every =o$.
$(.%ssuing orders: Supervisor issues orders to the wor-ers for achieving coordination in his
wor-.
c(.2roviding guidance and leader ship: 1he supervisor leads the wor-ers of his department.
d(.E<plains the policies and programmes of the organi"ation to his su$ ordinates and provide
guidance
e(.Ma-e necessary arrangement for supply of materials and ensure they are efficiently
utili"ed.
f(. Deviations from the target if any are to $e rectified at the earliest.
g(. 1o help the personnel departments in recruitment and selection of wor-ers.
/73+1hat is #eant 4y ;Estee# nee)s( an) ;%el!-actuali,ation nee)s( in "elation to
#oti&ation o! the e#ployees5 :M
0: i. Esteem 3eeds: these needs are needs for self esteem and need for other esteem .or
E<ample: Self-respect, self-confidence etc.
ii. Self-actuali"ation 3eeds: 1his is the needs to $e what one is capa$le of $ecoming and
includes needs for optimal development.
/73+It is th"ouh #oti&ation that #anae"s can inspi"e thei" su4o")inates to i&e thei"
4est to the o"anisation(+ In the liht o! this state#ent? e6plain? in 4"ie!? the i#po"tance
o! #oti&ation+ <@7M
0: %mportance of motivation:
i. Motivation sets in motion the action of people: Motivation $uilds the will to wor- among
employees and puts them into action.
ii. Motivation includes the efficiency of wor- performance: 2erformance of employees
dependence not only on individual a$ilities $ut also on his willingness.
iii. Motivation ensures achievement of organi"ational goals: %f employees are not motivated,
no purpose can $e served $y planning organi"ing and staffing.
iv. Motivation creates friendly relationships: Motivation creates friendly and supportive
relationships $etween employer and employees.
> .Motivation leads to sta$ility in the employees: Motivation helps in reducing a$senteeism
and turnover.
vi. Motivation helps to change negative ? indifferent attitudes of an employee
/A3+=All #anae"s a"e lea)e"s? 4ut all lea)e"s a"e not #anae"s+> Do you a"ee 'ith
this state#ent5 Gi&e any th"ee "easons in suppo"t o! you" ans'e"+ 9@: M
0: @es, % agree with this statement.
Difference $etween leadership and management :
-asis *ea)e"ship Manae#ent
.rigin !eadership originates out of
individual influence
Management originates out
of official power and rights.
ormal 5ights 0 leader has no formal rights 0 manager has certain
formal rights
ollower A
su$ordinates
0 leader has followers 0 manager has
su$ordinates
/B3 E6plain the &a"ious lea)e"ship styles5 7M
0ns(:0utocratic leadership style: 1his style is also -nown as leader centered style. 1he leader
-eeps all the authority and employees have to perform the wor- e<actly as per his order. ;e
does not decentrali"es his authority. 1he responsi$ility of the success or the failure of the
management remains with the manager.
Democratic leadership: 1his style is also -nown as group centered leadership style.
Managerial decisions are not ta-en $y the manager in consultation with employees. 1his
leadership style is $ased on decentrali"ation. Managers respect the suggestions made $y his
su$ ordinates.
!aisse"-faire leadership style: this style as leadership is also -nown as free $rain leadership or
individual centered style. 1he manger ta-es little interest in managerial functions and the su$
ordinates are left on their own. Manager e<plain over all o$=ectives# help su$- ordinates in
determining their own o$=ectives. 1hey provide resources. 1hey also advise the employees.
/2C3 Mention the cha"acte"istics o! autoc"atic lea)e"ship style+ 9M
0ns(.'.Centrali"ed authority ).Single man decisions *.9rong $elief regarding employees
+..nly downward communication.
/223+ E6plain th"ee a)&antaes an) th"ee )isa)&antaes o! autoc"atic lea)e"ship style+
0ns(.0dvantages: '.6uic- and clear decisions ).Satisfactory wor- *.3ecessary for less
educated employees
Disadvantages: '.lac- of motivation ).0gitation $y employees *.2ossi$ilities of partiality. 7M
/283+ E6plain th"ee a)&antaes an) th"ee )isa)&antaes o! )e#oc"atic lea)e"ship+ 7M
'( 0ns: 0dvantages:'.Democratic leadership style advantages,).Morale,*.Creation of
more efficiency and productiv$ity,+.0vaila$ility of sufficient time for constructive
wor-
)( Disadvantages:'.5e6uirement of educated su$ ordinates ).Delay in decisions
*.!ac- of responsi$ility and managers
/293+ Mention !eatu"es o! )e#oc"atic lea)e"ship style5 9M
0ns: '( co operative relations )(.5elief in employees *(..pen communication
/2:3+ Mention the cha"acte"istics o! laisse,-!ai"e lea)e"ship style 9M
0ns: ull faith in su$- ordinates '(.%ndependent decision ma-ing system )(.Decentrali"ation
of authority
*(.Self directed
/2<3+ Mention th"ee a)&antaes an) th"ee )isa)&antaes o! laisse,-!ai"e 7M
0ns: -'.Development of self confidence in su$ ordinates, ).;igh level motivation, *.;elp in
development of e<tension and enterprise
Disadvantages: '.Difficulty in co operation, ).!ac- of importance of managerial post,
*.Suita$le only for highly educated employees
/273+ =Manae"ial !unctions cannot 4e ca""ie) out 'ithout an e!!icient syste# o!
co##unication+> Do you a"ee5 Gi&e any th"ee "easons in suppo"t o! you" ans'e"+:M
0: @es, % agree with this statement.
Communication is important $ecause of the following reasons.
i. Communication facilitates planning in a num$er of ways
ii. Communication helps management in arriving at vital decisions
iii .Communication is necessary in creating unity of action of action
/273+ Mention one 4a""ie" to e!!ecti&e co##unication+ 2M
0: 2oor listening s-ills of people.
/2A3+ Gi&e any one #easu"e to i#p"o&e co##unication+ 2M
0: Communicate according to the needs of receiver.
/2B3+ 1hat )o you #ean 4y "ape&ine5 E6plain t'o types o! "ape&ine alon 'ith
)ia"a#+
0: Brapevine: 1he networ- or pathway of informal communication is -nown as grade point
communication.
1wo types of grapevine communication
Bossip Single Strand
/8C3+ E6plain any th"ee #easu"es to o&e"co#e the 4a""ie"s to i#p"o&e
co##unications e!!ecti&eness+
0na: '.Clarify the areas $efore communication: 4efore communicating to employees a
manager should ma-e an analysis of the su$=ect matter.
). Consult others $efore communication: 0 manager should encourage participation of
su$ordinates which will ensure their support and cooperation.
*. Communicate according to the needs of receiver: 1he manager should ma-e ad=ustments
according to the needs of the receiver.
/0E%TION% 1ITH DI$$ERENT DI$$IC0*T. *EDE*%
23+It is conce"ne) 'ith inst"uctin ui)in an) inspi"in people in the o"ani,ation to
achie&e its o4Eecti&es+ Na#e it+ 2 M
0: Directing
83 E&e"y #anae" !"o# top e6ecuti&e to supe"io" pe"!o"#s the !unction o!
)i"ectin+ 1hich cha"acte"istic o! )i"ectin is "e!e""e) he"e5 2M
0( Directing ta-es place every level of management.
93 It #eans o&e"seein the su4o")inates at 'o"F+ 1hich ele#ent o! )i"ectin is
"e!e""e) to5 2M
0: Supervision.
:3 %upe"&iso" acts as a linF 4et'een 'o"Fe"s an) #anae#ent+ Ho'5 2M
0: Supervisor conveys management ideas to the wor-ers on one hand and wor-ers pro$lems
to the management on the other.
<3 It "e!e"s to the 'ay in 'hich u"es? )"i&es? )esi"es? aspi"ations? st"i&ins o" nee)s
)i"ect cont"ol an) e6plain the 4eha&io" o! hu#an 4eins+ 1hich ele#ent o! )i"ectin is
in)icate) he"e5 2M
0: Motivation.
73 Moti&ation can 4e eithe" positi&e o" neati&e+ Gi&e t'o e6a#ples o! neati&e
#oti&ation+ 2M
0( a( Stopping increments $( 1reating
73+1hich nee) in the hie"a"chy theo"y o! #oti&ation "e!e"s to a!!ection? acceptance an)
!"ien)ship5 2M
0: 4elonging needs
A3 It is an incenti&e o!!e"e) o&e" an) a4o&e the 'aes@sala"y to the e#ployees+
Na#e the type o! !inancial incenti&e "e!e""e) he"e+ 2M
0( 4onus
B3 Na#e the incenti&e 'hich "e!e"s to ;i&e #o"e autono#y an) po'e"s to
su4o")inates( an) ho' a"e people a!!ecte) 4y this incenti&es5 2M
0( Employee Empowerment : Due to this incentive people start feeling that their =o$s are
important and they contri$ute positively to use their s-ills and talent in the =o$ performance.
2C3 It is )e!ine) as a p"ocess o! in!luencin othe" people to 'o"F 'illinly !o" "oup
o4Eecti&es+ Mention this ele#ent o! )i"ectin+ 2 M
0( !eadership
223 It is p"ocess 4y 'hich people c"eate an) sha"e in!o"#ation 'ith one anothe" in
o")e" to "each co##on un)e"stan)in+ 1hich ele#ent o! )i"ectin is "e!e""e) he"e5
2M
0( Communication.
283 1hich ele#ent in co##unication p"ocess "elates to the p"ocess o! con&e"tin
enco)e) sy#4ols o! the sen)e"5 2M
0( Decoding
293 In 'hich Fin) o! co##unication net'o"F? a su4o")inate is allo'e) to
co##unicate 'hich his i##e)iate supe"io" as 'ell as his supe"io"(s supe"io"5 2M
0( %nverted >.
2:3 A#it an) MiFFi a"e 'o"Fin in the sa#e o"ani,ation 4ut )i!!e"ent )epa"t#ents+
One )ay at lunch ti#e MiFFi in!o"#e) A#it that )ue to co#pute"i,ation #any people
a"e oin to 4e "et"enche) soon !"o# the o"ani,ation+ :M
0( %t is an e<ample of informal communication.
*i#itations o! in!o"#al co##unication:
Messages tend to $e distorted.
%t often carries rumors.
%t is unsystematic.
2<3 The"e a"e so#e 4a""ie"s in co##unication 'hich a"e conce"ne) 'ith the state
o! #in) o! 4oth the sen)e" an) the "ecei&e"+ %tate any th"ee such 4a""ie"s+ 9@ : M
0( %t refers to physiological $arriers: i. premature evaluation ii. !oss $y transmission and
poor retention. %ii .!ac- of attention.
Você também pode gostar
- Habits Loop PDFDocumento37 páginasHabits Loop PDFGhassan Qutob94% (34)
- Leadership Management Development StrategyDocumento17 páginasLeadership Management Development Strategybilo1984100% (1)
- Organizational BehaviourDocumento9 páginasOrganizational BehaviourAfiqah Z AlhusayniAinda não há avaliações
- The Ethical Issues Arising From The Relationship Between Police and MediaDocumento76 páginasThe Ethical Issues Arising From The Relationship Between Police and Mediaj_townendAinda não há avaliações
- Leadership in Professional PracticeDocumento12 páginasLeadership in Professional PracticeSamuel Ks TeeAinda não há avaliações
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) - SEM IV-GTUDocumento115 páginasSupply Chain Management (SCM) - SEM IV-GTUkeyur100% (1)
- Organizational BehaviorDocumento17 páginasOrganizational BehaviorAnonymous olkUZ9Ainda não há avaliações
- Human Resource Management - AssignmentDocumento16 páginasHuman Resource Management - AssignmentLazy FrogAinda não há avaliações
- Guide to Ace Your Job InterviewDocumento7 páginasGuide to Ace Your Job InterviewAisha ShahabAinda não há avaliações
- Sap PSDocumento3 páginasSap PSSaif Ali MominAinda não há avaliações
- Performance Appraisal Sahara GroupDocumento82 páginasPerformance Appraisal Sahara GroupPratishtha Nirmal100% (1)
- Management TheoriesDocumento7 páginasManagement TheoriesMohamedMoideenNagoorMeeran100% (1)
- Summary of An Everyone Culture: by Robert Kegan and Lisa Lahey, with Matthew Miller, Andy Fleming, Deborah Helsing | Includes AnalysisNo EverandSummary of An Everyone Culture: by Robert Kegan and Lisa Lahey, with Matthew Miller, Andy Fleming, Deborah Helsing | Includes AnalysisAinda não há avaliações
- Company Management…Policies, Procedures, PracticesNo EverandCompany Management…Policies, Procedures, PracticesAinda não há avaliações
- PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT TG v9 April 28, 2016 PDFDocumento174 páginasPERSONAL DEVELOPMENT TG v9 April 28, 2016 PDFHerxhie Branzuela Magallanes100% (4)
- Employee MotivationDocumento84 páginasEmployee MotivationVenkata Siva ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- TQM AssignmentDocumento9 páginasTQM AssignmentDileepHaraniAinda não há avaliações
- 01-Nature of Management Concept of Management:: Grade-XII Business Organization & Office ManagementDocumento6 páginas01-Nature of Management Concept of Management:: Grade-XII Business Organization & Office ManagementHina KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Organization Development: Carl TaylorDocumento85 páginasOrganization Development: Carl TaylordodverdaaaAinda não há avaliações
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS OBJECTIVES CHALLENGESDocumento71 páginasHUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS OBJECTIVES CHALLENGESviper9930950% (2)
- HRM in Insurance (100 Marks Project)Documento58 páginasHRM in Insurance (100 Marks Project)Gristy Grana100% (6)
- Contribution of F.W. TaylorDocumento15 páginasContribution of F.W. TaylorflaksherAinda não há avaliações
- MGT-502 Organizational Behavior (Lecture 01-15) 2nd Semester-1Documento16 páginasMGT-502 Organizational Behavior (Lecture 01-15) 2nd Semester-1Mmonie MotseleAinda não há avaliações
- Viva QuestionsDocumento41 páginasViva Questionslin_guardianangelAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Management NotesDocumento188 páginasEngineering Management NotesTesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Organisation & ManagementDocumento7 páginasOrganisation & ManagementEletroJivAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter - 7 Directing: Motivation-Motivation Process of Stimulating People To Accomplish Desired Goals. ItDocumento9 páginasChapter - 7 Directing: Motivation-Motivation Process of Stimulating People To Accomplish Desired Goals. ItManan SuchakAinda não há avaliações
- Human Resources Development (HRD)Documento12 páginasHuman Resources Development (HRD)Nagendra SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Question-1 Describe The Concept of Vision and Mission in An Organisation. AnswerDocumento9 páginasQuestion-1 Describe The Concept of Vision and Mission in An Organisation. AnswerHiren RaichadaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - III Eng EconomicsDocumento20 páginasUnit - III Eng Economicsasit619Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12 - Managing HumanDocumento51 páginasChapter 12 - Managing Humanpolkadots939100% (5)
- Absent or Absence (Scheduled Time Off)Documento9 páginasAbsent or Absence (Scheduled Time Off)balki123Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 ConceputalDocumento16 páginasUnit 5 ConceputalGangadhara RaoAinda não há avaliações
- BHASIN CLASSES 94531219: Directing MeaningDocumento3 páginasBHASIN CLASSES 94531219: Directing MeaningSoniya Omir VijanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - I: Cmrit Redefining QualityDocumento236 páginasUnit - I: Cmrit Redefining QualityRahul RockyAinda não há avaliações
- Management Overview, Functions, Levels, EvolutionDocumento77 páginasManagement Overview, Functions, Levels, EvolutionMano PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Why Study ManagementDocumento6 páginasWhy Study Managementmazhar abbas GhoriAinda não há avaliações
- Performance AppraisalDocumento85 páginasPerformance AppraisalSakhamuri Ram'sAinda não há avaliações
- Management NotesDocumento90 páginasManagement NotesAbhishek SinghAinda não há avaliações
- POM Short QuestionsDocumento23 páginasPOM Short QuestionsRamalingam ChandrasekharanAinda não há avaliações
- Management Functions OverviewDocumento35 páginasManagement Functions OverviewRachen AnneAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1Documento27 páginasUnit 1realguy556789Ainda não há avaliações
- Principles of Management Question PaperDocumento21 páginasPrinciples of Management Question PaperIcfai Distance Learning DelhiAinda não há avaliações
- Organization Type:: The Two Types of Organizations AreDocumento8 páginasOrganization Type:: The Two Types of Organizations AreShariful HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Management Unit 1Documento28 páginasManagement Unit 1Swastik GroverAinda não há avaliações
- Concept, Nature, Scope and Functions of ManagementDocumento8 páginasConcept, Nature, Scope and Functions of Managementrohan_jangid889% (18)
- Swetha R, Dept of Cse, Citncpage 1Documento15 páginasSwetha R, Dept of Cse, Citncpage 1RamanAinda não há avaliações
- FINAL Question bank-POMDocumento24 páginasFINAL Question bank-POMAashu RajputAinda não há avaliações
- Human Resources Development (HRD)Documento5 páginasHuman Resources Development (HRD)Brijesh ShuklaAinda não há avaliações
- MG2351 POM Unit 1 Lecture NotesDocumento25 páginasMG2351 POM Unit 1 Lecture Notesrkar1304100% (2)
- RefaceDocumento17 páginasRefaceSajib JahanAinda não há avaliações
- Pom 1 Part 2Documento13 páginasPom 1 Part 2Sachin SahooAinda não há avaliações
- D E F I N I T I On: 1. The Top ManagementDocumento7 páginasD E F I N I T I On: 1. The Top ManagementnkchandruAinda não há avaliações
- Leadership inDocumento48 páginasLeadership inVictor SavaAinda não há avaliações
- Management & Its FunctionDocumento38 páginasManagement & Its FunctionMd. Zahidul IslamAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor's New ClothesDocumento11 páginasThe Emperor's New ClothesSaleh RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Compensation, Integration, and Separation of Human Resources To The End ThatDocumento12 páginasCompensation, Integration, and Separation of Human Resources To The End Thatcynicallol100% (1)
- Principles of ManagementDocumento17 páginasPrinciples of ManagementLenny Emelda100% (1)
- Bussiness Studies PersonalDocumento4 páginasBussiness Studies PersonalAnjan anjuAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - 1, Assignment-1 KapilDocumento10 páginasUnit - 1, Assignment-1 KapilSandeep KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Nme-Managemet ConceptsDocumento61 páginasNme-Managemet ConceptsabiramanAinda não há avaliações
- How Do You Define Management?/ How Would You Define Management? October-2010, November-2007Documento117 páginasHow Do You Define Management?/ How Would You Define Management? October-2010, November-2007Nahid HossainAinda não há avaliações
- SBI Report Banking Sector Report On HRDocumento66 páginasSBI Report Banking Sector Report On HRAditya ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- MB0038 - Understanding Organizational Vision, Behavior and Emotional IntelligenceDocumento8 páginasMB0038 - Understanding Organizational Vision, Behavior and Emotional IntelligencevinodniralaAinda não há avaliações
- The Field of Management: 1.1. About Management and ManagersDocumento6 páginasThe Field of Management: 1.1. About Management and ManagersVlad IftodeAinda não há avaliações
- Ba4102 Management ConceptDocumento56 páginasBa4102 Management ConceptrinshadpppmAinda não há avaliações
- OB2Documento15 páginasOB2kashfi35Ainda não há avaliações
- 12 Business Studies Impq CH08 ControllingDocumento9 páginas12 Business Studies Impq CH08 ControllingdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Police Injustice Responding Together To Chaengnge The StoryDocumento4 páginasPolice Injustice Responding Together To Chaengnge The StorydeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Article Speech Writing PDFDocumento14 páginasArticle Speech Writing PDFdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Article Speech Writing PDFDocumento14 páginasArticle Speech Writing PDFdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Pages Froebom Police StoriesDocumento17 páginasPages Froebom Police StoriesdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Eng20110310 100610 Media Backgrounder ANPDocumento1 páginaEng20110310 100610 Media Backgrounder ANPdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Areportnnual Report 2009Documento67 páginasAreportnnual Report 2009deepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Business Studies Impq CH09 Financial ManagementDocumento13 páginas12 Business Studies Impq CH09 Financial ManagementdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- English MattersDocumento1 páginaEnglish MattersdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Eng080221 LawSocietyReviewPolicingDocumento44 páginasEng080221 LawSocietyReviewPolicingdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- 38432reading 4Documento28 páginas38432reading 4deepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Police Injustice Responding Together To Chaengnge The StoryDocumento4 páginasPolice Injustice Responding Together To Chaengnge The StorydeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- 170 Eng 10Documento224 páginas170 Eng 10deepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- QLD Legislative Assembly Standing RulesDocumento130 páginasQLD Legislative Assembly Standing RulesdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Police On Police ShootingsDocumento83 páginasPolice On Police ShootingsJason SmathersAinda não há avaliações
- Nucenglear DisarmamentCF909Documento20 páginasNucenglear DisarmamentCF909deepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Commonlit Reading LiteratureDocumento77 páginasCommonlit Reading LiteraturedeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Aswrmilan Document Jan10Documento5 páginasAswrmilan Document Jan10deepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- NWMP Engfull PackageDocumento38 páginasNWMP Engfull Packagedeepashaji100% (1)
- Readingporqn01 - 2586Documento1 páginaReadingporqn01 - 2586deepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Disreadingarmament Yearbook-Other Publications Fact SheetDocumento2 páginasDisreadingarmament Yearbook-Other Publications Fact SheetdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Engl 07Documento17 páginasEngl 07deepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Readingporqn01 - 2586Documento1 páginaReadingporqn01 - 2586deepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Reading PM1781Documento16 páginasReading PM1781deepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Thesis 07Documento82 páginasThesis 07Dhanyaa NairAinda não há avaliações
- Parliamentary Procedure: Simplified Handbook ofDocumento23 páginasParliamentary Procedure: Simplified Handbook ofdeepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- Engl 07Documento17 páginasEngl 07deepashajiAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Hmef5023 T1Documento43 páginas05 Hmef5023 T1Najwa NajihahAinda não há avaliações
- MBO Is One of The Rational School of Management's Successful ProductsDocumento7 páginasMBO Is One of The Rational School of Management's Successful Productsdinesh07_1984Ainda não há avaliações
- ACCERT CDO CHAPTER Vision and Core ProgramsDocumento2 páginasACCERT CDO CHAPTER Vision and Core ProgramsMyla Barbs100% (1)
- Kaizen Approach Best for Continuous ImprovementDocumento2 páginasKaizen Approach Best for Continuous Improvementstarleonikko dinulosAinda não há avaliações
- Session 13 LD11 Authentic LeadershipDocumento22 páginasSession 13 LD11 Authentic LeadershiprajatvarnaAinda não há avaliações
- The Relationship Between Readiness To Change and WDocumento11 páginasThe Relationship Between Readiness To Change and WAhmad RabayaAinda não há avaliações
- Ch06 The Production ProcessDocumento75 páginasCh06 The Production ProcessTommyutomowijaya0% (1)
- Buffalo Public Schools Organizational ChartDocumento16 páginasBuffalo Public Schools Organizational ChartSandra TanAinda não há avaliações
- Business Logistics/Supply Chain-A Vital SubjectDocumento32 páginasBusiness Logistics/Supply Chain-A Vital Subjectmamun gaziAinda não há avaliações
- Ethnocentrism The Hidden Adversary of Effective Global LeadershipDocumento5 páginasEthnocentrism The Hidden Adversary of Effective Global LeadershipKehinde EstherAinda não há avaliações
- ADEC - Al Seddeq Private School 2016-2017Documento19 páginasADEC - Al Seddeq Private School 2016-2017Edarabia.comAinda não há avaliações
- Border Force Officer Advanced Apprenticeship National Candidate Pack 04-01-2016Documento38 páginasBorder Force Officer Advanced Apprenticeship National Candidate Pack 04-01-2016Bogasi Q.Ainda não há avaliações
- Writing References for StudentsDocumento4 páginasWriting References for StudentsRyan OktafiandiAinda não há avaliações
- MBA School ComparisonDocumento1 páginaMBA School ComparisonSAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristics of A LeaderDocumento2 páginasCharacteristics of A LeaderMariel Crista Celda MaravillosaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter5 Contingency Leardership TheoryDocumento25 páginasChapter5 Contingency Leardership TheoryUlyviatrisnaAinda não há avaliações
- SummaryDocumento14 páginasSummaryRejwan Ahmed ShovonAinda não há avaliações
- The War On Drugs in The PhilippinesDocumento18 páginasThe War On Drugs in The PhilippinesRONEL B. VALDEZAinda não há avaliações
- Leadership, culture and performanceDocumento4 páginasLeadership, culture and performanceyusjayusmanAinda não há avaliações
- Factors Affecting IT ImplementationDocumento132 páginasFactors Affecting IT ImplementationImran Mehmood100% (2)
- Presentation On Employee Turnover Rate-BRMDocumento13 páginasPresentation On Employee Turnover Rate-BRMMir Hossain EkramAinda não há avaliações
- Zanzibar CommunicationDocumento5 páginasZanzibar CommunicationJackson M AudifaceAinda não há avaliações
- 47 Project Processes Input - Output - SummaryDocumento10 páginas47 Project Processes Input - Output - Summaryjimbox88Ainda não há avaliações
- 人力资源管理 英文版 - 14287428Documento663 páginas人力资源管理 英文版 - 14287428chilamelonAinda não há avaliações