Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Put Everything in Motion? The Conflict Is Introduced and The Situation Intensifies Through The RISING ACTION
Enviado por
tchristianberwicksdoDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Put Everything in Motion? The Conflict Is Introduced and The Situation Intensifies Through The RISING ACTION
Enviado por
tchristianberwicksdoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
I.
Short Story
The short story was first formally defined in 1842 by Edgar Allen Poe as an artistic composition controlled to produce
a single unified effect.
The short story is, in the broadest sense, a prose narrative that can be told or read in a single sitting.
From this point of view, the short story is the oldest and most natural form of prose fiction.
II. Terms:
1. Prose- is unmetered, unstructured writing.Prose is the opposite of Poetry
Ex. of prose: Short Story, non-fiction
2. Fiction- A prose story based on the imagination of the author
3. Plot- A plot is the sequence of events that make up a story. The action of the plot progresses because of a conflict
between opposing forces/ conflicts.
Note: Of course, this "sequence" doesn't necessarily have to be in order - detective stories or thrillers can often work
backwards or jump from one event to another - however, everything does
come together. Keep in mind that stories can b e plot driven, character driven or theme driven.
4. Conflict- A struggle between opposing forces (There are two types)
a. Internal conflict- A conflict within the mind of a character; self-imposed challenges
i. Man vs. Self
b. External conflict- A conflict that occurs outside the person.
i. Man vs. Man
ii. Man vs. Nature
iii. Man vs. Society
iv. Man vs. Supernatural / Fate
v. Man vs. Technology
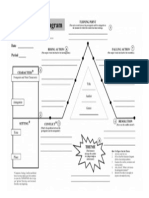
5. Plot structure:
a. Exposition- This is the introduction of story background information that is needed to properly understand
it. The part of the work that introduces the characters, the setting and the basic situation. The inciting
incident occurs here the initial event which triggers the rest of the story. In other words, what was it that
put everything in motion? The conflict is introduced and the situation intensifies through the RISING ACTION.
b. Rising Action- All events that occur before the climax. During this time, the events intensify the conflict.
Twists and turns occur in the plot.
Note: For example, in Harry Potter and the Sorcerers Stone, Harry must go through a set of tasks to reach
where the sorcerers stone is hidden where he will have the final battle. These tasks are the rising action,
and the final battle would be considered the climax.
c. Climax-The high point of interest or suspense in the story. The conflict is about to be revealed.
d. Falling Action- Events that occur after the climax. This is where the conflict unravels and leads to the
resolution.
e. Resolution- The end of the conflict; Things are explained; Often involves a change or an insight.
f. Denouement- Any events that untie or occur after the resolution. (Often stories are not resolved.
g. **Draw Plot Structure
6. Inciting incident- The incident which introduces the central conflict
7. Setting-The time and place of action
8. Characterization- The method (s) used by an author to create and develop the characters in the story.
a. Methods of characterization:
i. What a character says
ii. The characters actions
iii. The characters thoughts
iv. What others say about the character
v. How the character looks: Appearance
9. Characters-are the people, animals or sometimes objects who participate in the action of a literary work. A character
may be main or minor, depending on their roles in the short story. Successful characters are not the only individuals
but also in some way examples of the universal human conditions.
EX. Characters in Little Red Riding Hood:
LRRH, The Big Bad Wolf, The Woodsman, Grandmother
Protagonist: Red Antagonist: The Wolf
10. Round character-A complicated character that exhibits numerous qualities or traits. The reader can see many sides of
the character. The author develops this type of character in the story.
11. Flat character- A character that has only one or two traits. The author does not develop this type of character.
12. Antagonist Villain / Bad Guy
13. Protagonist Hero/ Good Guy
Narrator/ point of view
14. Narrator- The character who tells the story (does not have to be a person
15. Point of view- The relationship of the narrator/ storyteller to the story. The perspective or vantage point from which
the story is told
a. First person The narrator in the story tells the story directly using I, we, me and / or us.
b. Third person- The narrator speaks in third person using he, she it, and they.
c. Third Person Omniscient The narrator has an all-knowing point of view. The narrator supplies more
information about all the characters and events than any one character could know. The narrator knows
what every character is thinking.
16. Theme- The main idea or thread that holds the story together. The central idea in a literary work.
17. Universal Theme- A theme that is timeless. All people can relate to the theme. Example: Love, Hate, Death, Betrayal,
free will vs. fate, good vs. evil.
18. Symbol- Anything that stands for or represents something else.
19. Inference- A reasonable conclusion drawn from evidence
20. Denotation- The dictionary definition of a word
21. Connotation- A suggested, personal or implied definition of a word
22. Foreshadowing- The use of hints or clues to suggest what will happen later in the story.
23. Flashback- Takes the reader back to an event/ action that happened in the past
24. Mood- The climate or feeling based on characters, setting, plot, etc.; The atmosphere; the feeling created in the reader
by a literary work .
25. Tone-The authors attitude toward the readers and toward the subject. Formal or informal; friendly or distant;
personal or impersonal.
26. Irony- The general name given to literary techniques that involve surprising, interesting or amusing contradiction.
27. Local/ Global color- The use of characters and details from a specific geographic region
28. Personification- Giving human-like characteristics to a non-living/ non-human object
29. Anecdote- A brief story about an amusing, interesting or strange event
30. Allegory- A form of extended metaphor, in which objects, persons, and actions in a narrative, are equated with the
meanings that lie outside the narrative itself. The underlying meaning has moral, social, religious, or political
significance, and characters are often personifications of abstract ideas as charity, greed, or envy.
Thus an allegory is a story with two meanings, a literal meaning and a symbolic meaning.
31. Figurative Language- Writing or work that is interpreted beyond the literal meaning.
32. Metaphor- A comparison of two unlike things NOT using like or as
a. Our school is a mighty fortress
b. Her grandmother is a superhero
33. Simile- A comparison of two unlike things USING like or as
a. She is like a rose
b. "Good coffee is like friendship: rich and warm and strong
Você também pode gostar
- The Short Story: World Literature Mrs. Theresa ChristianDocumento19 páginasThe Short Story: World Literature Mrs. Theresa ChristiantchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Literary Term DefDocumento6 páginasLiterary Term DefWolf Borst100% (1)
- ModulefictionDocumento8 páginasModulefictionMarie stokesAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 11 Notes 2019updateDocumento8 páginasGrade 11 Notes 2019updateapi-247699970Ainda não há avaliações
- CBCS NotesDocumento10 páginasCBCS NotesAryan GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Elements of ProseDocumento40 páginasElements of Prosekate villanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Eng4u Elements Devices Active ReadingDocumento8 páginasEng4u Elements Devices Active ReadingΑθηνουλα Αθηνα100% (1)
- Genres of LiteratureDocumento21 páginasGenres of LiteratureMaricris Cahuyong CadienaAinda não há avaliações
- Pointer To Review: Tpes of Poetry 1. Narrative PoetryDocumento12 páginasPointer To Review: Tpes of Poetry 1. Narrative PoetryLeslie PasionAinda não há avaliações
- Elemets of FictionDocumento4 páginasElemets of FictionLaura Sophia BondocAinda não há avaliações
- A Lesson Plan in CNF2Documento4 páginasA Lesson Plan in CNF2HappyNeversmilesAinda não há avaliações
- Literary TermsDocumento3 páginasLiterary Termstrishamae pimentelAinda não há avaliações
- Module 3 Creative WritingDocumento40 páginasModule 3 Creative Writingsydney.socoAinda não há avaliações
- 8 Elements of Fiction - ANSWER KEYDocumento5 páginas8 Elements of Fiction - ANSWER KEYDavid Velez GonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- BAHASA DAN SASTRA INGGRIS Short StoryDocumento11 páginasBAHASA DAN SASTRA INGGRIS Short StoryMutia ArumAinda não há avaliações
- Fiction (Final)Documento16 páginasFiction (Final)Hasnor DS50% (4)
- Elements of StoryDocumento38 páginasElements of StoryEmily S. NañadiegoAinda não há avaliações
- CNF LESSON 5-6 WEEK 5-6 ADocumento45 páginasCNF LESSON 5-6 WEEK 5-6 AGuillermo AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- ProseDocumento5 páginasProseAJ LlegoAinda não há avaliações
- LiteratureDocumento8 páginasLiteraturePearl Jean Quimson MedallaAinda não há avaliações
- Literary Elements Techniques and Devices 2023 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocumento16 páginasLiterary Elements Techniques and Devices 2023 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The Worldorangeshibuya99Ainda não há avaliações
- Short Story ElementsDocumento5 páginasShort Story ElementsMina Miller100% (1)
- Literary Elements HandoutDocumento7 páginasLiterary Elements HandoutSusana Dalmao100% (1)
- 9-5.basic Elements of A Short StoryDocumento4 páginas9-5.basic Elements of A Short StoryMaureen Mae Estanol100% (1)
- PAGE 1 Liked For This YearDocumento2 páginasPAGE 1 Liked For This YearJake MinearAinda não há avaliações
- LESSON 5 Short Story WritingDocumento13 páginasLESSON 5 Short Story WritingTanya HerrellAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1 Literature in GeneralDocumento5 páginasLesson 1 Literature in GeneralCarmie Lactaotao DasallaAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Quarter LESSON 2Documento7 páginas2nd Quarter LESSON 2Salve BayaniAinda não há avaliações
- I. Definitions: Literary TermsDocumento4 páginasI. Definitions: Literary TermsKristina UhlířováAinda não há avaliações
- A Short Story Is A Brief Work of 2Documento10 páginasA Short Story Is A Brief Work of 2airagarcia_18Ainda não há avaliações
- Short Story ElementsDocumento27 páginasShort Story ElementsGlormarie Nieves100% (2)
- Creative Nonfiction Handout 1 HUMSS 12Documento3 páginasCreative Nonfiction Handout 1 HUMSS 12Kyla BallesterosAinda não há avaliações
- Hog10m1 M3Documento4 páginasHog10m1 M3Verna Jane NatividadAinda não há avaliações
- All About Fiction: Subject Teacher: Ms. Janessa Mae N. DalimoconDocumento35 páginasAll About Fiction: Subject Teacher: Ms. Janessa Mae N. DalimoconPio DalimoconAinda não há avaliações
- FictionDocumento17 páginasFictionMaKenJi100% (1)
- What Is Literature?: Oral or Traditional Literature Has Some Form of Stories Often Told by Word of MouthDocumento7 páginasWhat Is Literature?: Oral or Traditional Literature Has Some Form of Stories Often Told by Word of MouthHadjer TalbiAinda não há avaliações
- Literary Analysis - Elements of LiteratureDocumento5 páginasLiterary Analysis - Elements of LiteratureEistellaAinda não há avaliações
- ContemporaryDocumento37 páginasContemporaryEdnylyn Joyce CapaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson: Reading and Writing FictionDocumento4 páginasLesson: Reading and Writing FictionTrix DizonAinda não há avaliações
- Definition of The Short StoryDocumento4 páginasDefinition of The Short Storycrezantel100% (1)
- CNF Lesson 2 ReviewerDocumento2 páginasCNF Lesson 2 ReviewerGabriel SakrilianteAinda não há avaliações
- Aspects of The NovelDocumento5 páginasAspects of The Novelanisha.patandin13Ainda não há avaliações
- Romeo and Juliet Literary DevicesDocumento5 páginasRomeo and Juliet Literary Devicesapi-26212985Ainda não há avaliações
- v061 Feliciano, Ricky A. AssignmentDocumento2 páginasv061 Feliciano, Ricky A. AssignmentRicky FelicianoAinda não há avaliações
- BAHASA DAN SASTRA INGGRIS Short StoryDocumento11 páginasBAHASA DAN SASTRA INGGRIS Short StoryMutia ArumAinda não há avaliações
- San Jose, Antique High School Department: St. Anthony'S CollegeDocumento4 páginasSan Jose, Antique High School Department: St. Anthony'S Collegeshey mahilumAinda não há avaliações
- Elements of FictionDocumento9 páginasElements of FictionEmilce Soledad ToneattiAinda não há avaliações
- 10-25 Backgroung Info-Terms To KnowDocumento3 páginas10-25 Backgroung Info-Terms To KnowlaysuAinda não há avaliações
- Creative Non Fiction q3 Week 4Documento18 páginasCreative Non Fiction q3 Week 4mary ann gulenAinda não há avaliações
- NarrativeDocumento8 páginasNarrativeEvaAinda não há avaliações
- CNF Lesson 1Documento37 páginasCNF Lesson 1Jewel PascuaAinda não há avaliações
- Creative Writing 6Documento4 páginasCreative Writing 6reamiecimene03Ainda não há avaliações
- Lit ReviewerDocumento10 páginasLit ReviewerMonn BilledoAinda não há avaliações
- Elements of A Short StoryDocumento3 páginasElements of A Short StoryKans SisonAinda não há avaliações
- Elements of DramaDocumento12 páginasElements of DramaGleann CorpuzAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Fiction (Handouts)Documento3 páginasUnit 3 Fiction (Handouts)creative writingAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Fiction (Handouts)Documento3 páginasUnit 3 Fiction (Handouts)creative writingAinda não há avaliações
- Elements of FictionDocumento6 páginasElements of FictionCzarina Pauline CunananAinda não há avaliações
- OMMResearch ReportRubricDocumento1 páginaOMMResearch ReportRubrictchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Problem/ Solution Brainstorm SheetDocumento1 páginaProblem/ Solution Brainstorm SheettchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Problemsolution Info Sheet 1Documento2 páginasProblemsolution Info Sheet 1tchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 Outline DetailsDocumento1 página2018 Outline Detailstchristianberwicksdo0% (1)
- Problemsolution Info Sheet 1Documento2 páginasProblemsolution Info Sheet 1tchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- One Note Notebook - Research Notes/ FormatDocumento3 páginasOne Note Notebook - Research Notes/ FormattchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Romeo and JulietDocumento11 páginasIntroduction To Romeo and JuliettchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Evidence List Contents of A Dead Man's PocketsDocumento1 páginaEvidence List Contents of A Dead Man's PocketstchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Of Mice and Men ResearchDocumento2 páginasOf Mice and Men ResearchtchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Video Comments Jane ElliotDocumento1 páginaVideo Comments Jane ElliottchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Monday, - : Bell Ringer / Closure FormDocumento2 páginasMonday, - : Bell Ringer / Closure FormtchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Solution RubricDocumento1 páginaProblem Solution RubrictchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Paragraph Essay Format Theresa ChristianDocumento1 página5 Paragraph Essay Format Theresa ChristiantchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Conducting Surveys For Newspaper ArticlesDocumento6 páginasConducting Surveys For Newspaper ArticlestchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Problemsolution Info Sheet 1Documento2 páginasProblemsolution Info Sheet 1tchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Articles, Essays and SpeechesDocumento20 páginasArticles, Essays and Speechestchristianberwicksdo100% (4)
- Editoria PowerPointlDocumento7 páginasEditoria PowerPointltchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Poetry TermsDocumento2 páginasPoetry TermstchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Two Tramps in Mud TimeDocumento1 páginaTwo Tramps in Mud TimetchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Plot StructureDocumento1 páginaPlot StructuretchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Problem/Solution Essay Draft Essay TopicDocumento3 páginasProblem/Solution Essay Draft Essay TopictchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- 5-Para Solution OutlineDocumento1 página5-Para Solution OutlinetchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Scarlet Ibis WebquestDocumento3 páginasScarlet Ibis WebquesttchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Articles, Essays and SpeechesDocumento20 páginasArticles, Essays and Speechestchristianberwicksdo100% (4)
- SAMPLEMISSINGPERSONANDTEMPLATEDocumento4 páginasSAMPLEMISSINGPERSONANDTEMPLATEtchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- CaskreportrevisedDocumento1 páginaCaskreportrevisedtchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Berwick Police Department Berwick High School 1100 Fowler Avenue Berwick, Pennsylvania 18603Documento2 páginasBerwick Police Department Berwick High School 1100 Fowler Avenue Berwick, Pennsylvania 18603tchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Unfortunate Fortunato RubricDocumento2 páginasUnfortunate Fortunato RubrictchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Berwick Police Department Berwick High School 1100 Fowler Avenue Berwick, Pennsylvania 18603Documento2 páginasBerwick Police Department Berwick High School 1100 Fowler Avenue Berwick, Pennsylvania 18603tchristianberwicksdoAinda não há avaliações
- Barbara H. Watters - Horary Astrology and The Judgement of Events PDFDocumento226 páginasBarbara H. Watters - Horary Astrology and The Judgement of Events PDFyuorme88% (8)
- Ethics: Ryanbalbuenakatigbak Universityof BatangasDocumento35 páginasEthics: Ryanbalbuenakatigbak Universityof BatangasFiroSmokeAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamics of Organisational CultureDocumento10 páginasDynamics of Organisational CulturesahilAinda não há avaliações
- The Twelve Steps of SLAADocumento1 páginaThe Twelve Steps of SLAAAdam WhiteAinda não há avaliações
- Psychology PDFDocumento5 páginasPsychology PDFKarlaAinda não há avaliações
- Things To Do On The Blessed 10 Days of Dhul Hijjah PDFDocumento5 páginasThings To Do On The Blessed 10 Days of Dhul Hijjah PDFRoshan ZaheerAinda não há avaliações
- Identity-Protective Cognition ThesisDocumento37 páginasIdentity-Protective Cognition ThesisJohn BurkeAinda não há avaliações
- Violence in Football (Soccer) : Overview, Prevalence, and Risk FactorsDocumento12 páginasViolence in Football (Soccer) : Overview, Prevalence, and Risk FactorsDušan ČolovejićAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Unit 3 Marriage & Family Life - IGCSE Religious StudiesDocumento27 páginasRevision Unit 3 Marriage & Family Life - IGCSE Religious Studiesaneeshj1Ainda não há avaliações
- Book of Proceedings EsdParis2018 OnlineDocumento535 páginasBook of Proceedings EsdParis2018 Onlineca taAinda não há avaliações
- Using Games in Teaching English To Young LearnersDocumento30 páginasUsing Games in Teaching English To Young LearnersRatri Sudarno Putri82% (11)
- (Mebooksfree Com) An&int&men&hea&nur&wry&1st PDFDocumento272 páginas(Mebooksfree Com) An&int&men&hea&nur&wry&1st PDFDeepak KumarAinda não há avaliações
- What Anarchy Isn't - Larken RoseDocumento41 páginasWhat Anarchy Isn't - Larken RoseEscudoVoluntario100% (8)
- Solution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Documento18 páginasSolution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Gulshan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Approaches and Innovation in PsychologyDocumento206 páginasModern Approaches and Innovation in Psychologykohinoorncmaip67% (3)
- Dangerous Liaisons The Marriages and Divorces of Marxism and FeminismDocumento155 páginasDangerous Liaisons The Marriages and Divorces of Marxism and FeminismNia FromeAinda não há avaliações
- Flusser - About The Word DesignDocumento2 páginasFlusser - About The Word DesignMiryam GonzálezAinda não há avaliações
- The 327 TOEFL Words You Need To KnowDocumento18 páginasThe 327 TOEFL Words You Need To KnowJennifer Ponce Cori SjlAinda não há avaliações
- Barangay Ambassador: Republic of The Philippines Province of Benguet Municipality of TublayDocumento3 páginasBarangay Ambassador: Republic of The Philippines Province of Benguet Municipality of TublayKathlyn Ablaza100% (1)
- Anatomical Terms of MotionDocumento21 páginasAnatomical Terms of MotionDana Karem100% (1)
- The Council of FlorenceDocumento35 páginasThe Council of FlorenceakimelAinda não há avaliações
- The Secret Codes The Formula of Mind Control-2015Documento136 páginasThe Secret Codes The Formula of Mind Control-2015Joe HinderbergenAinda não há avaliações
- Causes of Failure of Housing ProjectsDocumento7 páginasCauses of Failure of Housing Projectschill007Ainda não há avaliações
- Legal Ethics CasesDocumento126 páginasLegal Ethics CasesKaye TolentinoAinda não há avaliações
- General Management TopicsDocumento25 páginasGeneral Management TopicsEkala XuhalxAinda não há avaliações
- Apropiacion - Marcel Duchamp - Isaac PDFDocumento39 páginasApropiacion - Marcel Duchamp - Isaac PDFIsaac OlveraAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Cosmology Matt Roots - IndexDocumento9 páginasIntroduction To Cosmology Matt Roots - IndexTiago MarquesAinda não há avaliações
- Buddhism and Medicine An Anthology of PRDocumento12 páginasBuddhism and Medicine An Anthology of PRrwoestenAinda não há avaliações
- Present Simple and Present ContinuousDocumento10 páginasPresent Simple and Present ContinuousNgan HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Listening Styles and Listening StrategiesDocumento4 páginasListening Styles and Listening StrategiesBladyPanopticoAinda não há avaliações