Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Biology Questions
Enviado por
leti332Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Biology Questions
Enviado por
leti332Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Making sense of it all...
Lecture 1
Is the phospho-myosin protein complex phosphorylated?
What is the difference between phosphorylation and the addition of a inorganic
phosphate?
How many stages of attachment and reattachment does the myosin protein complex
undergo before it returns to its original state?
What is the original state of the myosin protein complex? Bounded to actin filament?
Phosphorylated?
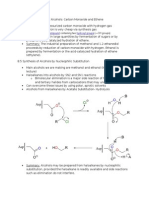
Lecture 1 Summary states that larger particle assemblies composed of two or more molecules held
in close (< 1nm) and association for > 1 microsecond as a molecule complex, e.g, a protein-protein complex
that is called an actin filament or microfilament [Fig. 4.10A, Fig. 36.8]. What does that mean?
What exactly is a particle system?
What is kinetic energy?
What is potential energy?
What is a photon?
What is the total energy of the system? What does it mean/represent?
http://ocw.mit.edu/high-school/biology/chemistry-of-life/organic-molecules-in-organisms/
http://ocw.mit.edu/high-school/biology/chemistry-of-life/organic-molecules-in-
organisms/7_014_spring_2005_biochem1_3.pdf
What is hydrolysis?
Water molecules dissociates into two ions, H+ and OH-, thereby allowing the ions
to react with other molecules in the solution.
Is ATP made of ribose?
Every nucleic acid is comprised of 3 subunits
A sugar (ribose in this case)
A nucleotide (Adenine)
And a phosphate group
What is a free amino acid?
What does it mean to be in a transition state?
What does it mean to be in a ground state?
What is the difference between inorganic phosphate (Pi) and a phosphate group?
What is kinetic energy?
Work need to make an object move
What is potential energy?
Stored energy in a system
What is a photon?
exchange particle for electromagnetic force (ParticleSystems.pdf)
What is mechanical energy?
Sum of the PE + KE of all particles in system
What is electromagnetic energy?
What does it mean to be ionized?
Actively changing an atom or molecule by adding or removing charged particles
What does BDE represent?
What is condensation?
2 molecules come together to make a polymer and water is lost (also known as
dehydration synthesis).
http://www.biotopics.co.uk/as/condensation_and_hydrolysis.html
What is a phosphodiester linkage?
A group of strong covalent bonds between a phosphate group and two 5-carbon
What is an ester bond?
A bond formed by the reaction of an acid and an alcohol.
Is the green regulatory protein part of the myosin?
Particle System
What are the other types of energy representative of (not including KE or PE)?
Lecture 2
What is the equilibrium state?
How do molecules become in the transition state?
Are there molecule collisions happening constantly?
What is a system?
Does phospho-myosin have potential energy?
Should we know the place of smooth muscle involved in piloerection?
How does force generate force?
How do you create a simplier model for work?
How do you know the conditions at which work should be done? Is it just convention to
use 25 degrees celcisus? Why not body temperature (37 degrees celcius)? What about
salt content?
How much of the muscle is added? How do you know that the amount of muscle will be
sufficient to lift the mass of the human hair?
What does negative work mean?
What are myofibrils?
Slide 11 states, Note the alignment of actin filaments and myosin filaments is not as
regular in smooth muscle cells compared to skeletal muscle cells. What does that
mean?
What is the difference between an oligonucleotide and a polynucleotide?
Lecture 3
how do we know that state 1 has potential energy?
go over L304
If there is no ATP present in the myosin (only water present) are the myosin heads
attached to the actin filament?
what keeps the phosphomyosin from returning back to myosin and Pi?
How is the ratio for the reverse reaction the same as the forward reaction? (L310)
Is one mole only equal to 6.02x10^23 molecules only at standard temperature?
Does L322 also represent the distribution of KE in other molecules?
What is the relevance of displacement on slide L324?
What does a negative delta g value mean? KE? PE?
Is the kinetic stability of ATP always ~7days? does it vary on the concentration of ATP?
What is PNP? p-nitrophenol molecule?
What are typical elements that a phosphate group attaches to? proton, carbon, and?
What would a good hydrolysis model look like? Would it include relevant bond changes?
Collisions to demonstrate transition state?
What is the difference between mehcanical energy and electrical energy?
What is chemical potential energy? (L338)
Memorize relevant bond changes
How would you estimate the Kinetic stability of diglycine at 25C in H20? (L342)
Lecture 4
Whats the difference between delta G and delta G zero/prime?
L403 states protein instead of myosin. Are the same results produced for any protein?
Or solely myosin?
What are coupled reactions? What is the purpose of having coupled reactions?
What does endergonic mean? (L405)
What is the purpose of having a prime on the carbons in ribose? (L406)
I dont seem to understand the logic on L407. Shouldnt the ground state have the
highest BDE?
What is the difference between ground state and transition state of reactants?
Adding Pi to protein =phosphorylated protein? Adding terminal phophate group to
protein=phosphorylation as well?
What is the difference between hydrolysis and condensation?
What is affinity? What causes a molecule to have a high affinity for another molecule?
Should we develop a general model for ligands binding to proteins? How would we go
about doing so? (L4A20)
Is myosin ATPase? If so which part acts as the ATPase? The regulatory protein? Why
does it say that in a test tube? Is it not the same in the body?
How is ATP the most involved nucleotide? What about CTP? GTP? TTP? dATP? and so
forth
Go over delta G L4B04
When we are determining the distribution probabilities for delta S do you disregard the
BDE? Is the probability more of a relationship in space?
What makes delta S large? (greater than 1nm?)
How can we determine the proximity of molecules for delta S? What is close enough to
disregard delta S?
How is the delta G with delta H and delta S & T an alternate expression for the delta g
with delta g star? (L4B13)
How does G6P to G1P allow PE to be stored as poly-glucose?
What is the biomolecules referring to on L4B20?
Lecture 5
What is the difference between delta G zero and delta G star?
Go over L5A13. So does the enzyme hold the molecule and then molecules collide into
the suspended molecule?
How is PE stored in a bond?
How is energy absorbed when a bond breaks? (L5A18)
How are slides 5A18 and 5A19 saying the same thing but reverse pictures?
How is the correct orientation of molecules for a reaction not sufficient? need to be in
transition state?
Other questions:
What happens if you decrease the concentration of sodium chloride?
Or add another ionic compounds in a large concentration?
Increase or decrease the temperature?
Add nonpolar or polar substances to the environment?
Resources:
1. http://web.virginia.edu/Heidi/chapter1/chp1.htm (Change the chapter# and chp# to
search different subjects)
2. http://www.biotopics.co.uk/as/condensation_and_hydrolysis.html
3. http://ocw.mit.edu/high-school/biology/chemistry-of-life/organic-molecules-in-organisms/
Sample Exam Questions:
What are the relevant bond changes in a hydrolysis model?
Think simpler. Dont overcomplicate things.
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (120)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocumento26 páginasIntermolecular Forces of AttractionEsaïe GreñaAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical Chemistry Notes, Problems PDFDocumento32 páginasAnalytical Chemistry Notes, Problems PDFKuo Sarong100% (1)
- ICENV 2015 EproceedingsDocumento922 páginasICENV 2015 EproceedingsAhmad Anas Nagoor GunnyAinda não há avaliações
- Varieties: Fabric Softener (Also Called Fabric Conditioner) Is Used To PreventDocumento10 páginasVarieties: Fabric Softener (Also Called Fabric Conditioner) Is Used To PreventCeehs FamorcanAinda não há avaliações
- GeneticsDocumento6 páginasGeneticsleti332Ainda não há avaliações
- Genetics 2Documento2 páginasGenetics 2leti332Ainda não há avaliações
- Muscle PDFDocumento42 páginasMuscle PDFleti332100% (1)
- BIO253 Lecture 1Documento3 páginasBIO253 Lecture 1leti332Ainda não há avaliações
- Adiolisa Containing Two (-OH Groups) .: Chemical Compound Hydroxyl GroupsDocumento5 páginasAdiolisa Containing Two (-OH Groups) .: Chemical Compound Hydroxyl Groupsleti332Ainda não há avaliações
- Wednesday, January 18 01/29/2012: o Biosphere o Ecosystem o Community o PopulationDocumento37 páginasWednesday, January 18 01/29/2012: o Biosphere o Ecosystem o Community o Populationleti332Ainda não há avaliações
- Bio 111 PcoloniesDocumento1 páginaBio 111 Pcoloniesleti332Ainda não há avaliações
- 職業(しょくぎょう) / a, an occupation 就職する(しゅうしょくする) / find work, get a 職人(しょくにん) / a craftsman, an artisanDocumento1 página職業(しょくぎょう) / a, an occupation 就職する(しゅうしょくする) / find work, get a 職人(しょくにん) / a craftsman, an artisanleti332Ainda não há avaliações
- Pad Cardiovascular Study GuideDocumento6 páginasPad Cardiovascular Study Guideleti332Ainda não há avaliações
- CH 13 BondingDocumento4 páginasCH 13 Bondingleti332Ainda não há avaliações
- Jabir Ibn Hayyan: Born in 722 Father of Chemistry (Prsented by Momina)Documento12 páginasJabir Ibn Hayyan: Born in 722 Father of Chemistry (Prsented by Momina)Ayesha RazzaqAinda não há avaliações
- Balancing Redox EquationsDocumento10 páginasBalancing Redox EquationsGlen Mark MacarioAinda não há avaliações
- CHEMISTRY IpeDocumento2 páginasCHEMISTRY IpeRam MohanAinda não há avaliações
- Process For The Production of Sucrose Esters of Fatty AcidsDocumento5 páginasProcess For The Production of Sucrose Esters of Fatty AcidsHarry CortezAinda não há avaliações
- Yarn Modification: Cotton MercerizationDocumento49 páginasYarn Modification: Cotton Mercerizationsolomonsai1Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Record Work-XiiDocumento23 páginasChemistry Record Work-XiiPREJAN RAJAAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 Properties of HaloalkaneDocumento5 páginasChapter 6 Properties of HaloalkaneRen Liew Jia QingAinda não há avaliações
- Bond Strength of Resin Cement To Zirconia Ceramic With Different Surface TreatmentsDocumento8 páginasBond Strength of Resin Cement To Zirconia Ceramic With Different Surface TreatmentsjosecarlosjAinda não há avaliações
- Green Synthesis of Nano ParticlesDocumento9 páginasGreen Synthesis of Nano ParticlesSurender DilipAinda não há avaliações
- Pages From Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress Third Ed 2011 TitluDocumento28 páginasPages From Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress Third Ed 2011 TitluCoțovanu IulianAinda não há avaliações
- Brief Update: Visual MINTEQ Modeling Effort (And Writing)Documento7 páginasBrief Update: Visual MINTEQ Modeling Effort (And Writing)jamesAinda não há avaliações
- CPD IsoprenoDocumento12 páginasCPD IsoprenoRodrigo Ortiz SotoAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 6: "The Cell Membrane"Documento25 páginasExperiment 6: "The Cell Membrane"Angela MagnoAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Chemistry UNIT 3Documento8 páginasApplied Chemistry UNIT 3Mikdhad MikkuAinda não há avaliações
- AL Chemistry 1996 Paper 1+2Documento12 páginasAL Chemistry 1996 Paper 1+2api-3734333Ainda não há avaliações
- Estudio FlotaciónDocumento13 páginasEstudio FlotaciónCamila Correa MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Transition Elements WS (MCQ)Documento6 páginasTransition Elements WS (MCQ)Torenku100% (1)
- Drug Acceptor InteractionsDocumento430 páginasDrug Acceptor InteractionsALAinda não há avaliações
- Rolls-Royce M250-C20R SERIES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE 73-20-03Documento4 páginasRolls-Royce M250-C20R SERIES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE 73-20-03anony8103Ainda não há avaliações
- CRP PH-4 Paper - 1 QP (Xii)Documento12 páginasCRP PH-4 Paper - 1 QP (Xii)Ananya AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ Science ChemistryDocumento4 páginasMCQ Science ChemistrypmagrawalAinda não há avaliações
- Soda Ash: Calcium Contamination RemoverDocumento1 páginaSoda Ash: Calcium Contamination RemoverMannar1Ainda não há avaliações
- BMCDocumento24 páginasBMCAhsan Sial AhsanAinda não há avaliações
- Electroless Nickel IntroductionDocumento56 páginasElectroless Nickel Introductionabhishek_giteAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Covalent Bond?Documento4 páginasWhat Is A Covalent Bond?Gunjeet KaurAinda não há avaliações
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2019Documento30 páginasMark Scheme (Results) January 2019Ahmad MohdAinda não há avaliações