Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NCP Anemia
Enviado por
mashup100%(3)100% acharam este documento útil (3 votos)
9K visualizações1 páginaAnemia related to gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to Aspirin use
Título original
Ncp Anemia
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoAnemia related to gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to Aspirin use
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
100%(3)100% acharam este documento útil (3 votos)
9K visualizações1 páginaNCP Anemia
Enviado por
mashupAnemia related to gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to Aspirin use
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
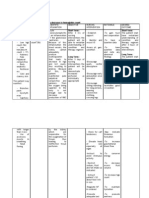
Nursing Care Plan
Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Objectives:
Patient appears
weak and
lethargic, sub
conjunctiva is pale,
lips are dry and
pale, slow capillary
refill, skin is cold,
dry with poor skin
turgor, Palms and
sole of feet is pale.
Hgb: 77g/L (140-
160)
Hct: 22% (40-54)
Deficient fluid
volume related
to active fluid
loss due to
gastrointestinal
bleeding as
evidenced by
Hgb of 77g/L
and Hct 22%
Severe bleeding
may reduce the
flow of blood to
the brain, causing
confusion,
disorientation,
sleepiness, and
even extremely
low blood
pressure (shock).
Slow, chronic
blood loss may
cause symptoms
and signs of
anemia (such as
weakness, easy
fatigue, paleness
[pallor], chest
pain, and
dizziness).
Source: Merck
Manual 2012
edition p.213
Short term:
After 8 hours of
nursing
intervention the
patient will be
able to Exhibit
relevant normal
levels of
laboratory value
such as in
hemoglobin and
red blood cell
level
Long term:
After 3 days of
nursing
intervention the
patient will be
able to maintain
adequate fluid
and electrolyte
balance.
Independent:
-Assess patient general
condition and establish
rapport
-Assess vital signs
-Raise bedside rails
-Do bed bath and
changing of bed linens
- Note patients
individual physiological
response to bleeding
-Monitor intake and
output (I&O), and
correlate with weight
changes.
- Maintain bed rest;
prevent vomiting and
straining at stool.
- Provide clear/bland
fluids when intake is
resumed. Avoid
caffeinated and
carbonated beverages
Dependent:
-Facilitate in blood
transfusion
- Administer
medications, as indicated
Collaborative:
- Monitor laboratory
studies, e.g.:Hb, Hct, RBC
count;
-To know condition of
patient and to gain trust
and cooperation from the
client
- To gather baseline data
- To provide safety
- To promote hygiene
- Worsening of symptoms
may reflect continued
bleeding or inadequate
fluid replacement.
- Provides guidelines for
fluid replacement.
- Activity/vomiting
increases intra-abdominal
pressure and can lead to
further bleeding.
- Caffeine and carbonated
beverages stimulate
hydrochloric acid (HCl)
production, possibly
potentiating rebleeding.
- Transfused all blood
components that are low
in the laboratory results.
- Histamine (H2)-receptor
antagonists may be given
parenterally during
bleeding to reduce HCL
acid production
-To monitor effectiveness
of therapy and to monitor
patients status.
Short term:
After 8 hours of
nursing intervention
the patient had to
Exhibited relevant
normal levels of
laboratory value
such as in
hemoglobin and red
blood cell level
Long term:
After 3 days of
nursing intervention
the patient had
maintained
adequate fluid and
electrolyte balance.
Você também pode gostar
- Nursing Care Plan AnemiaDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Anemiaderic89% (133)
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis82% (33)
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocumento10 páginasAnatomy and Physiology Reviewermashup100% (14)
- NCP Anemia Format 1Documento2 páginasNCP Anemia Format 1Jha Jei Quiambao100% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageCyrus De Asis92% (25)
- 5 Levels of HealingDocumento7 páginas5 Levels of HealingFlorencia Maria Rodriguez Colindres100% (1)
- Anemia NCPDocumento10 páginasAnemia NCPCharmz_asherah100% (9)
- NCP For DehydrationDocumento3 páginasNCP For Dehydrationpeter_degamo200025% (4)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodDocumento2 páginasIneffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodYllejann Manez60% (20)
- NCP - AnemiaDocumento7 páginasNCP - AnemiaJulian Ivaran Naceda90% (10)
- Anemia Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 páginasAnemia Nursing Care PlanMaverick Lim100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan-AnemiaDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan-AnemiaAdrian Mallar100% (2)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocumento2 páginasImpaired Urinary EliminationHaon Anasu67% (3)
- Nursing Management A. Nursing Care PlanDocumento12 páginasNursing Management A. Nursing Care Planmabzbutterfly69% (13)
- CHF Concept MapDocumento4 páginasCHF Concept MapLisaSanders99Ainda não há avaliações
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento9 páginasDecreased Cardiac OutputChinita Sangbaan75% (4)
- Shy Narcissist (Akhtar) PDFDocumento10 páginasShy Narcissist (Akhtar) PDFcuriositykillcatAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelody B. MiguelAinda não há avaliações
- NCP AnemiaDocumento3 páginasNCP AnemiaJadeAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 páginaHyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanRenie Serrano100% (1)
- NCP Arra AnemiaDocumento2 páginasNCP Arra AnemiaShin GuevaraAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan NephritisDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Nephritisderic82% (17)
- NCP For PoisoningDocumento2 páginasNCP For PoisoningLorie Yvonne Quibin Agullana100% (1)
- NCP AnemiaDocumento6 páginasNCP AnemiaJudeLax100% (1)
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocumento4 páginasNCP - Activity IntoleranceRoyce Vincent TizonAinda não há avaliações
- NCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento3 páginasNCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeNica RespondoAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Volume Deficit (GI Bleeding) NCPDocumento2 páginasFluid Volume Deficit (GI Bleeding) NCPReina Samson100% (1)
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocumento3 páginasNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleAinda não há avaliações
- NCP EdemaDocumento1 páginaNCP EdemaKurtt Evan Valino100% (1)
- EdemaDocumento2 páginasEdemaVirus50% (2)
- NCP For CHDDocumento2 páginasNCP For CHDMonica Rivera100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Acute Renal FailureDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Acute Renal FailureKian HerreraAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM)Documento1 páginaDiabetes Mellitus (DM)Bheru LalAinda não há avaliações
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Sickle Cell Anemia: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocumento1 páginaNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Sickle Cell Anemia: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Renal FailureMark Jason Rabadan100% (1)
- Ncp.-Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento1 páginaNcp.-Fluid Volume DeficitAdia Cavrinni De JesusAinda não há avaliações
- NCP 1Documento1 páginaNCP 1hsiriaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan 1 DiagDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan 1 Diagguysornngam100% (1)
- Renal Failure NCPDocumento3 páginasRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanAinda não há avaliações
- Pre NCP FatigueDocumento2 páginasPre NCP Fatigueirisjabines67% (3)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 páginaIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotAinda não há avaliações
- Anemia NCPDocumento20 páginasAnemia NCPNursidar Pascual Mukattil80% (5)
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocumento2 páginasAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 páginasNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- NCP - Patient For Electrocardiogram (ECG)Documento1 páginaNCP - Patient For Electrocardiogram (ECG)SelwynVillamorPatenteAinda não há avaliações
- NCP 3 DEFICIT IN FLUID VOLUMEDocumento2 páginasNCP 3 DEFICIT IN FLUID VOLUMEGenEsis CarandangAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 páginasFluid Volume DeficitRuby AnneAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento12 páginasFluid Volume DeficitKersee GailAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Fluid Volume Excess Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlansDocumento3 páginas1 Fluid Volume Excess Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlansMichael Baylon DueñasAinda não há avaliações
- Algorithms For IV Fluids Replacement in Midgets and Poodles PDFDocumento5 páginasAlgorithms For IV Fluids Replacement in Midgets and Poodles PDFAnonymous XbmV9JU5Ainda não há avaliações
- Fluid Imbalance (NCP)Documento9 páginasFluid Imbalance (NCP)Putry RainismAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing DiagnosisDocumento4 páginasNursing DiagnosisMavy AndresAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento2 páginasNCP For Nephrotic SyndromeLee Jenny100% (5)
- Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento1 páginaDeficient Fluid VolumeSheila ErpeloAinda não há avaliações
- Seminars 2019 PDFDocumento200 páginasSeminars 2019 PDFpaingmyintAinda não há avaliações
- NCP DMDocumento21 páginasNCP DMKate ManalastasAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 IF Fluids in AdultsDocumento19 páginas2013 IF Fluids in AdultsltgcanlasAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento2 páginasNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaAinda não há avaliações
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Adults in Hospital Algorithm Poster Set 191627821Documento5 páginasIntravenous Fluid Therapy in Adults in Hospital Algorithm Poster Set 191627821crsscribdAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocumento23 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentWendy EscalanteAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento28 páginasNursing Care PlanChristine Karen Ang Suarez67% (3)
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocumento40 páginasFluid and ElectrolytesMaria Kathrina NadayaoAinda não há avaliações
- High Yield OSCE - SurgeryDocumento2 páginasHigh Yield OSCE - SurgerymashupAinda não há avaliações
- Nag2019 PDFDocumento288 páginasNag2019 PDFmashupAinda não há avaliações
- National Tuberculosis Control Program Manual of Procedures 5th EditionDocumento192 páginasNational Tuberculosis Control Program Manual of Procedures 5th EditionBlue Pielago100% (9)
- Importance of MicrobiologyDocumento1 páginaImportance of MicrobiologymashupAinda não há avaliações
- QuestionsDocumento3 páginasQuestionsmashupAinda não há avaliações
- Physical AssessmentDocumento2 páginasPhysical AssessmentmashupAinda não há avaliações
- Hot Cold CompressDocumento3 páginasHot Cold CompressmashupAinda não há avaliações
- CTT, Bed Sore, Diabetic FootDocumento4 páginasCTT, Bed Sore, Diabetic FootmashupAinda não há avaliações
- Hot Cold CompressDocumento3 páginasHot Cold CompressmashupAinda não há avaliações
- Collaboration:: The Possibility of Acidosis Accompanied byDocumento2 páginasCollaboration:: The Possibility of Acidosis Accompanied bymashupAinda não há avaliações
- Physical AssessmentDocumento2 páginasPhysical Assessmentmashup100% (1)
- Medical-Surgical Nursing I & Ii Course Description Text:: NCLEX-PN Examination (5Documento89 páginasMedical-Surgical Nursing I & Ii Course Description Text:: NCLEX-PN Examination (5Musa yohanaAinda não há avaliações
- Module 8 PERDEVDocumento4 páginasModule 8 PERDEVmich100% (3)
- HDJDDocumento64 páginasHDJDploxis10Ainda não há avaliações
- PB - Using A Spirometer To Investigate Human Lung Function SsDocumento6 páginasPB - Using A Spirometer To Investigate Human Lung Function SsMariam AymanAinda não há avaliações
- People v. VenturaDocumento1 páginaPeople v. VenturaAphrAinda não há avaliações
- Naomi Adams AAT Lit ReviewDocumento23 páginasNaomi Adams AAT Lit Reviewzb789Ainda não há avaliações
- Irrigation in EndodonticsDocumento7 páginasIrrigation in EndodonticsAasim YousufAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Documentation ReportDocumento4 páginasNursing Documentation ReportRicco Valentino CoenraadAinda não há avaliações
- Transgender SpeechDocumento61 páginasTransgender Speechjreljosh1994100% (1)
- MK Sastry Nada Protocol The Grassroots TreatmentDocumento12 páginasMK Sastry Nada Protocol The Grassroots Treatmentwilyanto yangAinda não há avaliações
- Gensco Pharma Announces ColciGel®, A New Transdermal Medication Indicated For The Treatment of Acute Gout Flares in AdultsDocumento3 páginasGensco Pharma Announces ColciGel®, A New Transdermal Medication Indicated For The Treatment of Acute Gout Flares in AdultsPR.comAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Journal of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy July-Sep 2009 PDFDocumento116 páginasIndian Journal of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy July-Sep 2009 PDFAshoka VanjareAinda não há avaliações
- Multi Axial AssessmentDocumento14 páginasMulti Axial AssessmentPranay PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- 02-10 8 Applied Behavior Analysis or Lovaas Therapy For AutismDocumento4 páginas02-10 8 Applied Behavior Analysis or Lovaas Therapy For AutismAhmed AlghamdiAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Thinking QuestionsDocumento2 páginasCritical Thinking QuestionsJulie Ann EscartinAinda não há avaliações
- Guerilla CardioDocumento7 páginasGuerilla Cardiomishelll100% (1)
- AnalgesicDrugs Combinations in Thetreatment of Different Types of PainDocumento68 páginasAnalgesicDrugs Combinations in Thetreatment of Different Types of PainAnuj MairhAinda não há avaliações
- Coagulation DisordersDocumento26 páginasCoagulation DisordersLia pramita0% (1)
- Sexy Forever by Suzanne Somers - ExcerptDocumento20 páginasSexy Forever by Suzanne Somers - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group75% (4)
- Asthma by ConsensusDocumento87 páginasAsthma by ConsensusSatnam KaurAinda não há avaliações
- OT Sample Exam QuestionsDocumento4 páginasOT Sample Exam Questionsagatha2108Ainda não há avaliações
- HIMAS Handbook On Spa and MassageDocumento36 páginasHIMAS Handbook On Spa and MassageBenjie Eugenio67% (6)
- Active Cycle of Breathing TechniqueDocumento3 páginasActive Cycle of Breathing TechniqueSurya KalaAinda não há avaliações
- ACLS Practical Case Scenarios (1 June 2011)Documento15 páginasACLS Practical Case Scenarios (1 June 2011)nersAinda não há avaliações
- Broncho Pneumonia 1Documento28 páginasBroncho Pneumonia 1NocReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Mind Control Video - ConsciousnessDocumento2 páginasMind Control Video - ConsciousnesstanyatewaAinda não há avaliações
- Soft Tissue InjuryDocumento13 páginasSoft Tissue InjuryAhmad FauzanAinda não há avaliações
- P CPLDocumento10 páginasP CPLJean FlorencondiaAinda não há avaliações