Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
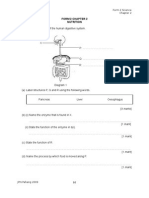
RPT Form 4 2014
Enviado por
Gloria NguTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
RPT Form 4 2014
Enviado por
Gloria NguDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
YEARLY LESSON PLAN
SCIENCE FORM 4
SM HOLY TRINITY 2014
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVE LEARNING OUTCOMES SUGGESTED ACTIVITIES VOCABULARY
THEME: INTRODUCING SCIENCE
LEARNING AREA: 1. SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION
1
2 - 4
Jan
1.1 Analysing method in
Scientific investigation
A student is able to:
explain the steps in scientific investigation,
cay out a scientific investigation,
!ite a epot on a scientific investigation,
explain the impotance of scientific investigation.
"ay out a scientific investigation, e.g. investigate ho!
suface aea affects the ate of cooling.
Students !ill:
a# identify the poblem,
b# identify the vaiables,
c# ma$e a hypothesis,
d# plan the investigation to:
i. detemine the appaatus and mateials needed,
ii. detemine the pocedue of the investigation, the method
in data collection and data analysis.
e# cay out the investigation,
f# collect data,
g# analyse and intepet data,
h# da! conclusions,
i# !ite a epot.
%iscuss the impotance of scientific investigation method
in ac&uiing scientific $no!ledge.
analyse ' menganalisis
appaatus ' radas
conduct ' jalankan
conclusion ' kesimpulan
detemine ' tentukan
hypothesis ' hipotesis
identify ' kenal pasti
intepet ' tafsirkan
investigate ' siasat
mateial ' bahan
obseve ' memerhati
planning ' merancang
pocedue ' prosedur,
tatacara
steps ' langkah-langkah
vaiables ' pemboleh
ubah
1
2 - 4
Jan
1.2 (ealising the need to
pactice scientific attitudes
and noble values !hen
caying out scientifi"
investigations
A student is able to:
identify scientific attitudes and noble values
pactised by scientists,
explain the need to pactice scientific attitudes
and noble values !hen caying out a
scientific investigation,
pactise scientific attitudes and noble values
!hen caying out a scientific investigation.
)ie! videos o compute simulations then gathe and
intepet data on the scientific attitudes and noble values
pactised by scientists.
%iscuss the need to pactice scientific attitudes and
noble values !hen caying out scientific investigations.
*oble values-nilai murni
+actise ' mengamalkan
scientific attitudes ' sikap
saintifik
THEME: MAINTENANCE AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE
LEARNING AREA: 1. BODY COORDINATION
2
, - 1-
Jan
1.1 .ndestanding /ody
coodination
A student is able to:
descibe !hat body coodination is,
identify the body systems that contol and
egulate coodination,
"ay out activities to obseve and discuss body
coodination.
0xamine models, vie! chats o videos to identify the body
systems !hich contol coodination, i.e. the nevous
body coodination '
koordinasi badan
endocine system ' sistem
endokrin
nevous system ' sistem
1
iii. state the impotance of body
coodination.
system and the endocine system.
%iscuss the impotance of body coodination in daily
activities.
saraf
2
, - 1-
Jan
1.2 .ndestanding the
human nevous system
A student is able to:
identify the component pats of the human
nevous system,
state the function of each component pat of
the nevous system,
state !hat a neuone is,
identify the pats of a neuone,
vi.state the function of each pat of the
neuone,
vii. identify the diffeent types of neuone,
viii. state the function of each type of the
neuone compae and contast the diffeent
types of neuone.
1bseve models, vie! chats o videos and identify the
human nevous system !hich consists of:
a# cental nevous system, i.e. bain and spinal cod,
b# peipheal nevous system, i.e. canial neves and spinal
neves and thei banches !hich lin$ the eceptos and
effectos !ith the cental nevous system.
%iscuss the function of each component pat of the
nevous system.
)ie! videos, chats o examine models and discuss the
follo!ing:
a# neuone as the basic unit of the nevous system,
b# pats of a neuone namely cell body, axon, dendite, and
myelin sheath
c# functions of vaious pats of a neuone,
d# types of neuone namely the sensoy neuone, moto
neuone, and the elay neuone,
e# functions of vaious types of neuons
%a! a labelled diagam of the sensoy neuone, the moto
neuon and the elay neuone.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast the diffeent
types of neuone and pesent the similaities and diffeences
in a gaphic oganise.
axon ' akson
cell body ' badan sel
cental nevous system '
sistem saraf pusat
moto neuone ' neuron
motor
myelin sheath ' salut
mielin
peipheal nevous system '
sistem saraf periferi
elay neuone ' neuron
perantaraan
sensoy neuone ' neuron
deria
2
12 - 13
Jan
1.2 Analysing *evous
coodination
A student is able to:
state !hat eceptos and effectos ae,
state the functions of eceptos and effectos,
explain !ith examples !hat a eflex action is,
descibe a eflex ac,
illustate the path ta$en by an impulse in the
eflex ac.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# meaning of eceptos and effectos,
b# functions of eceptos and effectos.
"ay out activities to demonstate the eactions of
sense ogans to vaious stimuli.
"ay out activities and discuss eflex actions such as
$nee-4e$and eaction to touching a hot o shap ob4ect.
)ie! compute simulations o chats sho!ing the path
ta$en by an impulse in a eflex ac.
%a! a diagam to sho! the path ta$en by an impulse in
a eflex ac.
eflex action ' tindakan
refleks
eflex ac ' arka refleks
2
4
21 - 25
Jan
1.4 .ndestanding the ole
of popioceptos in
maintaining balance and
coodination
A student is able to:
explain !hat popioceptos ae,
explain the impotance of popioceptos.
"ay out the follo!ing activities to sho! the
impotance of popioceptos:
a# stac$ing ob4ects !ith both eyes closed,
b# maintaining balance of thebody.
)ie! chats, videos o compute simulations and
discuss the follo!ing:
a# popioceptos and thei functions,
b# the impotance ofpopioceptos in maintaining
balance and coodination.
popioceptos ' reseptor
regang
4
21 -25
Jan
1.6 Analysing the
effects of excessive
consumption of alcohol
body coodination and
health
A student is able to:
list examples of alcoholic din$s,
descibe the effects of excessive
consumption of alcohol on body coodination
descibe the effects of
excessive consumption of alcohol on ealth,
4ustify the impotance of avoiding
excessive consumption of alcohol.
7athe infomation fom boo$s, ne!spapes,
maga8ines o 9ntenet and discuss the follo!ing:
a# examples of alcoholic din$s,
b# effects of excessive consumption of alcohol on
body coodination :effect on eaction times# and
health.
c# the impotance of avoiding excessive
consumption of alcohol.
+esent and exhibit the collected
infomation.
alcoholic din$s ' minuman
beal$ohol
excessive consumption '
pengambilan belebihan
eaction time ' masa
tinda$ balas
5
2- - 1
;eb
1.1- (ealising the
impotance of a sound and
healthy mind
A student is able to:
state !hat mind is,
identify factos that affect the mind,
explain ho! substance abuse can affect the
mind,
4ustify the impotance of a sound and healthy
mind.
7athe infomation fom boo$s, maga8ines,
ne!spapes and 9ntenet and discuss the follo!ing:
a# the meaning of mind,
b# factos that affect the mind, !hich include,
homone imbalance, excessive consumption of
alcohol, dug abuse, mental stess and bain in4uy,
ho! homone imbalance, excessive consumption of
alcohol and dug abuse can affect the mind,
d# the impotance of a healthy and sound mind.
homonal imbalance '
ketidakseimbangan
hormon
mind ' minda
mental stess ' tekanan
mental
healthy and sound mind '
minda yang sihat dan baik
THEME: MAINTENANCE AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE
LEARNING AREA: 2. HEREDITY AND VARIATION
5
2- - 1
;eb
2.1 .ndestanding
cell division
A student is able to:
state !hat genes, deoxyibonucleic
acids :%*A# and chomosomes ae,
descibe the elationship bet!een
gene, %*A and chomosome,
state !hat mitosis is,
descibe the pocess of mitosis,
state !hat meiosis is,
)ie! videos, compute simulations o chats to
study the follo!ing:
gene, %*A and chomosome,
mitosis and meiosis.
Simulate the pocess of mitosis and meiosis.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast
mitosis !ith meiosis and pesent the similaities
and diffeences in a gaphic oganise.
cell division '
pembahagian sel
centomees ' sentromer
chomosome ' kromosom
deoxyibonucleic acid '
asid deoksiribonukleik
gene ' gen
polaisation ' pengutuban
spindle fibes ' gentian
3
descibe the pocess of meiosis,
compae and contast mitosis !ith
meiosis,
explain the impotance of mitosis and
meiosis.
%iscuss the impotance of mitosis and meiosis. spindel/gelendung
,
4 - <
;eb
2.2 .ndestanding
the pinciples and
mechanism of
inheitance
A student is able to:
explain !hat dominant genes and ecessive
genes ae,
identify dominant taits and ecessive taits in
human,
llustate the mechanism of inheitance of taits
using a schematic diagam,
pedict the genotype and phenotype atios of
a monohybid coss.
1bseve and identify dominant and ecessive taits
among students and thei family membes.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# dominant genes and dominant taits,
b# ecessive genes and ecessive taits.
c# )ie! videos o compute simulations on genetic
expeiments caied out by 7ego =endel to study
the mechanism of tait inheitance.
.se schematic diagams to illustate monohybid
cosses and pedict the follo!ing using =endel>s
la!:
a# genotype atio of the ?fist filial> o ;1 geneation
and the ?second filial> o ;2 geneation,
b# phenotype atio of the ?fist filial> o ;1
geneation and the ?second filial> o ;2 geneation.
dominan
genotype ' genotip
inheitance ' pe!aisan
=endel>s la! ' hu$um
=endel
monohybid coss '
$acu$an monohibid
phenotype ' fenotip
ecessive taits ' sifat
esesif
3
11- 15
;eb
2.2 .ndestanding sex
detemination and the
occuence of t!ins in
human beings
A student is able to:
explain !hat sex chomosomes ae,
explain ho! sex is detemined,
explain the fomation of identical and non-
identical t!ins,
compae and contast identical !ith non-
identical t!ins,
explain !hat siamese t!ins ae.
)ie! compute simulations, videos o chats and
discuss the follo!ing:
a# sex chomosomes,
b# detemination of sex,
c# the occuence of identical and non-identical
t!ins,
d# the occuence of Siamese t!ins.
.se schematic diagams to illustate the follo!ing:
a# ho! sex is detemined,
b# ho! identical and non identical t!ins ae
fomed.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast
identical t!ins !ith non-identical t!ins and illustate
the similaities and diffeences in a gaphic
oganise.
(ead and intepet data fom boo$s, aticles,
maga8ines o 9ntenet on siamese t!ins.
identical t!ins ' kembar
seiras
non-identical t!ins '
kembar tak seiras
sex chomosomes '
kromosom seks
sex detemination '
penentuan seks
siamese t!ins ' kembar siam
3 2.4 .ndestanding mutation A student is able to:
state !hat mutation is,
)ie! videos, compute simulations o chats and
discuss the follo!ing:
a# mutation and types of mutation such as
albinism ' albinisme
colou blindness ' buta
warna
4
11- 15
;eb
state the types of mutation,
list examples of mutation,
identify causes of mutation,
state the advantages and
disadvantages of mutation.
chomosome mutations and gene mutations,
b# conse&uences of chomosome mutations in
humans such as %o!n>s syndome, @linefelte>s,
syndome, and Aune>s syndome,
d# conse&uences of gene mutations in humans
such as colou blindnes, albinism and
thalassaemia.
"ay out an activity to test colou blindness among
pupils
%iscuss the advantages and disadvantages of
mutation.
%o!n>s syndome '
sindrom Down
@linefelte>s syndome '
sindrom Klinefelter
=utation ' mutasi
Aune>s syndome '
sindrom Turner
*ote:
"hange in genes and
chomosomes
at the molecula
level is not
e&uied
<
1< - 22
;eb
2.5 0valuating the effects of
genetic eseach on human
life
A student is able to:
list the contibutions
of genetic eseach in
vaious fields,
explain selective beeding in plants and
livestoc$,
state the impotance of selective beeding in
plants and livestoc$,
descibe the technology used fo selective
beeding,
pesent aguments fo and against genetic
eseach.
Seach the 9ntenet, ead boo$s, maga8ines and
ne!spapes fo infomations on genetic eseach
and discuss the follo!ing:
a#genetic eseach in the field of medicine, such as
the discovey of vaious types of heeditay
diseases and the latest techni&ues fo teating
specific diseases, and Buman 7enome +o4ect.
b# genetic eseach in the field of agicultue such
as genetically- modified food :7=;#, cloning,
selective beeding in plants such as paddy, oil
palm, papaya, duian, chilli, and livestoc$ such as
daiy co! and chic$en.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# selective beeding in plants and livestoc$,
b# the impotance of selective beeding in plants
and livestoc$,
livestoc$ ' ternakan
selective beeding '
pembiakbakaan pilihan
6
25 - 1
=ac
2., Analysing vaiation
among living things
A student is able to:
i. state !hat vaiation is,
ii. list vaiation in humans,
iii. classify vaiation into
continuous and discontinuous vaiation,
iv. compae and contas continuous and discontinuous
vaiation,
v. identify factos that cause vaiation,
vi. explain the impotance of vaiation.
"ay out activities to identify and classify vaiation among
students in a class.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# continuous vaiation and discontinuous vaiation,
b# examples of continuous vaiation and discontinuous
vaiation,
c# factos !hich cause vaiation,
d# the impotance of vaiation.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast continous
continuous vaiation ' variasi
selanjar
discontinuous vaiation '
variasi tak selanjar
family tee 'salasilah
left-handed ' kidal
vaiation ' variasi
5
2.3 (ealising the need to
adhee to a code of ethics in
genetic eseach
A student is able to:
i. explain ho! the misuse of $no!ledge in the field of
genetics can endange life,
ii. descibe the impotance of establishing and adheing
to ethics and moals in scientific eseach fo the
benefit of man$ind
vaiation !ith discontinous vaiation and illustate the
similaities and diffeences in a gaphic oganise.
"onstuct a family tee based on vaiation among family
membes such as having staight o culy hai, being
ighthanded o left- handed, the pesence o absence of ea
lobes, and the ability to oll the tongue.
(ead boo$s, aticles, maga8ines o seach the 9ntenet and
discuss ho! misuse of $no!ledge in the field of genetics can
endange life.
%iscuss the impotance of establishing and adheing to ethics
and moals in scientific eseach fo the benefit of man$ind
THEME: MATTER IN NATURE
LEARNING AREA: 1. MATTER AND SUBSTANCE
1-
4 - <
=ac
1.1 Analysing changes in
the states of matte
A student is able to:
i. explain the $inetic theoy of matte,
a# elate changes in heat to changes in $inetic enegy
of the paticles in matte,
b# explain the inteconvesion of the thee states of
matte based on the $inetic theoy of
matte.
"ay out an activity to obseve changes in the states of
matte !hen heat is absobed o eleased.
)ie! videos o compute simulations and discuss the
follo!ing:
a# the $inetic theoy of matte,
b# changes in $inetic enegy of paticles in
matte duing heat change,
c# changes in the states of matte involving
the absoption o elease of heat,
d# changes in matte duing melting,
boiling, condensation, fee8ing
and sublimation based on the
$inetic theoy of matte.
absobed ' diserap
boiling ' pendidihan
condensation '
kondensasi
fee8ing ' pembekuan
inteconvesion '
perubahan dari satu
keadaan ke keadaan lain
dan sebaliknya
$inetic enegy ' tenaga
kinetik
$inetic theoy of matte 'teori
kinetik jirim
melting ' peleburan
paticle movement '
pergerakan zarah
11
11- 15
=ac
1.2 .ndestanding the
stuctue of an atom
A student is able to:
i. descibe the stuctue of an atom,
ii. identify the subatomic paticles,
iii. compae and contast the subatomic paticles.
0xamine models , vie! compute simulations and discuss the
follo!ing:
a# the stuctue of an atom,
b# the subatomic paticles namely poton,
electon, and neuton. %a! a labelled
diagam of a model of an atom.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast the subatomic
paticles in tems of location, elative mass and chage.
9llustate the similaities and diffeences of subatomic
paticles in a gaphic oganise.
eleased ' dibebas$an
states of matte ' $eadaan
4iim
sublimation '
peme4al!apan
chage ' cas
elative mass ' 4isim elatif
subatomic paticles ' 8aah
8aah subatom
6
11
11- 15
=ac
1.2 Applying the idea of
poton numbe and nucleon
numbe in atoms of elements
A student is able to:
i. state !hat poton numbe is,
ii. state !hat nucleon numbe is,
iii. elate the numbe of potons, neutons and
electons in an atom to its poton numbe and nucleon
numbe,
iv. deduce the numbe of potons, electons and
neutons in atoms of diffeent elements,
v. ma$e a genealisation on the numbes of potons
and electons in atoms of diffeent elements,
vi. state !hat isotopes ae,
vii. give examples of isotopes.
"ollect and intepet data on the follo!ing:
- poton numbe, nucleon numbe,isotopes.
"onstuct a table to sho! the elationship bet!een the
numbe of potons, neutons and electons in an atom and its
poton numbe and nucleon numbe.
%iscuss and ma$e a genealisation that atoms of diffeent
elements consist of diffeent numbes of potons and
electons.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# isotopes,
b# examples of isotopes such as isotopes of
hydogen and cabon.
isotopes ' isotop-isotop
ma$e genealisation '
membuat pengitla$an
nucleon numbe ' nombo
nu$leon
poton numbe ' nombo
poton
*otes:
1nly elements !ith poton
numbes in
the ange of 1-1- ae e&uied.
12
1< - 22
=ac
1.4 .ndestanding the
classification of elements in
the +eiodic Aable
A student is able to:
i. descibe the aangement of elements in the +eiodic
Aable,
ii. descibe !hat is meant by goups and peiods in the
+eiodic Aable,
iii. identify the locations of metals, non-metals and
semimetals in the +eiodic Aable,
iv. state the impotance of the +eiodic Aable.
)ie! compute simulations o nchats and discuss the
follo!ing aspects of the +eiodic Aable:
a# aangement of elements based on
inceasing poton numbe,
b# goup as vetical column containing
elements !ith simila chemical
popeties,
c# peiod as hoi8ontal o! containing
elements that
change thei chemical and physical popeties gadually fom
those eflecting metal to those eflecting non-metal,
d# locations of metals, non-metals and
semimetals.
"ay out a cad game to fill up the missing elements in the
+eiodic Aable. Ahe cads contain the follo!ing details:
a# poton numbe,
b# nucleon numbe,
c# metal, non-metal and semimetal.
%iscuss the impotance of the +eiodic Aable in tems of:
a# assisting in an odely and systematic
appoach to the study of elements,
b# $no!ing the popeties of the elements,
c# pedicting the popeties and uses of
elements.
pemainan $ad
chemical popeties ' sifat
$imia
goup ' $umpulan
hoi8ontal o!s ' bais
mendata
metals ' logam
non-metals ' bu$an logam
peiod ' $ala
+eiodic Aable ' Jadual
/e$ala
semimetals ' sepauh
logam
vetical columns ' tuus
menega$
12 : 22 - 2- =ac# ".A9 +0(A0*7ABA* +0*77AC 1
14 1.5 .ndestanding the
popeties of ubstances
A student is able to:
i. descibe !hat atoms, molecules and ions ae,
)ie! compute simulations o chats to study the follo!ing:
a# atoms, molecules and ions,
boiling point -
takat didih
7
1 - 5
Ap
based on the paticles
pesent in them
ii. identify the paticles in substances as atoms,
molecules and ions,
iii. state examples of substances made of atoms,
molecules and ions,
iv. compae and contast substances that ae made of
atoms, molecules and ions based on thei physical
popeties,
v. elate the physical popeties of substances made up
of atoms, molecules and ions to the
aangement of paticles and the foces of attaction
bet!een them.
b# substances !hich ae made of atoms,
molecules and ions,
c# physical popeties of substances made of
atoms, molecules and ions such as:
i# physical state at oom tempeatue,
ii# melting point,
iii# boiling point,
iv# electical conductivity.
d# aangement of paticles and the foces of attaction
bet!een paticles in substances made of atoms, molecules
and ions.
"ay out an activity to study the melting point and electical
conductivity of substances made up of:
a# atoms such as lead,
b# molecules such as sulphu,
c# ions such as lead bomide.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast substances that
ae made of atoms, molecules and ions based on thei
physical popeties. 9llustate the similaities and diffeences
in a gaphic oganise.
%iscuss the aangement of paticles and the foces of
attaction bet!een paticles in elation to the physical
popeties of substances made up of atoms, molecules and
ions.
electical conductivity '
kekonduksian elektrik
foces of attaction ' daya
tarikan
melting point ' takat lebur
oom tempeatue ' suhu
bilik
15
< - 12
Ap
1., .ndestanding the
popeties and uses of
metals and non-metals
A student is able to:
i. list examples of metals and non-metals,
ii. list the popeties of metals and non-metals,
iii. list the uses of metals and non-metals in daily life,
iv. compae and contast metals and non-metals based
on thei physical popeties,
v. elate the physical popeties of metals and non-
metals to thei uses in daily life.
"ay out an activity to identify ob4ects in the classoom
!hich ae made of metals and non-metals.
"ollect and intepet data on the popeties and uses of
metals such as ion, aluminium, 8inc, coppe, lead, tin, gold
and non-metals such as cabon, sulphu and chloine.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast the popeties
of things made of metal and nonmetal and illustate the
similaities and diffeences in a gaphic oganise.
"ay out an activity to study the physical popeties of
metals and non-metals such as:
a# luminosity, b# ductility,
c# malleability, d# tensile stength,
e# electical and heat conductivity.
%iscuss the physical popeties of metals and non-metals
elating to thei uses in daily life.
chloine ' klorin
coppe ' kuprum
ductility ' kemuluran
electical and heat
conductivity '
kekonduksian elektrik dan
haba
gold ' emas
ion ' besi
lead ' plumbum
luminosity ' kekilauan
malleability '
ketertempaan
sulphu ' sulfur
tensile stength '
kekuatanregangan
tin ' timah
8
1, - 13
15 - 2,
Ap
1. Analysing methods of
+uifying substances
A student is able to
i. state the chaacteistics of pue substances,
ii. descibe the diffeent methods of
puification of substances,
iii. elate the chaacteistics of substances to
the methods of puification used,
iv. explain !ith examples the methods of
puification used to poduce substances
used in daily life.
"ollect and intepet data on the follo!ing:
a# chaacteistics of pue substances,
b# diffeent methods of puification of substances.
"ay out activities to study the follo!ing:
-ho! the pesence of impuities such as salts affects the
boiling point of !ate,
-puification of substances by the follo!ing methods:
i. distillation, e.g. puifying alcohol fom a
mixtue of alcohol and !ate,
ii. cystallisation,e.g. puifying salt fom a
satuated solution of common salt.
-7athe infomation and discuss the follo!ing:
a# factos to be consideed !hen selecting the
methods of puification. 0xamples ae as
follo!:
i. sepaating a li&uid fom a solution of a solid in
a li&uid, such as poducing pue !ate fom sea
!ate,
ii. sepaating a li&uid fom a mixtue of miscible
li&uids such as emoving ethanol fom a
mixtue of ethanol and !ate,
iii. sepaating insoluble impuities fom a
soluble substance such as emoving sand
and othe impuities fom salt.
b# methods of puification used in poducing
substances needed daily such as salt, suga,
petoleum factions and distilled !ate.
cystallisation '
penghabluran
distillation ' penyulingan
distilled !ate ' air suling
impuities ' bendasing
petoleum factions '
pecahan petroleum
pue substances ' bahan
tulen
puification of substances
'penulenan bahan
satuated solutions '
larutan tepu
solutes ' zat-zat terlarut
miscible ' larut campur
13
22- 2,
Ap
1.< Appeciating the
existence and uses of
vaious substances of
diffeent chaacteistics
A student is able to:
i. descibe ho! man uses vaious substances of
diffeent chaacteistics and states in eveyday life,
ii. 4ustify the impotance of the existence of vaious
substances of diffeent chaacteistics and states that
benefit man$ind.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# ho! vaious substances of diffeent
chaacteistics can be utilised to benefit
man$ind,
b# the impotance of the existance of
vaious substances of diffeent
chaacteistics.
22 - 2 A!"#$ 201
MONTHLY TEST 2
THEME: ENERGY IN LIFE
LEARNING AREA: 1. ENERGY AND CHEMICAL CHANGES
1< 1.1 .ndestanding physical A student is able to: %iscuss the follo!ing in tems of physical and chemical chemical changes '
9
26 - 2
=ei
and chemical changes i. explain !hat physical
change is,
ii. explain !hat chemical
change is,
iii. give examples of physical
changes in daily life,
iv. give examples of chemical
changes in daily life,
v. compae and contast
physical changes and
chemical changes.
changes:
a# buning of pape,
b# melting of ice,
c# change in colou of sliced
apples,
d# evapoation of !ate.
"ay out the follo!ing activities to study physical and
chemical changes:
a# heating ion !ith sulphu,
b# buning magnesium in ai,
c# mixing 8inc !ith coppe
sulphate solution,
d# soa$ing clean ion nails in
!ate until they ust,
e# heating coppe cabonate,
f# mixing potassium iodide !ith
lead nitate,
g# dissolving suga in !ate,
h# cystallising sodium chloide
fom its satuated solution,
i# heating iodine cystals in a
closed containe,
4# slo! heating of !ax.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast physical
change and chemical change and illustate the similaities
and diffeences in a gaphic oganise.
perubahan kimia
coppe cabonate salt '
garam kuprum karbonat
coppe sulphate solution -
larutan kuprum sulfat
evapoation of !ate '
penyejatan air
lead nitate ' plumbum
nitrat
physical changes '
perubahan fizik
potassium iodide ' kalium
iodida
eaction ' tindak balas
ust ' karat
satuated solution ' larutan
tepu
sodium chloide ' natrium
klorida
!ax ' lilin
16
,- 1-
=ei
1.2 Analysing heat change
in "hemical eactions
A student is able to:
i. state that chemical
eactions involve heat
change,
ii. identify eactions involving
heat loss,
iii. identify eactions involving
heat gain,
iv. elate changes in
tempeatue of eactants to
exothemic eactions,
v. elate changes in
tempeatue of eactants to
endothemic eactions,
vi. explain though examples
heat changes that occu
"ay out the follo!ing activities to study heat changes in
chemical eactions:
a# dissolving ammonium chloide in !ate,
b# dissolving sodium hydoxide in !ate.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# the elationship bet!een heat loss o heat gain and
changes in tempeatue,
b# exothemic and endothemic eactions based on changes
in heat.
)ie! compute simulations then gathe and intepet data on
heat changes that occu duing industial chemical eactions,
such as:
a# the poduction of ammonia
fom ammonium poducts
b# the poduction of sulphuic acid.
ammonium chloide '
ammonium klorida
chemical eaction '
tindak balas kimia
endothemic ' serap haba
exothemic ' buang haba
heat change ' perubahan
haba
eactant ' bahan tindak balas
sodium hydoxide '
natrium hidroksida
sulphuic acid ' asid
sulfurik
10
duing industial chemical
eactions.
2-
12 - 13
=ei
1.2 Synthesising the
eactivity seies of
metals
A student is able to:
i. descibe the eactivity of
metals !ith !ate,
ii. descibe the eactivity of
metals !ith acids,
iii. descibe the eactivity of
metals !ith oxygen,
iv. compae and contast the
eactivity of metals !ith
!ate, acids and oxygen,
v. aange metals in ode of
eactivity,
vi. constuct the eactivity
seies of metals based on
eactivity of metals !ith
oxygen,
vii. identify the position of
cabon in the eactivity seies.
"ay out activities to study the follo!ing eactions:
a# sodium, calcium, magnesium,
aluminium, 8inc and coppe !ith !ate.
b# magnesium, aluminium, 8inc
and coppe !ith dilute acids.
c# magnesium, aluminium, 8inc,
coppe !ith oxygen.
"ay out activities to compae and contast the eactivity of
metals !ith !ate, acids and oxygen. 9llustate the similaities
and diffeences in a gaphic oganise.
%iscuss and aange metals in ode of eactivity.
"ollect and intepet data on the eactivity of metals !ith
oxygen to
constuct the eactivity seies of metals.
"ay out an expeiment to detemine the position of cabon
in the eactivity seies.
dilute acids ' asid cair
eactivity seies ' siri
kereaktifan
20 - 21
%0& - 2 M'#(FIRST TERM E)AMINATION
22 - 22
: 2< =ei - < Jun#
".A9 +0(A0*7ABA* AAB.*
24
1- - 14
Jun
1.4 Applying the concepts of
eactivity seies of metals
A student is able to:
i. elate the position of
metals in the eactivity
seies to the method of
extaction of metals fom
thei oes,
ii. explain !ith examples the
pocess of extaction of a
metal fom its oe using
cabon,
iii. state the impotance of the
eactivity seies.
)ie! compute simulations o videos on methods of
extacting metals fom thei oes and then cay out the
follo!ing activities:
a# elate the position of
metals in the eactivity
seies to the method of
extacting metals fom thei
oes, such as using
cabon and by electolysis,
b# discuss the pocess of
extacting tin fom its oe.
%iscuss the impotance of the eactivity seies.
0 lectolysis ' elektrolisis
extaction '
pengekstrakan
oe ' bijih
tin ' timah
24 1.5 .ndestanding
electolysis
A student is able to:
i. state !hat electolysis is,
ii. state !hat anode, cathode,
anion, cation and
"ay out activities on electolysis and
discuss the follo!ing:
a# definition of electolysis,
b# !hat anode, cathode, anion,
anode ' anod
cathode ' katod
electode ' elektrod
electolyte ' elektrolit
11
1- - 14
Jun
electolyte ae,
iii. descibe the electolysis of
an electolyte using cabon
electodes,
iv. explain the uses of
electolysis
in industy.
cation and electolyte ae,
c# the pocess and poduct of
electolysis of an electolyte
using cabon electodes,
d# use of electolysis in
electoplating metal ob4ects.
)ie! compute simulations and study the follo!ing
pocesses:
a# electolysis of molten lead
bomide using cabon electodes,
b# electoplating ob4ects made
of ion !ith coppe.
)ie! videos o compute simulations and discuss the uses of
electolysis in industy, including the extaction of metals,
puification of metals and electoplating.
electoplating '
penyaduran elektrik
lead bomide ' plumbum
bromida
molten ' lebur
25
13 - 21
Jun
1., .ndestanding
electolysis
A student is able to:
i. descibe ho! a simple cell
!o$s,
ii. list the vaious types of
cells and thei uses,
iii. state the advantages and
disadvantages of vaious
types of cells.
"ay out an activity to study the poduction of electical
enegy by a simple cell.
0xamine vaious types of cells such as dy cells, lead-acid
accumulatos, al$aline batteies, silve oxide-mecuy
batteies and nic$el-cadmium batteies and discuss:
a# thei uses,
b# the advantages and
disadvantages
in using each of these types of cells.
al$aline batteies ' bateri
alkali
lead-acid accumulatos '
akumulator asid-plumbum
nic$el cadmium batteies '
bateri nikel-kadmium
silve oxide-mecuy
batteies ' bateri argentum
oksida-merkuri
simple cell ' sel
otes!
0&uations to
sho! the
eactions at the
positive and
negative
teminals of a
simple cell ae
not e&uied
2,
24 - 2<
Jun
1.3 .ndestanding chemical
eactions that occu in the
pesence of light
A student is able to:
i. give examples of chemical
eactions !hich e&uie
light,
ii. explain the effect of light on
photosensitive chemicals,
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# chemical eactions !hich
e&uie light fo example
photosynthesis in geen
plants,
b# the effect of light on
photogaphic pape '
kertas fotografi
photosensitive chemicals '
bahan kimia yang peka
cahaya
photosynthesis '
12
iii. explain !hy cetain
chemicals ae stoed in
da$ bottles.
photosensitive chemicals.
"ay out an activity to study the effect of light on
photogaphic pape and silve chloide.
%iscuss ho! photosensitive chemicals ae stoed by elating
to the effect of light on these chemicals.
fotosintesis
silve chloide ' argentums
klorida
*ote:
1nly a bief
desciption of
splitting of !ate
molecules by
light enegy in
photosynthesis
is e&uied.
"hemical
e&uations ae
not e&uied
2,
24 - 2<
Jun
1.< Appeciating the
innovative effots in the
design of e&uipment using
chemical eactions as
souces of enegy
A student is able to:
i. descibe ho! enegy
obtained
fom chemical eactions
should be used efficiently to
pevent !astage,
ii. descibe ho! e&uipment
utilising chemical eactions
as souces of enegy
should be disposed to
educe envionmental
pollution,
iii. give suggestions on ne!
!ays of using chemical
eactions as souces of
enegy fo e&uipment,
iv. put into pactise good
habits !hen using and
disposing e&uipment that
uses chemical eaction as a
souce of enegy.
+epae folio and scap boo$ on the follo!ing topics:
a# ho! enegy obtained fom
chemical eactions should be
used efficiently to pevent
!astage,
b# ho! e&uipment utilising
chemical eactions as
souces of enegy
should be disposed to educe
envionmental pollution,
"ay out a bainstoming session on
ne! !ays of using
chemical eactions
as souces of enegy fo
e&uipment.
"ay out activities to illustate good habits of using and
disposing e&uipment that uses chemical eaction as a souce
of enegy
THEME : ENERGY IN LIFE
LEARNING AREA: 2. NUCLEAR ENERGY
23 2.1 .ndestanding
(adioactive substances
A student is able to:
i. state !hat adioactive
substances ae,
)ie! compute simulations, videos o chats and study:
a# adioactive substances,
b# adioactive adiations,
penetation po!e ' kuasa
penembusan
adiation " sinaran
13
1 - 5 Jul ii. give examples of
adioactive substances,
iii. descibe the pocess of
adioactive decay,
iv. name the thee types of
adioactive adiations,
v. descibe the chaacteistics
of each type of adioactive
adiation,
vi. compae and contast
adioactive adiations,
vii. explain !hat adioisotopes
ae,
viii. give examples o
adioisotopes,
ix. explain the uses of adioactive
substances.
c# adioisotopes.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# adioactive substances,
b# adioisotopes of cabon, cobalt and iodine,
c# the pocess of adioactive decay and the emission of alpha
paticles, beta paticles and gamma adiation.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast the
chaacteistics of the thee types of adioactive adiations i.e.
alpha, beta and gamma adiation in tems of:
a. type of paticles,
b. chage,
c. penetating po!es.
9llustate the similaities and diffeences in a gaphic
oganise.
)ie! compute simulations, videos o chats and discuss the
uses of adioactive substances in the follo!ing fields:
a# agicultue,
b# medicine,
c# achaeology,
d# industy,
e# food pesevation.
Access !ebsites o visit =alaysian 9nstitute of *uclea
Aechnology :=9*A# to collect infomation on adioactive
substances and nuclea enegy
adioactive decay '
pereputan radioaktif
adioisotope ' radioisotop
*otes:
Balf-life is not
e&uied.
2<
< - 12
Jul
2.2 .ndestanding the
poduction of nuclea
enegy and its uses
A student is able to:
i. descibe the poduction of
nuclea enegy though
fission,
ii. descibe the poduction of
nuclea enegy though
fusion,
iii. state the uses of nuclea
enegy,
iv. descibe the pocess of
geneating electicity fom
nuclea enegy,
v. explain the effects of nuclea
enegy poduction.
)ie! compute simulations, video and chats and discuss the
poduction of nuclea enegy though the follo!ing:
a# fission,
b# fusion.
%iscuss the pocess of geneating electicity fom nuclea
enegy.
(ead aticles and do a goup
pesentation on the follo!ing:
a# the uses of nuclea enegy,
b# the effects of nuclea enegy
poduction.
fission ' pembelahan
fusion ' pela$uan
nuclea enegy ' tenaga
nu$lea
*otes:
Ahe concept of chain eaction
is
not e&uied
26 2.2 A!aeness of the need
fo pope handling of
adioactive substances
A student is able to:
i. state the effects of
adioactive adiations on
(ead aticles, vie! videos o chats and discuss the
follo!ing:
a. "henobyl nuclea disaste
adioactive !astes ' sisa
bahan adioa$tif
nuclea po!e station ' stesen
14
15 -16
Jul
living things,
ii. descibe the coect !ay of
handling adioactive
substances and adioactive
!aste,
iii. explain the need fo pope
handling of adioactive
substances and adioactive
!aste.
and othe nuclea disastes,
b. handling of adioactive
substances and adioactive
!aste.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
:i# the shot tem and long tem
effects of adioactive
substances on living things,
:ii# the need fo pope handling
of adioactive substances and
adioactive !aste.
%ebate on the need to have nuclea po!e stations.
tenaga nu$lea
1* - 1+ J,$- 201
MONTHLY TEST
THEME : ENERGY IN LIFE
LEARNING AREA: . LIGHT. COLOUR AND SIGHT
2-
22 - 2,
Jul
2.1 Synthesising the
fomation of image by plane
mios and lenses
A student is able to:
i. state the chaacteistics of
images fomed by a plane
mio,
ii. state the chaacteistics of
images fomed by a
convex lens,
iii. state the chaacteistics of
images fomed by a
concave lens,
iv. compae and contast
images of distant ob4ects
fomed by convex lenses
and concave lenses,
v. da! a labelled ay diagam
to sho! the fomation of
image by light ays passing
though a convex lens,
vi. da! a labelled ay diagam
to sho! the fomation of
image by light ays passing
though a concave lens,
vii.da! ay diagams to
explain ho! chaacteistics
of images fomed by
"ay out activities to obseve the follo!ing:
a# 9mages fomed by a plane mio,
b# 9mages fomed by convex
and concave lenses.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast images of
distant ob4ects fomed by convex lenses and concave lenses.
9llustate the similaities and diffeences in a gaphic
oganise.
.se compute simulations,videos o chats to demonstate
the constuction of ay diagams.
%a! ay diagams fo light passing though:
a# convex lens !ith ob4ects
located at vaious distances,
b# concave lens.
Cabel the follo!ing on the ay diagams:
a# pincipal axis,
b# optical cente,
c# focal point,
d# focal length,
e# ob4ect distance,
f# image distance.
%iscuss ho! chaacteistics of images fomed by convex
lenses vay !ith ob4ect distance,
+lan and cay out an activity to detemine the focal length of
a convex lens.
concave lens ' kanta
cekung
convex lens ' kanta
cembung
distant ob4ect ' objek jauh
focal length ' panjang
fokus
focal point ' titik fokus
image ' imej
image distance ' jarak
imej
ob4ect distance ' jarak
objek
optical cente ' pusat
optik
plane mio ' cermin
satah
pinciple axis '
paksi utama
ay diagam ' rajah sinar
15
convex lenses vay !ith
ob4ect distance,
viii.detemine the focal length
of a convex lens.
21
26 - 2
1gos
2.2 Synthesising the
fomation of image by optical
nstuments
A student is able to:
identify the pats of optical
instuments involved in
image fomation,
da! ay diagams fo light
ays passing though an
optical instument,
compae and contast the
mechanisms in focusing
and contolling the amount
of light that entes human
eyes and a camea,
explain the stuctue and
function of vaious pats of
the eye using a camea as
an analogy.
9nvestigate the image fomed in a camea using a pin-hole
camea !ith and !ithout lens.
"onstuct a simple peiscope and telescope.
%iscuss the fomation of image by these optical instuments.
.se compute simulations to demonstate constuction of ay
diagams fo the light ays passing though the eye and
optical instuments.
/ased on the simulations, da!
and label ay diagams to sho! the fomation of images in
the follo!ing optical instuments:
a# camea, b# peiscope,
c# telescope. d# eye
%iscuss the similaities and diffeences bet!een camea and
eye in tems of focusing and contolling the amount of light.
image fomation '
pembentukan imej
magnifying glass ' kanta
pembesar
optical instuments '
alatan optik
pin-hole camea ' kamera
lubang jarum
22
5 - 6
1gos
2.2 Analysing light
dispesion
A student is able to:
i. state !hat light dispesion
is,
ii. explain though examples
ho! dispesion of light
occus.
"ay out activities to investigate the follo!ing :
a# light dispesion using a pism,
b# ainbo! fomation.
%iscuss !hat light dispesion is.
.se compute simulations to demonstate light dispesion.
%a! a labelled diagam to sho! dispesion of light.
%iscuss light dispesion in a phenomenon, such as the
fomation of ainbo!.
light dispesion '
penyebaran cahaya
phenomenon ' fenomena
ainbo! ' pelangi
22 - 22
:3 - 1< 1gos# ".A9 +0(A0*7ABA* AAB.* 2
24
16 - 22
1gos
2.4 Analysing light
scatteing
A student is able to:
i. state !hat light scatteing is,
ii.give examples of
phenomena elated to light
scatteing,
iii.explain though examples
ho! scatteing of light
occus in natual phenomena.
"ay out an activity to study light scatteing and its effects.
.se compute simulations to demonstate the pocess of light
scatteing.
%iscuss light scatteing in phenomena such as blue s$ies
and ed sunset
light scatteing 'penyerakan
cahaya
25 2.5 Analysing the addition
and subtaction of coloued
A student is able to:
i. identify pimay and
"ay out an activity to intoduce pimay and seconday
colous.
coloued filte ' penapis
warna
16
2, - 2-
1gos
lights seconday colous,
ii. explain ho! addition of
pimay colous poduces
seconday colous,
iii.explain the subtaction of
colous by coloued filtes.
"ay out activities to:
a# investigate the addition of pimay colous to fom
seconday colous,
b# investigate the effects of pimay and seconday coloued
filtes on !hite and coloued light.
.se compute simulations to demonstate the addition and
subtaction of coloued lights.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# ho! seconday colous ae obtained fom the addition of
pimay colous,
b# subtaction of coloued lights
by coloued filtes.
pimay colou ' warna
primer
seconday colou " warna
sekunder
subtaction of coloued
light ' penolakan cahaya
berwarna
2,
2 - ,
Sept
2., Applying the pinciple of
subtaction of coloued light
to explain the appeaance of
coloued ob4ects
A student is able to:
i. explain subtaction of coloued
lights by coloued ob4ects,
ii. explain the appeaance of
coloued ob4ects unde !hite light.
iii. explain the appeaance of coloued ob4ects unde
coloued
lights,
state the function of od and
cone cells in the eye.
"ay out activities to obseve and
study the colou of ob4ects unde !hite and coloued lights.
)ie! compute simulations and discuss the subtaction of
coloued lights by coloued ob4ects.
%iscuss the follo!ing:
a# functions of od and cone cells,
b# the appeaance of coloued ob4ects unde !hite and
coloued light.
cone cell ' sel kon
od cell ' sel rod
23
6 - 12
Sept
2.3 Analysing the
effect of mixing
pigments
A student is able to :
i. state !hat pigment is,
ii. list the uses of pigments,
iii. compae and contast the
mixing of pigments !ith the
addition of coloued lights,
iv. explain though examples
the effects of pigments on
light,
v. ma$e conclusions about
the mixing of pigments.
"ay out activities to obseve and study pigment and the
effect of mixing pigments.
)ie! compute simulations and discuss the mixing of
pigments and the effects of pigments on light.
"ay out an activity to compae and contast the mixing of
pigments !ith the addition of coloued lights. 9llustate the
similaities and diffeences in a gaphic oganise.
/ased on the above activities ma$e conclusions about the
mixing of pigments and discuss the uses of pigments.
mixing of pigments '
pencampuran pigmen
pigment ' pigmen
2<
1, - 2-
Sept
2.< 0valuating the
impotance 1f colou in
daily life
A student is able to:
i. list the uses of colou in
daily life,
ii. state !ith examples the
impotance of colou to
living things,
iii.4ustify the impotance of
)ie! compute simulations o videos to gathe infomation
and discuss the follo!ing:
a# the uses of colou in pinting,
electical !iing, taffic lights,
symbols and signals,
b# the impotance of colou to
humans, animals and plants.
17
colou to living things. %iscuss !hat life is li$e !ithout colou.
2<
1, - 2-
Sept
2.6 Appeciating the benefits
of vaious types of
optical instuments to
man$ind
A student is able to:
i. elate the inventions of
vaious types of optical
instuments to thei
contibutions to man$ind.
%iscuss the advantages of having vaious $inds of optical
instuments such as:
a# to ovecome the limitation of
the sense of sight,
b# extending the capability o
po!e of vision,
c# inceasing human $no!ledge
and undestanding about
natue.
1+ - 1& S'!/'01'" 201
MONTHLY TEST 4
THEME : TECHNOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY
LEARNING AREA : 1. CHEMICALS IN INDUSTRY
26
22 - 23
Sept
1.1 .ndestanding
the popeties of alloys
and thei uses in industy
A student is able to:
i. state !hat an alloy is,
ii. give examples of alloys,
iii. explain ho! the fomation
of alloy can change the
popeties of metals,
iv. elate the changes in the
popeties of metals !hen
they ae conveted to alloys
to the aangment of
paticles in the alloys,
v. elate the popeties of
alloys to thei uses in daily
life,
vi. descibe the impotance of
alloys in industy,
vii.state !hat supeconducto
alloys ae.
0xamine things made of alloys and discuss thei
composition, popeties and uses.
"ollect and intepet data on the follo!ing:
a# !hat an alloy is, b# examples of alloys,
c# composition, popeties and the uses of vaious alloys
including steel, pe!te,
bon8e, bass and dualumin.
)ie! videos o compute simulations and discuss:
a# ho! fomation of alloys can change the popeties of
metals, such as to incease
hadness, pevent coosion and impove appeaance,
b# !hat supeconducto alloys ae.
%iscuss the impotance of alloys in industy.
alloy ' aloi
bass ' loyang
bon8e ' gangsa
coosion ' pengkakisan
steel ' keluli
supeconducto alloy ' aloi
superkonduktor
4-
2- - 4
1$t
1.2 Analysing the
poduction and
uses of ammonia
in industy
A student is able to
list the uses of ammonia
and its compounds in daily
life,
descibe ho! ammonia is
poduced in industy,
"ollect and study poduct labels to identify the ammonium
compounds pesent.
%iscuss the uses of ammonia and its compounds in the
ma$ing of substances such as fetilises, nitic acid,
colouing, cleaning agents and explosives.
)ie! videos o compute
ammonium salt ' garam
ammonium
catalyst ' mangkin
cleaning agents ' agen
pencuci
colouing ' pewarna
18
state the factos !hich
affect the poduction of
ammonia in industy,
state the industial uses of
ammonia,
descibe ho! ammonia is
used
to poduce ammonium salt
fetilises and uea.
simulations to gathe and intepet data on the follo!ing:
a# the pocess of poducing ammonia in industy,
b# factos !hich affect the optimum poduction of ammonia
such as
tempeatue, pessue and catalysts.
%a! a flo! chat to sho! the poduction of ammonia.
"ollect and intepet data on the lage scale uses of
ammonia in industy such as manufactuing fetilises and
nitic acid.
"ay out an activity to pepae ammonium fetilise such as
ammonium sulphate, ammonium nitate and ammonium
phosphate.
explosives ' bahan
letupan
fetilises ' baja
flo! chat ' carta aliran
pessue ' tekanan
41
3 - 11
1$t
1.2 Analysing the effects of
9ndustial !aste disposal
on the envionment
A student is able to
i. identify manufactuing
activities !hich ae
souces of pollution,
ii. explain the effects of
impope industial !aste disposal,
iii. elate the effects of
industial !aste disposal to
the suvival of living things,
iv. state !ith examples the
methods of contolling
industial !aste disposal to
avoid pollution.
)ie! videos o compute simulations to gathe and intepet
data on envionmental pollution aising fom:
a# buning of fossil fuels,
b# disposal of industial !aste
such as toxic substances
fom the chemical industy,
adioactive !aste, oil palm
and ubbe !aste fom the
agicultual industy,
c# effects of impope industial
!aste disposal on the
envionment,
d# methods of contolling
industial !aste disposal to
avoid envionmental pollution.
%iscuss and elate the effects of impope disposal of
industial !aste to the suvival of living things.
Select an industy and do a pesentation on ho! !astes ae
managed in the industy.
envionmental pollution '
pencemaran alam sekitar
fossil fuels ' bahan api
fosil
industial !aste ' bahan sisa
industry
41
3 - 11
1$t
1.4 (ealising the need fo
+esevation and
consevation of the
envionment fom
industial !aste pollution
fo the !ellbeing of
man$ind
A student is able to:
i. descibe the conse&uences
of uncontolled and
hapha8ad disposal of
industial !aste,
ii. explain the impotance of
pactising esponsible !ay
of disposing industial
!aste.
)ie! videos o compute simulations on industial !aste
pollution and its effects on envionment.
%iscuss:
a# conse&uences of uncontolled
and hapha8ad disposal of
industial !aste,
b# the need to teat industial
pollution seiously in ode to
peseve and conseve the
envionment,
envionmental pollution '
pencemaran alam sekitar
consevation '
pemuliharaan
pesevation '
pemeliharaan
19
c# the impotance of pactising
esponsible !ay of disposing
industial !aste.
4- - 42
1 - 25 1$t
FINAL YEAR E)AMINATION
44 - 4,
2< - 15 *ov
REVISION
1, *ov - 2 Jan 2-14
SCHOOL HOLIDAYS
20
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Cefr Global ScaleDocumento4 páginasCefr Global ScaleGloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- AMS5662Documento11 páginasAMS566213421301508Ainda não há avaliações
- Esab Electrode Storage RecommendationsDocumento22 páginasEsab Electrode Storage RecommendationsDhanush NairAinda não há avaliações
- List of Regular VerbsDocumento5 páginasList of Regular Verbssasauball100% (1)
- Chem Study Guide Answer KeyDocumento4 páginasChem Study Guide Answer Keyapi-240689882100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocumento8 páginasChapter 2 Cell As A Unit of Lifenaza9775100% (5)
- Form 2 Chapter 2Documento7 páginasForm 2 Chapter 2naza977579% (19)
- Reducing Agents in The Leaching of Manganese Ores - A Comprehensive ReviewDocumento19 páginasReducing Agents in The Leaching of Manganese Ores - A Comprehensive ReviewDaniela AbarcaAinda não há avaliações
- Aboveground Storage Tanks Corrosion Monitoring and AssessmentDocumento15 páginasAboveground Storage Tanks Corrosion Monitoring and Assessmentemre gedikliAinda não há avaliações
- 005 Simple Present Tense 1Documento6 páginas005 Simple Present Tense 1Rasul AghayevAinda não há avaliações
- Sabah Junior Tennis Tournament Fact SheetDocumento2 páginasSabah Junior Tennis Tournament Fact SheetGloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Dinamik 2018Documento1 página1 Dinamik 2018Gloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- CYF 2nd Meeting Handouts (6 March 2017)Documento2 páginasCYF 2nd Meeting Handouts (6 March 2017)Gloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Form 3 Induction Set (Set 2)Documento3 páginasForm 3 Induction Set (Set 2)Gloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Bil Kod Papan Notis Tinggi (CM) Lebar (CM) Catatan Harga (RM) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. J (Grids Board) 11Documento3 páginasBil Kod Papan Notis Tinggi (CM) Lebar (CM) Catatan Harga (RM) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. J (Grids Board) 11Gloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Ninja clausesDocumento1 páginaNinja clausesGloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- SM HOLY TRINITY, TAWAU ENGLISH FORM 4 YEARLY PLANDocumento7 páginasSM HOLY TRINITY, TAWAU ENGLISH FORM 4 YEARLY PLANGloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- SM HOLY TRINITY, TAWAU ENGLISH FORM 4 YEARLY PLANDocumento7 páginasSM HOLY TRINITY, TAWAU ENGLISH FORM 4 YEARLY PLANGloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Teknik Menjawab SainsDocumento13 páginasTeknik Menjawab SainsGloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Soalan SPM 2014 BI PDFDocumento22 páginasSoalan SPM 2014 BI PDFNooraina IdrisAinda não há avaliações
- My Greatest Achievement - SEO Optimized Title for Idea Box DocumentDocumento3 páginasMy Greatest Achievement - SEO Optimized Title for Idea Box DocumentGloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- F3 Science Yearly Plan PBS 2016Documento17 páginasF3 Science Yearly Plan PBS 2016Gloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Clauses at the Mall AnalysisDocumento2 páginasClauses at the Mall Analysisshiveta1chaitali4511Ainda não há avaliações
- Scan 1Documento1 páginaScan 1Gloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Teknik Menjawab SainsDocumento13 páginasTeknik Menjawab SainsGloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Graphic Organiser For Essay WritingDocumento2 páginasGraphic Organiser For Essay WritingGloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Closet in Meaning 1Documento1 páginaCloset in Meaning 1Gloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- St Anthony Church Batu 18 Lahad DatuDocumento1 páginaSt Anthony Church Batu 18 Lahad DatuGloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- f2 Eng Jsu Exam 1 2016Documento4 páginasf2 Eng Jsu Exam 1 2016Gloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Form 3 Induction Set (Set 2)Documento3 páginasForm 3 Induction Set (Set 2)Gloria NguAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 1 - Introduction To Plumbing Module 1-DEFINITIONDocumento85 páginasTopic 1 - Introduction To Plumbing Module 1-DEFINITIONJersey PerlasAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen ChemistryDocumento3 páginasNitrogen ChemistryjammyjammersAinda não há avaliações
- Marshall's Reagent: Origins, Modifications, and New ApplicationsDocumento2 páginasMarshall's Reagent: Origins, Modifications, and New Applicationso_l_0Ainda não há avaliações
- Jorge Menacho - ChileDocumento45 páginasJorge Menacho - ChileBelen TapiaAinda não há avaliações
- Dust CleanerDocumento2 páginasDust CleanercendraAinda não há avaliações
- Enzymes and Their ClassificationDocumento30 páginasEnzymes and Their ClassificationSadia DinAinda não há avaliações
- Klueberfood NK1 Z 8 001 Spray GB enDocumento2 páginasKlueberfood NK1 Z 8 001 Spray GB enHicham BoukhariAinda não há avaliações
- PBL Chemistry MCQSDocumento18 páginasPBL Chemistry MCQSMaazullahAinda não há avaliações
- Maximising Namibia's copper value with Tschudi's refined cathodeDocumento22 páginasMaximising Namibia's copper value with Tschudi's refined cathodeMuhamad IchlasAinda não há avaliações
- Acids 1Documento22 páginasAcids 1Pratima JainAinda não há avaliações
- Atoms and Chemical Formulae ExplainedDocumento70 páginasAtoms and Chemical Formulae ExplainedAzie Nurul Akhtar75% (4)
- Submis 2Documento14 páginasSubmis 2Cao Chen-RuiAinda não há avaliações
- Iodine Test For StarchDocumento2 páginasIodine Test For StarchNoora MubarakAinda não há avaliações
- Hardness Removal MethodsDocumento5 páginasHardness Removal MethodsShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Ch18.pdf Aldehyde and Ketone PDFDocumento43 páginasCh18.pdf Aldehyde and Ketone PDFShakesha HemmingsAinda não há avaliações
- ITP CommissioningDocumento1 páginaITP CommissioningKannan GnanaprakasamAinda não há avaliações
- Flyer ChameleoBoost ConsolDocumento26 páginasFlyer ChameleoBoost ConsolAnchita MitraAinda não há avaliações
- Shale Oil Impacts on RefiningDocumento24 páginasShale Oil Impacts on RefiningAnonymous NmOXutCKAinda não há avaliações
- Silicate DaluminiumDocumento1 páginaSilicate DaluminiumrosemaryAinda não há avaliações
- B.Sc I yr CHEMISTRY SYLLABUS SEMESTER IDocumento30 páginasB.Sc I yr CHEMISTRY SYLLABUS SEMESTER ITitikshaAinda não há avaliações
- THE ION PRODUCT CONSTANT OF WATER - StudentsDocumento26 páginasTHE ION PRODUCT CONSTANT OF WATER - StudentsJanne Lorraine Garcia-EleazarAinda não há avaliações
- Aquatrol Safety Relief Valve Series GuideDocumento36 páginasAquatrol Safety Relief Valve Series GuideALEJANDROAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of Vitamin Content in Sample Tablets by TitrationDocumento2 páginasDetermination of Vitamin Content in Sample Tablets by TitrationmagicianchemistAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation KPTDocumento79 páginasPresentation KPTNor Fatihah Ab Malek100% (1)
- Potential of Indonesian Palm Oil Biomass for Bioethanol ProductionDocumento15 páginasPotential of Indonesian Palm Oil Biomass for Bioethanol ProductionKomanghAinda não há avaliações