Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
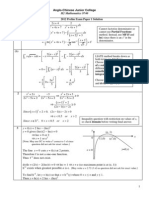
Sample Exam 1 EE 210
Enviado por
doomachaleyDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sample Exam 1 EE 210
Enviado por
doomachaleyDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SAN JOSE STATE UNIVERSITY
College of Engineering
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
EE210-2 Fall 2003
Date: 10/02/03
First Midterm Exam
(closed-book exam)
Exam Time: 20:30 21:45
Student: SOLUTION
Last, First M.I. (last 4 digit SS#)
Important notes
This is a closed-book, closed-note exam
Basic calculator is allowed
Derivative tables, integration tables, and transform tables are
provided
You are required to show your work clearly and in details for all
problems. Answer without showing your work will get ZERO credit
even if it was correct
You are required to BOX/UNDERLINE your final answers clearly for
full credit consideration
DO NOT UNSTABLE THE EXAM (absolutely!)
You can use both sides of the papers
Please follow the exam rule
When the exam time is over, please immediately stop working
on the exam and turn the exam in
Page 2 of 6
1. [20 pts] For a system with transfer function H(), input signal x(t) and output signal y(t). The
input signal and the system transfer function are as listed below:
x t
t
t
t
t
H
A
otherwise
c
b g
b g
= + <
=
< R
S
T
sin sin
;
1 2
1 2
0
By Fourier transform method, calculate y(t) for cases of:
a. 0 <
c
<
1
b.
1
<
c
<
2
Solution
a. 0 <
c
<
1
x t
t
t
t
t
X
Y H X A A
Y A y t A A
t
t
c c
c c
c
b g b g
b g b g b g
b g b g
= + =
F
H
G
I
K
J
+
F
H
G
I
K
J
= =
F
H
G
I
K
J
+
F
H
G
I
K
J
=
F
H
G
I
K
J
=
F
H
G
I
K
J
R
S
T
U
V
W
=
sin sin
;
sin
1 2
1 2
1 2
1
2 2
2 2
2
2
2
2
2
b.
1
<
c
<
2
x t
t
t
t
t
X
Y H X A A
Y A A
y t A A A
t
t
A
c c
c
c
b g b g
b g b g b g
b g
b g
= + =
F
H
G
I
K
J
+
F
H
G
I
K
J
= =
F
H
G
I
K
J
+
F
H
G
I
K
J
=
F
H
G
I
K
J
+
F
H
G
I
K
J
=
F
H
G
I
K
J
+
F
H
G
I
K
J
R
S
T
U
V
W
= +
sin sin
;
sin sin
1 2
1 2
1 2
1
1
1
1
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2
c
t
t
Page 3 of 6
2. [20 pts] For a system and signals as shown below:
a. For
b
=
m
, find Y() and sketch its amplitude spectrum (you must clearly label the sketch)
b. Find the system impulse response h(t)
Solution
a.
x t m t t X M M
M
A
A
otherwise
H
B
otherwise
Y H X
Y H X
AB
AB
otherwise
m
m
b
b m
m
m
a f a f a f b g b g
a f a f
a f a f a f
a f a f a f
b g
= = + +
=
+
R
S
|
T
|
=
< < + R
S
T
= =
= =
+ +
R
S
|
T
|
cos ; ;
;
0 0 0
0 0
0 0 0
1
2
1
2
0
0
0
0
For and
b.
h t H e d Be d Be d
B
Be d
B
Be d
B
t
t t
j t j t j t
j t j t
m
m
m
m m
b g b g
b g m r
= = +
= +
= +
+
+
+ +
z z z
z z
1
2
1
2
1
2
2 2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0 0
sin sin
AB
Y()
-
0
-
m
-
0
0
0
-
0
+
m
A
M()
-
m
0
m
H()
x(t)
y(t)
m(t)
cos
0
t
B
H()
-
0
0
0
b
b
Page 4 of 6
3. [20 pts] In time-domain, solve the differential equation below for the zero-state response and
the zero-input response
d y t
dt
dy t
dt
y t e t y
dy
dt
t
t
2
2
2
0
4 3 0 0 1 1
b g b g
b g b g + + = = =
=
; , ,
Solution
Zero-input response: There is no input but system responds to initial state. So:
d y t
dt
dy t
dt
y t t y
dy
dt
y t C e C e t
y C e C e C C
dy t
dt
C e C e C C
C C
y t e e t
zi zi
zi zi
zi
t
zi
t t
zi
zi
t
zi
t t
2
2
0
1 2
3
1
0
2
3 0
1 2
0
1
0
2
3 0
1 2
1 2
3
4 3 0 0 0 1 1
0
0 1 1
3 3 1 2
1 2 2 1
2 0
a f a f
a f a f
a f
a f a f
a f
a f
a f a f
a f
a f
a f
+ + = = =
= +
= + = + =
= = =
= =
=
=
=
; , ,
;
;
and and
Zero state response: Initial condition is zero and system responds to the input. So:
d y t
dt
dy t
dt
y t e t y
dy
dt
y t Ae
dy t
dt
Ae
d y t
dt
Ae
d y t
dt
dy t
dt
y t Ae Ae Ae Ae e A
y t e
y t C e C e e
zs zs
zs
t
t
p
t
p
t
p
t
p p
p
t t t t t
p
t
zs
t t
2
2
2
0
2 2
2
2
2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1 2
3 2
4 3 0 0 0 0
2 4
4 3 4 8 3 1
a f a f
a f a f
a f
a f a f
a f a f
a f
a f
a f
+ + = = =
= = =
+ + = + = = =
=
= +
; , ,
; ;
t
zs
zs
t
zs
t t t
t
y C e C e e C C
dy t
dt
C e C e e C C
C C
y t e e e t
;
. .
. . ;
= + = + =
= + = + =
= =
= +
=
0
0 1 0 1
3 2 3 2 0 2
1 2 0 5 0 5
0 5 0 5 0
1
0
2
3 0 2 0
1 2
0
1
0
2
3 0 2 0
1 2
1 2
3 2
a f a f
a f
a f
a f a f
a f
a f a f
a f a f
and and
Page 5 of 6
4. [25 pts] Taking Convolution: Taking the convolution for the output y(t) and sketch the
output y(t) as a function of t. BOX YOUR FINAL ANSWER
a y t x t h t h t e u t x t u t u t t k
b y t x t h t h t t u t x t u t
t
k
. ; , . .
. ; cos ,
b g b g b g b g b g b g b g b g m r b g
b g b g b g b g b g b g b g b g
= = = +
= = =
2
01 501
2 1
Solution
a x t u t u t t k t t t t t
h t e u t
y e u t e u t e u t e u t e u t e u t
k
t
t t t t t t
. . .
;
b g b g b g m r b g b g b g b g b g b g b g
b g b g
b g b g b g b g b g b g
= + = + + + + +
=
= + + + + +
=
01 501 0 1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
2
2
1
2
2
2
3
2
4
2
5
2
We so do convolution with shifted impulses:
b h t t u t x t u t
t u t t u t
h t u t d d t u t
h t u t t u t
t t
. cos ;
cos cos
cos cos sin
sin
b g b g b g b g b g
b g b g b g b g
b g b g b g b g b g b g
b g b g b g b g
= =
= = =
=
z z
2 1
2 2
2
1
2
2 2
1
2
2
1
1
2
2 1 1
0 0
Convol with 1 is as taking the integral of :
Page 6 of 6
5. [15 pts] General Fourier Series: BOX YOUR ANSWER
a. For x t C e y t x t D e
k
jk t
k
k
jk t
k
x
y
b g b g b g = = =
=
; ; Calculate D
k
from C
k
and
y
from
x
b. For x t C e y t x t D e
k
jk t
k
k
jk t
k
x
y
b g b g b g = = =
=
; 2 ; Calculate D
k
from C
k
and
y
from
x
?
c. For x t C e y t x t D e
k
jk t
k
k
jk t
k
x
y
b g b g b g = = =
=
; ; Calculate D
k
from C
k
and
y
from
x
Solution
a.
x t C e
y t x t C e C e e D e
D C e
k
jk t
k
k
jk t
k
k
jk t jk
k
k
jk t
k
k k
jk
y x
x
x x x x
x
b g
b g b g
b g
=
= = = =
= =
=
;
b.
x t C e
y t x t C e D e
D C
k
jk t
k
k
jk t
k
k
jk t
k
k k y x
x
x
y
b g
b g b g
=
= = =
= =
=
2
2
2
;
c.
x t C e
y t x t C e D e
D C
k
jk t
k
k
jk t
k
k
jk t
k
k k y x
x
x x
b g
b g b g
=
= = =
= =
=
Você também pode gostar
- Bobcat 225: May 2003 Eff. W/serial Number KE582332Documento52 páginasBobcat 225: May 2003 Eff. W/serial Number KE582332juan felipe alzate aristizabalAinda não há avaliações
- Formulas For Calculus Integral DifferentialDocumento3 páginasFormulas For Calculus Integral DifferentialilovethisnamelikeyeaAinda não há avaliações
- Continuous and Discrete Time Signals and Systems (Mandal & Asif) Solutions - Chap05Documento51 páginasContinuous and Discrete Time Signals and Systems (Mandal & Asif) Solutions - Chap05mvalderm100% (2)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Verification 2003: Technology, Tools and MethodologyDocumento5 páginasFunctional Verification 2003: Technology, Tools and MethodologydoomachaleyAinda não há avaliações
- Discover The Small Switch Mode Power Supplies Modification SecretsDocumento10 páginasDiscover The Small Switch Mode Power Supplies Modification Secretscarlos1670201480% (5)
- Calculus SummaryDocumento3 páginasCalculus SummaryJay JayAinda não há avaliações
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesNo EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesNota: 1.5 de 5 estrelas1.5/5 (2)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNo EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Solutions Manual - Linear Algsolutions Manual - Linear Algebra With Applications, 2nd Edition by W. Keith Nicholson Chapter 1ebra With Applications, 2nd Edition by W. Keith Nicholson Chapter 1Documento8 páginasSolutions Manual - Linear Algsolutions Manual - Linear Algebra With Applications, 2nd Edition by W. Keith Nicholson Chapter 1ebra With Applications, 2nd Edition by W. Keith Nicholson Chapter 1고봉기100% (1)
- Operating Manual: Logic Module BST Prologic Cpu 32XDocumento42 páginasOperating Manual: Logic Module BST Prologic Cpu 32XDs Kuzmenko100% (1)
- Fórmulas de Cálculo Diferencial e IntegralDocumento3 páginasFórmulas de Cálculo Diferencial e IntegralurielxidoAinda não há avaliações
- Formula RioDocumento2 páginasFormula RioCocodrilo AstronautaAinda não há avaliações
- Formulario Calculo Diferencial e Integral PDFDocumento3 páginasFormulario Calculo Diferencial e Integral PDFvictor10kAinda não há avaliações
- Jesús Rubí M.: Fórmulas de Cálculo Diferencial e IntegralDocumento0 páginaJesús Rubí M.: Fórmulas de Cálculo Diferencial e IntegralSergio1218Ainda não há avaliações
- Centro de Cortante J Constante de Torsión, CM C Constante de Alabeo, CMDocumento3 páginasCentro de Cortante J Constante de Torsión, CM C Constante de Alabeo, CMAle CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics S1Documento65 páginasMathematics S1Manish KaliaAinda não há avaliações
- 64 Trigonometri Equations Part 1 of 1Documento15 páginas64 Trigonometri Equations Part 1 of 1Mayank SainiAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Trigonometric Ratio & Equation HWT - 1Documento6 páginasSolutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Trigonometric Ratio & Equation HWT - 1varunkohliinAinda não há avaliações
- Analyzing Insertion Sort As A Recursive AlgorithmDocumento10 páginasAnalyzing Insertion Sort As A Recursive AlgorithmHehe 'Heny' CaemAinda não há avaliações
- Formulario Matematicas 2009Documento0 páginaFormulario Matematicas 2009JJOCAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5Documento11 páginasLecture 5Red ManAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics TrigonometryDocumento4 páginasMathematics TrigonometryVara Prasad VemulaAinda não há avaliações
- More Trigonometric SubstitutionDocumento35 páginasMore Trigonometric SubstitutionArsalan JumaniAinda não há avaliações
- Jee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Solutions Complex NumbersDocumento12 páginasJee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Solutions Complex NumbersvarunkohliinAinda não há avaliações
- Chöông 1: Coâng Thöùc Löôïng Giaùc: I. Ñònh NghóaDocumento21 páginasChöông 1: Coâng Thöùc Löôïng Giaùc: I. Ñònh NghóaMinhhoang PhamAinda não há avaliações
- 62 Trigonometric Ratio & Identity Part 1 of 2Documento12 páginas62 Trigonometric Ratio & Identity Part 1 of 2Mayank SainiAinda não há avaliações
- EE - 210 - Exam 3 - Spring - 2008Documento26 páginasEE - 210 - Exam 3 - Spring - 2008doomachaleyAinda não há avaliações
- R R G G: Zadatak 3.1Documento9 páginasR R G G: Zadatak 3.1Elvis PonjevićAinda não há avaliações
- Jeffrey Reynaldo Ridwan (1010951016)Documento9 páginasJeffrey Reynaldo Ridwan (1010951016)Jeffrey Reynaldo RidwanAinda não há avaliações
- Curs 5Documento20 páginasCurs 5wexlerAinda não há avaliações
- Parallel Plate Transmission Line: Region Air The in - K, 0: Modes TM With Variation No, Variation AssumeDocumento16 páginasParallel Plate Transmission Line: Region Air The in - K, 0: Modes TM With Variation No, Variation AssumejafunggolAinda não há avaliações
- 2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math SolnDocumento15 páginas2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math Solnckhowh_23284524667% (3)
- Algebra FormulasDocumento1 páginaAlgebra FormulasdarkingreyleighAinda não há avaliações
- 2010 TJC SolDocumento12 páginas2010 TJC SolPooja KapurAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Inverse Trigonometry HWT - 1Documento8 páginasSolutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Inverse Trigonometry HWT - 1varunkohliinAinda não há avaliações
- Targate'14: Icp-Intensive Classroom Program Egate-Live Internet Based Classes DLP Targate-All India Test SeriesDocumento12 páginasTargate'14: Icp-Intensive Classroom Program Egate-Live Internet Based Classes DLP Targate-All India Test SeriesAbhishek ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- Control System TheoryDocumento60 páginasControl System TheoryNishant SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- Movie Segment: Learning Locomotion With Littledog, University of Southern California, 2010Documento4 páginasMovie Segment: Learning Locomotion With Littledog, University of Southern California, 2010Muhammad SumeetAinda não há avaliações
- 26 Ms 181Documento16 páginas26 Ms 181ispiracAinda não há avaliações
- MillNotes MithrilDocumento2 páginasMillNotes MithrilChristopher MillerAinda não há avaliações
- CFD Lecture 3: Dr. Thomas J. BarberDocumento24 páginasCFD Lecture 3: Dr. Thomas J. BarberTareq DahbAinda não há avaliações
- 2008 Ext1 PDFDocumento3 páginas2008 Ext1 PDFBrandi RoseAinda não há avaliações
- Toan Tap Luong Giac 2011Documento169 páginasToan Tap Luong Giac 2011Toan PhungAinda não há avaliações
- Exercises FonT LatexDocumento56 páginasExercises FonT LatexRamezAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2-Mass Reactor Model (102 P)Documento102 páginasChapter 2-Mass Reactor Model (102 P)shardulkaviAinda não há avaliações
- Vektor Untuk Kalkulus 2Documento77 páginasVektor Untuk Kalkulus 2svitri94Ainda não há avaliações
- Exam 2solutionDocumento5 páginasExam 2solutionJames Steven HaneyAinda não há avaliações
- F C D I: Jesús Rubí MirandaDocumento2 páginasF C D I: Jesús Rubí Mirandalmarobesg94Ainda não há avaliações
- (CSM51A / EE16 S10) Solutions For Midterm: Problem Points Score 1 15 2 10 3 20 4 20 5 15 6 20 Total 100Documento10 páginas(CSM51A / EE16 S10) Solutions For Midterm: Problem Points Score 1 15 2 10 3 20 4 20 5 15 6 20 Total 100krazykrnxboyAinda não há avaliações
- Trigonometrical Equations Properties of Triangles and Heights and Distances StudyaddaDocumento20 páginasTrigonometrical Equations Properties of Triangles and Heights and Distances StudyaddaAvinash GanesanAinda não há avaliações
- Mathcad - Tarea Final EF3Documento21 páginasMathcad - Tarea Final EF3EskorbutanoAinda não há avaliações
- Solution: U Vi I I JDocumento3 páginasSolution: U Vi I I JChegrani AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions of The System Modeling Course Examination: March 7, 2003Documento9 páginasSolutions of The System Modeling Course Examination: March 7, 2003sashikant31Ainda não há avaliações
- 14 DETEMINANTS & MATRICES PART 3 of 6 PDFDocumento10 páginas14 DETEMINANTS & MATRICES PART 3 of 6 PDFsabhari_ramAinda não há avaliações
- DeretDocumento88 páginasDeretMuhammad WildanAinda não há avaliações
- MATH 121 - MIDTERM 1 Solutions: P Q R Q R (P Q) (P Q) RDocumento3 páginasMATH 121 - MIDTERM 1 Solutions: P Q R Q R (P Q) (P Q) RmahiruserAinda não há avaliações
- Integrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofDocumento5 páginasIntegrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofuditagarwal1997Ainda não há avaliações
- Mid IDocumento11 páginasMid IpassmefoolAinda não há avaliações
- Testing 11Documento18 páginasTesting 11doomachaleyAinda não há avaliações
- Testing 7Documento20 páginasTesting 7doomachaleyAinda não há avaliações
- A UVM-Based Smart Functional Verification Platform: Concepts, Pros, Cons, and OpportunitiesDocumento6 páginasA UVM-Based Smart Functional Verification Platform: Concepts, Pros, Cons, and OpportunitiesdoomachaleyAinda não há avaliações
- Soc Level Verification Using System VerilogDocumento3 páginasSoc Level Verification Using System VerilogdoomachaleyAinda não há avaliações
- Verification of AMBA Bus Model Using SystemVerilogDocumento5 páginasVerification of AMBA Bus Model Using SystemVerilogdoomachaleyAinda não há avaliações
- Section 2 - 7 DC Imperfections LectureDocumento35 páginasSection 2 - 7 DC Imperfections LectureAbhishek VarshneyAinda não há avaliações
- Process Automation Factory Automation Terminal AutomationDocumento4 páginasProcess Automation Factory Automation Terminal AutomationRitaban R. BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- A Project Report On Smart Bell With Electronic Time Table DisplayDocumento85 páginasA Project Report On Smart Bell With Electronic Time Table Displaytamma mounika58100% (1)
- 30W Gan Wide-Band Power Amplifier: RF in VGQ Pin 1 (CUT) RF Out VDQ Pin 2 GND BaseDocumento7 páginas30W Gan Wide-Band Power Amplifier: RF in VGQ Pin 1 (CUT) RF Out VDQ Pin 2 GND BaseRajneesh VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Confidential: Highly Integrated Current Mode PWM ControllerDocumento2 páginasConfidential: Highly Integrated Current Mode PWM ControllerRaulAinda não há avaliações
- Service Manual: KV-25FS12 KV-25FS12CDocumento108 páginasService Manual: KV-25FS12 KV-25FS12CCesar Augusto Camargo MejiaAinda não há avaliações
- HA17458 - RenesasDocumento9 páginasHA17458 - RenesasStevenAinda não há avaliações
- Keyence LR Tb5000 Self Contained Tof Laser LR T Series SensorDocumento5 páginasKeyence LR Tb5000 Self Contained Tof Laser LR T Series SensorEve ValAinda não há avaliações
- 2.2 - Mathematical Modeling & Transfer Function PDFDocumento25 páginas2.2 - Mathematical Modeling & Transfer Function PDFFatinnnnnn100% (1)
- File 3 EMI and AC Group 4Documento13 páginasFile 3 EMI and AC Group 4JOHNAinda não há avaliações
- Shev - Control Units Emb7300Documento3 páginasShev - Control Units Emb7300FathyAinda não há avaliações
- Energizer L92: Product Datasheet Product DatasheetDocumento2 páginasEnergizer L92: Product Datasheet Product DatasheetDot N SpotAinda não há avaliações
- Micom P740: Numerical Busbar ProtectionDocumento386 páginasMicom P740: Numerical Busbar ProtectionDinh Xuan Duyet100% (1)
- PathfinderDocumento91 páginasPathfinderShashi SagarAinda não há avaliações
- SRAS GuidelinesDocumento28 páginasSRAS GuidelinesJack ClarkeAinda não há avaliações
- Cerberus Pyrotronics Strobes 2 4952870316 2Documento2 páginasCerberus Pyrotronics Strobes 2 4952870316 2Rafael DantasAinda não há avaliações
- 132 KV GSS Training ReportDocumento35 páginas132 KV GSS Training ReportTREGIC FUN100% (2)
- Analisis en DC Con QucsDocumento13 páginasAnalisis en DC Con Qucscayo_sincheAinda não há avaliações
- Basic TransformerDocumento10 páginasBasic TransformerPin SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Clab ProblemsDocumento5 páginasClab ProblemsWyndellRioAinda não há avaliações
- DungDocumento88 páginasDunghoang dungAinda não há avaliações
- Huvitz CCP-3100 Chart Projector - User ManualDocumento33 páginasHuvitz CCP-3100 Chart Projector - User ManualwiroarAinda não há avaliações
- Tayug I Substation Operating Procedures and GuidelinesDocumento6 páginasTayug I Substation Operating Procedures and GuidelinesTrenchera SubstationAinda não há avaliações
- LAb 2Documento4 páginasLAb 2June del MundoAinda não há avaliações
- Science SOL 4.3 - Electricity: Lightning Is Caused by Static ElectricityDocumento3 páginasScience SOL 4.3 - Electricity: Lightning Is Caused by Static ElectricityKrishnaKumar PodagatlapalliAinda não há avaliações
- SigmaWin+5.72 Release NotesDocumento6 páginasSigmaWin+5.72 Release NotesLeoSilvaAinda não há avaliações
- AE301 UserDocumento20 páginasAE301 Userlavalley.nicolasAinda não há avaliações