Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ice Do
Enviado por
Brett HeadDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ice Do
Enviado por
Brett HeadDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
A.
Use your engineering knowledge and understanding to make the most of existing and
emerging technology
A1 Broaden and deepen your engineer knowledge (B)
For Example
Identify limits of own personal knowledge and skills. Acquisition of engineering
knowledge in chosen field of operations. Knowledge of engineering principles. Codes,
standards and specifications. Technological developments in the construction industry.
B. Apply appropriate theoretical and practical methods to the analysis and solution of
engineering problems
B1 Identify engineering* problems and define possible solutions (B)
For Example
Client/user needs. Feasibility. Constraints and opportunities. Links to codes, standards,
specifications and contract conditions. Application of engineering principles. Specific
solutions. Departures from established practice, where appropriate.
B2 Conduct appropriate research and analysis relating to engineering* problems (B)
For Example
Apply and know the limitations of established best practice as defined by codes,
standards and specifications. Links to contract conditions. Feasibility assessments,
surveys and costing. Risk analysis. Presentation of solutions and secure acceptance.
Consider Health, Safety and Welfare, quality, cost, time, buildability, sustainability.
Value engineering. Whole life costing.
B3 Implement solutions to problems and evaluate their effectiveness (B)
For Example
Health, Safety and Welfare, quality, cost, time, buildability, risk assessment. Link to
codes, standards, specifications and contract conditions. Monitoring outputs and results.
C. Provide technical and commercial management
C1 Plan for effective project implementation (B)
For Example
Planning and resourcing. Programming. Method statements. Contractual obligations.
Tenders. Fees. Information and administration systems. Instructions. Records. Project
risk and opportunities. A project can be whatever you are responsible for eg a design,
some research work, a feasibility study, a site-based project, etc.
C2 Control budgets, tasks, people and resources (B)
For Example
Management systems. Team working. Competences. Co-ordination of project activities:
programme, quality, cost, labour or staff, other contractors, suppliers, supply chains,
plant/equipment, materials. Monitoring. Payment processes. Project funding and
financing. Influence work teams.
C3 Develop people to meet changing technical and managerial needs (E)
For Example
Objectives and work plans. Lead by example. Support other individuals training and
development.
C4 Bring about continuous improvement through quality management (B)
For Example
Quality plans and systems. Maintain quality standards. Quality records. Recommend
improvements. Contribute to the improvement of quality systems.
C5 Manage contractual issues (B)
For Example
Forms of contract. Responsibility of parties to a contract. Procurement methods. Forms
of payment. Contractual records. Insurances. Instructions and variations.
D. Demonstrate effective interpersonal skills
D1 Communicate with others at all levels (B)
For Example
Reports. Letters. Drawings. Presentations. Exchange of information. Advice to technical
and non-technical colleagues. Contribute to meetings. Consider the views of others.
Consultation. Knowledge and use of IT. Present your case and defend it. Conduct
discussions.
D2 Demonstrate personal and social skills (B)
For Example
Awareness of the needs and concerns of others. Develop good working relationships to
achieve collective goals. Equal opportunities and diversity. Set an example for others to
follow. Identify, and agree collective goals.
E. Demonstrate a personal commitment to professional standards, recognizing obligations to
society, the profession and the environment effective interpersonal skills
E1 Comply with relevant codes of conduct (E)
For Example
Purpose and history of ICE. Comply with ICE Codes of Conduct. Current developments
and issues affecting the construction industry. Ethical and professional behavior.
Promotion of the construction industry.
E2 Manage and apply safe systems of work (B)
For Example
Identify and take responsibility for own obligations for Health, Safety and Welfare issues.
Implement Health, Safety and Welfare systems. Current Health, Safety and Welfare
codes and legislation. CDM Regulations. Risk assessments. Method statements.
Recommend improvements. Contribute to the development and improvement of
systems. Understand compliance costs. Have detailed knowledge of the hazards
applicable to your field of work. Apply risk management techniques appropriate to your
field of work. Safety briefings, inductions. Prepare and review risk assessments and
method statements. Proactive approach to Health, Safety and Welfare practice and
management.
E3 Contribute to sustainable development through engineering* activities (E)
For Example
Comply with legislation and codes. Environmental impact. Environmental management
(interaction between design, construction and operation). Social and economic issues in
implementing solutions. Project whole life cycles. Knowledge of sustainable
development tools.
E4 Manage your own continuing professional development, and assist others (E)
For Example
Review of your own development needs. Development Action Plans. Record CPD
activities (Personal Development Record). Evaluate CPD outcomes. Company appraisals.
See ICE 3006A.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Abusing Science The Case Against Creationism by Kitcher, PhilipDocumento225 páginasAbusing Science The Case Against Creationism by Kitcher, PhilipIván Antony Toribio LeónAinda não há avaliações
- SSR Assignment 2Documento9 páginasSSR Assignment 2lilzenithAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson PLan in Teaching ProfessionDocumento5 páginasLesson PLan in Teaching Professionmarjorie bondoc67% (3)
- Appendix 9.1 Sads 15 Output For Ground Floor R.C. BeamsDocumento1 páginaAppendix 9.1 Sads 15 Output For Ground Floor R.C. BeamsBrett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- Prestressed Concrete Design To EurocodesDocumento13 páginasPrestressed Concrete Design To EurocodesBrett Head20% (10)
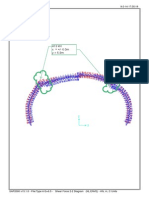
- 413 KN 413 KN X +/-6.0m y 6.9mDocumento1 página413 KN 413 KN X +/-6.0m y 6.9mBrett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- Beyond BIM - What Else? and So What?: Ms. Argoon ChuangDocumento1 páginaBeyond BIM - What Else? and So What?: Ms. Argoon ChuangBrett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- 484 KN 484 KN X +/-6.25m y 6.7mDocumento1 página484 KN 484 KN X +/-6.25m y 6.7mBrett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- Plaxis ParametersDocumento9 páginasPlaxis ParametersBrett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- Shell Element Internal Forces/Stresses Output ConventionDocumento5 páginasShell Element Internal Forces/Stresses Output ConventionBrett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- Ias Symposium On Activated Sludge-Past and Next 100 Years: 26 - 28 August 2014Documento18 páginasIas Symposium On Activated Sludge-Past and Next 100 Years: 26 - 28 August 2014Brett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- 建 造 業 議 會 Construction Industry Council: SCW (Q)Documento2 páginas建 造 業 議 會 Construction Industry Council: SCW (Q)Brett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- Linden 2100 Tower CraneDocumento2 páginasLinden 2100 Tower CraneBrett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Seminar: Date, Assembly Time & Place: Registration & EnquiriesDocumento1 páginaTechnical Seminar: Date, Assembly Time & Place: Registration & EnquiriesBrett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- VehicleDocumento1 páginaVehicleBrett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- Seismic Resistant Structures - 2014Documento5 páginasSeismic Resistant Structures - 2014Brett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- SS WeldingDocumento1 páginaSS WeldingBrett HeadAinda não há avaliações
- 2parents' Involvement and Pupils' Reading ComprehensionDocumento31 páginas2parents' Involvement and Pupils' Reading Comprehensionrodel acupiadoAinda não há avaliações
- Annual Report 2020-21Documento212 páginasAnnual Report 2020-21HarshAinda não há avaliações
- State of L2 Reading SDO Navotas PDFDocumento31 páginasState of L2 Reading SDO Navotas PDFmarco24medurandaAinda não há avaliações
- Outlining Reading Najwa ShihabDocumento3 páginasOutlining Reading Najwa ShihabjustnayangAinda não há avaliações
- ORGANISATIONAL CULTURE - QuestionnaireDocumento7 páginasORGANISATIONAL CULTURE - Questionnairesrenth24Ainda não há avaliações
- Application For GraduationDocumento2 páginasApplication For GraduationmsamrasAinda não há avaliações
- PHOTOMOD Lite Project ContestDocumento1 páginaPHOTOMOD Lite Project ContestgeomongoliaAinda não há avaliações
- 23 Laxamana v. Borlaza RojasDocumento2 páginas23 Laxamana v. Borlaza RojasIñigo Mathay RojasAinda não há avaliações
- SyllabusDocumento41 páginasSyllabusDeewakarsingh AuthelsinghAinda não há avaliações
- Communication PDF DefinitionDocumento2 páginasCommunication PDF DefinitionAaronAinda não há avaliações
- Networking Essentials Release Notes: PurposeDocumento2 páginasNetworking Essentials Release Notes: PurposeGLAinda não há avaliações
- Project 101082749Documento2 páginasProject 101082749muddassir razzaqAinda não há avaliações
- 3-Day Summer School Flyer-IIT BhubaneswarDocumento5 páginas3-Day Summer School Flyer-IIT BhubaneswarHanumantha Rao BAinda não há avaliações
- Recruitment and Selection Policy in NaharDocumento23 páginasRecruitment and Selection Policy in NaharSai PrintersAinda não há avaliações
- ADJECTIVEDocumento4 páginasADJECTIVEJunrey MalonAinda não há avaliações
- Air Force Follow-On Review: Protecting The Force, Lessons From Fort Hood: Preventing Violence, Enhancing Response... Every Airman A WingmanDocumento222 páginasAir Force Follow-On Review: Protecting The Force, Lessons From Fort Hood: Preventing Violence, Enhancing Response... Every Airman A WingmanB. BryantAinda não há avaliações
- A-501 A-502 A-503 A-504 A-505Documento24 páginasA-501 A-502 A-503 A-504 A-505Bhanu ViswanadhAinda não há avaliações
- Consumer BehaviourDocumento5 páginasConsumer BehaviourVedant HingeAinda não há avaliações
- Science 10 Q2 M12 1Documento15 páginasScience 10 Q2 M12 1Bien DivinaflorAinda não há avaliações
- The Usefulness of Reading Comprehension Strategies: Brief Instruction inDocumento8 páginasThe Usefulness of Reading Comprehension Strategies: Brief Instruction inJesús Rosel MartínezAinda não há avaliações
- Ivey MSC Final 2020Documento30 páginasIvey MSC Final 2020Kruttika ShuklaAinda não há avaliações
- From Hearthstone To Headstone Rethinking PDFDocumento11 páginasFrom Hearthstone To Headstone Rethinking PDFMariana ÁlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Mr. Bean in Room 426 Part 1 Suggested Lesson Plan: Warmer: (5-10 Mins)Documento4 páginasMr. Bean in Room 426 Part 1 Suggested Lesson Plan: Warmer: (5-10 Mins)haldanmihaelaAinda não há avaliações
- Standard English - History - LinguisticsDocumento295 páginasStandard English - History - Linguisticsrima93Ainda não há avaliações
- 10 2 Dr. P. I Philosophical Research in Law The PossibilitiesDocumento32 páginas10 2 Dr. P. I Philosophical Research in Law The PossibilitiesShivaraj ItagiAinda não há avaliações
- 06 CHolland, Readingand Identitya Psychoanalytic RevolutionDocumento4 páginas06 CHolland, Readingand Identitya Psychoanalytic RevolutionabiiktkAinda não há avaliações
- The First Term Revision Grade 11Documento5 páginasThe First Term Revision Grade 11Cường NgọcAinda não há avaliações